-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Research in Obstetrics and Gynecology
p-ISSN: 2326-120X e-ISSN: 2326-1218
2015; 3(1): 5-7
doi:10.5923/j.rog.20150301.02
A Case of Female Breast Cancer Presenting with Pleural Effusion
Syed Hassan1, Andee Dzulkarnaen Zakaria1, Ikhwan Sani1, Tanveer Azam2, Amer Hayat Khan2
1Department of Surgery, School of Medical Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Health Campus, Kelantan, Malaysia
2Department of Clinical Pharmacy, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences Universiti Sains Malaysia, Penang, Malaysia
Correspondence to: Andee Dzulkarnaen Zakaria, Department of Surgery, School of Medical Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Health Campus, Kelantan, Malaysia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Breast cancer is a malignant tumor that starts in the cells of the breast. A malignant tumor is a group of cancer cells that can grow into (invade) surrounding tissues or spread (metastasize) to distant areas of the body. Case: A 38 year old Malay lady was admitted to Hospital Universiti Sains Malaysia (HUSM) on 18 February, 2013, with complaining of shortness of breath and chest discomfort started few weeks earlier. Patient was diagnosed with breast cancer at right side in March, 2012. Patient rejected the clinical intervention. Malignant pleural effusions occur commonly in patients with cancer. The malignancies responsible for more than 75% of all of pleural effusions in order of frequency are lung, breast, lymphoma, and ovarian cancer. The treatment receives to treat breast cancer is TAC chemotherapy and for pleural effusion, drainage had been done as initial treatment. Based on study, chemotherapy achieved symptom relief and objective response in a large majority of patients (in 78% and 86% of cases respectively).
Keywords: Carcinoma, Breast cancer, Pleural effusion
Cite this paper: Syed Hassan, Andee Dzulkarnaen Zakaria, Ikhwan Sani, Tanveer Azam, Amer Hayat Khan, A Case of Female Breast Cancer Presenting with Pleural Effusion, Research in Obstetrics and Gynecology, Vol. 3 No. 1, 2015, pp. 5-7. doi: 10.5923/j.rog.20150301.02.
1. Introduction
- Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer relating deaths among women worldwide [1]. Brest cancer is originated commonly from breast tissues, lining of milk duct and can develop in all mammals [2, 3]. Breast cancer is not limited to the females, males can also develop it [4]. Histological breast cancer can be invasive or in situ [5]. Most appropriate approach about breast cancer type is based on different receptors such as estrogen (ER+/ER-), progesterone (PR+/ PR-) and Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (HER+/HER-) [6]. According to American Cancer Society one out of eight American develops breast cancer with 232340 new cases annually [7]. In Malaysia one out of 20 women is diagnosed with breast cancer with an estimated 4000 women per annum [8].Females are usually get concern with breast cancer regarding their normal family life [9]. Breast cancer patient might develops fatigue, sleep disturbance, and depression that might reduce the effectiveness of treatment protocol [10, 11]. Pleural effusion is the sign of malignancy and low survival rate in certain cancer types including breast cancer [12-14]. This case represents the attitude of patient toward breast cancer treatment and complication arising from the noncompliance of proper treatment.
2. Case Report
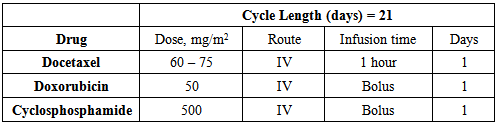
- A 38 year old Malay woman presented in Hospital Universiti Sanis Malaysia(USM) with the complaining of shortness of breath and pain in her right breast on 18 February, 2013. Patient’s past history revealed that she has been diagnosed with breast cancer in March, 2012. A surgical intervention was suggested to remove the solid tumour mass but patient refused to go under any medical treatment at that time and proffered alternative remedies. On 18 February, 2013 patient came with severe respiratory discomfort. She suspected to develop right pleural effusion. Physical examination revealed poor air entry is the lungs that were confirmed by respiratory examination test by using spirometry. Her blood pressure recorded as 93/59mmHg, pulse rate 94beats/min and temperature 37℃. Chest X-ray report revealed complete opacification of the right thoracic cavity and accumulation of fluid in right lungs. CT scan was done to observe the degree of plural effusion and lungs condition. Laboratory findings showed her haemoglobin level was 9.5 g/dl and other blood parameters were normal. Patient was first treated for the pleural effusion by using pleuroscopy and pleurodesis. Pleuroscopy was performed on 19 February, 2013 to access pleural effusion and examine airway in situ by inserting chest tube at the right axillary line in between the 5th and 6th intercostals spaces. Patient was recommended for chemical pleurodesis procedure using bleomycin to prevent recurrent pleural effusion. Physical examination and mammography of breast revealed a 5x5cm tumour mass with ulceration and right nipple shrinks. Skin anterior to the breast lesion was thickened with streakiness of fat tissue and evidence of peau de’ ore, left tissue region was normal with no lesion. Cancer was diagnosed as triple negitive advance invasive ductal carcinoma. Patient was advised a neoadjuvant treatment plan. Four cycle of following chemotherapy was commenced at first for patient.
|
3. Discussion
- Different studies reported that female diagnosis with breast cancer feel a higher distress. It might affect quality of life [15]. In this case patient was diagnosed with breast cancer a year ago but she refuses any surgical intervention. Her basic concern was regarding family life. She preferred alternative remedies. Different reports suggested that the trend of use of alternative medicines is increasing among breast cancer patients [16]. Women with breast cancer usually develop stress that triggers the motive to use alternative medicines regardless of safety and efficacy of treatment [17, 18]. Most cases of breast cancer among Malaysian women are presented in advance stage [19]. Psychological support might help in overcome stress and depression in breast cancer patients to increase the quality of life [20].Condition of Patient on second admission was critical; she has developed malignant pleural effusion. Pleural effusion is secondary characteristics of malignant tumour [21, 22]. Pleural effusion is accumulation of fluid in potential space between the visceral and partial layer around the lungs [23]. In order of frequency lung, breast, lymphoma, and ovarian cancers are responsible of 75% of all pleural effusions [23]. According to guidelines complete drainage of effusion is appropriate approach for malignant pleural effusion along with pleurodesis [24-26]. In this case patient was suggested with chemical pleurodesis that help in relieving the symptoms of dyspnea. Cancer treatment approaches are usually adopted on the basis of types and stages of breast cancer. In advance breast malignancies neoadjuvant treatment plan is appropriate approach [27]. Study reveals that preoperative use of Docetaxel, Doxorubicin and Cyclophosphamide (TAC) help in disease free survival and reduce the chances of reoccurrence [28, 29]. In a study martin et al. reported a high disease free survival with TAC regimen in adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer [30].
4. Conclusions
- Although Incidence of Breast cancer is low among population of Malaysia comparing it with developed countries still it remains apex reason of mortality. Most patients are diagnosed have advance stages of malignancy that results in low survival rate among breast cancer patients. Second reason of low survival rate might be increasing trend toward use of alternative treatment remedies. Patient in this case was diagnosed at early stage of breast carcinoma year ago but she refuses medical intervention as suggested instead she decided to go for the alternative medicine therapy. Her attitude resulted in the spread of cancer and malignant pleural effusion. This mind-set can be seen in many developing countries particularly in south Asian population that resulting in severity of disease. There are number of triggering factors behind this approach. Early diagnosis in breast cancer is important to reduce the complication and to increase the disease free survival. Health care authorities must be equipped with technical support. There is a need of public awareness campaigns and counselling sessions for population at risk on community level. For awareness regarding breast cancer women must be equipped with self examining practice. Use of alternative medicine among public need a serious attention. These approaches are lacking regarding safety and efficacy. Attention must be drawn to assess the safety and efficacy of these methods and patients must be told about pros and prone of these technologies. Use psychological support can reduce the stress level in cancer patient that could help increase disease free survival of patients.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML