-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Resources and Environment
p-ISSN: 2163-2618 e-ISSN: 2163-2634
2022; 12(3): 76-87
doi:10.5923/j.re.20221203.02
Received: May 22, 2022; Accepted: Nov. 11, 2022; Published: Nov. 17, 2022

Wastewater Irrigation and Associated Health and Environmental Factors in Pakistan: A Scoping Review
Walvala Almas Kasi1, Sanaullah Panezai1, Shahab E. Saqib2
1Department of Geography and Regional Planning, University of Balochistan, Quetta, Pakistan
2Department of Commerce Education & Management Sciences, Higher Education Department, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan
Correspondence to: Sanaullah Panezai, Department of Geography and Regional Planning, University of Balochistan, Quetta, Pakistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Background: Wastewater is used increasingly in the agricultural sector to cope with the depletion of freshwater resources as well as water stress linked to change to the climate conditions. Research focusing on the human and environmental health risks is critical because exposure to a range of contaminants needs to be weighed with the benefits to food security, nutrition, and livelihoods. Purpose: The aim of this scoping review is to examine the studies on human and environmental risks and factors associated with wastewater irrigation in the agricultural fields of Pakistan and to identify research trends and gaps. Methods: The literature for this scoping review article was identified from Google Scholar, Science Direct, Scopus, PubMed, PubMed health, full pdf (web of scientific publications), JSTOR, Research Gate, Google, and the free browser Kopernio. The studies focusing on Pakistan were discovered spanning from 1996-2020 and a total of 138 published studies were summarized and reviewed accordingly. Findings: The findings of the review showed that among the total 138 studies, the geographical distribution was as follows: Punjab (85), Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (24), Balochistan (7), Sindh (4), Islamabad (2), Gilgit Baltistan (1) and Azad Jammu Kashmir (1). Most studies had used experimental, descriptive, and cross-sectional survey designs. The samples of crops, vegetables, and fruits, raw milk, and soil were collected and tested in laboratories for assessing health and environmental risks. Major themes included heavy metals contamination, human, animal, and environmental health risks, ecological risk assessment, wastewater treatment, soil salinity, and groundwater contamination, wastewater characteristics, impacts on crops production, wastewater management and regulations, effects on aquaculture, and socio-economic impacts were identified in the scoping review. Conclusion: The screening of the reviewed articles indicated that future research should consider wastewater treatment strategies, disease profiling caused by wastewater, socio-economic impacts, and effects on aquaculture and animal health. Policymakers are suggested to utilize the results of this research for revamping policies and strategies for wastewater management.
Keywords: Wastewater,Wastewaterirrigation, Environmental risks, Health risks, Pakistan, Scoping review
Cite this paper: Walvala Almas Kasi, Sanaullah Panezai, Shahab E. Saqib, Wastewater Irrigation and Associated Health and Environmental Factors in Pakistan: A Scoping Review, Resources and Environment, Vol. 12 No. 3, 2022, pp. 76-87. doi: 10.5923/j.re.20221203.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Water scarcity refers to a condition of imbalance between freshwater availability and demand where freshwater demand exceeds availability [1]. Water is essential for socio-economic development, agricultural production, food security, and for maintaining a healthy ecosystem [2-5]. The water scarcity raises major concerns about the sustainable future of humanity, and the conservation of important ecosystem functions [6]. Increasing agricultural production has been focused by agriculture policies globally [7,8]. However, water scarcity can cut production, and severely affect food security worldwide [9-11]. The brutality of the water crisis has prompted the United Nations [12], to conclude that water scarcity and climate change will have significant impacts on agriculture by increasing water demand, limiting crop productivity, and reducing water availability in areas where irrigation is direly needed [13-15]. Agriculture is accountable for the largest extraction of water and thus considered the chief, ‘culprit’ under conditions of local absolute scarceness [2]. As water becomes scarcer, it is fundamentally important to tackle the issue head-on. Agriculture is equally a foundation cause and a targeted victim of water scarcity. The issue of water scarcity and socio-economic impact of water shortage on small scale farmers is the reality in many developing countries. Wastewater reuse is an essential and elementary way to handle the water demand management promoting the protection of high-quality freshwater and plummeting both environmental pollution and overall supply cost [16,17]. Wastewater generates from domestic, commercial, and industrial sources. In many networks, the domestic components are the largest accounting for as much as 50-80% of the total water use [18]. The amount of collected wastewater is likely to increase considerably with population growth, rapid urbanization, and improvement of sanitation service coverage [19,20]. Wastewater irrigation has recently emerged as a focused subject in the developing world where it is used by urban and peri-urban farming communities and it is increasingly becoming a livelihood reality. Pakistan is an agrarian country of Southeast Asia and enlarged industrialization and urbanization result in a discharging of effluents of toxic nature into the waterways [21], thus contaminating and rendering the water bodies inadequate for consumption in agriculture sector [22]. Plants can take the toxic pollutants in their bodies in a high amount and the food chain can reach through human and animal beings causing a serious threat to their health. The water pollution impacts are noticed and perceived at longer detachments, although these are often ignored [23]. The wastewater utilization in irrigation, pathogen and chemicals are the main hazards to human health. Longley, wastewater irrigation does not only affect accumulation of heavy metals in soil but also spoiling the food crops with heavy metals [24]. The heavy metals are obtained from industrial effluents, agriculture waste and domestic sewage through biological actions. The wastewater with beneficial nutrients, organic and inorganic pollutants is useful for crops, and it leaves no need for use of fertilizers [25]. In Pakistan, municipal wastewater is typically not treated and none of the cities have any biological treatment method except Islamabad and Karachi, and even these cities treat only a less amount of their wastewater before disposal [26]. Contrary to this, the wastewater is hazardous too for health of human and other living organisms. Due to frequent contact with untreated wastewater, agricultural workers experience skin diseases and parasitic disease (hookworms and giardiasis) [27,28]. The high ratio of heavy metals including arsenic, cadmium, lead and zinc solubility and its deficiency can cause diarrhea, poor wound healing, and anemia [29,30]. In the context of health risks, the high ratio of wastewater contaminants demands further exploration. The existing research studies have investigated health or environmental risks separately, focusing different aspects, i.e., accumulation of heavy metals in vegetables irrigated by wastewater, risk of hookworm infection and wastewater irrigation in Pakistan. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, no study has comprehensively reviewed the existing literature on wastewater irrigation and associated factors with a focus on Pakistan. Therefore, this scoping review aims to critically examine the current literature on the wastewater irrigation and associated health and environmental risks in Pakistan.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Deign
- This study uses a scoping review design to map out the existing literature supporting wide-ranging research questions on a specific topic [31]. Scoping studies are an increasingly vogueish approach to reviewing health research evidence [31,32]. The method for this scoping review was constructed on the framework presented by Arksey and O’Malley [33]. The review assessment encompassed the tracking five key phases: (1) identifying the research question; (2) identifying appropriate studies; (3) study screening and selection; (4) charting the data; and (5) collating, summarizing, and reporting the consequences.
2.2. Data Souarces
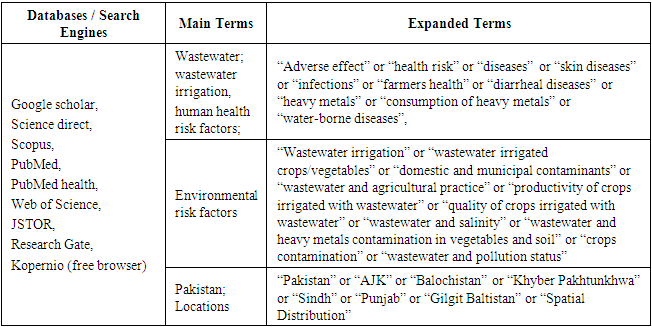
- The literature for this scoping review was identified in major databases and search engines such as Google Scholar, Science Direct, Scopus, PubMed, PubMed health, full pdf (web of scientific publications), JSTOR, Research Gate, Google and the most helping free browser Kopernio (Table. 1).
|
2.3. Search Strategy
- For the searching the research articles, several keywords and phrases were used. The search strategy used broad search terms (Table. 1) to ensure that publications are not skipped, and many publications were than excluded following exclusion criteria. The reference table of all relevant articles were hand-searched to identify any further relevant studies not captured in database search. They include; “wastewater irrigation in Pakistan/ Punjab/ Sindh/ Balochistan/ Khyber Pakhtunkhwa/Azad Jammu and Kashmir (AJK)”, “wastewater irrigation and health risks”, “wastewater irrigation and environmental risks”, “wastewater reuse in agricultural fields”, “wastewater and diseases”, wastewater irrigation and crops/vegetables”, “wastewater and heavy metals”, “wastewater and contamination of water resources”, “wastewater and soil salinity”, “wastewater and agricultural practice in Pakistan”, “productivity and quality of crops irrigated by wastewater”, “spatial distribution of wastewater”, “consumption of vegetables grown by wastewater”. The first study was discovered in 1996 and second in 1997. So, the published articles were reviewed from the year 1996 to 2020. Only those papers were peer-reviewed that were written in English language and their geographic focus was Pakistan.
2.4. Screening of Relevance and Eligibility Criteria
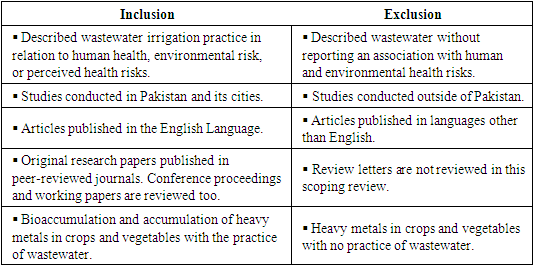
- After searching each database and search engine, the article titles, abstracts, and keywords were assessed to determine their relevancy to the topic of this scoping review. The title abstracts and full-text of each research and reviewed articles and each citation were independently screened. Many categories of empirical studies were included in the review that have directly measured the health and environmental risk of wastewater irrigation such as using quantitative risk assessment, survey, WHO guideline, health index and daily intake index of heavy metals, experimental studies and studies that had measured contamination of crops used for human and animal consumption. In this scoping review, the studies measuring soil salinity/soil health, water contamination for drinking, consumption of vegetables grown by wastewater, the productivity yield of the crops/vegetables, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH)s quantity in wastewater and their effect on human health, heavy metals contamination of water, soil and vegetables/crops in agricultural farmlands, hookworm and giardia duodenalis in wastewater irrigated location were included (Table. 2).
|
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Description of Published Studies
- Through searching and visualizing strategy, the searched databases identified 3,860 research studies from the above-mentioned electronic searched engines. The duplicated articles were removed, succeeding in 3,052 unique recorded citations. After initial and final screening of titles and abstracts, 136 published studies were selected on the ground of relevancy and underwent the inclusion criteria. The reference lists from the integrated articles resulted in the accumulation of 2 more studies which were allied to botanical research writing (Figure. 1).
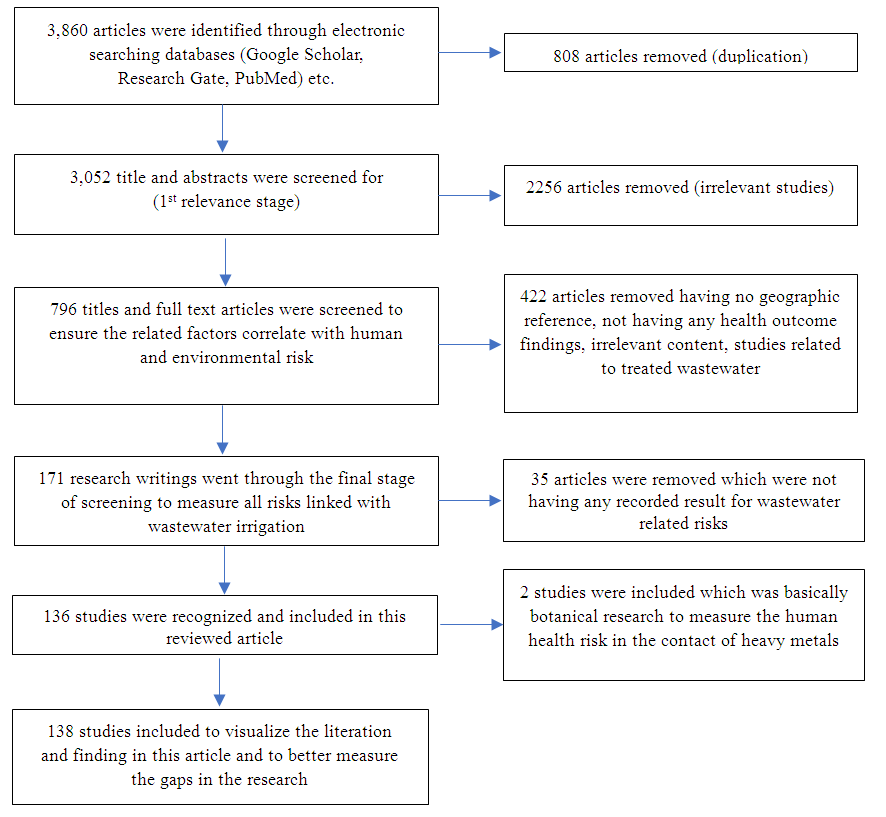 | Figure 1. Flow chart of the selected studies and scrutiny criteria |
3.2. Geographical Distribution of Published Studies
- The total number of published studies were 138 for this scoping review. The findings showed that out of total 138 research studies, majority (85) were conducted in Punjab province, followed by Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (24), Balochistan (7), Sindh (4), Islamabad (2), Azad Jammu Kashmir (1), and Gilgit Baltistan (1) respectively (Figure. 2). Most of the studies were baseline and many of them were conducted to find out the health and environmental risks. The analsyis of thematic coverage revealed that many studies were conducted on heavy metals and associated risks not only to human health but also to animal health and environment contamination (soil, vegetable, and water contamination). The screened studies had suggested that the use of wastewater in agricultural activities as a risk for human, animal, and environment safety. The consumption of wastewater irrigated forage having heavy metals contaminations by the buffaloes resulted in the production of raw milk [34] (Figure. 2).
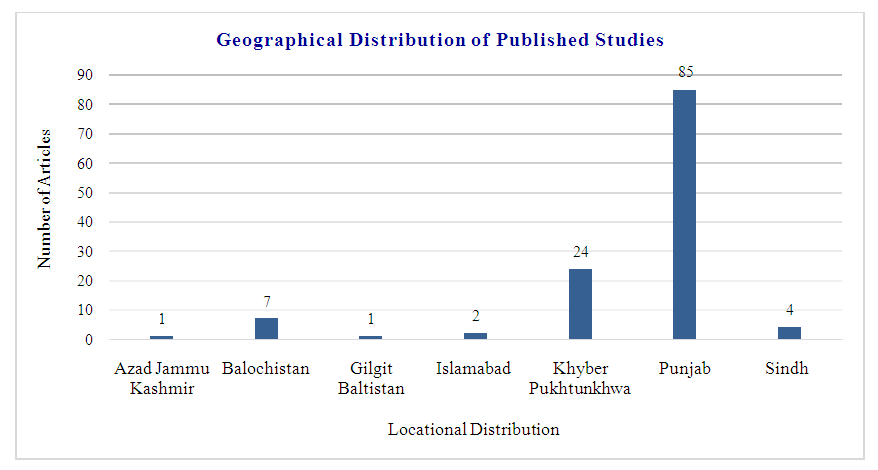 | Figure 2. Geographical distribution of published articles in Pakistan |
3.3. Temporal Distribution of Published Studies
- According the findings of this study, the research on wastewater irrigation and usage started in 1996 (Figure. 3). In the last decade, majority of research studies had been published with highest number of articles in 2020 and 2019 respectively.
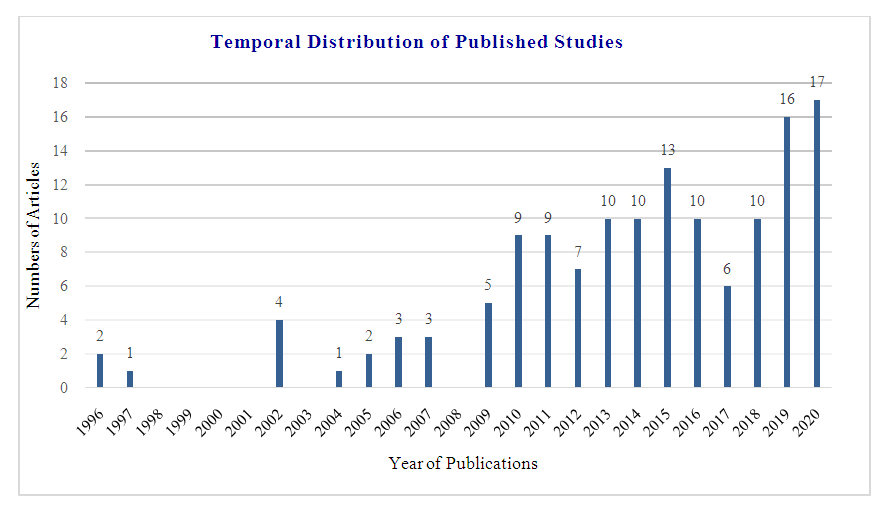 | Figure 3. The temporal distribution of published studies from 1996 to 2020 |
3.4. Description of Published Studies
- The Table 3 shows description of reviewed articles conducted on wastewater irrigation and associated factors in Pakistan. Most studies had used experimental, descriptive, and cross-sectional survey designs, respectively. The samples of crops, vegetables and fruits, and soil were collected and tested in laboratories for assessing health and environmental risks. The analysis of the findings showed that wastewater irrigation in the agricultural field had affected the agricultural products such as crops, vegetables, and plants.
|
3.5. Thematic distribution of Published Studies
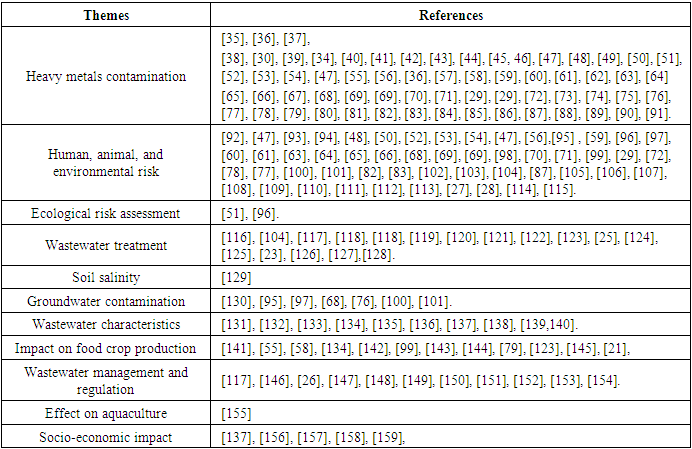
- The thematic distribution of the reviewed studies identified 11 themes (Figure. 4). The findings in the graph shows that heavy metals contamination (63), human, animal and environment risks (57), wastewater treatment (15) and impact on crop production (12) were the mostly covered themes respectively. Contrarily, ecological risk assessment (2), the effects on wastewater use on aquaculture (1), and soil salinity (1) were less explored themes.
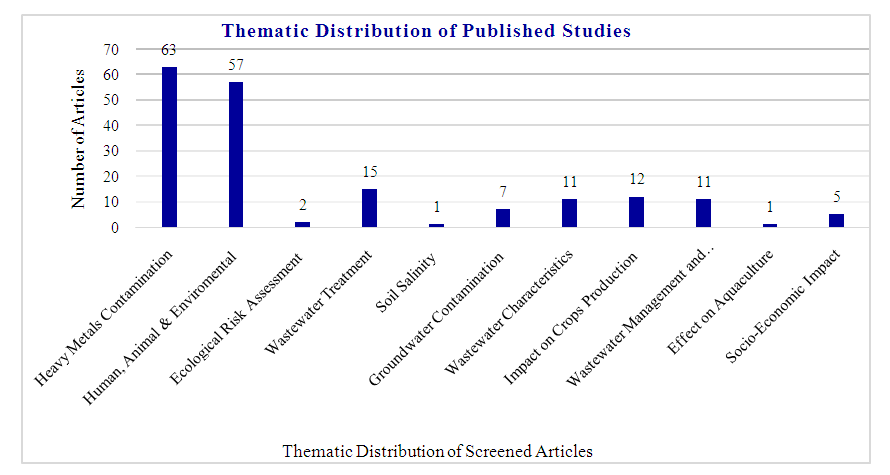 | Figure 4. Thematic distribution of Published studies |
4. Conclusions
- The findings of scoping review showed that published studies have been conducted mostly on the heavy metal contamination, human, animal and environment risks, wastewater treatment, and impacts on crop production. Contrarily, less has been explored about the ecological risk assessment, the effects on wastewater use in aquaculture, socio-economic impacts of wastewater use and groundwater contamination due to waste water irrigation. The use of wastewater in agricultural fields is making human and environmental health extremely vulnerable. The untreated industrial and municipal waste have posed multiple health and environmental risks for public health, and sustenance of aquatic life. In fact, the use of wastewater, municipal, and sewage water are said to be the leading cause of death for human across the globe. Heavy metal in drinking water is high risk in some regions of Pakistan. In Pakistan, research is needed on the infections and diseases related to wastewater irrigation not only on the irrigated area and respondent shouldn’t only be farmers and their family members, but the consumers should be also the part of the research. The research should be conducted on wastewater irrigation and associated economic problems. Moreover, how farmers can be trained for the safe use of wastewater for irrigation in order to mitigate the adverse impacts on human life. The attention of wastewater management authorities and policymakers are needed to introduce policies and new strategies for the safe use of wastewater because in the use of wastewater is inevitable in several water deficient agrarian regions of Pakistan. Specifically, the screening of the reviewed articles indicated that future research should consider wastewater treatment strategies, disease profiling caused by wastewater, socio-economic impacts, and effects on aquaculture and animal health. Policymakers are also suggested to utilize the results of this research for revamping policies and strategies for wastewater management.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML