-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Resources and Environment
p-ISSN: 2163-2618 e-ISSN: 2163-2634
2019; 9(3): 65-70
doi:10.5923/j.re.20190903.03

The Role of Riparian Vegetation in Secondary Irrigation Channels at Slamet Village, Tumpang District, Malang Regency to Improve Irrigation Water Quality
Faidatu Ummi , Catur Retnaningdyah , Bagyo Yanuwiadi
Department of Biology, Faculty of Mathematic and Natural Science, Brawijaya University, Malang, Indonesia
Correspondence to: Faidatu Ummi , Department of Biology, Faculty of Mathematic and Natural Science, Brawijaya University, Malang, Indonesia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Secondary irrigation channel in Slamet Village has four types; the irrigation channel of the riparian vegetation with two sides and trees, two sides riparian vegetation without trees, only one side riparian vegetation, and without riparian vegetation. This study aims to determine the riparian vegetation and water quality profile in four types of secondary irrigation channel at Slamet Village, and to figure out the interaction between riparian vegetation and water quality. Water quality that is measured includes temperature, pH, conductivity, turbidity, DO, and BOD. In addition, riparian vegetation community structure was also observed in each irrigation channel. Riparian vegetation was analyzed by determining the abundance and diversity index, while water quality was analyzed by using bar charts. The relationship between riparian vegetation and water quality was analyzed by employing cluster and biplot using the PAST 3.20 program. The results showed that there were differences regarding the diversity index values of riparian vegetation in each irrigation channel. Each irrigation channel has a diverse riparian vegetation community structure. Irrigation channels with two sides riparian vegetation and trees have better water quality than other types of the irrigation channels. This is indicated by the high value of taxa richness (42 herbs species), H’ index (5.12), evenness (0.95), DO (5.49) and low of a dominance index (0.03). Irrigation channels without riparian vegetation have low diversity and DO index. However, based on Government Regulation of the Republic of Indonesia No.82 of 2001, the water quality of the four types of irrigation channels still meets the quality standards of class II. Therefore, it can be concluded that the profile of riparian vegetation indirectly correlates with water quality.
Keywords: Riparian vegetation, Water quality, Secondary irrigation channels
Cite this paper: Faidatu Ummi , Catur Retnaningdyah , Bagyo Yanuwiadi , The Role of Riparian Vegetation in Secondary Irrigation Channels at Slamet Village, Tumpang District, Malang Regency to Improve Irrigation Water Quality, Resources and Environment, Vol. 9 No. 3, 2019, pp. 65-70. doi: 10.5923/j.re.20190903.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Malang Regency is one of the districts in East Java Province which has high potential in the agricultural sector. About 1.394.5 km2 of 3.535 km2 in total area of Malang Regency is used for agricultural land (East Java Provincial Statistics Agency, 2013). Conventional farming practices using chemical fertilizers are still widely applied by farmers in Malang Regency. The use of chemical fertilizers will have implications for pollution of water sources used as irrigation facilities. Pollution of irrigation water will trigger a decrease in water quality which has an impact on eutrophication and algal blooming (Retnaningdyah, C., Suharjono, A. Soegianto, B. Irawan, 2010).On the other hand, the decline of irrigation water quality was also caused by changes in the design of irrigation channels and the degradation of riparian vegetation.Degradation of riparian vegetation causes mechanical riparian functions, as a source of nutrition, and as phytoremediation decreases (Agustina, L., 2013). Based on the Agriculture Minister Decree No.2 of 2019 about Technical Guidelines for Irrigation Network Rehabilitation, regulation of irrigation channels are made from thin reinforced concrete walls made by hydraulic cement mortar. This is because this irrigation building has several advantage, such as increasing efficiency and reducing water loss due to leakage and seepage. In addition to avoiding blockages in the flow of irrigation water into rice fields. However, not all secondary irrigation channels in Slamet Village are made from stone walls. Secondary irrigation channel in Slamet Village has four types; the irrigation channel of the riparian vegetation with two sides and trees, two sides riparian vegetation without trees, only one side riparian vegetation, and without riparian vegetation. Riparian vegetation is known to play a role in maintaining and improving irrigation water quality by being able to reduce nitrate contamination in fertilizers (Oktaviani, R., & Yanuwiadi, B., 2016). Riparian vegetation has also been known to act as a phytoremediation agent for chemicals and contaminants in the aquatic environment. The ability of water purification by riparian is an important factor that determines the success of phytoremediation (Dhir, 2013). Mukhtar's (2010) study concluded that planting various plants in the asteraceae family, such as Helianthus annus has the potential to reduce lead (Pb) and nickel (Ni) in polluted waters with an effectiveness until 85%. Other riparian vegetations such as Sesbania grandiflora have the ability to reduce KMnO4, TDS, orthophosphate and ammonium levels, Cyperus rotundus functions to phytoextraction mercury levels in contaminated soil, and accumulates Sn, Zn, As, Cu and Pb (Siahaan, 2014). Based on the above, the purpose of this study is to determine riparian vegetation and water quality profile in four types of secondary irrigation channels at Slamet Village, and determine interaction between riparian vegetation and water quality.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Area
 | Figure 1. Map of Slamet Village |
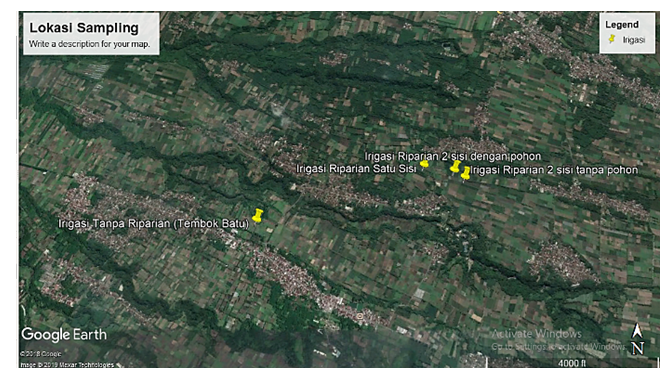 | Figure 2. Sampling Locations of in Slamet Village |
2.2. Sample Collection
- Each type of riparian vegetation is calculated based on coverage, lushness and density. Riparian vegetation that found was recorded, observing the morphological character and status of species belonging to the exotic species or not. Observations of riparian vegetation are classified into two groups, i.e. herbs and shrubs with trees.On the other hand, water quality is calculated based on several parameters, including the water temperature measured by a digital thermometer, turbidity with turbidity meters, conductivity with conductivity meters, pH with pH meters, DO and BOD measured by the titration method.
2.3. Data Analysis
- The results riparian vegetation and water quality analysis were analyzed using Ms. Excel and the ANOVA test using SPSS v16.0 program, then followed by Tukey HSD (if the data variant is homogeneous) or by Brown-Forsythe test and then followed by Gamess-Howell (if the data variant is not homogeneous). Riparian vegetation is represented by determining the shannon-winner diversity index, evenness index, dominance index, and taxa richness. All data on riparian vegetation and water quality were analyzed by cluster and biplot using the PAST 3.20 program.
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Riparian Vegetation Profile of Four Types Secondary Irrigation Channels at Slamet Village, Malang Regency
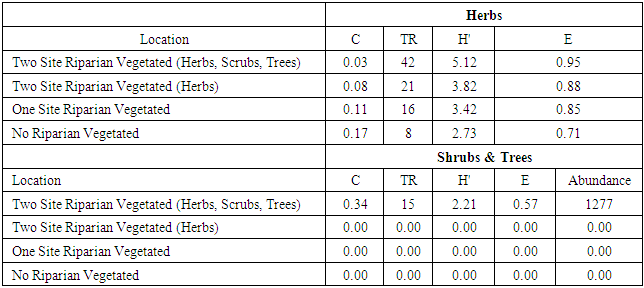
- Riparian vegetation profile of four types of irrigation channels is described through the shanon-winner index (H’), evenness index (E), dominance index (C), and taxa richness (TR). The vegetation community structure that has been observed in all four locations shows various variations. In the four observation locations found 41 species of herbs and 15 species of shrubs and trees. The highest H’ value of herbs in irrigation with two side riparian vegetation with trees combination (5,12) and the lowest H’ value in the stone wall irrigation channel (2.73) (Table 1). According to Barbour et al., (1987) the value of the diversity index can range from 0-7, with criteria: 0-2 (low), 2-3 (moderate), and >3 (high). So, the results of diversity index analysis show that four locations still have high diversity. It because H’ value for all locations is more than 3.
|
3.2. Water Quality Profile of Four Types Secondary Irrigation Channels at Slamet Village, Malang Regency Based on Physical-Chemical Parameters
- Physical and Chemical parameters can be used as the indicators of water quality. The result of water monitoring indicates that the water temperature shows a considerable variation in the range of 22.11-28.26°C (Figure 3). The highest water temperature value is in the irrigation channel without riparian vegetation, and the lowest one is in the irrigation with two sides of riparian vegetation and trees combination. The water temperature is suitable for plants growing in the range of 20-30°C. Water temperatures which contain more than 30°C can cause damage and decay the plants. A high value of water temperature in the locations without riparian vegetation is strongly influenced by the lack of riparian vegetation covering at the edge channels. Finally, this causes irrigation channels to be exposed to the direct sunlight. Water temperature also plays an indirect role in river animals through DO arrangements. The Increased temperature will reduce pH and DO (Lee, 2004). Based on the results of the ANOVA test and Tukey-HSD test, water temperature shows significant differences with the increase in water temperature in each location.
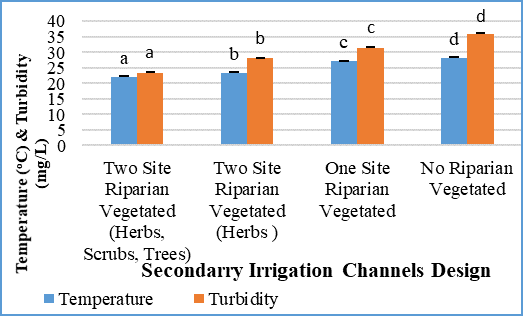 | Figure 3. Average of temperature and turbidity values in four secondary irrigation channels design |
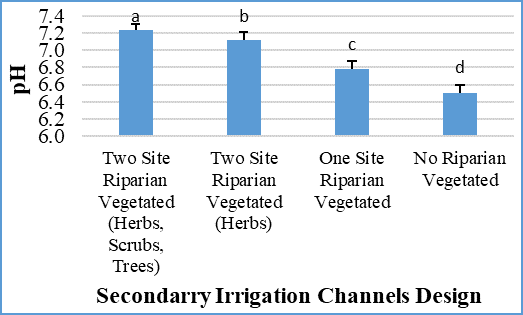 | Figure 4. pH values in four secondary irrigation channels design |
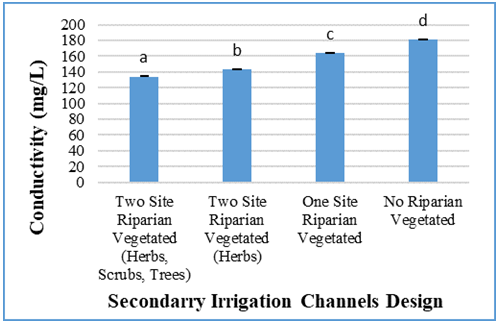 | Figure 5. Conductivity values in four secondary irrigation channels design |
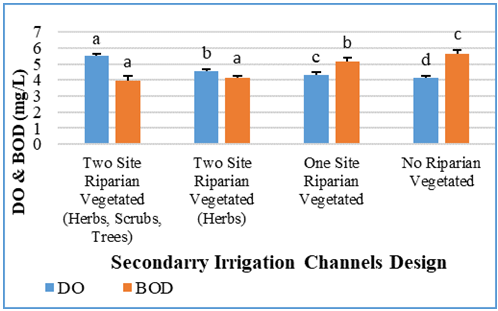 | Figure 6. DO and BOD values in four secondary irrigation channels design |
3.3. Interaction of Riparian Vegetation and Water Quality in Four Types Secondary Irrigation Channels at Slamet Village, Malang Regency
- Based on Figure 7, it can be seen that secondary irrigation channels with four different riparian types have an influence on the physical chemical water quality. The results of riparian vegetation profiles and water quality indicate that each location has different characteristics. This can be seen based on cluster and biplot analysis. Based on cluster analysis, there are four sub-groups. However, irrigation with two side riparian vegetation and trees combination has almost the same characteristics with two sides riparian vegetation without trees combination. Whereas irrigation with one sided riparian vegetation have the same characteristics with stone wall irrigation channels. Two sides riparian type irrigation with trees and without trees is characterized by high H', Taxa Richness, Eveness, pH, and DO values. Riparian vegetation in one-sided and without riparian vegetation (stone walls) have high values of conductivity, BOD, turbidity and Dominance. It shows that in irrigation channels with lower riparian vegetation it has low water quality.
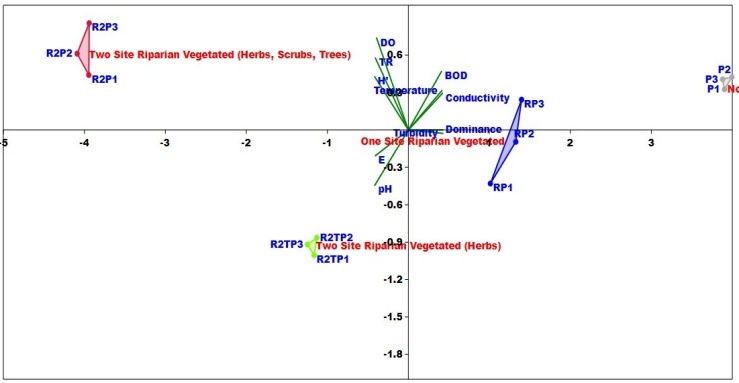 | Figure 7. Characteristics profile in each locations based on riparian vegetation and water quality |
4. Conclusions
- Irrigation channels with two sides riparian vegetation and trees have better water quality than other types of the irrigation channels. This is indicated by the high value of taxa richness (42 herbs species), H’ index (5.12), evenness (0.95), DO (5.49) and low of a dominance index (0.03). Irrigation channels without riparian vegetation have low diversity and DO index. However, based on Government Regulation of the Republic of Indonesia No.82 of 2001, the water quality of the four types of irrigation channels still meets the quality standards of class II. Therefore, it can be concluded that the profile of riparian vegetation indirectly correlates with water quality.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- Thanks to Purnomo, S.Si who have helped and supported my research in the field and in the Laboratory of Ecology and Animal Diversity, University of Brawijaya, Malang.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML