Razafitsiferana Theophile, Bruno Razanamparany, Mihasina Rabesiaka, Mandrimanana Andrianainarivelo
Faculty of Science, Antsiranana University, Madagascar
Correspondence to: Razafitsiferana Theophile, Faculty of Science, Antsiranana University, Madagascar.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2018 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
The district of Nosy-Be located in the Mozambique Channel, north-west of Madagascar, between latitude 13° 11' and 13° 30' south and between 48° 8 'and 48° 22' east longitude. The district of Nosy-Bese finds in the region DIANA, of the autonomous pronation of Antsiranana of the Country Madagascar. Is made up of five districts, the district of CITE SEIMAD is in the first Arrondissement. The objective of this work is to determine the concentrations of physicochemical and microbiological parameters of well water in the CITE SEIMAD neighborhood. Temperature 16.1°C per thermometer, turbidity 1.3 NTU per turbidimeter and the pH is 6.22 per pH meter. The physical parameters found are eligible for international standards (WHO, EU and EM). Dissolved oxygen is 0.3 mg / L, salinity is 0.05 mg / L, Ammonium is 0.05 mg / L, Sodium is 3.38 mg / L, Potassium is 13.5 mg / L, Calcium is 4.8 mg / L, Magnesium is 0.97 mg / L, Iron Assay 0 mg / L, Aluminum is 0 mg / L, Lead is 0 mg / L, Copper is 0.5 mg / L and Chloride is 8.87 mg / L. The chemical parameters are admissible to the standards of potability of the water in spite of the insufficiency of some found concentrations. The anions are measured by the spectrometer and the cations by atomic absorption. The microbiological: microorganisms at 36°C is 5 Ufc / ml, Bacteria coliform is 0.01Ufc / 100ml, Eschérchia coli is 0.005 Ufc / 100ml, Intestinal enterococci is 0 Ufc / 100ml and Spores of microaracisms is 0 Ufc / 100ml, we use the method of H. Vicent, modified techniques of Diénert and the method of R. Buttiaux. CITE SEIMAD well water is not microbial.
Keywords:
Water, Physicochemical And microbiological parameters
Cite this paper: Razafitsiferana Theophile, Bruno Razanamparany, Mihasina Rabesiaka, Mandrimanana Andrianainarivelo, Physico-Chemical Analysis of Wellwater in the Area of City Seimad Located in the First Borough of Nosy be Hell-Ville (District of Nosy be), Resources and Environment, Vol. 8 No. 1, 2018, pp. 14-20. doi: 10.5923/j.re.20180801.03.
1. Introduction
The district of Nosy-Be is composed of five districts, this study concerns in the district CITE SEIMAD on the first district. A quarter of the population in the first district is in the CITE SEIMAD neighborhood. The number of inhabitants in this district is given by the following table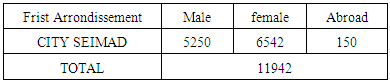 The people who live on the CITY SEIMAD use a large well for drinking water. The characteristic of this Well is given in the following table
The people who live on the CITY SEIMAD use a large well for drinking water. The characteristic of this Well is given in the following table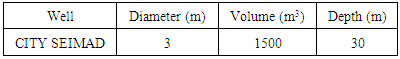 This study is divided into three parts: the first by the bibliographic synthesis, then the results of analyzes for the physicochemical and microbiological parameters, the interpretation and the discussion of these results, we will conclude with the conclusion.
This study is divided into three parts: the first by the bibliographic synthesis, then the results of analyzes for the physicochemical and microbiological parameters, the interpretation and the discussion of these results, we will conclude with the conclusion.
2. Bibliographic Synthesis
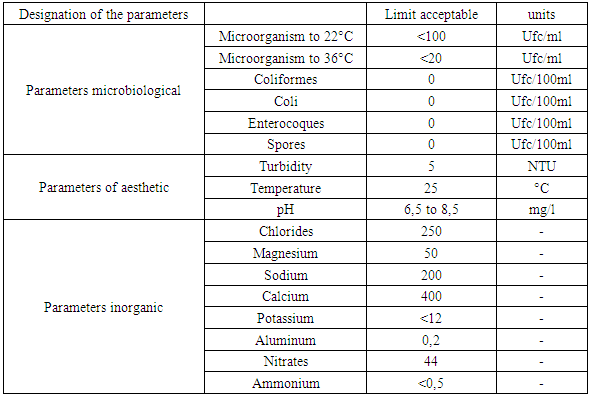
Well water is groundwater: the porosity and the structure of the ground determine the type of groundwater and the mode of underground circulation of the water. Generally pollution is absence in the underground water.Classification:Depending on the situation of the water table: free water table, captive water table and water table.Depending on the geological nature of the terrain: alluvial aquifer, karstic nappe and basement ply. Main Features the quality of the water depends on the land because there is a balance and an exchange of materials between the ground and the water that is there. Groundwater has: Low turbidity Temperature is one of the physical parameters.Table 1. Recommendation of the WHO
 |
| |
|
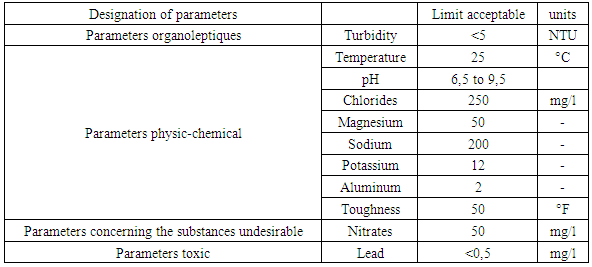
Table 2. Recommendation of the EU
 |
| |
|
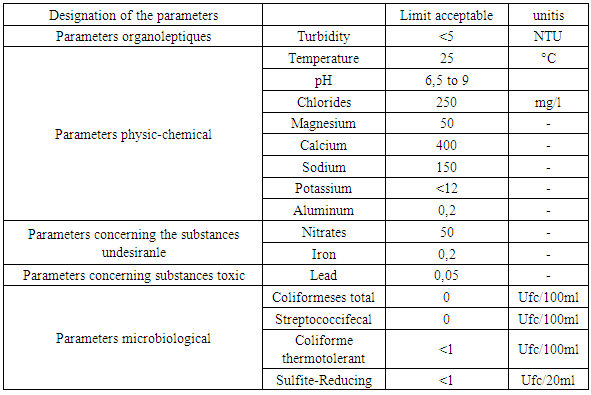
Table 3. Recommendation of the EM
 |
| |
|
Low oxygen concentrationLow contamination (bacteria, viruses ...) the source of drinking water in general is surface water and groundwaterA free web is sensitive to the captive web.The free layer is fed by the whole surface of the ground situated above it.Metals can exist in water the presence of pollution in drinking water is very dangerous Quality standard: for drinking water is referenced by the recommendation of the World Health Organization (WHO), the European Union (U.E) and the Malagasy State (E.M).Norm of quality1 - Recommendation of the WHO 2 - Recommendation of EU 3 - Recommendation of the EM
3. Analysis Parameters
Temperature, turbidity to know the transparency of the water, pH to know the water is acidic, basic or neutral. Dissolved oxygen makes it possible to estimate the amount of organic matter in the water.Salinity is the measure of the concentration of salt in water. Ammonium to know the existence of pollution in water. Calcium, magnesium, sodium and potassium are essential elements for the nutrition of human life.
4. Results of Measures
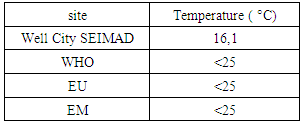
I – Physical parameters1 – TemperatureTable 4. Represents of the temperature
 |
| |
|
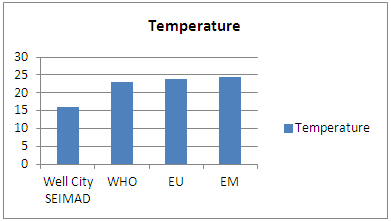 | Figure 1. Temperature measurement |
The value of the temperature found is 16.1°C so it is acceptable for the three potability standards because the value is <25°C. [3]2 – TurbidityTable 5. Represents the measurement of the turbidity
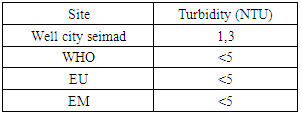 |
| |
|
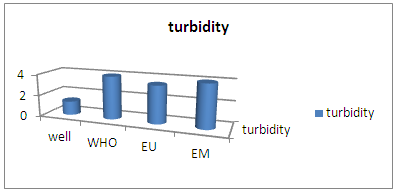 | Figure 2. Turbidity measurement. [1] |
For turbidity, the acceptable value for drinking water is 5 NTU gold for the CITY SEIMAD Well is equal to 1.3 NTU; it perfectly meets the required condition.3 – pHTable 6. Represents the measurement of the pH
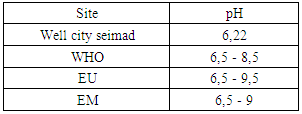 |
| |
|
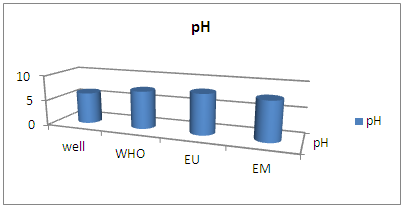 | Figure 3. pH measurement |
The pH is outside the required value because for CITY SEIMAD Well water is 6.22, while the three potability standards require this value to be 6.5 to 9, according to this results therefore the water in the vicinity of the acid. [3]II – CHEMICAL PARAMETERS1 – Dissolved oxygenTable 7. Measurement results of dissolved oxygen concentration
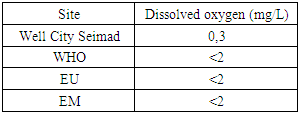 |
| |
|
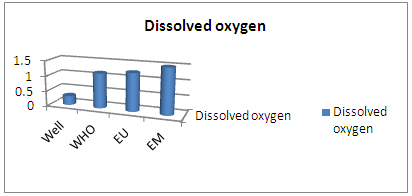 | Figure 4. Dissolved oxygen |
Dissolved oxygen is 0.3 mg / L less than the value requested for WHO, EU and EM. [2]2 – SalinityTable 5. Measurement results of salinity concentration
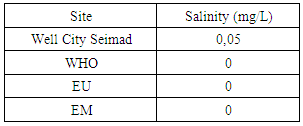 |
| |
|
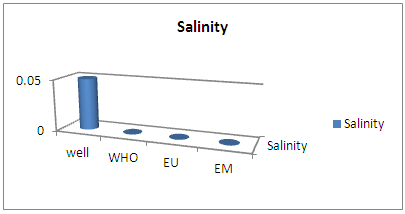 | Figure 5. Results salinity |
Salinity is 0 so exactly meets the required condition.3 – AmmoniumTable 6. Measurement results of ammonium concentration
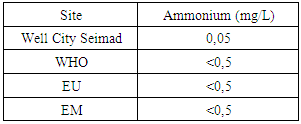 |
| |
|
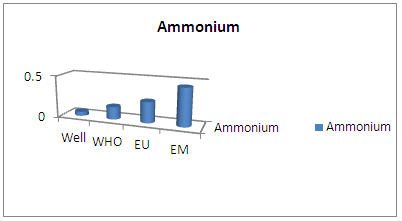 | Figure 6. Results ammonium |
The concentration of ammonium found is 0.05 mg / L, are lower than the three concentration values for international standards. [5]4 – SodiumTable 7. Measurement results of sodium concentration
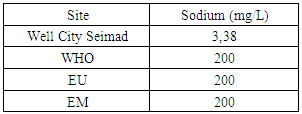 |
| |
|
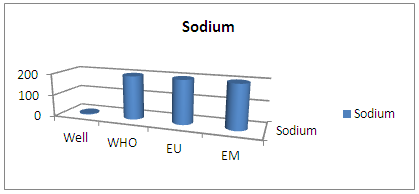 | Figure 8. Results sodium concentration |
The sodium concentration found is very low compared to the required values is for the Well is 3.38 mg / L, and the standard is 200mg / L.5 – PotassiumTable 8. Measurement results of potassium concentration
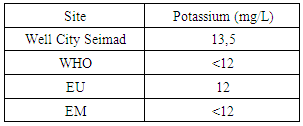 |
| |
|
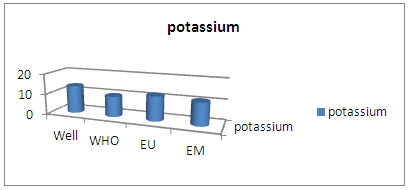 | Figure 9. Results potassium concentration |
The potassium concentration of CITY SEIMAD wells is in excess of the values required for drinking water standards6 – CalciumTable 9. Measurement results of calcium concentration
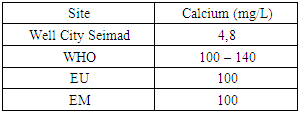 |
| |
|
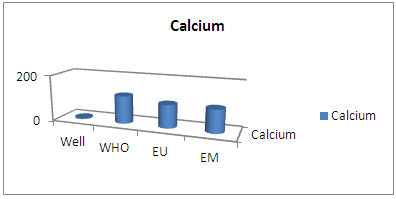 | Figure 10 |
The concentration of calcium found is very small compared to the standards required for drinking water. So the well of City SEIMAD is not good. [6, 10]7 – MagnesiumTable 11. Measurement results of magnesium concentration
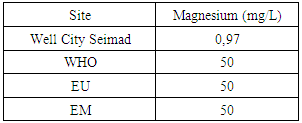 |
| |
|
 | Figure 11. Results of magnesium concentration |
The magnesium concentration is very low at the values required for international standards. [10]8 – Iron dosageTable 12. Measurement results of iron concentration
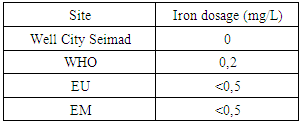 |
| |
|
 | Figure 12. Results of iron concentration |
Iron is only available for CITY SEIMAD well water. [9]9 – AluminumTable 13. Measurement results of Aluminum concentration
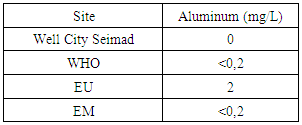 |
| |
|
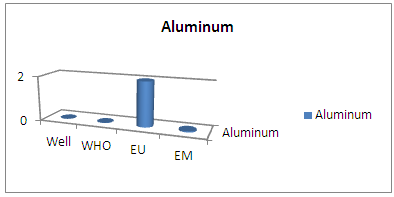 | Figure 14. Results of Aluminum concentration |
Aluminum is only available for CITY SEIMAD well water. [4]10 – CopperTable 14. Measurement results of copper concentration
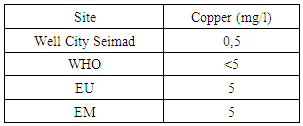 |
| |
|
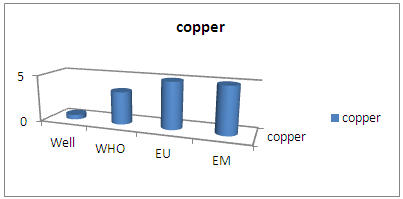 | Figure 15. Results of copper concentration |
Copper exists but in the form of a trace, so no problem for drinking water [8].11 – LeadTable 15. Measurement results of lead concentration
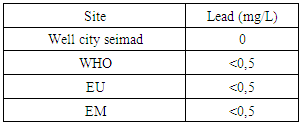 |
| |
|
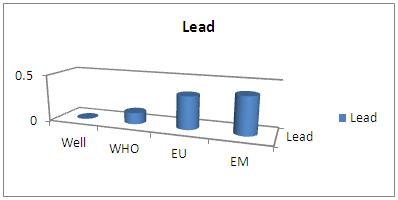 | Figure 16. Results of lead concentration |
Lead also does not exist for this water [11].12 – ChloridesTable 16. Measurement results of chlorides concentration
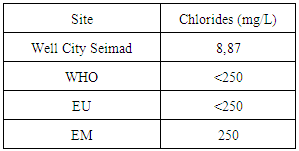 |
| |
|
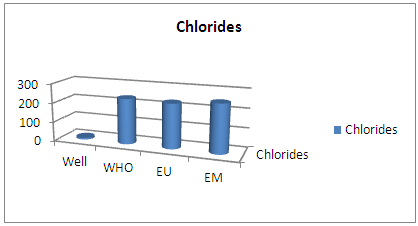 | Figure 17. Results of chlorides concentration |
The concentration of chloride found is very low by international standards for drinking water, so the water is not good. [7]III- MICROBIOLOGICAL ANALYSIS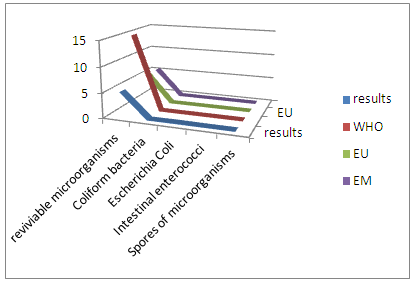 | Figure 18. Results of the microbiological |
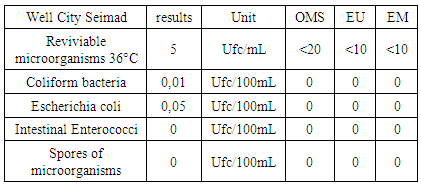
Table 18. Measurement results of the microbiological
 |
| |
|
The water CITY SEIMAD Well is not microbial.
5. Interpretation of results
- Physical parametersThe temperature is 16.1°C, below 25°C for international standards, the turbidity 1.3 NTU less than 5 NTU for the condition of drinking water and the pH is 6.22 excluded for the standard of potability. The turbidity is 100%, the pH is 88% and the temperature is 100% for the standards required for drinking water, so from these values it can be written that the physical parameter corresponds perfectly to 96% of the values required for international standards.- Chemical parametersThe dissolved oxygen is 0.3 mg / L, the required concentration is <2mg / L so it is acceptable.Salinity does not exist for the water of CITY SEIMAD.Ammonium is 0.05 mg / L, the required value is <0.5 mg / L, so the water is less polluting.The potassium concentration is higher than the values requested for WHO, EU and ME.The concentration of sodium found is 3.38 mg / L, but the required values are 200 mg / L; the calcium concentration found is 4.8mg / L, their required values are 100mg / L and the magnesium is 0.97mg / L, the required value is 50mg / L.In conclusion, according to this comparison the water is low in sodium, calcium and magnesium.Metals like copper, aluminum, iron and lead do not exist for the water of CITY SEIMAD.- Microbiological analysisfrom the values found have can write: Revive microorganism at 36°C, Intestinal Enterococci and Spores of microorganisms meet 100% for the standards required for drinking water, while Coliform bacteria and Eschercia coli respond to 95%, In conclusion at the bacteriological level, according to this value, it is possible to write the result that it meets 98% of the norm required for drinking water.
6. Conclusions
Physical parameters are eligible for the three international standards required for drinking water.Chemical parameters: the concentrations found are almost insufficient to drinking water standards, for which I propose the demineralization before being used. No trace of metals for this water well CITY SEIMAD.No danger also at the level of the bacteria for the well water of CITY SEMAD.
References
| [1] | C.C.HACH et al. (1995). Unerstanding turbidity measurement. Hach Co. Technical information Ser Booklet 11, Loveland. Colo. |
| [2] | S.MUANGKAEW et al. (2002). A reverse-flow injection analysis method for the determination of dissolved oxygen in frensh and marines waters, Talanta.58: 1285. |
| [3] | W.F. LANDELER. (1964). Effet of temperature on the pH natural. J.A.W.W.A. 38, p.179. |
| [4] | H.H. YEH et T.M. CHUANG (1994). The analysis of residual aluminium and its application in drinking waters treatment, Aqua.43: 76. |
| [5] | G. VAN BENEDEN (1953). Les techniques de dosage des azotes dans les eaux. C.B.E.D.E. 36. P. 112. |
| [6] | T.J. CAROWELL. Et al. (1990). Determination of calcium in waters, milk and by discontinuous-flow analysis. Analyst. 115:1235. |
| [7] | A.T. HAJ-HUSSEN (1996). Ultraviolet determination of chloride in water by flow injection analysis. Analytical Letters, 29: 793. |
| [8] | A.R. GAHLER (1954). Colorimetric determination of copper with neocuproine; Anal. Chem. 28 p. 174. |
| [9] | M.T. DOIG and D.F. MARTIN (1971). Effect of humic acids on iron analyses in naturel water. Water Ress, 5: 689. |
| [10] | Z. CHEN et M.A. ADAMS (1998). A metallic cobalt electrode for the indirect potentiometric determination of calcium and magnesium in natural waters using flow injection analysis. Talanta 47: 779. |
| [11] | J. RANCHET et coli. (février 1992). Essais interlaboratoires: dosage de Cd, Ct, Cu et Pb dans des solutions synthétiques par spectrométrie d’absorption atomique sans flamme. Analusis. 10. p. 71-77. |


 The people who live on the CITY SEIMAD use a large well for drinking water. The characteristic of this Well is given in the following table
The people who live on the CITY SEIMAD use a large well for drinking water. The characteristic of this Well is given in the following table This study is divided into three parts: the first by the bibliographic synthesis, then the results of analyzes for the physicochemical and microbiological parameters, the interpretation and the discussion of these results, we will conclude with the conclusion.
This study is divided into three parts: the first by the bibliographic synthesis, then the results of analyzes for the physicochemical and microbiological parameters, the interpretation and the discussion of these results, we will conclude with the conclusion. 















 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML

















