-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Resources and Environment
p-ISSN: 2163-2618 e-ISSN: 2163-2634
2013; 3(2): 15-19
doi:10.5923/j.re.20130302.01
Impact of Pollution from Kosova’S Power Plant in Obiliq on Some Biochemical Parameters of the Local Population of Garden Snail (Helix Pomatia L.)
Kemajl Bislimi1, Avni Behluli2, Jeton Halili3, Ilir Mazreku1, Fetah Halili1
1University of Prishtina, Faculty of Mathematical and Natural Sciences, Department of Biology
2University of Prishtina, Faculty of Agriculture and Veterinary, Gene Bank of Kosovo for Plant Genetic Resources
3University of Prishtina, Faculty of Mathematical and Natural Sciences, Department of Chemistry
Correspondence to: Avni Behluli, University of Prishtina, Faculty of Agriculture and Veterinary, Gene Bank of Kosovo for Plant Genetic Resources.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Garden snail specimens (Helix pomatia L.) were collected from the area surrounding the Obiliq Power Plant in the central area of Kosova to determine the potential impact of pollution. The concentrations of hemocyanin (Hc) and the activity of transaminases (ASTand ALT) in the hemolymph plus catalase in hemolymph, hepatopancreas and albumen gland were determined. Results showed a significant increase of transaminases activity in hemolymph and catalse in albumen gland, a significant decrease of hemocyanin concentration in hemolymph as well as non-significant decrease of catalase activity in hemolymph and hepatopancreas, compared to respective values for these parameters in control group of snails. A significant increase of transaminases and catalase activity were reported also to the group of snails treated with Pb-acetate in their hemocoel, compared to control who received physiological solution instead. Statistical data analyses were calculated using different statistical software as ANOVA and MINITAB 16.
Keywords: Snail, Hepatopancreas, Hemocyanin, Transmaninase, Catalase
Cite this paper: Kemajl Bislimi, Avni Behluli, Jeton Halili, Ilir Mazreku, Fetah Halili, Impact of Pollution from Kosova’S Power Plant in Obiliq on Some Biochemical Parameters of the Local Population of Garden Snail (Helix Pomatia L.), Resources and Environment, Vol. 3 No. 2, 2013, pp. 15-19. doi: 10.5923/j.re.20130302.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Kosovo is among of the countries with the highest degree of pollution in Europe. Currently, the main sources of pollution are Kosovo’s Power Plants. According to the present data, coal resources in Kosovo are estimated in about 10.5 milliard tones[3]. Almost entirely, this coal is being used for producing of the electricity in Kosovo’s power plants. Monitoring showed that only one of five units of Power Plant “Kosova A”, within one hour releases 25 tones of dust and ash. Emission level is about 74 times above the European standards[4]. Particular environmental problem represents ash landfill, not only for microlocality where it’s located but even far away including Prishtina. Chemical gamma- spectroscopical analysis of dust and particles showed that it contains several toxic elements (As, Pb, etc.), and radionuclides (238U, 235U, 226Ra, etc.) which endanger plant, animal and human health in vicinity of power plants[5],[6]. Currently, about 700,000 citizens inhale the mixture of toxic gases released from Power Plants “Kosova A and B”. Indicator of this pollution is the level of public health in Kosovo, the number of deaths of newborn infants that is the highest in Europe. According to a report published by the UNDP (2002), the infant mortality rate in Kosovo is around 34-35 per 1000 live births[7].Literature data indicate that snails and other pulmonate gastropods have capability to accumulate heavy metals[8]. Research has shown that plants which feed snail accumulating heavy metals and radionuclides and this made possible the transfer of these components from the environment to the organism[9],[10].Some authors found a decrease in peroxidase activity in hemolymph of Helix pomatia caused by environmental pollution from power plants, degenerative changes in kidneys and liver of hen Hisex brown as well as genetic disorders in Drosophilla mellanogaster of the same source of pollution[11],[12],[13]. Another author found changes in the activity of enzymes acetylcholinesterase, catalase, glutation-s-transferase and glucose absorption in the digestive tract of the snail Helix aspersa from a contaminated area[14]. From the above mentioned citations, could be concluded that the species Helix sp is an excellent bio-indicator of environmental degradation. Therefore the aim of this research is that by applying passive and active bio-monitoring and garden snail Helix pomatia L. as biomonitor, to evaluate the effects of environmental pollution from Kosovo’s Power Plants in the concentration of hemocyanine (Hc), activity of transaminases (AST & ALT) in hemolymph and antioxidant enzyme-catalase in hemolymph, albumen Gland and hepatopancreas.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
- Studies were performed with the natural population of snail (Helix pomatia L.) in Kosovo. Experimental group of snails is taken from a ‘green oasis’ with spontaneous plants in the base of ash landfill deposited from coal-fired of power plant in Obiliq, while control specimens were obtained from a non contaminated area, far away from power plants (the village Gaçkë, Ferizaj). For this research were analyzed 20 individuals (snails) from each location (20 per test locality and 20 per control locality). Snails were taken in an area approximately 15,000 - 20 000 m2, as we tried to cover as more as larger surface of researching area.Snails were mainly old; it is based on the size (dimensions) and number of spirals of the shell (most of them had a large shell). Snails were approximately of the same age and this estimation was done based on the shell characteristics also.In order to test the effects of Pb acetate, one of two groups of snails with 10 individuals, taken on control region are intoxicated (in hemocoel) with Pb -acetate (dose 150mg/kg/72h), while the control group with 10 individuals also were injected with RINGER solution for Helix pomatia[15]. In order to avoid differences in the content of hemolymph and tissues depending from the age or weight or from the season or implications of circadian rhythm in results snails of both groups experimental and control were taken in the same time, were of about same body weight and analyzed at the same time[16].
2.2. Methods
- Hemocyanin is determined in hemolymph indirectly from copper with sodium diethyldithiocarbamate[1]. The amount of copper is assigned based on the intensity of the yellow color which developed as a result of copper interaction with the sodium diethyldithiocarbamate. Hemocyanin is expressed in g%.The activity of transaminases (AST and ALT) in hemolymph is determined with kinetic method[17]. Extinction is read in 340 nm in the spectrophotometer Shimadzu UV160-U UV-VIS spectrophotometer and expressed in U/L. While catalase activity in hemolymph and tissues is determined according the volumetric method and is expressed in mlO2/ml/3’ in hemlymph, respectively ml O2/100mg/3’ in albumin gland and hepatopancreas[2].
3. Results
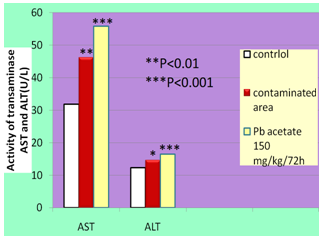
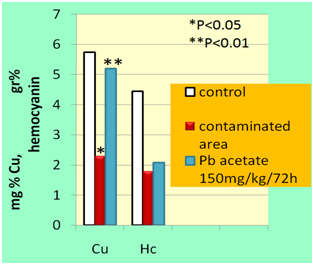
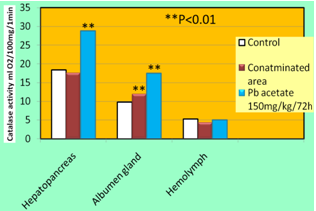
- Biochemical analysis of hemolymph of the snails from the polluted region of power plants (Obiliq) and those treated with Pb-acetate (72h after injection of Pb-acetate, doses 150 mg/kg/72h) show a significant decrease (P<0.05, P<0.01) in copper and hemocyanine concentration in the hemolymph, compared with the control group of snails which instead of Pb-acetate was injected in their hemocoel the same dose of physiological solution for Helix pomatia (Fig. 1). While, in terms of the activity of enzymes AST and ALT, there is a significant increase (P<0.01, respectively P<0.001) of their activity in hemolymph of snails from the polluted region of Kosovo’s Power Plants and snails treated with Pb-acetate, compared with the control group (Fig2).Related to catalase activity in hemolymph and hepatopancreas, there is a nearly significant decrease (P<0.05) to the snails of the region polluted by Power Plants, while a high significant increase (P<0.01) of the activity of this enzyme in hepatopancreas and albumen Gland (but not in hemolymph also) of the snails treated with Pb-acetate, compared with the control group (Fig3).
4. Discussion
- It is known that hemocyanin presents 90 – 98% of total proteins in snail’s hemolymph, therefore our conclusion for decrease of hemocyanin concentration in snails of contaminated area can be connected with the decreasing of the amount of total proteins in the serum of different animals and humans as well, in cases of intoxication with Pb or other heavy metals[18],[19],[20].Regarding transaminases activity it is to be mentioned that there are many data in literature which confirm that several factors impact activity of these enzymes in body fluids (hemolymph and blood), such as: traumas, fatigue, clinical changes on liver, diabetes, muscle work, feeding regime, hemolysis, animal transport, hipo and hiper function of endocrine glands, pathological condition of organism caused by different ecological factors such as: poisons, diseases of skeletal muscles, liver and myocard, etc.[21].Increase of transaminase activity in hemolymph of natural population of garden snail taken in contaminated area as well as of intoxicated with Pb acetate, respectively with contaminated water from ash landfill in Obiliq, compared with control groups is in agreement with results of other authors, who concluded the increased activity of these enzymes in the serum of laboratory rats exposed for six months in the yard of Smelt Factory for Pb and Zn “Trepça” in Zveçan[22]. Increase of transaminase activity is a characteristic test not only in cases of different poisonings, but in cases of different diseases connected to necrosis of liver and other organs, also (cirrhosis and liver hepatitis, heart infarct etc), in such cases, transaminases as intracellular enzymes discharge in body fluids[23],[24]. In our case it could also be possible that in snails hemolymph are discharged transamizes from hepatopancreas which is according to functionality analog with vertebrate’s liver that accumulate mostly heavy metals compared to other organs, and which damage it also[25],[26],[27],[28]. Increase of transaminases activity in snails of contaminated area is in tightly connected with decrease of the amount of total proteins in hemolymph[19]. This negative correlation is made obvious when we have in mind the fact that snails similar to high animals have the ability of gluconeogenesis, transformation of proteins in energetic resources, precisely in carbohydrates[29],[30].Data from literature regarding activity of antioxidant enzymes, catalase and peroxidase, in cases of intoxication of organism with different toxicants (heavy metals, pesticides, radionucleids), are contradictory. Some authors conclude increase, while others decrease of activity of these enzymes in intoxicated animals[31],[32],[33],[34]. The decrease of enzyme activity could be as a result of decrease in protein biosynthesis or blockage of active groups of enzymes[35]. As a result of catalase and peroxidaze activity inhibition, the amount of hydrogen peroxide is increased, and it causes peroxidation of lipid components of cell membrane and has got also mutagen and cancerogen effects[11]. In this context our results which show decrease of catalase activity in hemolymph and hepatopancreas of snails in contaminated area (Obiliq) compared to control snails, are in agreement with data found in the natural population of turtle Testudo hermani Gmel. of contaminated area located on Pb metallurgy in Zvecan[33]. Some authors showed for a significant increasing of the activity of detoxifying enzymes, catalase respectively in Helix aspersa taken near one area polluted with metal dust in Algeria[36]. An increase of catalase activity was observed on cerebellum and cerebrum of lead-treated rats[37].Increase of catalase activity in hemolymph of snails treated with Pb-acetate (acute intoxication) could be connected to the data given by some authors, who noticed an increased activity of this enzyme in rats exposed for 6 months to the pollution Pb-metallurgy in Zveçan[38].The increase of catalase activity is found in the plants also, as well as in the roots of plant Capsicum annum grown in solution where CdCl2 (10-50µmol) was added[39]. At the end, it could be concluded that the species Helix pomatia L., is an excellent bio-indicator of environmental degradation, it is sensitive to the presence of heavy metals and other pollutants and this sensitivity was shown by metabolic changes, disruption of the synthesis of enzymes and their activity in different organs.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML