-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Resources and Environment
p-ISSN: 2163-2618 e-ISSN: 2163-2634
2012; 2(1): 86-89
doi: 10.5923/j.re.20120201.11
Topsoil Contamination by Heavy Metals from a Local Brass Industrial Area of Nigeria
1Department of Chemistry, Federal University of Technology, Minna, Niger State, Nigeria
2Department of Chemistry, University of Abuja, Abuja, FCT, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Y. A. Iyaka , Department of Chemistry, Federal University of Technology, Minna, Niger State, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
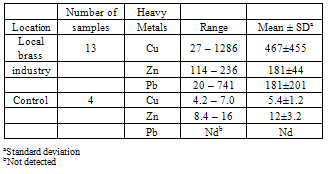
Contents of Cu, Zn and Pb in top soils of the vicinity of a local brass industrial site within a residential area in Bida, Niger State, Nigeria were determined. The obtained results from the soils of the vicinity of the local brass industrial site showed some extent of contamination with significant elevated mean values of 467± 455µgCug-1, 181± 44µgZng-1 and 181± 201µPbg-1, when compared to 5.4±1.2µgCug-1, 12±3.2µgZng-1 and not detectable value for Pb from the control soils. Hence, this study has helped to create the public awareness with regard to the risk of the adverse health effects that could possibly arise from the environmental pollution by heavy metals, particularly with regard to Pb in soils and the consequent need for immediate remediation of the studied area.
Keywords: Local Industrial Site, Heavy Metals, Contamination
Cite this paper: Y. A. Iyaka , S. E. Kakulu , "Topsoil Contamination by Heavy Metals from a Local Brass Industrial Area of Nigeria", Resources and Environment, Vol. 2 No. 1, 2012, pp. 86-89. doi: 10.5923/j.re.20120201.11.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Heavy metals play a significant role in the modern environmental problems that are associated with pollution and they occur naturally in earth’s crust in varying concentrations, while Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Sb and Zn are mostly used and discharged industrially [1]. In alloys and steels, heavy metal pollution occurs through production stage, corrosion in use, disposal to landfills and by recycling of the alloys in the scrap metal[2]. However, Cu pollution may arise from brass manufacture[1], and other major sources such as copper mining and smelting. Major uses of Zn have also been associated with the production of non – corrosive alloy; brass and in galvanized steel and iron products, and Zn may also contain small amounts of more toxic metals, such as Pb as impurities[3].Kabata- Pendias and Pendias[4] observed that soil acts as a geochemical sink for contaminants, and as a natural buffer controlling the environmental cycling of the chemical elements to the atmosphere, hydrosphere and biota. Moreover, the concern for heavy metals in soils is directly related to their interactions within all the systems through the food chain; soil heavy metals composition may influence uptake by plants, which consequently determines that of animals and humans[5-7]. Previous researchers have reported heavy metal pollution in soils from the vicinity of industrial areas with peculiar feature of decrease in concentration with increase in distance from industrial sites[8-10].Local brass industry in Bida, Niger state, Nigeria may be traced back to the settlement of Egyptian emigrants in 1834, and their products are mainly bangles, cups, rings and swords[11]. The local brass industrial site is located within the residential areas and the public concern over the possible potential adverse health effects has been undermined. Furthermore, there has been no major research study reported in literature about the heavy metal contents in soils from the vicinity of this local brass industrial area. Hence, this study examined the total metal concentrations of Cu, Zn and Pb in the topsoil within the vicinity of the local brass industrial area with the aim of investigating the possible impacts the enrichment of these heavy metals may have on the environment, particularly on humans.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Sampling Sites and Sample Collection
- Soil samples of topsoil were collected from thirteen (13) locations within the vicinity of a local brass industry in Bida, Niger State, Nigeria. Four (4) control soil samples were collected from locations within the city that were far from any major pollution sources. The sampling approach was random and systematic; at each sampling location or point a stainless steel auger was used to collect five sub-samples from the top layer at a depth of 0-20cm. The collected sub-samples were then pooled together to form a composite of each individual sample.
2.2. Preparation of Samples
- The soil samples were air-dried for one week, ground, passed through 2.0mm sieve, further pulverized to a fine powder and passed through 0.5mm sieve for the total metal content determination.
2.3. Chemical Analysis of Samples
- Soil samples were digested with HNO3 - H2O2 - HCl using USEPA SW-846, method 3050[12]. The USEPA SW-846, method 3050 developed for total sorbed heavy metals in soils, gives a reliable measure of the amount of the metals added to soils as nonsilicates[13] that is potentially available for natural leaching and biological processes. The concentrations of Pb, Cu and Zn in the digestion solution were determined with a Unicam 969 Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer - solar in the flame mode.
2.4. Quality Assurance and Quality Control (QA/QC)
- At least one reagent blank and one duplicate sample were run for every batch of four (4) samples for background correction and to verify the precision of the method. Accuracy was however, assessed by analyzing three (3) replicates of certified reference materials, soil sample S0-1, obtained from Canada Centre for Mineral and Energy Technology (CANMET). Recoveries were satisfactory; average values being in excess of 90% for Pb, Cu and Zn analysed.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Copper
- Cu has the highest concentration range for all the heavy metals examined in the soil samples from the vicinity of the local industrial area; varying considerably from 27µgg-1 to 1286 µgg-1( Table 1). In about 69% of the samples studied, Cu levels exceeded the Soil Quality Criteria values for many countries; 50 µgg-1 for Switzerland[14], 100 µgg-1 for Norway[15], and maximum allowable limit set by Kloke[16] was also exceeded. Up to 85% of the analysed soils from this local industrial area also had total Cu contents that exceeded the residential acceptable limit of 63µgg-1 recommended in Canadian Soil Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Environment and Human Health[17]. Furthermore, the Cu values obtained from soils in this study were significantly higher than the Cu ranged content of 11 µgg-1 to 116 µgg-1 reported by Ekosse et al.,[18] in their study of nickel – copper mine and smelter plant area of Botswana. The 2.4 µgg-1 to 6.5 µgg-1 Cu concentrations documented by Iyaka and Kakulu[19] in their study of urban agricultural soils of Bida, Niger state, Nigeria were also remarkably lower than obtained ranged value from this study. Nevertheless, the soil total Cu contents of the vicinity of this local brass industrial area were distinctly lower than those reported by Freeman and Hutchinson[20] in their study of the vicinity of a nickel- copper smelter at Sudbury, Ontario, Canada.
3.2. Zinc
- The Zn contents obtained from the vicinity of the local brass industrial site (Table 1) were generally higher than the normal concentration range of 17 - 125 µgZng-1 for top surface soils suggested by Ward[5]. The Zn levels in soil samples of this study also exceeded the 36 - 113 µgZng-1 range documented by Sharma et al.,[21] in their determination of total micronutrients in relation to pedogenesis in some soil samples in India. A lower ranged value of 10 - 85 µg Zng-1 than obtained in this study (Table 2) has also been reported by Iyaka and Kakulu[22] in their study of roadside topsoil of the Bida city. However, the Zn values of the soils in the vicinity of this local brass industrial site are within a soil level range of 0- 250µgZng-1 classified as being typical of uncontamination by the UK Department of the Environment for the recreational and Agricultural uses[23].
|
3.3. Lead
- The Pb contents in the examined soil samples from the vicinity of this local brass industrial site varied widely between 20µgg-1 and 741µgg-1(Table 1). The very high Pb concentrations in some locations may be attributed to the contribution or effect of Pb – based paint whose contamination may occur when paint chips from old buildings mix with the soil. EPA[24] asserted that soil adjacent to houses with exterior Pb – based paints may have Pb levels of as high as greater than 10, 000 µgg-1 . In three of the soil samples studied, Pb contents exceeded the 250 µgg-1 permissible level of Pb in soils proposed by Madhaven et al.,[25] ; this value applies to a worst – case scenario in which children below five years of age repeatedly use an area without grass cover (as experienced in this study) and mouthed objects frequently. ATSDR[26] stated that a soil Pb concentration of 250µgg-1 would add at most an estimated 2 µgPbℓ-1 to the blood Pb level of children.Furthermore, seven of the thirteen sample locations had Pb levels above the 100 µgg-1 recommended by Shellshear et al.,[27] as permissible level for protecting pica children or established as a bare soil standard by the Minnesota State Legislature[28] The dietary exposure that results in blood levels of concern has been estimated to be 6µgPbday-1 for children of six years or younger, with a further argument by ATSDR[26], that there may be no level of blood Pb that is not toxic, particularly in the developing central nervous system. Thus, given a soil Pb content of 100µgg-1; consumption of approximately two teaspoons of this soil per week (as it may occur in some environments) would be sufficient to produce the same amount of Pb found in a diet that can cause elevated blood levels of concern, depending on many factors that include the age of the child, diet and health. This calculation is however, based on the assumption that half of the Pb in the soil eaten by children is absorbed[28]. Juberg et al[29] observed that children absorb about 30 - 40% of ingested Pb , while adults absorb only 5 – 15% and retain less than 5% of what is absorbed.
3.4. Correlation Analysis
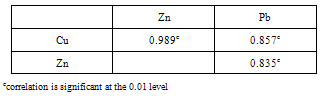
- Interelement association shows significant correlation between Cu, Zn and Pb in soils from the local brass industrial area (Table 3). The interelemental correlation between these elements in this study may possibly be ascribed to the control of the elemental association by factors such as soil genesis and properties as well as anthropogenic impact on the environment.
|
3.5. Percentage Enrichment Factor (%EF)
- Table 4 shows the evaluation of the soil contamination using the percentage enrichment factor adapted from Loska and Weichula[30], and Ali and Malik[31]. Generally, the obtained results showed that %EF of the studied heavy metals depicted contamination of the topsoil; however, Zn had the highest %EF probably because the minimum concentration of Zn from the soil samples of the local brass industrial area was about ten times the obtained mean value from the control soils. where, C is the mean total content, Cmin is the minimum content determined and Cmax is the maximum content determined.
|
|
4. Conclusions
- Average heavy metal contents in the topsoil of the local brass industrial area of this study were substantially higher than in the control soils (Table 2) ; the Pb concentration in the background level was however, too low to be detectable. Since Nigeria does not have quality criteria for soil metal levels, the mean heavy metal contents from this study were compared with criteria from other countries and USEPA upper limit values (Table 5). The mean contents for Cu and Pb in this study are higher than criteria for the various countries shown in Table 5, but lower than the USEPA upper limit of allowable heavy metals in soils. However, the Zn average value was generally lower in comparison to the cited concentrations. Hence, the findings of this study indicate that there is a significant accumulation of Cu, Zn and Pb above the background level in the studied soils of the local brass industrial site located in residential area, thereby increasing the public awareness with regard to the risk of the adverse health effects that could possibly arise from the environmental pollution by heavy metals and the consequent need for immediate remediation.
References
| [1] | B. J. Alloway, D. C. Ayres, Chemical Principles of Environmental Pollution, Blackie Academic and Professional, London, 1997 |
| [2] | R. U. Ayres, L. W. Ayres, Consumptive uses and losses of toxic heavy metals in the United States, 1880 – 1980, pp 259 -295, in R. U. Ayres, U. E. Simonis, Eds, Industrial metabolism: Restructuring for sustainable development, United Nations University Press, Tokyo, New York, Paris, 1994 |
| [3] | C. G. Elindar, Zinc, L. Friberg, G. F. Nordberg, V. B. Vouk, Handbook on toxicology of metals, 2nd ed, Elsevier, Amsterdam, New York, Oxford, 1986 |
| [4] | A. Kabata- Pendias, H. Pendias, Trace elements in soils and plants, CRC Press, London, 1992 |
| [5] | N. I. Ward, Trace elements, pp321 – 351. In : F. W. Fifield, H. R. J. Blackie, Eds, Environmental Analytical Chemistry, Academic and Professional, Glasgow, 1995 |
| [6] | Y. J.Cui, Y. G. Zhu, R. H. Zhai, D. Y. Chen, Y. Z. Huang, Y. Qiu, J. Z. Liang, “ Transfer of metals from soil to vegetables in an area near a smelter in Nanning, China”, Environment International vol. 30, pp 785 – 791, 2004 |
| [7] | C. N. Sridhara, C. T. Kamalaa, D. S. S. Raj, “Assessing risk of heavy metals from consuming food grown on sewage irrigated soils and food chain transfer”, Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety vol. 69, pp 513 – 524, 2008 |
| [8] | P. C. Onianwa, S. O. Fakayode, “Lead contamination of topsoil and vegetation in the vicinity of a battery factory in Nigeria”, Environmental Geochemistry and Health vol. 22, pp 211 – 218, 2000 |
| [9] | R. Schulin, F. Curchod, M. Mondeshka, A. Daskalove, A. Keller, “ Heavy metal contamination along a soil transect in the vicinity of the iron smelter of Kremikovtzi(Bulgaria)”, Geoderma vol. 140, pp 52 – 61, 2007 |
| [10] | M. L. Svendsen, E. Steinnes, H. A. Blom, “Vertical and Horizontal Distributions of Zn, Cd, Pb, Cu and Hg in uncultivated soil in the vicinity of a Zinc smelter at Odda, Norway”, Soil & Sediment Contamination vol. 16, pp585 – 603, 2007 |
| [11] | U. M. Gbate, S. Usman, “Profile of local craft with potentials of development into small scale industries in Gbako local Government Area, Bida, Niger State”, A paper presented at joint domestic trade fair, Sokoto, 1988 |
| [12] | United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA), Test methods for evaluating solid wastes. USEPA SW-846, method 3050, U. S. Govt Print Office, Washington D. C. , 1986 |
| [13] | J. A. Risser, D. E. Baker, Plant Analysis, pp390 – 427, in R. L. Westernman, Ed. , Soil Testing and Plant Analysis , Part III SSSA. SSA, U. S. A., 1990 |
| [14] | Federal Office of Environment Forest and Landscape (FOEFL), Commentary on the Ordinance relating to pollutants in soil, Bern, Switzerland, 1987 |
| [15] | C. Reimann, R. Boyd, P. deCarital, J. H. Hallareker, G. Kashulina, H. Niskavaara, I. Bogatyrev, “ Topsoil (0-5cm) composition in eight artic catchments in Northern Europe (Finland, Norway and Russia)”, Environ. Pollut. Vol. 95, pp45 – 56, 1997 |
| [16] | A. Kloke, Richwerte ’80, Orientierungsdaten fur tolerierbare Gesamtgehalte einiger Elemente in Kulturboden, Mitt. VDLUFA, No 2, 9 – 11, 1980 |
| [17] | Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (CCME), Canadian Soil Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Environment and Human Health: Summary Tables. In: Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines, 1999, Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment, Winnipeg |
| [18] | G. E. Ekosse, J. C. Ngila, N. Forcheh, “ Multivariate analyses of heavy metals in soils and colophospermum mopane leaves around the Selebi phikive nickel – copper mine and smelter/ concentrator plant area, Bostwana”, Journal of Applied Sciences and Environmental Management vol. 9, pp177 – 185, 2005 |
| [19] | Y. A. Iyaka, S. E. Kakulu, “Copper and Zinc contents in urban agricultural soils of Niger state, Nigeria”, African Research Review vol. 3, pp 23 – 33, 2009 |
| [20] | B. Freeman, T. C. Hutchinson, “ Pollutant inputs from the atmosphere and accumulation in soils and vegetation near the nickel – copper smelter at Sudbury, Ontario, Canada”, Can. J. Bot. Vol. 58 pp108 - 132 , 1980 |
| [21] | B. D. Sharma, S. S. Mukhopadhyay, H. Arora, “Total and DTPA – extractable micronutrients in relation to pedogenesis in some Alfisols of Punjab, India”, Soil Science vol. 170, pp 559 – 572, 2005 |
| [22] | Y. A. Iyaka, S. E. Kakulu, “Lead, Copper and Zinc concentrations in roadside topsoil of Niger state, Nigeria”, Journal of Emerging Trends in Engineering and Applied Sciences (JETEAS) vol. 2, pp 754 – 758, 2011 |
| [23] | B. J. Alloway, Heavy metals in soils, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1990 |
| [24] | Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Air quality criteria for lead, June 1986 and Addendum, September, 1986. Research Triangle Park, N. C., EPA 600/8 – 83 – 018F, 1986 |
| [25] | S. Madhaven et al., “Lead in soil: Recommended maximum permissible levels”, Environ. Res. Vol. 49, pp 136 – 142, 1989 |
| [26] | Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR), The nature and extent of lead poisoning in children in the United State: A report to congress, July, 1988 |
| [27] | I. Shellshear, D. Jordan, D. J. Hogan, F.T. Shannon, “Environmental lead exposure in Christchurch children: Soil lead potential hazard” N. Z. Med. J. Vol. 81, pp382 – 386, 1975 |
| [28] | C.J. Rosen, “Lead in the home Garden and Urban Soil Environment. Produced by Communication and Educational Technology Services, University of Minnesota Extension Service, 2002 |
| [29] | D. R. Juberg, C. F. Kleiman, S.C. Kwon, “Position paper of the American Council on Science and Health: Lead and Human Health”, Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety vol. 38, pp 162 – 180, 1997 |
| [30] | K. Loska,D. Weichula, “Application of principal component analysis for the estimation of source of heavy metal contamination in surface sediments from the Rybnik Reservoir”, Chemosphere vol. 51, pp 723 – 733, 2003 |
| [31] | S. M. Ali, R. N. Malik, “Spatial distribution of metals in top soils of Islamabad City, Pakistan”, Environ. Monit. Assess. Vol 172, pp 1 – 6, 2011 |
| [32] | Z. S. Chen, C. C. Tsai, C. C. Tsui, “Proposal regulation of soil pollutants in Taiwan soils”, in Proc. Of the 6th Workshop on Soil Pollution and Prevention: Soil Remediation Techniques on Soils Contaminated by Organic Pollutants, Taipei, Taiwan ROC., pp 169 – 207( in Chinese with English Abstract and Tables), 1999 |
| [33] | USEPA, Biosolids applied to land: Advancing standards and practices, p282, National Research Council, National Academy Press, Washington, D. C. 2002 |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML