-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Research In Cancer and Tumor
2021; 9(2): 23-27
doi:10.5923/j.rct.20210902.01
Received: Oct. 6, 2021; Accepted: Oct. 25, 2021; Published: Oct. 30, 2021

The Effect of the New Drug Decoglitz on Tumors of Mice and Rats with Oral and Intraperitoneal Use and Its Effect on Immunity
Enikeeva Z. M., Agzamova N. A., Ibragimov A. A., Ziyavidenova S. S., Kholturaeva N. R., Alimkhodjaeva L. T.
Republican Specialized Scientific and Practical Medical Center of Oncology and Radiology, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Aim of the work was to evaluate the antitumor activity of the new drug Decoglitz with intraperitoneal and oral use in animals with tumor strains of Sarcoma 45 (C-45), ovarian tumor and Ehrlich solid tumor in comparison with its intra-peritoneal use, as well as its effect on immunity with oral use. Material and methods. The study was carried out on 63 outbred rats and mice with transplantable tumors of the ovarian tumor, Sarcoma 45 (C-45) and Ehrlich solid tumor, which were injected with the drug orally and intra-peritoneally 10 times. The results were evaluated according to standard criteria: inhibition of tumor growth, animals’ body and spleen weight. The study of the immune status indicators was carried out in the circulating blood and spleen on the day of slaughter according to the methodological recommendations of the Institute of Immunology of the Russian Federation and the Institute of Immunology of the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Uzbekistan. The differences were considered significant at p<0.05. Results. The antitumor activity of the drug Decoglitz when injected orally at a dose of 20 mg / kg on the tumor strain of Ehrlich solid tumor was high - 92/89%. Its effect was 20-14% higher than the effect of Decoglitz when injected intra-peritoneal at a dose of 20 mg/kg. The effect of Decoglitz on C-45, with different methods of injection was the same (98/96%). The activity of Decoglitz on ovarian tumor with intra-peritoneal injection reached 89/76% with a remission rate of 40%, with oral - 96/86% with a remission rate of 60%. The effect of the drug Decoglitz on immunity injected orally was manifested in a slight decrease of the CD4, CD8 and CD19 receptors. Conclusion. The study of the new drug Decoglitz on animals with Ehrlich solid tumor, C-45 and ovarian tumor revealed its high activity when injected orally, on 2 tumors higher than intra-peritoneal injection. The effect on immunity of the drug Decoglitz does not imply a pronounced failure of immunity when it is used in the clinic.
Keywords: Antitumor activity, Sarcoma 45, Ovarian tumor, Ehrlich solid tumor, Decoglitz, Oral and intraperitoneal use, Decocin, Effect on immunity
Cite this paper: Enikeeva Z. M., Agzamova N. A., Ibragimov A. A., Ziyavidenova S. S., Kholturaeva N. R., Alimkhodjaeva L. T., The Effect of the New Drug Decoglitz on Tumors of Mice and Rats with Oral and Intraperitoneal Use and Its Effect on Immunity, Research In Cancer and Tumor, Vol. 9 No. 2, 2021, pp. 23-27. doi: 10.5923/j.rct.20210902.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The pronounced general toxic effect of a large number of used cytostatics, rapidly developing resistance, lack of sensitivity of a number of tumors to existing drugs dictate the need to create new antitumor drugs with a complex of new properties.On the basis of glycyrrhizic acid and the previously developed non-water-soluble drug Decocin which showed significant efficacy in clinical trials for skin cancer in the form of ointment [1-2], a new supramolecular complex called Decoglitz was obtained, differing in physico-chemical parameters from the original Decocin, as well as a 2.6-fold decrease in toxicity and solubility in water.For this drug, antitumor activity was studied with intraperitoneal injection on a number of tumor strains, both in comparison with Decocin and with other known drugs, which turned out to be 15-20% higher [3-4]. The positive characteristics of the drug suggest that it should be studied after oral application which will provide an easy-to-use dosage form of the drug.Aim of this work was to study the antitumor activity of the drug Decoglitz when injected orally in animals with tumor strains of Ehrlich solid tumor (EST), Sarcoma 45 and ovarian tumor (OT) in comparison with its intraperitoneal use, as well as to study the effect of Decoglitz on immunity with the best method of application.
2. Material and Methods
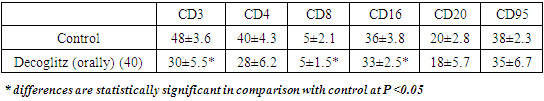
- The object of the study was the drug Decoglitz, as well as the drug Decocin, from which Decoglitz was obtained. Both drugs were synthesized from colchicine in the laboratory for the development of antitumor drugs of the Republican Specialized Scientific and Practical Medical Center of Oncology and Radiology.Mice and rats were injected with Decoglitz at a dose of 20 mg/kg and 40 mg / kg, decocin - at a dose of 15 mg/ kg. The drugs etoposide at a dose of 8 mg / kg (Etoposidephosphate, Bristol-MyersSquibb) and 5-fluorouracil at a dose of 15 mg / kg (GetwellPharmactuals, India). All drugs were injected 10 times every day.43 outbred rats weighing 90-140 g and 20 outbred mice weighing 19-20 g were used in our study. The animals were kept in 4-6 individuals under natural lighting conditions with free access to water and food. The experiment included 6 animals in the experimental groups and 6-8 rats in the control group (with the injection of saline solution). The study of antitumor activity was carried out on mice with an Ehrlich solid tumor (EST) and rats with strains of Sarcoma 45 and ovarian tumor (OT). Tumor strains were obtained from the tumor bank of the Institute of Oncology of Kazakhstan and passioned on donor rats according to the strain protocol.The tumors were transplanted according to generally accepted methods: tumors are inoculated subcutaneously with a suspension of tumor cells of 30-60 mg in 0.3-0.5 ml of nutrient medium per rat or mouse [5]: the tissue of the tumor strain was freed from necrotic areas under sterile conditions, and then passed through a homogenizer. 0.9% sterile saline was added to the tumor mass at a ratio of 1:10. Microscopically, the number of viable tumor cells was determined in Goryaev's chamber which made up 84.3% at average. A tumor suspension in a volume of 0.2 ml per 20 g of mouse weight and 0.3 ml per 100 g of rat weight was transplanted into the right thigh subcutaneously. After inoculation of the tumor strain, the animals were numbered on the coat using picrin dye.Treatment of animals was started 4-7 days after tumor implantation. The drugs were injected in all groups 10times. All animals of the tumor groups were injected with drugs in the amount of 0.2 ml per 20 g of mouse and 0.3 ml per 100 g of rat. The slaughter of animals was carried out on the 19th-35th day after the tumor implantation. All rats and mice were euthanized under ether anesthesia in accordance with the International Rules for the Protection of Vertebrates. All experiments were performed in accordance with the recommendations and requirements of the “World Society for the Protection of Animals (WSPA)” and “European Convention for the Protection of Experimental” (Strasbourg, 1986). The body weight of the animals was measured before the injection and at the end of the experiment.During the experiment, in order to study the dynamics of tumor growth, the volumes of tumors were measured through the skin of animals in the treated and control groups of rats (in 3 projections) at the beginning of the experiment, every 5 days after the start of treatment and before slaughter. At the end of the experiment in slaughtered animals, the efficiency was determined by the volume (V) of the extracted tumor tissue, as well as by the mass of the tumor in the compared groups. Inhibition of tumor growth (ITG) was calculated by the formulas [5]:ITG %=(Vtrial-Vcontrol)/ Vtrial х 100%ITG %=(Мtrial-Мcontrol)/ Мtrial х 100%where Vcontrol – the average tumor volume in animals of the control group, Vtrial - average tumor volume in animals of the experimental group or Mcontrol - average tumor mass in animals of the control group, Mtrial - average tumor mass in animals of the experimental group.The tolerability of the treatment was judged by the death of mice. The mass of the spleen and some elements of hematopoiesis were determined for an indirect assessment of possible hematotoxicity in slaughtered mice. To study the immune status indicators in in vivo, the immune status indicators in the circulating blood and spleen were studied on the day of slaughter according to the methodological recommendations of the Institute of Immunology of the Russian Federation and the Institute of Immunology of the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Uzbekistan. To study the parameters of the immune status in vivo, we studied the indicators of the immune status in the circulating blood and spleen on the day of slaughter. The slaughter was carried out by decapitation, when the tumor-bearing animals of the control group (C-1) began to die. The studies included counting the number of leukocytes and total lymphocytes; lymphocytes were isolated from 4-5 ml of heparinized peripheral blood according to Boyum (1968) on a density gradient of ficoll-verografin (1.077 g / l), determination of the number of total lymphocytes, phenotyping of lymphocytes were carried out using the method of indirect rosette formation using monoclonal antibodies manufactured by LLC "SORBENT", Russia (CD3 +, CD4 +, CD8 +, CD16 +, CD20 +, CD95 +) included in the panel of basic CD markers for the determination of T-lymphocytes, T-helpers / inducers, natural killer cells, T-cytotoxic / suppressors, B-lymphocytes and apoptosis receptors, respectively.Statistical processing was carried out using the Statistica program, version 6.0. p< 0.05 was taken as the level of statistical significance.
3. Results
- The study of the antitumor activity of the drug on the tumor strain of the EST began 7 days after the transplantation of tumors, the drug Decoglitz was injected10 times intra-peritoneally at a dose of 20 mg/ kg and orally at a dose of 20 mg/ kg. The slaughter was carried out on day 35. In all groups the death of mice was observed in 25%, which was associated with the duration of the experiment. In group 2, the drug Decoglitz, at intra-peritoneal injection at a dose of 20 mg / kg, showed antitumor activity in 72/63%. In group 3, Decoglitz also injected orally at a dose of 20 mg / kg, showed a more significant antitumor effect (92/89%). At the same time, there was no decrease in body weight in both groups, the weight of the spleen with intra-peritoneal injection decreased by 24%, with oral injection - by 14% (Tab. 1).
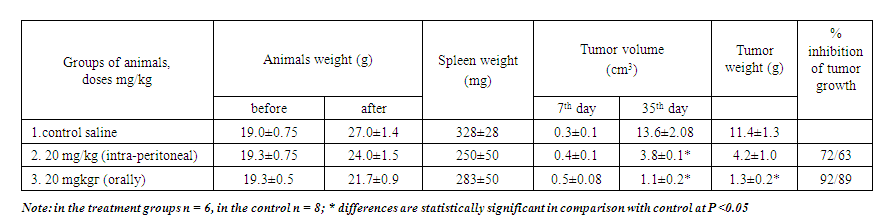 | Table 1. Antitumor activity of the drug Decoglitz on a tumor strain of an Ehrlich solid tumor (treatment from the 7th day, 10 injections of substances, slaughter on the 35th day) |
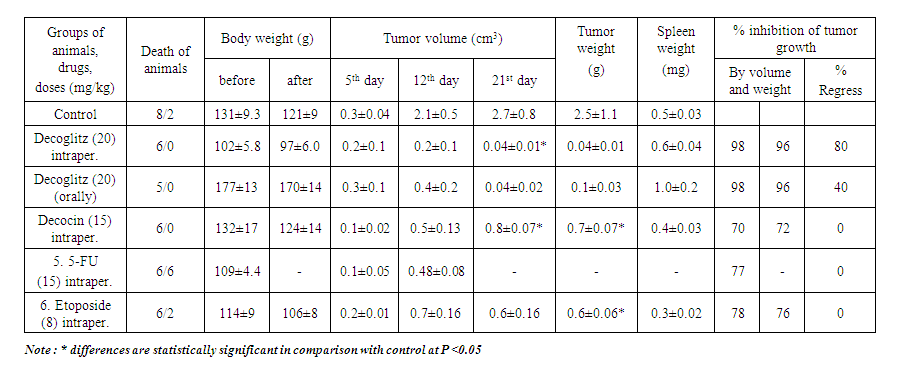 | Table 2. Antitumor activity of drugs in rats with Sarcoma 45 tumor (treatment from the 4th day, 10 injections, slaughter at the 21st day) |
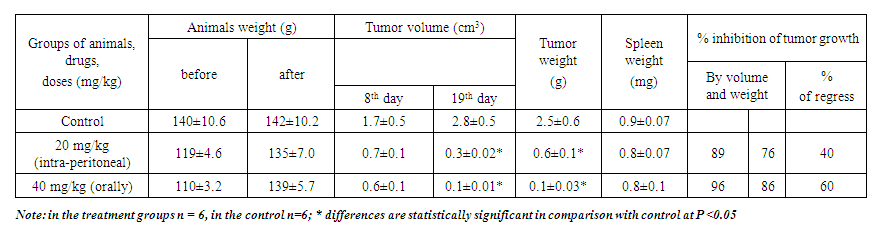 | Table 3. Antitumor activity of the drug Decoglitz in rats with ovarian tumor (treatment from the 4th day, 10 injections of substances, slaughter on the 19th day) |
|
4. Discussion
- Early inhibition of natural helper cells, cytotoxic T-lymphocytes and B-lymphocytes may indicate suppression of immunity indicators. It is known that anticancer drugs depending on the dose and time of administration can both suppress and stimulate the immune response. But, as a rule, repeated administration of an anticancer drug causes significant or complete immunosuppression, and also suppresses hematopoiesis. However, in general, the effect on immunity manifested in a slight decrease in the CD4, CD8 and CD19 receptors by the drug Decoglitz, does not imply a pronounced failure of immunity when it is used in the clinic.The activity of the new drug Decoglitz, both in comparison with Decocin, from which it was obtained, and well-known cytostatics, such as 5-fluorouracil and Etoposide, as well as with others [3-4], was 20-28% higher than the comparison drugs. At the same time, a decrease in side effects was noted. It should be noted that Decoglitz with intraperitoneal use was studied at a dose that was significantly lower in relation to LD50 than that of Decocin. Previously, it was noted for derivatives of Glucocorticoids [6] that their activity is manifested in doses 2-4 times less than the maximum tolerated, which is a significant difference between the complexes of Glucocorticoids with antineoplastic drugs and leads to a decrease in side effects during their use. It is important to note that usually at oral injection, the doses of cytostatics, as a rule, when achieving a high effect, are significantly higher than with intra-peritoneal injection. However, Dekoglitz shows high efficiency at the same dose of 20 mg / kg, both with intraperitoneal use and oral, which is unexpected for an antitumor drug and very convenient for subsequent use, since it does not cause side effects.The high antitumor activity of the drug Dekoglitz is confirmed by its more intense effect on the synthesis of nucleic acids which is 8-15% more than that of Decocin and 10-40% more than that of Etoposide taken as a control. It is also capable of performing internucleosomal degradation and fragmentation of tumor DNA [4] which explains its antitumor efficacy, greater than that of Decocin in experiments on tumors. The study of the drug Dekoglitz when administered orally on 3 tumors of mice and rats showed no less high activity of the drug when administered orally, and the doses of the drug in 2 cases were the same as when administered intraperitoneally (20 mg / kg), and only on the tumor ovary dose of 40mg / kg was used. It should be noted that intraperitoneal administration of Dekoglitz was studied at a dose that, in relation to LD50, was significantly less than that of Dekocin. It is important to note that usually with oral administration, the doses of cytostatics, as a rule, to achieve a high effect, are significantly higher than with intraperitoneal administration. However, Dekoglitz shows high efficacy at the same dose of 20 mg / kg, both with intraperitoneal use and oral, which is unexpected for an antitumor drug and very convenient for subsequent use, since it does not cause side effects.
5. Conclusions
- The new drug turned out to have reduced toxicity and 20-28% more pronounced activity after intraperitoneal administration, both in comparison with Dekocin, from which it was obtained, and known cytostatics such as 5-fluorouracil and etoposide, as well as with others. At the same time, a decrease in side effects was noted. The study of the drug Decoglitz with oral administration on 3 tumors of mice and rats showed no less high activity of the drug with oral administration, and the doses of the drug were in 2 cases the same as with intraperitoneal administration (20 mg / kg), and only a dose of 40 mg / kg was used on ovarian tumors. It should be noted that Decoglitz cin with intraperitoneal use was studied at a dose that was significantly lower in relation to LD50 than that of Dekocin. It is important to note that usually with oral administration, the doses of cytostatics, as a rule, to achieve a high effect, are significantly higher than with intraperitoneal administration. However, Dekoglitz shows high efficacy at the same dose of 20 mg / kg, both with intraperitoneal use and oral, which is unexpected for an antitumor drug and very convenient for subsequent use, since it does not cause side effects. The high antitumor activity of the drug Decoglitz is confirmed by a more intense effect of it on the synthesis of nucleic acids, which is 8-15% more than that of Decocin and 10-40% more than that of etoposide taken as a control, and also to carry out the internucleosomal degradation and fragmentation of tumor DNA, which explains its antitumor efficacy, greater than that of Decocin in experiments on tumors. Thus, the established fact of the formation of stable complexes of glycyrrhizic acid with the anticancer drug Decoglitz allows us to consider glycyrrhizic acid and its salts as promising molecular containers in drug delivery systems and for the creation of new drugs on their basis.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- This study has been executed at financial support of fund of applied researches of Republic Uzbekistan (the project № FV 2020196206).
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML