-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Research In Cancer and Tumor
2016; 5(1): 1-9
doi:10.5923/j.rct.20160501.01

Quince Polysaccharides Induced Apoptosis in Human Colon Cancer Cells (HCT-116)
Mahgoub M. Ahmed1, Gehan A. Elmenoufy2
1Molecular Drug Evaluation Department, National Organization for Drug Control and Research (NODCAR), Giza, Egypt
2Physiology Department, National Organization for Drug Control and Research (NODCAR), Giza, Egypt
Correspondence to: Mahgoub M. Ahmed, Molecular Drug Evaluation Department, National Organization for Drug Control and Research (NODCAR), Giza, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

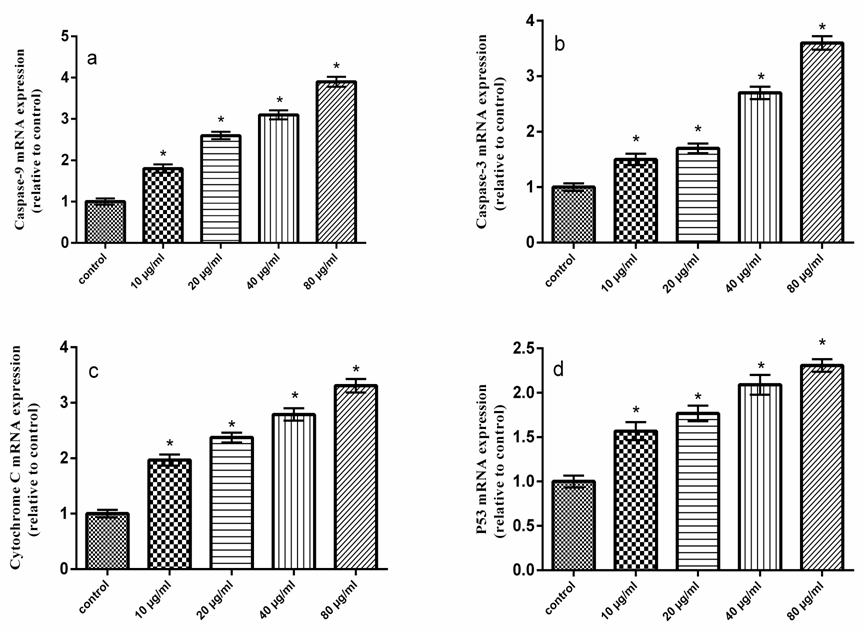
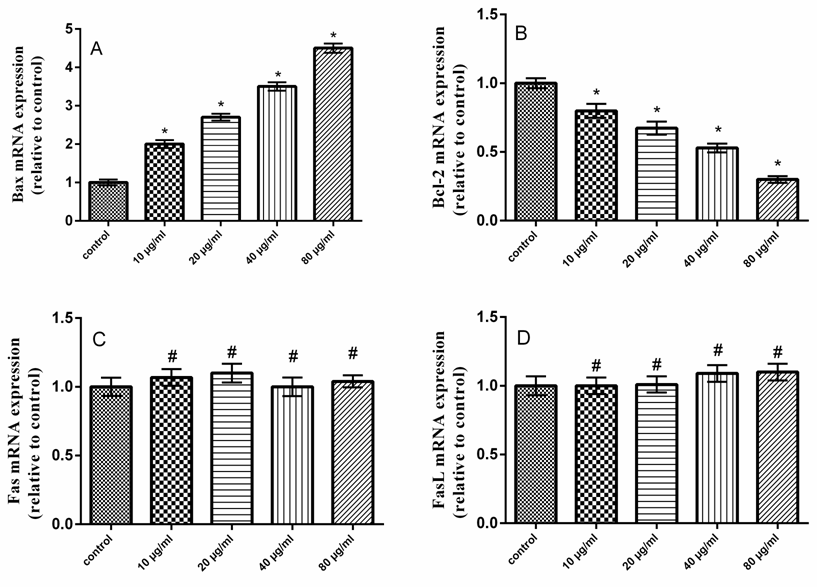
The objective of this study was to investigate the anti-tumor effects and analyze the mechanism of quince polysaccharides (QPS) action on human colon cancer (HCT-116) cell line in vitro. Cell viability of HCT-116 treated with various doses of QPS were observed using MTT colorimetric assay. The apoptosis effect of QPS was detected in HCT-116 by apoptosis ELISA assay and DNA damage. The expression of apoptosis-related proteins Bax, Bcl-2, cytochrome c, P53 and caspase-3 were detected through ELISA analysis. To evaluate the apoptotic pathway in HCT-116 cells exposed to QPS, protein and gene expressions of Bax, caspase 3, cytochrome c, Bcl-2 and P53 were measured by ELISA and quantitative real-time-PCR analysis. Moreover, effects of QPS on caspase-9, Fas and Fasl gene expressions were determined using quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis, caspase-3 activity was carried out as well. The present study showed that QPS significantly inhibited the proliferation of HCT-116 cells compared to the control group in a dose dependent manner. The protein and gene expressions of Bcl-2 were significantly reduced, whereas Bax, caspase 3, caspase-9 and cytochrome c were significantly increased in the QPS-treated groups compared to the control group. However, Fas and Fasl mRNA levels remained unchanged after QPS treatment by different concentrations, compared to the control. Furthermore, QPS activated caspase-3, which belong to the mitochondrial pathway of the apoptosis. In conclusions, QPS exerted its antitumor activity depending on activation of the Bax-mediated mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis in HCT-116 cells.
Keywords: Quince polysaccharides, Antitumor activity, Cell apoptosis, Colon cancer cell line
Cite this paper: Mahgoub M. Ahmed, Gehan A. Elmenoufy, Quince Polysaccharides Induced Apoptosis in Human Colon Cancer Cells (HCT-116), Research In Cancer and Tumor, Vol. 5 No. 1, 2016, pp. 1-9. doi: 10.5923/j.rct.20160501.01.
1. Introduction
- Cancer is still a major health problem in both developing and developed countries. Cancer, known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a broad group of various diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. Colon cancer is a common malignant tumor in the digestive tract and one of the most four common malignant tumors throughout the World. Clinically, anticancer agents used for treatment of HCT-116 colon cancer may result in serious adverse effects including neutropenia, peripheral neuropathy, nephrotoxicity and chemotherapy resistance. Thus, the development of novel anticancer agents with higher bioactivities and lower toxicity from nature for colon cancer has been an extreme active domain.Polysaccharides are composed of many monosaccharide units that are joined one another by a glycoside linkage to give a long chain. These polysaccharides are extracted from plant seeds, fruit, plant exudates, marine algae and animals. The high efficiency and lower toxicity of natural products have made them great candidates to be explored for cancer treatment [1]. The biological activities of the polysaccharides have attracted more attention due to their antibiotic, antioxidant, anti-mutant, anticoagulant, antidiabetic and immune-stimulation activities [2-4]. Recently, accumulated evidence has demonstrated that polysaccharides have anticancer effects [5-8]. Some studies investigated the cytotoxic effect of the polysaccharide from different sources against human cancer cell lines and showed that the polysaccharide might induce cell apoptosis in several kinds of human cancer cell lines [5, 9-11].Cydonia oblonga Miller (Quince) belongs to family Rosaceae. Quince fruits are recognized as a good, cheap, and important dietary and health-promoting source. Quince fruits have a broad spectrum of biological effects, such as anti-ulcerative [12], antimicrobial [13], antioxidant [14, 15], anti-allergic [16] and anti-proliferative [17]. The objective of the present study was to examine the in vitro cytotoxic activities of polysaccharides isolated from quince fruits in human colon cancer cell line (HCT-116 Cells) using a MTT cytotoxicity assay. In addition, the present study tested the possible mechanism of action involves induction of apoptosis.
2. Materials and Methods
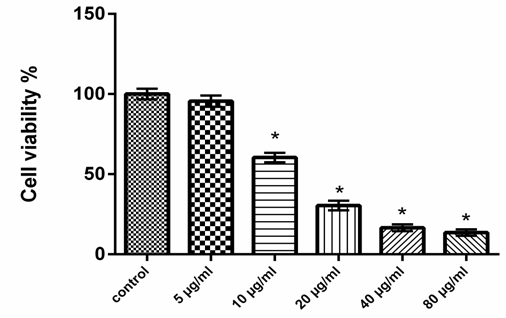
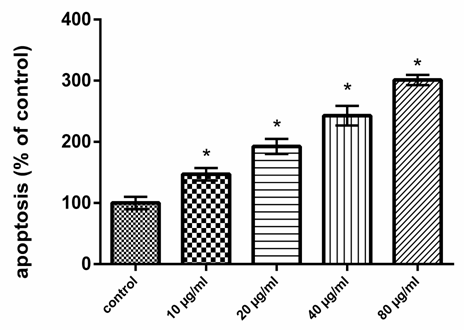
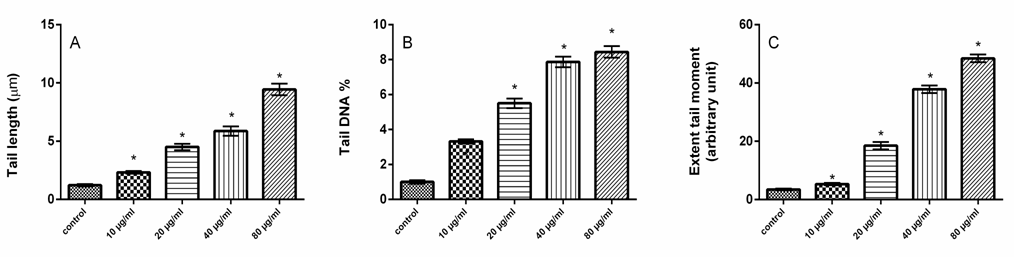
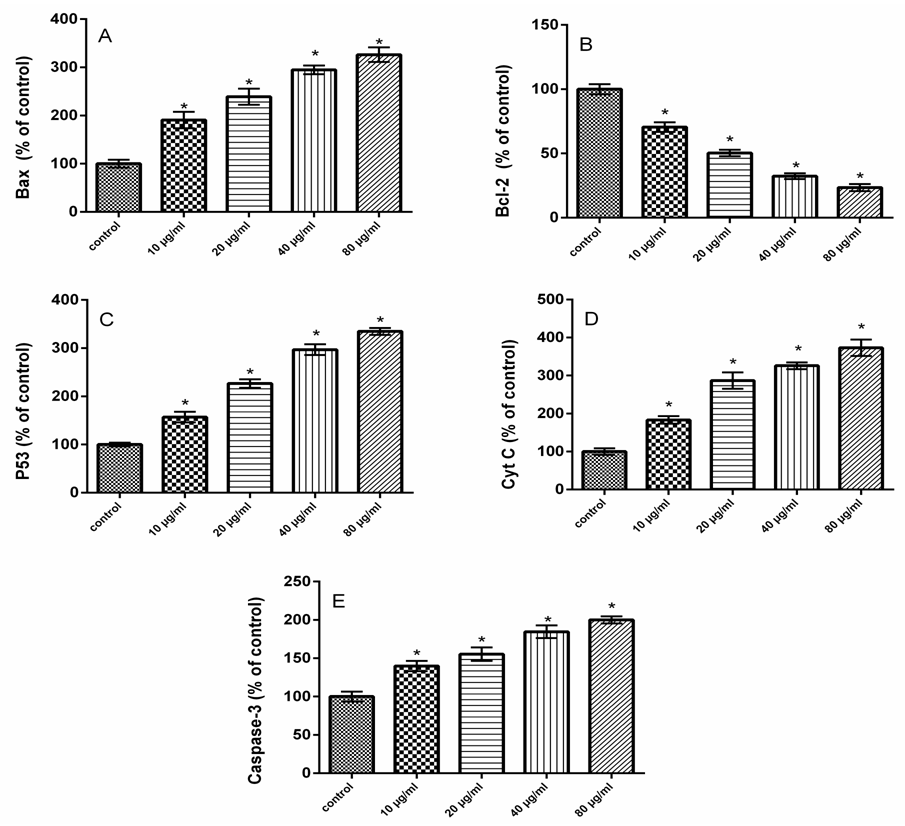
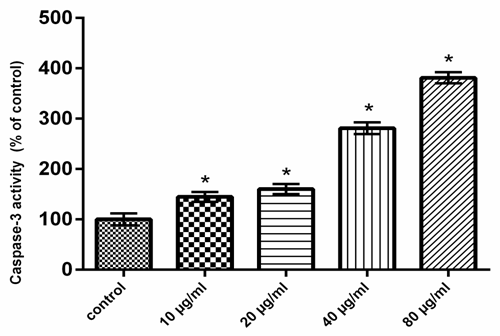
- Chemicals and Reagents 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT), was purchased from Carbosynth Limited (Berkshire, UK). Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) was purchased from Lonza (Verviers, Beligum). Dimethylsulphoxide (DMSO), Heat inactivated fetal calf serum, D-Mannose (Man), L-Rhamnose (Rha), D-Glucose (Glc), D-Galactose (Gal), L-Arabinose (Ara), and D-Xylose (Xyl) were obtained from Sigma Co. (USA). ApoStrand™ ELISA Apoptosis Detection Kit AK-120 (BIOMOL International LP, Plymouth Meeting, PA, USA) was obtained from Enzo Life Sciences. All chemicals and reagents used in this study were of analytical grade.Plant MaterialsQuince (Cydonia oblonga Mill.) fruits were obtained from Experimental Station of Medicinal Plants, Faculty of Pharmacy, Cairo University. Isolation and HPLC analysis of quince polysaccharides Polysaccharides of quince fruits were isolated, purified and analyzed by HPLC according to the method of Hopur et al [18]. Briefly, quince was grounded with liquid nitrogen and extracted with CHCl3:CH3OH (1:1), (1:10) (v:v) (2h, twice) and then with 90% ethanol using magnetic stirring. Afterwards polysaccharides were extracted twice with water in water bath for 3 h. Proteins were precipitated twice with CHCl3: butanol (4:1). Polysaccharides were precipitated by adding ethanol (1:10, w/v). The precipitate was isolated and then washed with ethanol, acetone, and diethyl ester, respectively. Then the precipitates were lyophilized to obtain polysaccharides. The monosaccharide compositions of the quince polysaccharides were determined by HPLC (Agilant Technology, 1200 series). Six monosaccharides (arabinose, mannose, rhamnose, galactose, xylose and glucose) were used as standards to identify the composition of the polysaccharides. Cell cultureHuman colon cancer HCT-116 cells were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (Rockville, MD, USA). HCT-116 cells were maintained in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% heat inactivated fetal calf serum, penicillin (100 U/ml) and streptomycin (100 µg/ml) at the 37°C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2. HCT-116 cells at a concentration of 5×104 were grown in a 25 cm2 flask in 5 ml of complete culture medium.MTT Cell Proliferation Assay MTT was used as a colorimetric assay to assess cell viability [19, 20]. It was utilized in examined HCT116 cell lines to evaluate QPS effects on cell proliferation. The cells (5×104) were allowed to attach overnight and were then treated with increasing concentrations of QPS starting at 0, 5, 10, 20, 40 and 80, µg/ml for 48 h. MTT was then mixed with HCT-116 cells at 37°C for 2 h in a humidified CO2 incubator at 5% CO2. MTT formazan product was dissolved in DMSO and absorbance was then measured at 570 nm using ELISA plate reader (BioTek Instruments, USA). Apoptosis assay Apoptosis effect of QPS was detected using an apoptosis ELISA assay kit (ApoStrand™ ELISA Apoptosis Detection Kit AK-120, Enzo Life Sciences Inc, NY, USA) according to the manufacturer's protocol. The ApoStrand™ ELISA is based on the sensitivity of DNA in apoptotic cells to formamide denaturation, which denatures DNA in apoptotic cells reflecting the changes in chromatin associated with apoptosis, but not in necrotic cells or in cells with DNA breaks in the absence of apoptosis. The denatured DNA was detected by conjugation with a monoclonal antibody to single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) of the HCT-116 lysates. Briefly, 5×104 cells were cultured in a 96-well microplate and treated with different concentrations of polysaccharide (10, 20, 40 or 80, µg/ml) for 48 h. After 30 min, cells were fixed and dried for attachment to the plate surface. Cells were then treated with formamide, after 10 min DNA was denatured by heating at 56oC for 30 min, followed by incubation with blocking solution for 1 h and incubation with antibody mixture for 30 min. After washing, peroxidase substrate was added to each well, and the absorbance was measured at 405 nm using an ELISA reader (BioTek Instruments, USA).Detection of DNA damageFor detection of apoptotic DNA cleavage, the DNA fragmentation in HCT-116 cells treated with QPS was performed the alkaline Comet assay proposed by Singh et al [21]. In brief, after treatment at a various concentrations of QPS, cells were trypsinized and washed in PBS. The cell suspension was mixed with an equal of 0.75% low melting agarose and kept at 37oC. The cell/agarose mixture was added to a fully frosted microscope slide coated with a layer of 500 ml of normal-melting agarose (1%). The slides were immersed into a cold and freshly made lysis solution for a minimum of 2 h. after that, the slides were incubated in freshly prepared alkaline buffer (300 mM NaOH and 1.0 mM EDTA, pH 13) for 30 min. DNA was subjected to electrophoresis for 15 min at and 1 V/cm and 30 mA. After electrophoresis, the slides were neutralized with 0.4 M Tris, pH 7.5. Finally, DNA was stained with ethidium bromide (2.0 mg/ml) for 15 min, washed in distilled water and examined under a fluorescence microscope (Lyca, USA). Tail length, tail DNA% and extent tail moment were measured using Komet 5 image analysis software developed by Kinetic Imaging, Ltd. (Liverpool, UK) linked to a CCD camera.Measurement of Bax, Bcl-2, cytchrome c, P53 and caspase-3 Protein levels Levels of Protein expression of Bax (SunRed, Biotechnology Company, China), caspase 3 (Wkea Med Supplies Corp., China), Cytchrome C, Bcl-2 and P53 (SunLong Biotech Co., LTD, China) were measured by ELISA methods. After treating cells with QPS extract for 48h, floated and adherent cells were pelleted and washed in cold PBS, and then cells were dissolved in PBS and lysed with one freeze/thaw cycle at -80°C. Lysed cells were centrifuged at 2000 rpm for 10 min to remove cell-debris. Protein concentration was determined according to the method proposed by Bradford [22]. RNA isolation and quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis Total RNA were extracted from HCT-116 cells with TRIzol Reagent following the manufacturer's instruction. The RNA quality was verified using spectrophotometric and agarose gel electrophoresis. cDNA was synthesized from 2 µg total RNA using Revert AidTM first strand cDNA synthesis kit (Ferments life science, Thermo Scientific, USA) by incubating at 37°C for l h with reverse transcriptase with random hexanucleotides according to the manufacturer's instructions. qRT-PCR was performed using the Real-Time PCR systems (Step One instrument, Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). Each 10 µl reaction contained 5 µl SYBR Green Master Mix (Applied Biosystems), 0.3 µl gene-specific forward and reverse primers (10 µM), 2.5 µl cDNA and 1.9 µl nuclease-free water. β-actin was simultaneously amplified along with the respective genes to confirm uniformity of RNA concentration taken for the expression studies. The relative expression of the studied genes was calculated using the comparative threshold cycle method. Determination of Caspase-3 Activity The activity of caspase-3 assay was carried out according to Caspase-3 activity assay Kit (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology, Haimen, China). After treatment with QPS (10, 20, 40 or 80, µg/ml), HCT-116 cells were harvested by centrifugation. The pellet was rinsed and incubated for 10 minutes on ice in chilled cell lysis buffer. The lysate was centrifuged for 1 minute at 10,000 ×g at 4°C, and the supernatant fluids were used for the caspase-3 activity assay. The protease activity was determined by spectrophotometric detection of chromophore ρ-nitroanilide (ρ-NA) after cleavage from the labeled substrate, acetyl-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp ρ-nitroanilide. The ρ-NA light emission was quantified with a spectrophotometer at 405 nm. All the experiments were performed in triplicate [23].Statistical analysisAll experiments were performed in triplicates. Data were expressed as means±SD. Differences between values of polysaccharides-treated versus untreated cells were compared by the One Way ANOVA and LSD test using SPSS 17.0 for Windows (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Values with P<0.05 were considered significant.
3. Results
- Monosaccharide composition analysis of quince polysaccharidesThe extracted polysaccharides of the quince fruits were 14% related to dried mass. According to the chromatographic peak of monosaccharide reference substances and sample, the composition of the polysaccharides in quince fruits was identified. The results of monosaccharides composition of quince polysaccharides are shown in Fig 1. The results show different component of monosaccharides. QPS were consisted of mannose, arabinose, glucose, galactose, rhamnose and xylose.
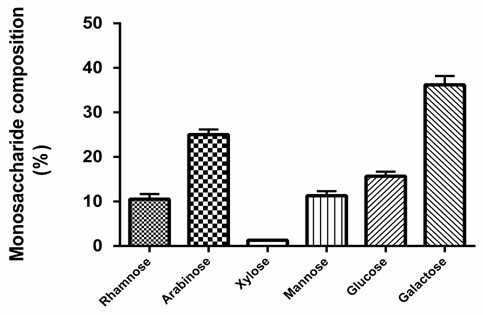 | Figure 1. The chemical compositions of quince polysaccharides hydrolysate. The monosaccharide compositions of the quince polysaccharides were determined by HPLC |
4. Discussion
- Dependant chemotherapeutic agents result in toxicity to normal cells and cause organs damage [24]. Consequently, there is an urgent need for the development of novel safe and effective drugs to treat colon cancer patients. It has been showed that natural polysaccharides derived from plant sources have antitumour activity [25]. The present study revealed that QPS possess antitumor activities in HCT-116 cells in a dose dependant manner. Moreover, our results showed that the expression levels of P53 and Bax were increased, whereas Bcl-2 expression level was decreased in QPS treated HCT-116 cells. The cytosolic level of the mitochondrial protein, cytochrome c, was increased. These results imply that mitochondrial disruption and cytochrome c release may be important events in polysaccharides induced apoptosis in HCT-116 cells. Furthermore, QPS activated caspase-3, which belong to the mitochondrial pathway of the apoptosis. The Tumor protein P53 is known to induce and/or repress the expression of target genes involved in central pathways, such as control of the cell cycle, DNA repair and apoptosis [26, 27]. A variety of triggers such as DNA damage, oncogene activation and telomere erosion can lead to the activation of P53 [28]. P53 may be involved in transcriptional regulation of pro-apoptotic genes associated with intrinsic and extrinsic pathways which results in activation of caspases-8 and -9 [29]. P53 induced proteins that localize to mitochondria such as Bax [30].Apoptosis has been considered a potential target when developing new anticancer drugs as it represented the major pathway of death in cancer cells. Several mechanisms of anticancer drugs induced apoptosis in cancer cells were reported, including down regulation of anti-apoptotic proteins (such as Bcl-2), in addition to up regulation of pro-apoptotic proteins (such as Bax), activation of caspases as well [31]. Our results indicated that the QPS had a dose dependent inhibitory effect on the growth of the human colon cancer cell lines in vitro, indicating that QPS possess antitumor activities.Apoptosis is an important regulatory mechanism in the development of tissues, involving biological events such as chromosome condensation, DNA laddering, membrane blebbing, and cytochrome C release, which leads to the removal of unnecessary cells [32].Apoptosis occurs through two main pathways. The first pathway is the intrinsic or mitochondrial pathway is mediated by Bcl-2 family of pro- and anti-apoptotic proteins, which induce the permeabilization of the mitochondrial outer membrane and cytochrome c released into the cytosol regulates this pathway [33, 34]. The second pathway is the extrinsic apoptosis pathway or cytoplasmic pathway, which mediated through the Fas death receptor, a member of the tumor necrosis factor.(TNF) receptor superfamily and caspase-8 is a major initiator caspase in this pathway [35]. Both pathways converge to a final common pathway involving the activation of a cascade of proteases called caspases that cleave regulatory and structural molecules, culminating in the death of the cell. A number of apoptosis related proteins associated with apoptosis were examined to clarify the mechanism by which QPS induces apoptosis of HCT-116 cells.Bax is a pro-apoptotic factor that translocates from the cytosol to the outer mitochondrial membrane where it can form heterodimers with Bcl-2 protein to create pores and mediate cytochrome C release [36].Raisova et al. [31] reported that high Bax/Bcl-2 ratio was an indicator of greater apoptotic activity. Pro- and anti-apoptotic proteins are principal regulators of the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis [37]. The mitochondrial apoptotic cascade requires the release of intermitochondrial membrane cytochrome c to the cytosol [38]. Cytochrome c released from mitochondria into cytosol was evaluated by a Western blot analysis. The ELISA and RT-PCR analysis indicated that the QPS-treatment induced a cytochrome c release.Mitochondrial dysfunction is an early event occurring during the process of apoptosis [39]. The integrity of the outer mitochondrial membrane can be disrupted due to any imbalance of the expression levels of anti- and pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins [40].In the present study, Bcl-2 was decreased and Bax was increased in HCT-116 cells treated with QPS, suggesting that the QPS induced apoptosis in the HCT-116 cells by depleting the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 and enhancing the pro-apoptotic Bax expression. It indicated that QPS might activate mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in the HCT-116 cells by increasing the permeability of the mitochondrial membrane. Thus, cytochrome c is released into the cytosol leading to activation of the apoptosome complex and a caspase cascade. Our results exerted that QPS treatment induces the release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria to the cytosol. Thus, these observations indicated that QPS had a role in provoking mitochondrial damage and regulating apoptotic proteins in HCT-116 cells. Caspases are cysteine-aspartic proteases families, which play an important role in apoptosis, necrosis and inflammation. They are specific proteases that function to mediate apoptotic destruction of the cell [41]. Caspases are activated by extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathways [42]. Caspase-3, called death protein, is one of the deeply studied proteases. It targets at N-terminal ascorbase site of substrate to enzymolysis related proteins. The activation of caspase-3 promotes cells into an irreversible apoptosis pathway [43]. In the present study, treatment of HCT-116 cells to QPS resulted in a dramatic increase in the caspase-3 activity (Fig. 8), which is the main executioner of apoptosis. Fas binding to its ligand, FasL, initiated the cell apoptosis [44]. Fas-FasL signaling pathway is known to induce apoptosis in a variety of cells by activating caspase-8 and -3 and by promoting DNA fragmentation [45]. However, the present results showed that Fas and FasL mRNAs were unchanged in HCT-116 cells treated with QPS.
5. Conclusions
- In the present study, the cell death induced by QPS was mainly caused by apoptosis. QPS induced apoptosis in HCT-116 cells via Bax up-regulation, Bcl-2 down-regulation, P53 activation, cytochrome c release and caspase activation. Therefore, QPS exerted the antitumor activity depending on activation of the Bax-mediated mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis in HCT-116 cells.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML