-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Research In Cancer and Tumor
2015; 4(2): 25-33
doi:10.5923/j.rct.20150402.01
Serum Micro RNA-122 as a Biomarker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Patients
Ashraf T. Abd Elmouttaleb1, Doaa M. Abd-Elatif2, Gamal M. Soliman3, Mostafa S. Taher4, Abdelraouf A. Abonar4
1Medical Biochemistry Department, Assisted Reproductive Unit, International Islamic Centre for Population Studies and Research, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt
2Medical Biochemistry Department, Faculty of Pharmacy (for Girls), Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt
3Tropical Medicine Department, Faculty of Medicine, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt
4Clinical Pathology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt
Correspondence to: Ashraf T. Abd Elmouttaleb, Medical Biochemistry Department, Assisted Reproductive Unit, International Islamic Centre for Population Studies and Research, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Background: HCV infection is considered the most common etiology of chronic liver disease in Egypt. The incidence of HCC has increased sharply in the last 5-10 years, in Egypt; there was an almost two fold increase in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) among chronic liver patients.Therefore, call for new and more specific markers for HCC are critically needed. In fact, the liver specific miRNA–122 is the most abundant miRNA in the liver, accounting for up to 72% of hepatic miRNAs. Objective: The aim of the present study was to explore the potential usefulness of serum miRNA–122 as a biomarker for diagnosis of hepatitis C virus related hepatocellular carcinoma. Subjective and Methods: This study was conducted on 75 HCV related chronic liver disease (CLD), seropositive for HCV in addition to 25 patients who are seronegative for HCV were enrolled as a control group. HCV related chronic liver disease patients were divided into three groups, group I comprised 25 patients with chronic hepatitis C, group II comprised 25 patients with cirrhosis, group III comprised 25 patients with HCC. All patients and controls are subjected to full clinical assessment and laboratory investigations.MicroRNAs-122 expression levels were determined by Real Time quantitative polymerase chain reaction method (RT-PCR).Results: Serum levels of miRNA-122 were significantly increased in chronic hepatitis virus infected patients, cirrhosis patient, and hepatocellular carcinoma patients compared to control group (P˂0.001). Serum levels of miRNA–122 correlate with serum necroinflammatory hepatic aminotransferase levels in all studied groups with highly significant positive correlations were found between serum miRNA–122 and ALT in all studied groups. There is negative significant correlation between miRNA–122 and prothrombin concentration in all studied groups. Conclusions: Micro RNA-122 can be used as a new biomarker for HCV associated liver disease and can differentiate patients with malignant liver disease from healthy, chronic HCV and cirrhosis groups, so serum miRNA-122 may be able to serve as a promising non invasive diagnostic marker for HCC. Serum miRNA-122 is a new potential parameter for liver function.
Keywords: MicroRNA-122, Chronic HCV, Liver cirrhosis, Hepatocellular carcinoma, AFP
Cite this paper: Ashraf T. Abd Elmouttaleb, Doaa M. Abd-Elatif, Gamal M. Soliman, Mostafa S. Taher, Abdelraouf A. Abonar, Serum Micro RNA-122 as a Biomarker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Patients, Research In Cancer and Tumor, Vol. 4 No. 2, 2015, pp. 25-33. doi: 10.5923/j.rct.20150402.01.
1. Introduction
- Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is a major health problem throughout the world [1]. HCV infection is considered the most common etiology of chronic liver disease in Egypt, where the prevalence of antibodies to HCV (anti HCV) approximately l0-fold greater than in the United States and Europe [2]. More than 90% of HCV isolated from Egyptian at least 70% of patients who contract HCV develop chronic hepatitis C with 20–50% of these patients eventually progressing to cirrhosis and 5–7% developing hepatocellular carcinoma in 10 – 20 years. Seventy percent of acute infections are rapidly established as chronic infections; which can lead to scarring of liver and ultimately to cirrhosis, liver cell failure and hepatocellular carcinoma [3]. More than 90% of HCC cases develop in chronically inflamed liver as a result of viral hepatitis, alcohol abuse and in increasing incidence in patient with non-alcohol fatty liver [4]. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is an increasing burden in the world and is the second leading cause of cancer- related mortality [5]. Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) serum levels remain the most commonly marker for severity of liver injury, but a chronic HCV infection may develop with or without ALT abnormalities. Thus, it is of great importance to find new biomarkers for the early and accurate diagnosis of liver injury and disease progression in chronic hepatitis C patients [6]. Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is the most widely used tumor biomarker currently available for HCC diagnosis. However, the specificity of AFP is low as serum AFP levels are elevated in patients with benign liver disease, such as hepatitis and cirrhosis. One third of cases of early stages HCC are missed using AFP. This highlights the need for other methods that would be minimally invasive, simple and reliable for early detection of HCC [7].Moreover, resistance to treatment, tumor recurrence or progression, and metastasis call for novel sensitive and specific molecular biomarker for early diagnosis, to predict prognosis and to develop more effective therapeutic strategies able to improve the clinical outcome of HCC [8]. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are class of short non-coding RNAs which are identified as candidate biomarkers for many diseases, since their discovery in 1993, miRNAs have emerged as a new class of small RNAs that control intracellular gene expression networks at post transcriptional level, there by regulating biological processes like inflammation, fibrogenesis or carcinogenesis. Plasma miRNAs exist in at least two different "protected" conditions: they can either be associated with RNA – binding proteins and lipoprotein complexes or they can be packaged into microparticles (exosomes, microvesicles and apoptotic bodies). Micro RNAs control the stability and translation of targeted messenger RNAs (mRNAs) through complementary interaction with 3 untranslated regions of target genes. They are estimated to regulate expression of about one – third of human genes [9].Micro RNAs indeed are involved in fundamental cellular processes, like embryonic development, differentiation, cell cycle, metabolism, and in carcinogenesis and tumor progression [10]. In fact, the involvement of miRNAs in tumorgenesis and tumor progression is well established, as they can behave as tumor suppressor or promoter of oncogenesis depending on cellular function of their targets. In particular, miRNA-122, and miRNA-1 act as tumor suppressor in HCC [11]. Micro RNAs probably in large part derived from cells with damaged plasma membrane. In liver, miRNAs play fundamental functional roles in the regulation of physiological and pathological processes. In fact, the liver specific miRNA–122 is the most abundant miRNA in the liver, accounting for up to 72% of hepatic miRNAs [12]. On a functional level, it was demonstrated that miRNA–122 is essential for liver homeostasis plays an important role in regulating hepatocyte development, differentiation, apoptosis and modulates hepatic lipid metabolism [13]. Loss of miRNA–122 promotes steatosis, inflammation, fibrosis and liver cancer by regulating hepatic networks of genes involved in cell cycle regulation, lipid metabolism, inflammation and oncogenesis, in humans miRNA–122 expression was associated with hepatocarcinogenesis and miRNA–122 loss was associated with a poor prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, while miRNA – 122 overexpression sensitized HCC cells to chemotherapy and was associated with long survival times [14]. The stability of hepatitis C virus (HCV) is dependent on a functional interaction between the HCV genome and miRNA-122. By blocking this interaction with a specific antisense oligonucleotide, it was possible to inhibit viral replication in HCV patients, thus demonstrating the potential of miRNAs as therapeutic targets in liver disease [15].
2. Patients and Methods
- This study was conducted on 75 HCV related chronic liver disease (CLD), seropositive for HCV in addition to 25 patients who are seronegative for HCV were enrolled as a control group. HCV related chronic liver disease patients are attending the outpatient clinic of Tropical Medicine Department, Al–Hussein University Hospital, during the period from September 2014 To March 2015. All patients have signed a written informed consent.Inclusion criteria: - Adult patients of both sexes (more than 18 years or older) who were seropositive for HCV antibodies by ELISA for at least 6 years from onset of the study. - All patients within the whole spectrum of HCV related chronic liver disease (chronic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma) with no previous interferon treatment.Exclusion criteria: - Patients with chronic HBV infection diagnosed by ELISA.- Patients who received previous treatment for HCC or any antiviral therapy for HCV.- Any associated malignancies other than HCC. - Liver transplantation patients.- Patients with auto immune disease, diabetes mellitus, chronic inflammatory disease, and chronic liver disease not related to HCV e.g. fatty liver, bilharziasis or alcoholic cirrhosis. Patients were assigned into: Group (1): Control group includes 25 participants who were negative for HCV and HBV by ELISA.Group (2): Includes 25 patients with chronic hepatitis C who were diagnosed seropositive for HCV antibodies, by third generation ELISA, and confirmed by real time-PCR.Group (3): Includes 25 patients with HCV related liver disease (liver cirrhosis) (child A – C): diagnosed by HCV positive antibodies, HCV RNA by RT–PCR and abdominal ultrasonography.Group (4): Includes 25 patients with HCV positive antibodies and hepatocellular carcinoma: diagnosed by third generation ELISA, MRI or CT scan ± AFP or histopathological examination (Bruix and Sherman, 2005). Sampling: Blood samples were taken from every patient, by vein puncture, serum samples were allowed to clotted then centrifugated at 2000g for 10 minutes, the serum samples were portioned in aliquots and stored at – 80°C until further use.For prothrombin time and concentration, the collected blood was added in 11 mol/L trisodium citrate, then centrifugated and the test was performed within 4 hours of sample collection. The selected patients were subjected to full clinical examination for detection of (hepatomegaly, splenomegaly ascites, jaundice, lower limb oedema or encephalopathy). Laboratory investigations.- CBC by Diatron Automated cell counter.- Complete liver biochemical profile (ALT, AST, ALP serum albumin and bilirubin) by clinical chemistry fully automated Hitachi (912) analyzer with commercial kits of Roche Company. - Prothrombin time and concentration by Thrombol-s kits using coagulation analyzer.- Serum AFP was measured using Cobas 411 by kit supplied from Roche Diagnostic GmbH, Germany).- Hepatitis markers, HCV antibodies and HBs Ag were detected by 3rd generation ELISA (Enzyme – Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay) by kits of (Diasorin – Italy) and confirmed by real time–PCR in HCV positive antibodies patients by real time PCR assay (Cobas Amplicor HCV monitor, version 2.0, Roche Diagnostics).Real Time quantitation of miRNA–122.Total RNA isolation: Total RNA was isolated using diazole (Qiagen, GmbH– Hilden– Germany), according to manufacturers’ protocol for total RNA isolation procedure, 200 μl of serum was mixed with 2ml equal volume of 2x denaturing solution followed by organic extraction using acid–phenol and chloroform. The aqueous phase was mixed with 1.25 volumes of room temperature 100% ethanol. After washing three times, RNA was finally eluted using 100 μl 95°C elution solution. PCR quantification: PCR quantification experiments were performed with PCR Kit (Qiagen, GmbH– Hilden– Germany), expression of miRNA–122 and its housekeeping gene Glyceraldehyde–3–phosphate dehydrogenase (used as endogenous control) were measured by quantitative real time – PCR. Real time RCR was performed using QuantiTect SYBR Green PCR Master Mix, the working master mix was prepared according to manufacturer's protocol, cDNA prepared using miScript kit with miScript HiFlex Buffer is the appropriate starting material. This protocol enable real - time PCR quantification of miRNA-122 using target - specific miScript Primer Assay (forward primer) and the miScript SYBR Green PCR kit, which contain miScript Universal Primer (reverse primer) and QuantiTect SYBR Green PCR Master Mix. Fluorescence measurements were made in every cycle and the thermal profile used as the follows: Reverse transcription 1 cycle 55°C for 10 min; polymerase activation 1 cycle of 95°C for 10 min; cycling 45 cycles of 95°C for 10 sec, 61°C for 10 sec and 72°C for 15 sec; melting curve analysis 95°C for 10 second, 65° for 15 sec; followed by a single cooling cycle 40°C for 30 sec. The expression levels of miRNA–122 in tested samples were expressed in the form of ∆CT (cycle threshold) value. ∆CT was calculated by subtracting the CT value of Glyceraldehyde –3–phosphate dehydrogenase. CT values of miRNA-122 expression levels were converted into copy number / ml.Abdominal ultrasonography; identified size of liver, spleen and presence of periportal fibrosis or ascites. Focal lesions were described with reference to size, site, echogenicity, portal vein thrombosis and presence of lymphadenopathy.Triphasic CT scan or MRI; for patients with detected hepatic focal lesion (HFL) on US and or elevated AFP. Ultra sound guided liver biopsy; from HFL that did not show typical vascular enhancement of HCC with histopathological examination.Statistical analysis:Statistical analysis was performed using statistical package for social science version 14.0 (Spss, Inc., Chicago, III, USA) for windows. Continuous variables were analyzed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Differences among different groups regarding continuous variables with normal distribution were analyzed with univariate ANOVA and Bon Ferroni post hoc test and those not normally distributed were analyzed by Kruskal Wallis test then pairwise comparison was done to detect differences between groups by Mann – whitney U–test. P value of >0.05 was considered statistically significant, the correlation coefficients (r) were calculated by using the spearman correlation.
3. Results
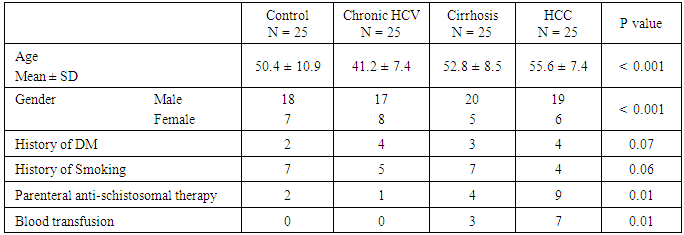
- The current study was conducted on 100 participants attending the outpatient clinic of tropical Medicine department Al – Hussein University Hospital, Cairo, Egypt. This study included 75 patients with HCV related chronic liver disease who are seropositive for HCV in addition to 25 patients who are seronegative for HCV as a control group.In table (1): There is a significant differences between the studied groups regarding Age, Gender, Parenteral schistosomal therapy, and Blood transfusion with P values (
 0.001,
0.001, 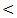 0.001, 0.01, 0.01) respectively.
0.001, 0.01, 0.01) respectively.
|
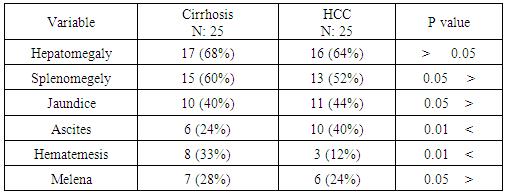
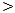 0.05. While ascites was significantly increased in HCC patients; P value 0.01, hematemesis was significantly higher in cirrhosis patients; P value
0.05. While ascites was significantly increased in HCC patients; P value 0.01, hematemesis was significantly higher in cirrhosis patients; P value 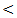 0.01.
0.01.
|
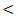 0.001.
0.001.
|
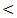 0.01.
0.01.
|
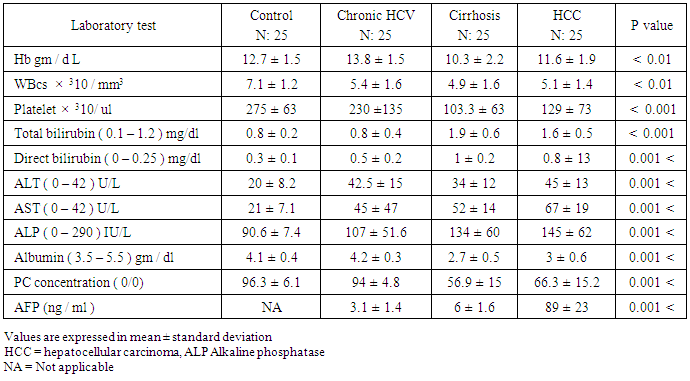
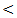 0.01.The platelet count also showed the highest mean value of 275 ± 63 × 103 / mm3 in control and the lowest value of 103± 63 × 103 / mm3 in cirrhosis patients with highly statistical significant differences between studied groups; P
0.01.The platelet count also showed the highest mean value of 275 ± 63 × 103 / mm3 in control and the lowest value of 103± 63 × 103 / mm3 in cirrhosis patients with highly statistical significant differences between studied groups; P 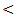 0.001. The mean value of serum bilirubin level was high in liver cirrhosis (1.9 ± 0.6 mg / dl) and in HCC group (1.6 ± 0.5 mg / dl) with normal serum level in other groups. There are highly significant differences between studied groups (P
0.001. The mean value of serum bilirubin level was high in liver cirrhosis (1.9 ± 0.6 mg / dl) and in HCC group (1.6 ± 0.5 mg / dl) with normal serum level in other groups. There are highly significant differences between studied groups (P 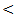 0.01), but no significant difference between chronic HCV and control group.The mean value of serum ALT level showed 1-2 fold elevation in HCC and chronic HCV groups only with highly significant differences between the studied groups (P
0.01), but no significant difference between chronic HCV and control group.The mean value of serum ALT level showed 1-2 fold elevation in HCC and chronic HCV groups only with highly significant differences between the studied groups (P 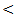 0.001).The mean value of serum AST level showed 1-2 fold elevation in HCC and cirrhosis groups only with highly statistical significant differences between the studied groups (P
0.001).The mean value of serum AST level showed 1-2 fold elevation in HCC and cirrhosis groups only with highly statistical significant differences between the studied groups (P 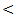 0.001).Serum ALP level had a normal mean value in all studied groups with highly significant differences between the studied groups (P
0.001).Serum ALP level had a normal mean value in all studied groups with highly significant differences between the studied groups (P 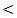 0.001).Concerning synthetic liver functions; the serum albumin level and prothrombin concentration had a low mean level in HCC and cirrhosis patient groups with a normal value in the two other groups. There were significant differences between the studied groups (P
0.001).Concerning synthetic liver functions; the serum albumin level and prothrombin concentration had a low mean level in HCC and cirrhosis patient groups with a normal value in the two other groups. There were significant differences between the studied groups (P 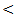 0.001) except between chronic HCV and control.The mean serum AFP level in HCC group was 98 ± 23 ng / ml which was higher than normal serum level. The other groups showed a normal AFP with highly statistical significant differences between the studied groups (P
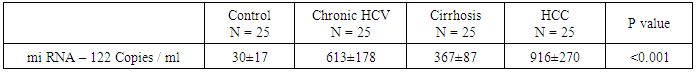
0.001) except between chronic HCV and control.The mean serum AFP level in HCC group was 98 ± 23 ng / ml which was higher than normal serum level. The other groups showed a normal AFP with highly statistical significant differences between the studied groups (P 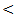 0.001).In Table (5): The highest serum miRNA–122 expression level was in HCC group (916 ± 270 copies / ml), followed by chronic HCV group with mean serum level (613 ±178 copies / ml). The lowest serum level of miRNA–122 is in cirrhosis group (367±87
0.001).In Table (5): The highest serum miRNA–122 expression level was in HCC group (916 ± 270 copies / ml), followed by chronic HCV group with mean serum level (613 ±178 copies / ml). The lowest serum level of miRNA–122 is in cirrhosis group (367±87 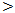 copies /ml), which is highly statistically significant compared to control group (30 ± 17 copies / ml). There are highly statistical significant differences in serum miRNA–122 levels between the studied groups (P
copies /ml), which is highly statistically significant compared to control group (30 ± 17 copies / ml). There are highly statistical significant differences in serum miRNA–122 levels between the studied groups (P 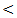 0.001).
0.001).
|
|
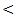 0.05; r = - 43, P
0.05; r = - 43, P 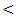 0.05; r = - 33, P
0.05; r = - 33, P 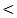 0.001; r = - 36, P
0.001; r = - 36, P 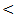 0.001) in control, chronic HCV, cirrhosis and HCC respectively.Serum levels of miRNA–122 correlate with serum necroinflammatory hepatic aminotransferase levels in all studied groups with highly significant positive correlations were found between serum miRNA–122 and ALT in all studied groups with ( r = 52, P
0.001) in control, chronic HCV, cirrhosis and HCC respectively.Serum levels of miRNA–122 correlate with serum necroinflammatory hepatic aminotransferase levels in all studied groups with highly significant positive correlations were found between serum miRNA–122 and ALT in all studied groups with ( r = 52, P 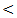 0.001; r = 40, P
0.001; r = 40, P 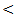 0.001; r = 43, P
0.001; r = 43, P 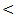 0.001; r = 56, P
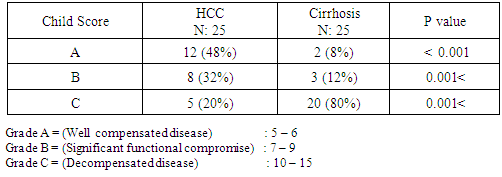
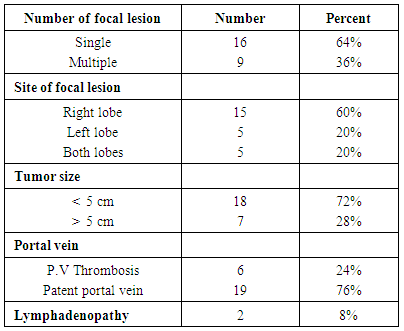
0.001; r = 56, P 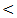 0.001) in control, chronic HCV, cirrhosis and HCC respectively. There were also positive significant correlations between miRNA-122 and AST levels in all studied groups.In contrast, there were no significant correlations between miRNA-122 serum levels and serum bilirubin or serum albumin.There was no statistical significant correlation between serum expression of miRNA – 122 and serum AFP in different studied groups. No significant correlations were found between miRNA – 122 and tumor size or child – Pugh grade in HCC group of patients.
0.001) in control, chronic HCV, cirrhosis and HCC respectively. There were also positive significant correlations between miRNA-122 and AST levels in all studied groups.In contrast, there were no significant correlations between miRNA-122 serum levels and serum bilirubin or serum albumin.There was no statistical significant correlation between serum expression of miRNA – 122 and serum AFP in different studied groups. No significant correlations were found between miRNA – 122 and tumor size or child – Pugh grade in HCC group of patients. 4. Discussion
- Various miRNAs are now being investigated in hepatitis virus infection with the most popular one being miRNA – 122 miRNA–122 in the most abundant miRNA in the liver [17]. Since the reliability of laboratory analysis biomarkers, alpha fetoprotein (AFP) and des- carboxyprothrombin (DCP) is still questionable, the accuracy of AFP is modest, especially in benign liver disease, such as hepatitis and cirrhosis and the elevated DCP activity in only in 50% of HCC patient with tumor
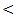 3 cm [18]. The quests for an optimal tumor marker hence continue, miRNAs have been implicated in roles affecting cellular proliferation and oncogenesis. Cellular miRNAs have been linked with HCC, their availability in the circulation makes them attempting target for early tumor detection [19]. Novel biomarkers for early HCC diagnosis are urgently needed, miRNAs have been very promising as diagnostic markers of HCC, in fact, miRNAs are stable in human serum / plasma as free miRNAs released from cancer cells; many studies have shown that circulating miRNAs are resistant to RNase activity, extreme ph and temperature [20]. Although several studies have investigated the role of miRNAs expression in liver cancer and produced conflicting results. The aim of the present study was to explore the potential usefulness of serum miRNA–122 as biomarker for diagnosis of hepatitis C virus related hepatocellular carcinoma.In our study there were positive significant correlation between miRNA-122 and necroinflamatory markers (ALT, AST) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) in all studied groups which concides with the study of köberle et al. [21] who reported significant correlation between serum miRNA-122 expression level and necroinflammatory markers (ALT, AST, GGT), and albumin but no significant correlation was found with bilirubin in HCC patients. In contrast to our study, the study of Wang et al. [22] who reported the lack of correlation between serum miRNA – 122 and ALT levels or liver injury in chronic hepatitis C patients, similarly the study of Yang et al. [23] who found no significant correlation between serum miRNA–122 and ALT levels in hepatitis B patient. El–Garem et al. [24] also demonstrated that no statistical significant correlation between serum miRNA–122 expression levels and patient character (age) or liver synthetic function tests (albumin, bilirubin, and prothrombin concentration) in HCC group. Whereas, in chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis groups' serum miRNAs –122 were correlated with higher ALT and AST levels. In the present study the serum level of miRNA–122 in chronic hepatitis C patients is (613 ± 178 copies / ml) while in control group is (30 ± 17 copies / ml), which is highly statistical significant P
3 cm [18]. The quests for an optimal tumor marker hence continue, miRNAs have been implicated in roles affecting cellular proliferation and oncogenesis. Cellular miRNAs have been linked with HCC, their availability in the circulation makes them attempting target for early tumor detection [19]. Novel biomarkers for early HCC diagnosis are urgently needed, miRNAs have been very promising as diagnostic markers of HCC, in fact, miRNAs are stable in human serum / plasma as free miRNAs released from cancer cells; many studies have shown that circulating miRNAs are resistant to RNase activity, extreme ph and temperature [20]. Although several studies have investigated the role of miRNAs expression in liver cancer and produced conflicting results. The aim of the present study was to explore the potential usefulness of serum miRNA–122 as biomarker for diagnosis of hepatitis C virus related hepatocellular carcinoma.In our study there were positive significant correlation between miRNA-122 and necroinflamatory markers (ALT, AST) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) in all studied groups which concides with the study of köberle et al. [21] who reported significant correlation between serum miRNA-122 expression level and necroinflammatory markers (ALT, AST, GGT), and albumin but no significant correlation was found with bilirubin in HCC patients. In contrast to our study, the study of Wang et al. [22] who reported the lack of correlation between serum miRNA – 122 and ALT levels or liver injury in chronic hepatitis C patients, similarly the study of Yang et al. [23] who found no significant correlation between serum miRNA–122 and ALT levels in hepatitis B patient. El–Garem et al. [24] also demonstrated that no statistical significant correlation between serum miRNA–122 expression levels and patient character (age) or liver synthetic function tests (albumin, bilirubin, and prothrombin concentration) in HCC group. Whereas, in chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis groups' serum miRNAs –122 were correlated with higher ALT and AST levels. In the present study the serum level of miRNA–122 in chronic hepatitis C patients is (613 ± 178 copies / ml) while in control group is (30 ± 17 copies / ml), which is highly statistical significant P 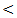 0.001. Our result copes with the result of Wang et al. [22] who showed that serum miRNA–122 levels were significantly higher in acute hepatitis and chronic hepatitis patients than in healthy donors. Similarly Bihrer et al. [25] reported that sera from patients with chronic hepatitis C contained higher levels of miRNA – 122 than sera from healthy control; they added that serum level of miRNA-122 strongly correlate with serum ALT and necroinflammatory activity in patients with chronic hepatitis C with elevated ALT level, but not with fibrosis stage and functional capacity of the liver. Our result also is in agreement with the study of Cermelli et al. [26] who reported that miRNA – 340 and miRNA–122 may represent novel non invasive biomarkers for diagnosis of histological disease severity in patients with chronic hepatitis C or NAFLD ( non-alcoholic fatty liver disease). In the present study the serum miRNA-122 level is high in all patient groups compared to control group, the highest serum miRNA-122 expression level is in HCC group, the mean serum level is (916±270 copies / ml) which is highly significant compared to control group (30 ± 17 copies / ml) .Our result is consistent with the result of Trebica et al. [27] who studied hepatic miRNA-122 expression in HCV related HCC in comparison to healthy liver sample; miRNA-122 was strongly up–regulated in malignant liver nodules in comparison to healthy liver. They suggested that miRNA- 122 might down regulate target miRNA of unknown tumor suppressor genes and thus lead to further tumor growth. Our result also is in agreement with the study of Varnholt et al. [28] who examined miRNA-122 expression in premalignant dysplastic liver nodules and hepatocellular carcinomas by quantitative PCR, they found that miRNA-122, miRNA–100 and miRNA–10 were overexpressed compared to normal liver parenchyma.Qi et al. [29] reported that miRNA-122 in serum was significantly higher in HCC patients than healthy controls. More importantly, they reported that the level of miRNA- 122 was significantly reduced in the postoperative serum samples when compared to the preoperative samples; they suggested that serum miRNA-122 might serve as novel and potential non invasive biomarker for detection of HCC in healthy subjects. Additionally, Coulouran et al. [30] reported higher miRNA-122 expression level in HCV versus HBV associated cancers. Several studies indicated that circulating miRNA-122; have the potential to differentiate patients with HCC from those without, especially in Asian patients suffering from chronic HBV infection [30, 31, 32, 33]. Contrary to our findings of miRNA-122 up regulation in HCV associated HCC; other authors have reported a down regulation in HCC cell line and rodent HCC [34, 35, 36] all of which had etiologies other than HCV infection. Because miRNA-122 closely interact with HCV genome and miRNA-122 expression pattern in HCV associated HCCs is directly opposed to non HCV infected HCC, further studies on the role of miRNA-122 in HCCs of non – HCV etiologies are needed to fully understand the function of this unique miRNA in the liver. In contrast to our result a significant down regulation of miRNA-122 in HCC compared to normal liver tissues were reported by Meng , Wang, and Huang et al. [37, 38, 39] who compared miRNA-122 expression profile of 3 different pairs of tumor and normal human liver derived RNA and 20 HCC liver tissues (mixed etiologies) to normal tissues using microarray. Ladeiro et al. [40] have established significant down expression of miRNA-122 in 28 HCC liver tissues (mixed etiologies) in comparison to 4 healthy liver tissues by q RT - PCR.In this study the mean serum level of miRNA-122 is (367 ± 87 copies / ml) in cirrhosis group compared to (30 ± 17 copies / ml ) in control group which is highly statistically significant (P
0.001. Our result copes with the result of Wang et al. [22] who showed that serum miRNA–122 levels were significantly higher in acute hepatitis and chronic hepatitis patients than in healthy donors. Similarly Bihrer et al. [25] reported that sera from patients with chronic hepatitis C contained higher levels of miRNA – 122 than sera from healthy control; they added that serum level of miRNA-122 strongly correlate with serum ALT and necroinflammatory activity in patients with chronic hepatitis C with elevated ALT level, but not with fibrosis stage and functional capacity of the liver. Our result also is in agreement with the study of Cermelli et al. [26] who reported that miRNA – 340 and miRNA–122 may represent novel non invasive biomarkers for diagnosis of histological disease severity in patients with chronic hepatitis C or NAFLD ( non-alcoholic fatty liver disease). In the present study the serum miRNA-122 level is high in all patient groups compared to control group, the highest serum miRNA-122 expression level is in HCC group, the mean serum level is (916±270 copies / ml) which is highly significant compared to control group (30 ± 17 copies / ml) .Our result is consistent with the result of Trebica et al. [27] who studied hepatic miRNA-122 expression in HCV related HCC in comparison to healthy liver sample; miRNA-122 was strongly up–regulated in malignant liver nodules in comparison to healthy liver. They suggested that miRNA- 122 might down regulate target miRNA of unknown tumor suppressor genes and thus lead to further tumor growth. Our result also is in agreement with the study of Varnholt et al. [28] who examined miRNA-122 expression in premalignant dysplastic liver nodules and hepatocellular carcinomas by quantitative PCR, they found that miRNA-122, miRNA–100 and miRNA–10 were overexpressed compared to normal liver parenchyma.Qi et al. [29] reported that miRNA-122 in serum was significantly higher in HCC patients than healthy controls. More importantly, they reported that the level of miRNA- 122 was significantly reduced in the postoperative serum samples when compared to the preoperative samples; they suggested that serum miRNA-122 might serve as novel and potential non invasive biomarker for detection of HCC in healthy subjects. Additionally, Coulouran et al. [30] reported higher miRNA-122 expression level in HCV versus HBV associated cancers. Several studies indicated that circulating miRNA-122; have the potential to differentiate patients with HCC from those without, especially in Asian patients suffering from chronic HBV infection [30, 31, 32, 33]. Contrary to our findings of miRNA-122 up regulation in HCV associated HCC; other authors have reported a down regulation in HCC cell line and rodent HCC [34, 35, 36] all of which had etiologies other than HCV infection. Because miRNA-122 closely interact with HCV genome and miRNA-122 expression pattern in HCV associated HCCs is directly opposed to non HCV infected HCC, further studies on the role of miRNA-122 in HCCs of non – HCV etiologies are needed to fully understand the function of this unique miRNA in the liver. In contrast to our result a significant down regulation of miRNA-122 in HCC compared to normal liver tissues were reported by Meng , Wang, and Huang et al. [37, 38, 39] who compared miRNA-122 expression profile of 3 different pairs of tumor and normal human liver derived RNA and 20 HCC liver tissues (mixed etiologies) to normal tissues using microarray. Ladeiro et al. [40] have established significant down expression of miRNA-122 in 28 HCC liver tissues (mixed etiologies) in comparison to 4 healthy liver tissues by q RT - PCR.In this study the mean serum level of miRNA-122 is (367 ± 87 copies / ml) in cirrhosis group compared to (30 ± 17 copies / ml ) in control group which is highly statistically significant (P 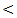 0.001). This result comes in agreement with the study of Trebica et al. [27] who reported significant fold decrease of expression in cirrhosis compared to normal controls. He stated that miRNA-122 is present abundantly in hepatocyte with much lower levels in the circulation in healthy subjects, with hepatocyte injury miRNA is released in the circulation more readily and serum levels rise, with eventual loss of hepatocyte and development of fibrosis with proliferation of myelofibroblasts and accumulation of extra cellular matrix, hence, the circulating miRNA – 122 levels drop again. Waidmen et al. [41] concluded that serum miRNA-122 was reduced in patients with hepatic decompensation in comparison to patients with compensatory liver disease, patients with ascites, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and hepatorenal syndrome had significantly lower miRNA-122 levels than patients without these complications. He explained that the lower levels of miRNA-122 in patients with more advanced disease are most likely the result of reduced release from hepatocyte. Another possibility is that miRNA-122 serum levels are reduced due to higher volume distribution in patients with ascites. This indicates that in patients with liver cirrhosis, the miRNA-122 serum level might be a marker for hepatic functional capacity, whereas at earlier stages of liver disease, the serum mi RNA-122 level is mainly an indicator of necroinflammatory activity and cell death in liver. As release from damaged hepatocyte might be the major source of hepatocyte – derived miRNAs, it is conceivable that in cirrhotic patients who lost a big proportion of hepatocyte and thus have less functional hepatic capacity, the release of miRNAs upon damage might be lower than in patients with higher amount of healthy liver tissues.Similarly, Köberele et al. [21] found that in patient with liver cirrhosis the serum concentration of miRNA-122 correlate with clinical chemistry parameters of hepatic necroinflammation and model of end stage liver disease (MELD) score, . He explained that miRNA-122 serum concentration also reflects residual functional liver tissue in patients with end stage liver disease.In this study the mean serum miRNA-122 in HCC is (916 ± 270 copies/ml) which is highly statistical significantly increased compared to cirrhosis group (367 ± 27 copies / ml). This result comes in agreement with the results of El-Garem et al. [24] and Trebica et al. [27]. Contrary to our result the study of Köberele et al. [21] who found higher but non significant elevation of serum miRNA-122 in HCC patients compared to liver cirrhosis without HCC, and concluded that serum miRNA-122 is not particularly useful to differentiate patients with liver cirrhosis from those with HCC. These different results may be due to selection of different stages of liver cirrhosis in our study. The current study showed that the results of mean serum level of AFP in all studied groups. It showed that HCC had the highest level compared to other groups with statistically significant difference (p
0.001). This result comes in agreement with the study of Trebica et al. [27] who reported significant fold decrease of expression in cirrhosis compared to normal controls. He stated that miRNA-122 is present abundantly in hepatocyte with much lower levels in the circulation in healthy subjects, with hepatocyte injury miRNA is released in the circulation more readily and serum levels rise, with eventual loss of hepatocyte and development of fibrosis with proliferation of myelofibroblasts and accumulation of extra cellular matrix, hence, the circulating miRNA – 122 levels drop again. Waidmen et al. [41] concluded that serum miRNA-122 was reduced in patients with hepatic decompensation in comparison to patients with compensatory liver disease, patients with ascites, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and hepatorenal syndrome had significantly lower miRNA-122 levels than patients without these complications. He explained that the lower levels of miRNA-122 in patients with more advanced disease are most likely the result of reduced release from hepatocyte. Another possibility is that miRNA-122 serum levels are reduced due to higher volume distribution in patients with ascites. This indicates that in patients with liver cirrhosis, the miRNA-122 serum level might be a marker for hepatic functional capacity, whereas at earlier stages of liver disease, the serum mi RNA-122 level is mainly an indicator of necroinflammatory activity and cell death in liver. As release from damaged hepatocyte might be the major source of hepatocyte – derived miRNAs, it is conceivable that in cirrhotic patients who lost a big proportion of hepatocyte and thus have less functional hepatic capacity, the release of miRNAs upon damage might be lower than in patients with higher amount of healthy liver tissues.Similarly, Köberele et al. [21] found that in patient with liver cirrhosis the serum concentration of miRNA-122 correlate with clinical chemistry parameters of hepatic necroinflammation and model of end stage liver disease (MELD) score, . He explained that miRNA-122 serum concentration also reflects residual functional liver tissue in patients with end stage liver disease.In this study the mean serum miRNA-122 in HCC is (916 ± 270 copies/ml) which is highly statistical significantly increased compared to cirrhosis group (367 ± 27 copies / ml). This result comes in agreement with the results of El-Garem et al. [24] and Trebica et al. [27]. Contrary to our result the study of Köberele et al. [21] who found higher but non significant elevation of serum miRNA-122 in HCC patients compared to liver cirrhosis without HCC, and concluded that serum miRNA-122 is not particularly useful to differentiate patients with liver cirrhosis from those with HCC. These different results may be due to selection of different stages of liver cirrhosis in our study. The current study showed that the results of mean serum level of AFP in all studied groups. It showed that HCC had the highest level compared to other groups with statistically significant difference (p 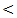 0.001) between HCC versus other groups, a finding that came in agreement with previous studied of many authors Mittal et al. [42] and Guan et al. [43]. Also comparable to Gad et al. [44] who found a significantly higher sensitivity of AFP in Egyptian patients in comparison with Japanese patients for HCC diagnosis (99% versus 67%, P
0.001) between HCC versus other groups, a finding that came in agreement with previous studied of many authors Mittal et al. [42] and Guan et al. [43]. Also comparable to Gad et al. [44] who found a significantly higher sensitivity of AFP in Egyptian patients in comparison with Japanese patients for HCC diagnosis (99% versus 67%, P 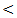 0.001). In contrary to our study, the study done by Huo et al. [45], who concluded that serum AFP level was a weak diagnostic predictor in HCC patients. Our study concluded that increased expression of serum miRNA-122 in chronic hepatitis virus infected patients, cirrhosis patient, and hepatocellular carcinoma patients compared to control group (P
0.001). In contrary to our study, the study done by Huo et al. [45], who concluded that serum AFP level was a weak diagnostic predictor in HCC patients. Our study concluded that increased expression of serum miRNA-122 in chronic hepatitis virus infected patients, cirrhosis patient, and hepatocellular carcinoma patients compared to control group (P 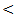 0.001). Thus miRNA-122 can be used as a new biomarker for HCV associated liver disease and can differentiate patients with malignant liver disease from healthy, chronic HCV and cirrhosis groups, so serum miRNA-122 may be able to serve as a promising non invasive diagnostic marker for HCC. There is positive significant correlation between miRNA-122 and necroinflammatory markers (ALT, AST) in all studied groups. Therefore, serum miRNA-122 is a new potential parameter for liver function.Our study has a limitation that we assessed the level of miRNA-122 in a limited number of patients. So, future studies on large population for use of miRNA-122 as a diagnostic, prognostic, predictor of cancer outcome, target of therapy and monitoring treatment response of HCC could be needed to fully understand the function of this unique miRNA in the liver.
0.001). Thus miRNA-122 can be used as a new biomarker for HCV associated liver disease and can differentiate patients with malignant liver disease from healthy, chronic HCV and cirrhosis groups, so serum miRNA-122 may be able to serve as a promising non invasive diagnostic marker for HCC. There is positive significant correlation between miRNA-122 and necroinflammatory markers (ALT, AST) in all studied groups. Therefore, serum miRNA-122 is a new potential parameter for liver function.Our study has a limitation that we assessed the level of miRNA-122 in a limited number of patients. So, future studies on large population for use of miRNA-122 as a diagnostic, prognostic, predictor of cancer outcome, target of therapy and monitoring treatment response of HCC could be needed to fully understand the function of this unique miRNA in the liver. Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML