-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Plant Research
p-ISSN: 2163-2596 e-ISSN: 2163-260X
2014; 4(1): 23-28
doi:10.5923/j.plant.20140401.05
Evaluation of Antibacterial Potentiation of Crude Extracts of Phyllanthus amarus, Tamarindus indica and Cleome viscosa and Their Formulation
Addai-Mensah Donkor 1, Kalifa Gumah Bugri 2, Edmond Akugbire Atindaana 1
1Department of Applied Chemistryand Biochemistry, Faculty of Applied Sciences, University for Development Studies, P.O.Box 24, Navrongo, Ghana
2Microbiology and Immunology Laboratory, Navrongo Health Research Center, Navrongo, Ghana
Correspondence to: Addai-Mensah Donkor , Department of Applied Chemistryand Biochemistry, Faculty of Applied Sciences, University for Development Studies, P.O.Box 24, Navrongo, Ghana.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Acetone crude extracts of Phyllanthus amarus and Tamarindus indica, acetone/methanol crude extracts of Cleome viscosa and crude extracts-Poly(ethylene glycol)ointment formulation of the plants were screened for antibacterial activity on clinical isolates; Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus which are associated with wound infection.Crude extracts of Phyllanthus amarus and its formulation showed no inhibition on both bacteria. Crude extracts of Tamarindus indica showed potency against Pseudomonas aeruginosa at varying concentrations and was dose dependent recording a maximum zone of inhibition of 12 ± 0.15 mm at 200 mg L-1 and zone of inhibition of 6 ± 0.25 mm at 25 mg L-1 but its formulation was not potent against both bacteria. Crude extracts of Cleome viscosa was potent against P. aeruginosa but was not significantly dose dependent at 95% confidence level with zone of inhibition of 8 ± 0.35 mm at 200 mg L-1 and 25 mg L-1 concentrations of the crude extracts. Its formulation showed an increased potency against P. aeruginosa that was highly significant with maximum zone of inhibition 14 ± 0.50 mm at 100 mg g-1 of Cleome viscosa crude extracts-PEG ointment formulation compared with chloramphenicol (positive control) Cleome viscosa crude extract-PEG ointment has therefore emerged a novel formulation against P. aeruginosa hence signifying their potential in treating Pseudomonas infections.
Keywords: Phyllanthus amarus, Tamarindus indica, Cleome viscosa, Poly (ethylene glycol), Formulation, Ointment formulation, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Zone of inhibition
Cite this paper: Addai-Mensah Donkor , Kalifa Gumah Bugri , Edmond Akugbire Atindaana , Evaluation of Antibacterial Potentiation of Crude Extracts of Phyllanthus amarus, Tamarindus indica and Cleome viscosa and Their Formulation, International Journal of Plant Research, Vol. 4 No. 1, 2014, pp. 23-28. doi: 10.5923/j.plant.20140401.05.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The management of wound infection is a challenge in terms of rational antimicrobial use, especially with the presence of a wide range of antimicrobial drugs and the unrelenting promotion by pharmaceutical companies. With more than 80% of the world’s population now depending on traditional medicine for their ailments, especially for wound management[1] coupled with bacterial resistance to antibacterial drug regiments, there is a need to explore and replace such bacterial-resistant drugs with more effective and cheaper alternatives[2].Plants have served as a source of medicine to man for several decades now and still remain a source for vast potent bioactive molecules for the treatment of ailments. Medicinal plants contain secondary metabolites that are bioactive and these bioactive substances are responsible for the medicinal properties of that particular plant.Leaves of Phyllanthus amarus are reported to contain lignans, alkaloids, flavonoids, galloatnoids and glycosides [3], thus its anti-hepatitis B activity[4], hepatoprotective[5], anticancerous[6], antimicrobial[7] and kidney stones dissolution properties[8]. Stem bark of Tamarindus indica has also been reported to contain tannins, saponins, sesquiterpenes, alkaloids and phlobatannins[9].In the past two decades, transdermal drug delivery has moved from a clinical reality to the point where it represents a viable diagnostic tool for noninvasive diagnosis. The advantages of this mode of drug administration are numerous, the patient conveniences, availability of large surface area, easy accessibility, application dynamics and non-invasive nature of therapy. It is important to ensure that the drug delivery systems do not irritate the skin, and the drug is not unduly metabolized and delivered according to the desired pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics[10]. It is well known that, the delivery vehicle markedly affects the permeability of drug. In this study a donor drug system has been designed, PEG ointment with a good texture which might be a suitable ointment base for tropical and subtropical weather conditions[11]. This research seeks to investigate the antibacterial properties of Phyllanthus amarus, Tamarindus indica and Cleome viscosa and their formulation on Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas auregenosa.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Source of Test Bacteria
- Clinical isolates of S. aureus and P. aeruginosa were obtained from incision type wounds at the Microbiology Department of the Tamale Teaching Hospital in the Northern Region of Ghana and stored at a temperature between 2 and 8℃ in nutrient broth. Pure cultures of each of the bacterial isolates were then obtained by sub-culturing the isolates on Chocolate agar (OXOID, Basingstoke, Hampshire, England). For isolates of S. aureus, the tube coagulase test was performed to confirm that isolates obtained were S. aureus.
2.2. Plant Material
- The plant Phyllanthus amarus leaves were collected from Navrongo in the Upper East Region of Ghana and Tamale in the Northern region, stem barks of Tamarindus indica and leaves of Cleome viscosa were collected at UDS Navrongo campus and near the TonoDam in the Upper East Region of Ghana respectively. The plants were authenticated by Dr. Isaac Sackey at the Department of Applied Biology of the University for Development Studies.
2.3. Extract of the Plant
- The plant material was air dried under shade for four weeks for leaves of P. amarus, and oven dried at 35oC for two days for stem barks of Tamarindus indica and leaves of Cleome viscosa and then powdered using mechanical grinder.
2.3.1. Phyllanthus amarus
- Two portions of fifty grams (50 g) each of the Phyllanthus amarus powdered leaves was macerated in 150 mL of acetone. The extract was filtered after 48 hours with the aid of a filter paper and the filtrate concentrated using rotary evaporator to obtain thecrude extract (20% yield). Jayaprasad research team[12], reported activity of acetone extract against P. aeruginosa and Bacillus subtillis
2.3.2. Tamarindus indica
- Powdered plant material, 100g of was plugged in 300mL of acetone and was shaken for 30 minutes. The extract was filtered after 48 hours with the aid of a filter paper and the filtrate concentrated using a rotary evaporator to obtain a 10% yield of the extract. Research by Doughari reported high antibacterial activity of acetone extract against test organisms compared with aqueous and ethanol extracts
2.3.3. Cleome Viscosa
- Powdered plant material, 33g of was plugged in 100mL of equal proportions of acetone and methanol. The extract was filtered after 48 hours with the aid of a filter paper and the filtrate concentrated using a rotary evaporator to obtain a yield of 15% of the extract. Saradha and Co.[13] reported significant antibacterial activity of methanol extract compared with that of aqueous extract
3. Preparation of Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) Ointment
- Poly(ethylene glycol) 4000 (PEG 4000) and Polyethylene glycol 400 (PEG 400), 15g each were weighed into a beaker and melted on a thermostatic water bath at 75℃ until liquefied to make 50% PEG 4000 and 50% PEG 400. It was then stirred with a glass rod under tap water at room temperature until congealed.
4. Preparation of Crude Extract
4.1. Phyllanthus amarus
- Phyllanthus amarus crude extracts were weighed into separate beakers and dispersed in DMSO to derive concentrations of 25 mg L-1, 50 mg L-1, 100 mg L-1 and 200 mg L-1 respectively. These concentrations were then used for the antibacterial studies.
4.2. Tamarindus indica
- Tamarindus indica crude extract was weighed into separate beakers and dispersed in DMSO to derive concentrations of 25 mg L-1, 50 mg L-1, 100 mg L-1 and 200 mg L-1 respectively. These concentrations were then used for the antibacterial studies after preliminary trials at various concentrations.
4.3. Cleome Viscosa
- Cleome viscosa crude extracts was weighed into separate test tubes and then dispersed in DMSO to derive concentrations of 25 mg L-1, 50 mg L-1, 100 mg L-1 and 200 mg L-1 respectively. These concentrations were then used for the antibacterial studies.
5. Preparation of Plant Crude Extract-PEG Ointment Formulations
- Phyllanthus amarus, Tamarindus indica and Cleome viscosa crude extracts were separately formulated together with PEG ointment to determine whether they could have potentiation effect on the bacterial isolates. Equal quantities (25, 50, 100, and 200 mg) of each crude extract were weighed into appropriately labeled separate beakers and 1.0 g of the PEG ointment was then added to each beaker and warmed at 70℃ while stirring with a glass rod. The mixtures were allowed to cool at room temperature to produce a crude extract- PEG ointment formulation at varying concentrations of 25 mg g-1, 50 mg g-1, 100 mg g-1 and 200 mg g-1 respectively of each plant extract. These concentrations were used for antibacterial activity tests on Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus.Poor solubility, inability of certain drugs to circulate long enough through blood stream and the tendency of particle aggregation mostly lead to poor activity. Polymeric carriers, which physically entrap molecules of interest, and polymer conjugates, to which such molecules are chemically bound, play an important role in modern pharmaceutical technology[14][15]. The shared task of carriers and conjugates is the targeted delivery of drugs to specific sites of action in the body.In the case of drug conjugates, in particular, the increase of the molar mass leads to reduced kidney excretion and results in a prolonged blood circulation time of the drug. Shielding of drug carriers and conjugates is required to avoid a fast recognition by the immune system followed by rapid clearance from the body. Drug-delivery vehicles can also be coated with a hydrophilic polymer to allow both inhibition of opsonization and enhancement of water solubility. Poly (ethylene) glycol (PEG) is the most commonly applied non-ionic hydrophilic polymer with stealth behavior. Furthermore, PEG reduces the tendency of particles to aggregate by steric stabilization, thereby producing formulations with increased stability during storage and application[16].
6. Agar Diffusion Bioassay
- The modified agar well diffusion method published procedure by[17] was employed. Colonies of a pure culture of each test organism was suspended in 100ml of sterile peptone water to get a turbidity of about 0.5 McFarland Standard. Within 15 minutes of its preparation, a sterile cotton swab was then dipped into the standardized inoculum suspension. Surplus moisture was removed by rotating the swab several times whilst pressed firmly against the walls of the tube above the peptone water. Agar plates (Mueller Hinton Agar, Oxoid) were then inoculated with the cotton swabs by rotating the swab while rubbing, taking care that the whole area is inoculated. The inoculated plates were allowed to dry and five-millimeter diameter wells were made on the culture plates with a sterile cork-borer at wide enough intervals(about 30 mm apart) and the wells corresponded with the prepared number of concentrations of each formulation and the positive and negative controls.For each formulation, 1 ml of each concentration was drawn into a labeled well with a sterile micropipette taking care to avoid spillage onto the surface of the culture plate. Same quantity of the negative control (99% DMSO) and positive control (Chloramphenicol at 30μg) was also introduced into a well each on the same plate. Plates were left to stand until complete diffusion of the formulations into the medium. Plates were incubated in inverted positions at 37°C for 24 hours after which they were observed for inhibitory activity depicted by zones of inhibition around the wells. Inhibition zone diameters were measured using a ruler and recorded in millimeters (mm).The experimentswere repeated three times to check for reproducibility. Chloramphenicol was used as positive control to test the choice of the local residents use of this drug in treatment of wounds.
7. Statistical Analysis
- Means and standard mean errors were calculated for the zones of inhibition measured for the three sets of experiments in each case. These means were statistically scrutinized using the one – way ANOVA to determine if they were significantly different at P < 0.05.
8. Results
8.1. Antibacterial Activity of Plants Crude Extracts
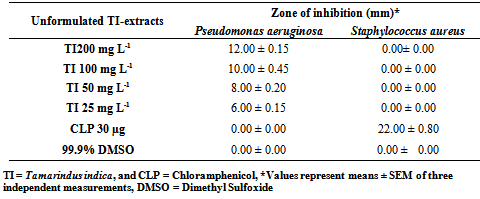
- The antibacterial properties of the ethanol and acetone extracts of Phyllanthus amarus, acetone extracts of Tamarindus indica and acetone-methanol extracts of Cleome viscosa at concentrations 200 mg/ml, 100 mg/ml, 50 mg/ml and 25 mg/ml were tested against two standard bacterial isolates Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. For the unformulated crude extracts of the plants, Tamarindus indica at 200 mg/ml showed the highest zone of inhibition of 12 ± 0.15 mm against Pseudomonas aeruginosa but was not potent against Staphylococcus aureus. Staphyloccocus aureus was resistant to all the plant extracts at the various concentrations as the extracts did not show any zones of inhibition. Tamarindus indica crude extracts showed promising results against P. aeruginosa (Table 1) however Tamarindus indica crude extracts-PEG ointment formulation showed no zones of inhibition on both bacteria (Figure 1).
|
 | Figure 1. A graphof zones of inhibition of formulated and unformulated extracts of Tamarindus indica on Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
|
8.2. Antibacterial Activity of the Plants Extracts-poly (Ethylene Glycol) Formulations
- The antibacterial properties of the ethanol and acetone crude extracts-PEG ointment formulation of Phyllanthus amarus, acetone crude extracts-PEG ointment formulation of Tamarindus indica and acetone-methanol crude extracts-PEG ointment formulation of Cleome viscosa at concentrations 200 mg/g, 100 mg/g, 50 mg/g and 25 mg/g were tested against two standard bacterial isolates Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Phyllanthus amarus crude extracts-PEG ointment formulation, no zones of inhibition were recorded for the various concentrations on both Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus.Results were promising with Cleome viscosa crude extracts-PEG ointment formulation as the antibacterial potency was enhanced as shown in their zones of inhibition (Table 3, Figure 2). However, there was no significant difference between Cleome viscosa crude extract and Cleome viscosa crude extract-PEG ointment formulation with P-value at 0.698 > 0.05 from One –Way ANOVA analysis. This clearly indicates that an increase in the concentration of PEG ointment did not influence the activity of the bioactive compound(s). Student’s t-test showed that there is a significant difference between the zones of inhibition of the Cleome viscosa crude extracts and its formulation.The Student’s t-test thus established that the PEG-ointment exerted some level of antibacterial effect and this effect is a subject of investigation in our laboratory.
|
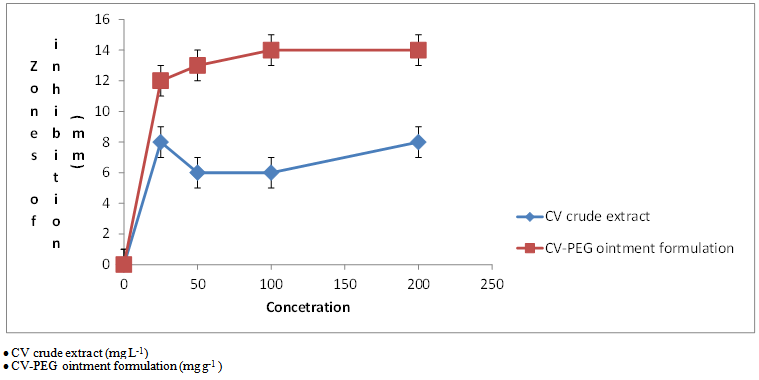 | Figure 2. A graph of zones of inhibition of various concentrations of formulated and unformulated crude extracts of Cleome viscosa on Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
9. Discussions
- Plant extracts are still used every day in the treatment of different ailments and most of which are as a result of the activity of pathogens. These plants usually contain bioactive compounds which act to either inhibit the growth and or kill microorganisms.The use of plants in the treatment of diseases dates back to ancient times. They have always served a huge resource in traditional medicine. Some of the medicinal usages have been proven in experimental models, which suggest that the extracts of the plant possess various pharmacological actions.The antibacterial activity of Cleome viscosa could be due to a wide variety of phyto principles present in Cleome viscosa[18][19] reported the presence of alkaloids, flavonoids, tannins, saponins and terpenoids in the leaves of Cleome viscosa. And research by[20] reported the presence of alkaloids and tannins but absence of flavonoids and saponins in Cleome viscosa. Tannins, alkaloids and saponins are associated with antibacterial activity.Traditionally, Cleome viscosa and Tamarindus indica are used in the treatment of wounds in the Northern Region of Ghana, thus their potency against a wound pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa as this experiment shows scientific justification for its use. Contrary to reports of the antimicrobial activity of Phyllanthus amarus[21], its crude extracts were not potent against both P. aeruginosa and S. aureus. This could be due to the geographic location and conditions prevailing in Navrongo and Tamale where the plant material was collected and explains why it is not popular in its use in the treatment of wounds in these areas. Medicinal plants produce secondary metabolites that are responsible for their therapeutic properties but the presence of these molecules and conversely their activities is affected by environmental factors like geographical location[22].Cleome viscosa crude extracts-PEG ointment formulation showed enhanced antibacterial potency compared to its unformulated form in this study and could be used for better efficacy. In addition to efficacy, it is easily washable with water without leaving any greasy layer.Although crude extracts of Tamarindus indica and Cleome viscosa showed various zones of inhibition at different concentrations (Table 1 & 2), the Tamarindus indica crude extract-PEG ointment formulation showed no inhibition. The addition of the ointment base resulted in an enhanced activity for Cleome viscosa crude extracts-PEG ointment formulation (Figure 2) and repressed the activity of Tamarindus indica might be due to the fact that the phyto principles responsible for the antibacterial potency of the plant extracts may be chemically different. This could explain the poor releasing ability of the bioactive compound in Tamarindus indica crude extracts-PEG formulation.
10. Conclusions
- Crude extracts of Cleome viscosa and Tamarindus indica has shown antibacterial potency against Pseudomonas aeruginosa which correlate with the claims made by traditional practitioners to use it in the treatment of wound infections. Cleome viscosa crude extracts-PEG ointment formulation has emerged as aninnovative formulation suitable for tropicaland subtropical conditions in the topical usage for the treatment of Pseudomonas infection.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- All materials and equipment used in this study were provided by the Department of Applied Chemistry and Biochemistry, while the microbiological studies were carried out at the Microbiology Laboratory of the Department of Applied Biology, both in the Faculty of Applied Sciences of the University for Development Studies, Navrongo. The authors are also grateful to the Head and staff of the Medical Microbiology (Bacteriology) Laboratory of the Tamale Teaching Hospital, for the clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Conflict of Interest
- It is hereby declared that the authors have no competing financial interests whatsoever in relation to the work described here. It is purely for academic and intellectual purposes.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML