-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Plant Research
p-ISSN: 2163-2596 e-ISSN: 2163-260X
2012; 2(2): 31-35
doi: 10.5923/j.plant.20120202.06
A Histopathological Analyses of in vivo Anti-tumor Effect of an Aqueous Extract of Aristolochia longa Used in Cancer Treatment in Traditional Medicine in Morocco
Ghita Benzakour 1, Mariam Amrani 2, Mounia Oudghiri 1
1Laboratory of Physiology and Molecular Genetics, Department of Biology, Faculty of Sciences Aïn Chock, University Hassan II, B.P 5366 Maarif, Casablanca, Morocco
2Laboratory of pathology, National Institute of Oncology, Moulay Abdallah Hospital, Rabat, Morocco
Correspondence to: Mounia Oudghiri , Laboratory of Physiology and Molecular Genetics, Department of Biology, Faculty of Sciences Aïn Chock, University Hassan II, B.P 5366 Maarif, Casablanca, Morocco.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
In Morocco, Aristolochia longa L. (AL) is commonly used in cancer treatment. The in vivo anti-tumour effect of this plant has never been investigated before. We therefore developed an experimental gingival hyperplasia model in immune-competent rats to study the in vivo action of an aqueous extract of AL on the evolution of the hyperplasia during the initiation and post-initiation phases of 4NQO-induced gingival tumorigenesis. We also aimed to understand its toxicological potential and to characterize the cellular inflammatory infiltrate present around these hyperplasic areas.The hyperplasia was amplified by the AL treatment compared to controls. The data demonstrated that the gingival topical application of AL at saturation limit dose (10%), induced significant pro-inflammatory reactions not limited to the tissue treated, but extended to different tissues of the oral cavity (lips, tongue) and to lungs tissues where we noted an intense peribronchiolar hyperplasic lymphoid follicles with a high number of eosinophils. When given for a long period (3 weeks), the high inflammatory potential of AL was responsible of severe toxic effects with irreversible tissue lesions, particularly in lungs which limits the utilization of this plant as an anti-tumour product and must be forbidden to use in folk medicine.
Keywords: Aristolochia Longa, Rat-4NQO-Hyperplasia, Histopathological Analyses
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- In recent years, there was a worldwide increase of folk medicine use based on plants. In Morocco, the use of traditional medicine is a widespread practice. The ethnobotanical and ethnopharmacological surveys conducted in different areas allowed the compilation of an inventory of 360 species and more than 500 prescriptions are recorded[1]. The use of plants in the form of infusions or decoctions is a common practice among people of rural communities and their use is increasing in urban populations. Despite the great number of plant extracts used in different human diseases[2] only a few of them have been scientifically explored.Aristolochia longa L. (AL) (Aristolochiaceae) locally known as “Barraztam” is a species communally used in Moroccan traditional medicine[1; 3-4] for different treatments but mostly in cancer treatment[5-7].The genus of Aristolochiaceae is a rich source of aristolochic acids (AAs) which are unique to this genus and of terpenoïds[8]. The AAs are associated with the development of aristolochic acid nephropathy (AAN) syndrome, characterized by chronic renal failure, tubule-interstitial fibrosis and urothelial cancer[9-11]. The use of AL during cancer treatment was reported in 16% of the renal failure observed in patients with malignancies[8; 10].In a previous study we have determined that sub-chronic administration of the aqueous extract of AL at saturation limit dose of the plant produced severe and irreversible renal toxic effects in mice due to high immune-stimulation activity[12].The in vivo anti-tumour effect of this plant has never been investigated before. We therefore developed an experimental gingival hyperplasia model in immune-competent rats to study the in vivo action of an aqueous extract of AL on the evolution of the hyperplasia. We also aimed to better understand its toxicological potential and to characterize the cellular inflammatory infiltrate present around these hyperplasic areas.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
- Aristolochia longa L. Subsp. Aristolochia paucinervis Pomel[13; 14] was collected in May 2009 at 30 Km south of Marrakech City (Morocco).The plant was authentified and a voucher specimen was deposited (No 61318) in the Herbarium of National Scientific Institute of Rabat (Morocco).
2.2. Preparation of the Aqueous Extract of Aristolochia longa L. rhizomes
- The vegetal material was washed with water, and then dried at room temperature for 48h to 92h. The aqueous extract was prepared by adding 500mL of distilled water to 50g of AL dry rhizomes powder. After 24h of maceration under magnetic stirring at room temperature, the mixture was centrifuged, filtered, and then concentrated in a rotary vacuum evaporator. The extracted material (yield of approximately 10% w/v) was dissolved in 0, 9% NaCl solution and stored at – 20°C in the dark until further use.
2.3. Animals and in Vivo Experiments
- Wistar rats (n=12) aged 8 weeks old weighting approximately 250g, were obtained from the animal colony of our department. They were maintained under controlled conditions of temperature (24 ± 2°C), light-dark periods of 12 hours, and housed in groups of three or four per cage with free access to water and commercial diet.4-Nitroquinoline-N-oxide (4-NQO) is a water soluble carcinogen, which induces tumours predominantly in the oral cavity. It produces all the stages of oral carcinogenesis[15; 16].The experiment was designed to examine the modifying effects of aqueous extract of (AL) during the initiation and post-initiation phases of 4NQO-induced oral tumorigenesis in Wistar rats[16; 17]. 4NQO (Sigma, USA) was obtained as a powder and was dissolved to a final concentration of 10 mg/ml. Fresh aliquots were obtained for every brush application. 4NQO was applied on gingival tissue with a No. 2 brush. The procedure was repeated 3 times a week for 16 weeks[18; 19]. The rats were restrained from drinking the first hour after 4NQO application. After the application period (16 weeks), a 10% AL solution was applied on gingival tissue of rats (n=6) with a No.2 brush daily for 3 weeks. A group of rats (n=6) not treated by AL solution was used as control.
2.4. Histopathological Examination
- At the end of the experimental period, the rats were sacrificed by cerebral dislocation after inhalation anesthesia and different tissues (lip, tongue, gingival, lung) were removed and fixed in freshly 10% buffered formalin. All the tissues were trimmed, dehydrated, cleared, embedded in paraffin blocks, sectioned into 5 μm sections and stained by hematoxylin and eosin (H.E.) stain. Histopathological evaluation was performed with a light microscope by a pathologist.All the experiments were performed in the morning according to current guidelines for the care of the laboratory animals and the ethical guidelines for the investigation of experimental pain in conscious animals[20], in accordance with the internationally accepted principles for laboratory animal use and care (EEC Directive of 1986; 86/609/EEC).
3. Results
- To obtain and validate evidence for or against the use of AL as an antitumor product and in order to learn about its in situ mechanisms of immunological reactions, slowly developing gingival hyperplasia was initiated by application of a carcinogen to the anterior surface of the gingival of immune-competent Wistar rats. After 12 weeks application of 4NQO, a carcinogenic product, all the animals developed a white rough appearance of their gingival (Fig. 1a). No apparent abnormal clinical signs were noticed on the lip, tongue, liver and lungs in all periods evaluated. After 3-weeks treatment by a topical application of an aqueous extract of AL (10%), an increase in ulcer surrounded with severe inflammation was observed (Fig.1b).
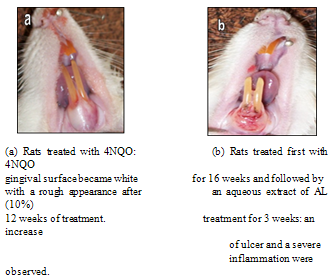 | Figure 1. Morphological change of gingival tissue of 4-NQO treated rats |
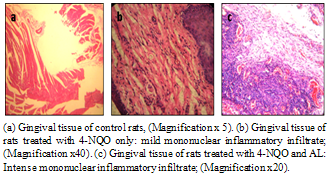 | Figure 3. Histopathological changes in gingival tissues |
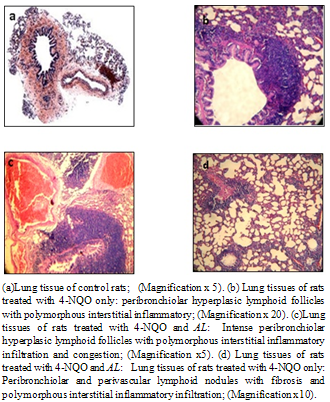 | Figure 4. Histopathological changes in Lung tissues |
4. Discussion
- The data presented in this study demonstrate that the gingival topical application of an aqueous extract of AL at saturation limit dose (10%), induced significant pro-inflammatory reactions not limited to the tissue treated, but extended to different tissues of the oral cavity (lips, tongue) and to lung tissues where we noted an intense peribronchiolar hyperplasic lymphoid follicles with polymorphous interstitial inflammatory infiltration and congestion.
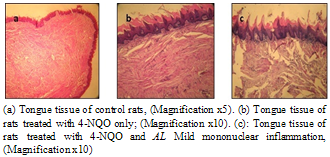 | Figure 5. Histopathological changes in tongue tissues |
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- This work was financially supported by the Minister of high education of the kingdom of Morocco and the CNRST of Morocco.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML