-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Public Health Research
p-ISSN: 2167-7263 e-ISSN: 2167-7247
2017; 7(3): 55-61
doi:10.5923/j.phr.20170703.01

Determinants and Distribution of Catastrophic Health Expenditures and Impoverishment in Kenya
Njuguna K. David1, Diana N. Kimani2, Bethuel Kinyanjui2
1Senior Economist, Ministry of Health, Nairobi, Kenya
2School of Economics, The University of Nairobi, Kenya
Correspondence to: Njuguna K. David, Senior Economist, Ministry of Health, Nairobi, Kenya.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

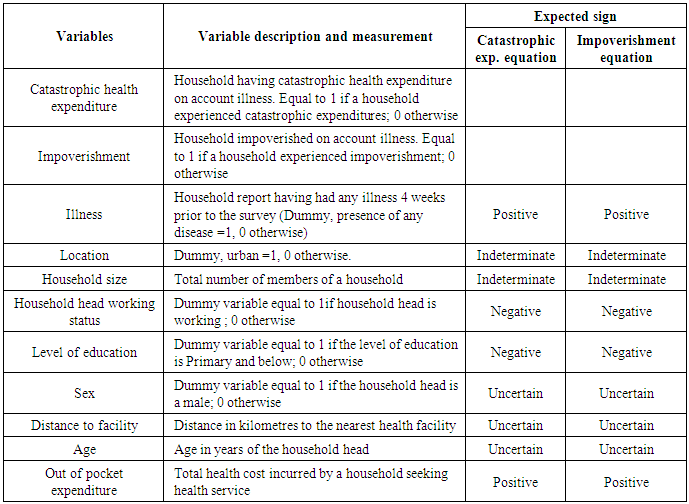
The Constitution of Kenya guarantees citizen the right to basic health care of the highest attainable standard that will adjust the quality of life for all Kenya. The Kenya health policy commits the government to offer easy, accessible, reasonable and valuable health care services to the entire population countrywide [35]. Health is not a consumer good, but rather a universal right, and therefore access to health care services cannot be a privilege for just a few. However, the government is faced with budgetary constraints; hence the health services are provided under a serious resource constrained setting. An analysis of patterns of health care expenditure is essential for assessing levels of inequalities in health care needs and access. Furthermore, analyses of differentials on health care expenditure by socioeconomic and demographic characteristics of population could be used to develop appropriate policies and models to new interventions. The research utilized the secondary data from the Kenya Household Health Utilization and Expenditure Survey (KHHEUS) 2013 to examine the association between households’ health care expenditures with socioeconomic variables. The goal of the research was to provide critical analyses on household out-of-pocket expenditures in Kenya and how these health expenditures become catastrophic pushing the households further into poverty. The findings will contribute towards a better understanding of existing variations in catastrophic health expenditures and impoverishment in Kenya. These results can be used by the government of Kenya, health planners and managers and other stakeholders to facilitate design of appropriate policies which will impact positively to households and particularly the vulnerable ones. The information could contribute to improving financial protection and equitable income redistribution and eventually towards poverty reduction strategies and better health for all Kenyans.
Keywords: Out of Pocket, Impoverishment, Catastrophic spending
Cite this paper: Njuguna K. David, Diana N. Kimani, Bethuel Kinyanjui, Determinants and Distribution of Catastrophic Health Expenditures and Impoverishment in Kenya, Public Health Research, Vol. 7 No. 3, 2017, pp. 55-61. doi: 10.5923/j.phr.20170703.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Health is a basic need that each person is entitled to enjoy. Good health, protection from diseases and quality medical care are necessary for human personal development and survival. Improved quality of life in any country depends on improving highly on the availability and accessibility to healthcare facilities at affordable costs. Especially, packages for poor and vulnerable age groups and implement healthcare campaigns for households in areas where the incidence of out-of-pocket payments is higher. In line with Vision 2030 and the Constitution of Kenya 2010, the government is committed to implementing strategic interventions aimed at accelerating the attainment of Universal Health Coverage (UHC) for all Kenyans [39]. The health sector plays a major role for the achievement of vision 2030, since maintaining a health nation is important for a working population which later translates to increased labor productivity. The country has progressed in improving the quality of life through robust health care reform programs such as pro-poor policies and progressive contributive healthcare policies such as Universal healthcare Coverage (UHC). A household’s expenditure on health services is always directly dependent on income, social networks and wealth position of the households [53]. A lot of Poor households in developing countries forego expenditure on health services in order to use their earnings on basic needs like food and as such positioning them in higher risks of mortalities when diseases become fatal [43]. According to WHO, a household faces “catastrophic” health costs if health expenditure is greater than or equal to 40 percent of a household's non-subsistence income, i.e. income available after basic needs have been met (“capacity to pay”). Households that incur huge OOP are at risk of getting poorer due to healthcare costs and will experience a phenomenon called catastrophic which varies across households [56].The main challenge of healthcare access in Kenya lies primarily in the acute scarcity of resources, and inefficient resource allocation. In the past few decades, the out-of-pocket (OOP) expenditure has been increasing since the introduction of user fees in the health sector. Moreover, to limit the rising publicly-financed health expenditures, OOP expenditures have continued to be implemented in the country. However, higher health-related OOP expenditure may burden social subgroups unequally.The literature reviewed gives an analysis of the theoretical underpinning on health care access and utilization and how it influences the productivity of individual and households. Empirical literature reviewed shows that increased out of pocket expenditure or occurrence of catastrophic health expenditure has been linked to negative effect on individuals and household health outcomes across the world as more households are pushed further into poverty [5, 8, 51, 47]. The reviewed literature relates to effects on household income and vulnerability to poverty relative to the economics status of individuals in a household. The survey shows that economic effects of ill health contrast widely depending on the account of illness and household characteristics [29, 51].The approaches used to assess catastrophic expenditure in a household in the reviewed literature point to two distinct approaches related to the measurement of catastrophic health expenditure in the literature. Assessments of catastrophic health expenditures show the impact of these costs on poor households. While some studies consider the share of OOP expenditure in a household, others measure the incidence and extent of OOP health expenditures across countries of different economic status [46, 32, 50, 51, 60]. Others evaluate both actual and potential incidence of catastrophic expenditure brings out the difference between households that seek healthcare and those that do not [46]. These studies conclude that catastrophic health expenditures increase the likelihood of a household to slide into poverty but has not looked at the determinants of catastrophic health expenditures and impoverishment and the distribution at sub national levels.Studies on catastrophic health expenditures and impoverishment done in Kenya have not estimated the incidence of catastrophic health expenditure and impoverishment at county level. Some are case studies, while the others are provide national and regional (province based) estimates [19, 33]. This study proposes to fill the identified information gap and do a comparison to the national estimates of catastrophic health expenditures and impoverishment.
2. Study Objective
- The study seeks to assess health expenditure taking into account health being a devolved function the country and existence of county variation in socio-economic characteristics. Because of future prospects of growth and development, it is important to provide information to policy makers in programming –health expenditures that are catastrophic leading to abject poverty.
3. Methodology and Data
- This study used data from the Kenya Household Expenditure and Utilization Survey (KHHEUS) conducted in 2013. In addition incorporated the Xu approach to estimate the catastrophic health expenditures and impoverishment levels. Households were classified as having catastrophic health spending when their out-of-pocket health payments were over 20% of their payment capacity. All other households were classified as not having catastrophic health spending. To examine the determinants of catastrophic health expenditure, the study uses logit model. Cameron and Trivedi indicated that either logit or probit can be used because there is little difference between the predicted probabilities from either probit and logit models [7, 37].A logit model was used to estimate the presence and at determining what factors influence the probability of catastrophic healthcare spending. Further, the fitted log-likelihoods often are very similar for the two models.The study specifies a logistic regression model of the form:
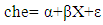 | (1) |
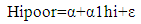 | (2) |
|
4. Results and Discussion
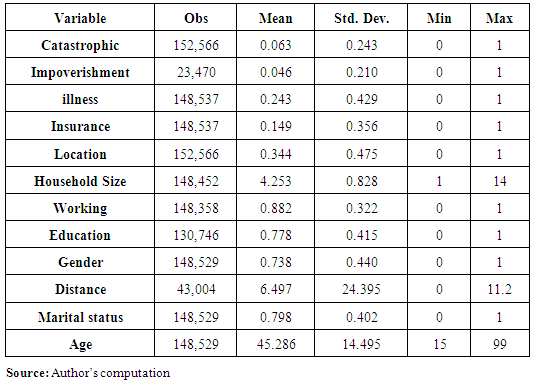
- This section presents the descriptive statistics for the dependent and independent variables used in estimating the Catastrophic Health Expenditure equation (equation 9, and 12) and the ones used in estimating the impoverishment equation (equation 10 and 13). The survey respondents had a mean age of was 45.29 years. Their average schooling was 7.78 years and the average household size was 4.3 persons. About 80 per cent of the respondents were married; 14.9 percent had insurance cover; and 88.2 percent of household heads were working. 24.3 percent of the households reported illness.Table 2 further shows that the majority (66 percent) of the households were residing in rural areas. On average household members travelled a distance of 6.497 kilometres to access health services from the nearest health facility. There was a large variation in the number of male and female in the survey with 73.8 percent of the respondent’s being male and 26.2 percent were female.
|
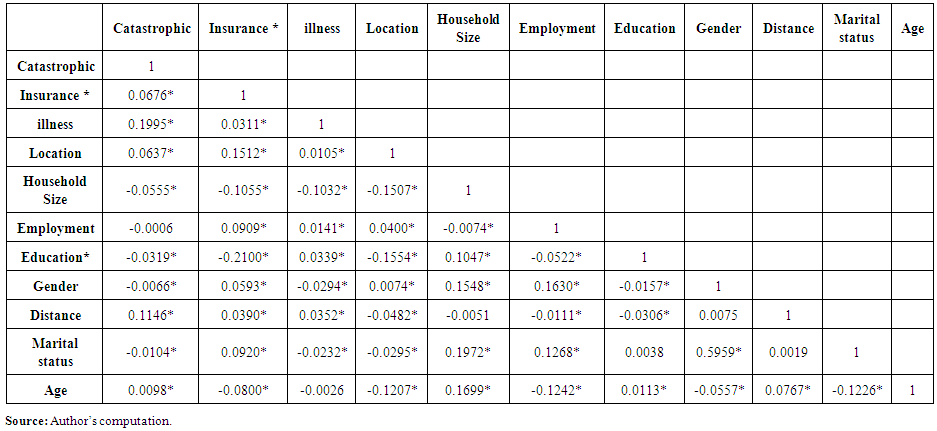 | Table 3. Correlation matrix for variables used in estimating che |
|
|
5. Conclusions
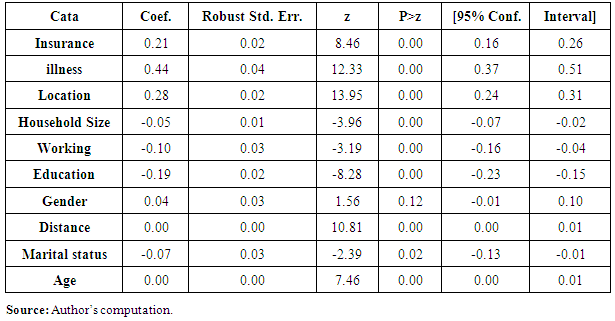
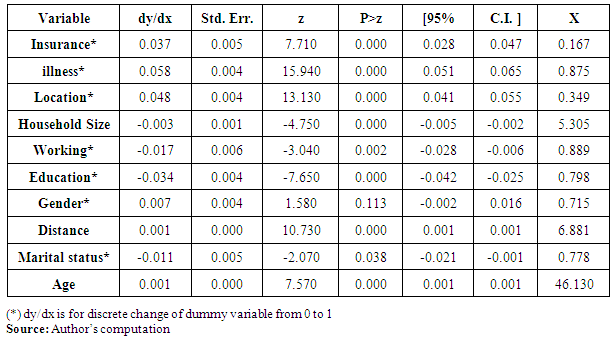
- The goal of the research was to provide critical analyses on household out-of-pocket expenditures in Kenya and how these health expenditures become catastrophic hence pushing the households into poverty. Further, analyses of differentials on health care expenditure by socioeconomic and demographic characteristics of population can contribute towards a better understanding of existing variations in catastrophic health expenditures and impoverishment that could be used to develop appropriate policies and models to new interventions.Insurances, illness, location, household size, employment status of household head, education level of household head, distances to health facility, marital status and age have an association with catastrophic expenditure while illness, location, employment status of household head, education level of household head, distances to health facility, have an association with impoverishment.The results suggest that catastrophic health expenditures continue to be experienced in Kenya and as a result, many families are pushed into poverty. The study used the Xu’s method in the estimation of catastrophic health expenditures and impoverishment. The results shows that 6.3 percent of households that used healthcare in 2013, incurred catastrophic health expenditures and 4.6 percent were impoverished. Moreover, the rates of catastrophic expenditures varied considerably between counties. From the results, 23 counties reported a rate of catastrophic health expenditure exceeding 40 percent of total non-food expenditure on health while 22 counties reported impoverishment. These rates were higher than the national average, suggesting that about 2.6 million and 1.7 million Kenyans experienced catastrophic health expenditures and were pushed into poverty line due to OOP expenditures. The result illustrates the extent to which health care payments can push a household into poverty but this is never captured in poverty estimation in the country i.e. many people are not classified as poor despite being below the poverty line after incurring health expenditures. Therefore, there is need to relook at the poverty estimation so as to capture the people (who were initially not poor) falling below poverty line due to health expenditures.Urban areas had the highest number of households incurring catastrophic expenditure at a count of 8.4 against the rural at 5.17 percent. Further, Catastrophic health expenditures were experienced highest in the account of illness at 10.4 percent while impoverishment was experienced highest by people with secondary education and above at 7.07 percent.This study has some limitations. The income and expenditures data is self-reported and thus not verifiable from other sources. The recall period of 12 months for expenditures on healthcare can be a limitation since it is difficult to ascertain possible inaccuracies in recall can occur for income or expenditures. Despite the limitations, this study provides critical and useful insights which can evoke important discussion that can inform health financing programming at both national and county levels. The study made several contributions. It examined the determinants of catastrophic health spending and impoverishment as well as the distribution at county level.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML