-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Public Health Research
p-ISSN: 2167-7263 e-ISSN: 2167-7247
2016; 6(5): 119-131
doi:10.5923/j.phr.20160605.01

Evaluation of Patients’ Satisfaction Towards the Primary Health Care Services in the Old City of Jerusalem, Palestine
Raghda Mustafa Radad1, Nor Malina Malek1, Samer Hatem Raddad2
1School of Social Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Malaysia
2Urban Sustainability Development Research Group, Al Quds Unversity, Palestine
Correspondence to: Samer Hatem Raddad, Urban Sustainability Development Research Group, Al Quds Unversity, Palestine.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The evaluation of patients’ satisfaction has become an important issue in the assessment of health care system because it is a key determinant of healthcare quality. Providers of health care service in the Old City of Jerusalem are divided into three main categories: Israelis, Palestinians and international organizations, but all of them are operating under the Israeli administration. Consequently, the comparison between different health care providers in the city led to different level of satisfaction among the patients. This study aims to assess the patients’ satisfaction as a tool to monitor and evaluate the quality of the primary health care services in the Old City of Jerusalem by investigating the main factors that affect the patient satisfaction and identifying the main problems facing the health sector in the city. A combination of quantitative and qualitative methods was applied to this research using questionnaires and interviews to collect primary data. Descriptive statistics and multiple regression analysis were used to evaluate patients’ satisfaction in the Old City of Jerusalem. Study findings showed dissatisfaction of the Arab community in the city towards some of the health care services such as emergency services, x-ray services, provision of bone specialist services and working hours of health care centers. The result of the regression analysis showed four factors that have effects on patients’ satisfaction in the Old City of Jerusalem which includes hierarchically, time and access, physical environment in the health care centers, cost and health insurance, and comprehensiveness and quality of the health care. Therefore, there is a critical need to improve the health services sector in the Old City of Jerusalem. Both Israeli and Palestinian authorities as well as the nongovernmental health organizations in the Old City of Jerusalem should pay more attention towards improving the quality of health care centers by providing more facilities and doctors especially bone specialists, obstetricians, pediatricians, x-ray departments and laboratory services, so that the people in the study area do not have to go outside of the walls to get these health services.
Keywords: Urban Health Development, Health Care Services, Patient Satisfaction, Old City of Jerusalem
Cite this paper: Raghda Mustafa Radad, Nor Malina Malek, Samer Hatem Raddad, Evaluation of Patients’ Satisfaction Towards the Primary Health Care Services in the Old City of Jerusalem, Palestine, Public Health Research, Vol. 6 No. 5, 2016, pp. 119-131. doi: 10.5923/j.phr.20160605.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Development does not only mean an increase or decrease in the national income but rather it is a process that enables the society to be more productive by improving the quality of their lives. The concept of development is about improving our living conditions and the access to necessary community services such as education, health services and availability of a safe living environment [1] [25]. Development, especially in developing countries, is affected by various factors such as poverty, health risks and diseases, as well as the environmental conditions [30].Health issues are among the critical and complex challenges which face the modern world. Therefore, it is important for all countries and international organizations to focus on health. Every government is working hard to develop its health care delivery systems so as to increase its capabilities in facing the rising health problems which may threaten the world population. Health sector has an important role in improving and ensuring sustainability of socio-economic development in the developing countries. It has many effects such as increasing labor productivity, increasing rates of domestic and foreign investments, improving human capital, increasing rates of national savings and influencing the demographic changes [19] [2]. In addition, the health care delivery system is one of the largest economic sectors around the world with a global spending rate of USD 6.5 trillion [35], and the International Labor Organization estimates that the number of health workers is about 35 million all over the world a decade ago [34]. Health development is also one of the MDGs because it is a basic human need and it is required for economic growth and development of a nation by reducing the child death rate, improving maternal health and combating diseases that hamper development. Examples of such diseases are like AIDS and malaria. Health care is highly correlated with many development aspects such as economic, social, environmental, and political aspects. Furthermore, health care and environment, which is free from diseases, are the basic and fundamental human rights recognized by the United Nations. Therefore, governments should increase the health budget as a fundamental element in the economic development of their countries [31].Moreover, the primary health care deals with all health problems such as acute, chronic diseases and it also has an important role in the early stage of serious diseases [8]. Primary health care built, over time, strong relationship between the patients and healthcare providers, as it is the service center for various community health needs [8] [6].The health is an essential component for development and it is an input and a goal of the development. For example, in the 1930s, the improvement of the mortality rate in Latin America was related to the increase of the development level [10]. Thus, improving people’s capabilities by upgrading and improving the education level, health services, training courses, and the development of their knowledge and technology skills will help them to be more productive in the modern economic system. It will also lead to economic growth in the country [12] [25]. Moreover, development is considered as one of the important tools in the investment of human resources. It also supports and increases the economic growth [22].Health care system is an important part of the society in any country [18]. It is a complex expression which includes all the activities that aim to promote and enhance health care. Moreover, it includes various parties such as professional medical attention, traditional medication, home care, health promotion, disease prevention and other health enhancing interventions like road and environmental safety improvement and education [34].Primary health care is “what happens when someone who is ill (or who thinks he or she is ill or who wants to avoid getting ill) consults a health professional in a community setting for advice, tests, treatment or transfer to specialist care” [8]. So, primary health care is the first patient’s contact point to health care system and it could reflect the health care situation in the country as it is widely connected to many health problems which patients suffer from [15] [8]. Primary health care in many countries includes care provided by certain clinicians including family medicine, general medicine, obstetrics and gynecology, pharmacy services, health checkup, dental care, small hospital, ambulance, emergency, service provided by general practitioners, school health services, maternal and child clinics and optometry care [20] [8] [15].The quality of health care services has three dimensions: customer quality, professional quality and management quality. Customer quality is the most important one because it helps in measuring the services quality. The customer quality shows the level of satisfaction in the services [7]. Thus, evaluating the customers’ or patients' satisfaction and studying patients' experiences are the ways that help to monitor the primary health care performance and provide the required information about the problems that the primary health care face. Moreover, patients’ suggestions can help in finding solutions and reducing health problems (Wong et al., 2008). Patients' satisfaction is an important measure of service quality and it is one of the important desired outcomes of the health care services. Furthermore, patients' satisfaction helps in planning, developing and improving health care system. There are many factors that have good impact on patients' satisfaction and through these factors we can measure the quality of health care services especially the quality of primary health care [17] [2] [24].The quality of health care services has three dimensions: customer quality, professional quality and management quality. Customer quality is the most important one because it helps in measuring the services quality. The customer quality shows the level of satisfaction in the services [7]. Thus, evaluating the customers’ or patients' satisfaction and studying patients' experiences are the ways that help to monitor the primary health care performance and provide the required information about the problems that the primary health care face. Moreover, patients’ suggestions can help in finding solutions and reducing health problems [36]. Patients' satisfaction is an important measure of service quality and it is one of the important desired outcomes of the health care services. Furthermore, patients' satisfaction helps in planning, developing and improving health care system. There are many factors that have good impact on patients' satisfaction and through these factors we can measure the quality of health care services especially the quality of primary health care [17] [2] [24]. Previous studies have focused on many factors that affect the patients’ satisfaction such as accessibility, cost, waiting time, environmental structure, responsiveness, communication, technical quality, availability, continuity, comprehensiveness and provision of health education. Health care services are divided into three types: primary, secondary and tertiary health care. This study focuses on the quality of primary health care services through the evaluation of patient satisfaction as a means to monitor the primary health care performance and gather information about the problems that facing the primary health care. Furthermore, the analysis of the evaluation of patient satisfaction can help in the planning and development of the health care system in the study area. This study also addresses the association between patient satisfaction and the main factors that impacted positively or negatively in the level of the patient satisfaction such as accessibility, waiting time, cost, health insurance, physical environment, communication, equity, comprehensiveness and overall health services quality.The Old City of Jerusalem has been under the Israeli military occupation since 1967. Due to the Israeli’s occupation, there are many health care issues that affect the quality of the population health in the Old City of Jerusalem. As a result of these strict policies, all health care services including the primary, secondary and tertiary health care services went under the Israeli administration. Health care service is one of the important public services and it is an essential need for every community. The providers of the health care service in the Old City of Jerusalem are divided into three main categories: Israelis, Palestinians and international organizations, but all of them are operating under the Israeli administration. The Israeli law imposes compulsory health insurance on all citizens of the Old City of Jerusalem. Therefore, Palestinian citizens in the Old City of Jerusalem have to choose from one of the four Israeli health fund insurance systems [3]. Israeli national insurance scheme is a semi public system which is provided by the Ministry of Health and the country’s four health funds, namely: Kupat Holim Clalit insuring 60%, Kupat Holim Maccabi insuring 20%, Meuhedet insuring 10% and Leumit insuring 10% of the population. This system is similar to the United States health care system while each citizen chooses from four non-governmental providers, called a kupat cholim (literally, "sick funds," the U.S. equivalent of "health care" providers) [9]. Consequently, the comparison between different health care providers in the city led to different level of satisfaction among the patients in the city.Patients are facing many health care problems such as the absence of 24 hours clinic, lack of some health services such as house care service especially for the elderly ones, patients with chronic diseases and the disabled people. There is also no single ambulance car available in the city (Rizq and Khader, 2002: 108) and there are insufficient blood test laboratories and x-ray departments. The only hospital in the city (Hospes hospital) was closed down by the Israeli authorities in the middle of 1980s. There are many studies on the Old City of Jerusalem health issues such as the studies by Hidmi (2000), Rizq and Khader (2002) which emphasize on the Israeli occupation practices through the control of the services sectors in the city that involve health care system [13] [23]. As a result of all these problems, the health care centers in the city fail to satisfy the patients’ needs in the Old City of Jerusalem especially in the Arab community zone [9]. Figure 1 shows the community services location in the Old City of Jerusalem and the distribution of the health care centers in the city.
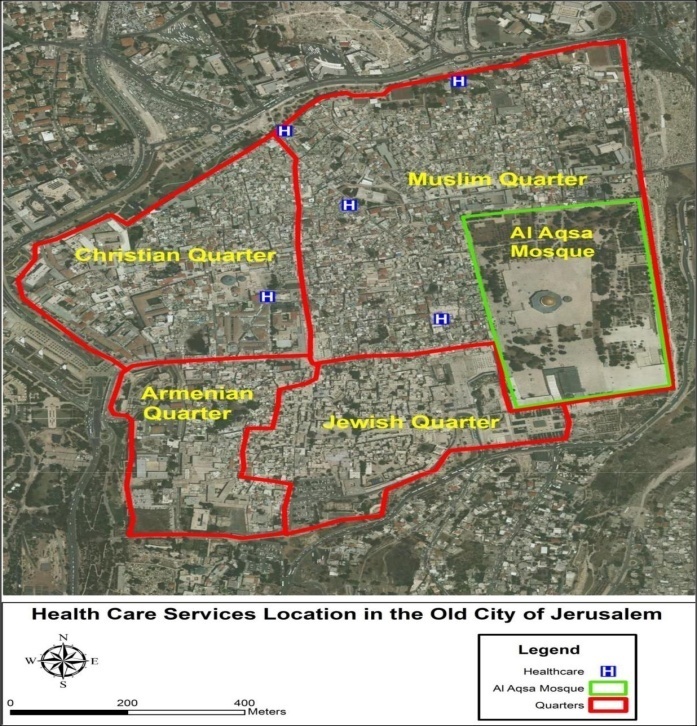 | Figure 1. Health Care Centers in Old City of Jerusalem |
2. Study Area
- The Old City of Jerusalem has been under the Israeli military occupation since 1967. With an area of about 900,000 square meters (0.9 square kilometer), this area constitutes approximately 0.71% of the total area of East and West Jerusalem city in 1999 (Figure 1). The Old city of Jerusalem is a home for 32,952 citizens within the 36,600 square meters area. This high density in population of the city led to a high pressure on the provision of public services [23]. The city is geographically divided into four quarters (see to Figure 1):1. Muslim quarter - an area of 460,000 square meters (the largest quarter). Muslim population in the Old City makes up 70.5% of the Old City population.2. Christian quarter - an area of 192,000 square meters with a Christian population of 15.4% of the Old City population.3. Jewish quarter - an area of 122,000 square meters. The Jewish population in the Old City makes up 6.9% of the Old City population.4. Armenian quarter - an area of 126,000 square meters. The Armenian population contributes 7.1% of the Old City population The Arab community can be found in the Muslim quarter, Christian quarter and Armenian quarter [28]. Therefore, The research is primarily conducted on the Arab community in the Old City of Jerusalem.
3. Methodology
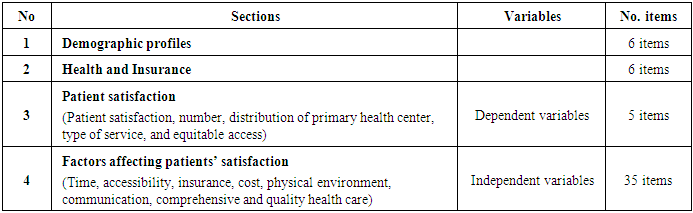
- Primary data in this study has been collected using a quantitative method and complemented by the qualitative methods. The quantitative method was the main approach to collect data for this study and it employs the close-ended questionnaires to collect the primary data. The use of questionnaires which aims to collect information about people’s knowledge, beliefs, attitudes and behavior is one of the most popular methods in satisfaction research [8]. In this study, the questionnaires were given directly to the residents in the Arab quarters in the Old City of Jerusalem to measure patients’ satisfaction towards the primary health care they receive. In this research, telephone interview is used as a tool to conduct questionnaire survey to those respondents who were not able to be reached by the researcher [3] [11] [36]. Phone calls were made by calling the Arab households in the city. This method is also used due to the difficulties faced by the researcher to move around the Arab quarters. This is caused by the stringent security measures imposed by the Israeli authorities. The researcher also conducted some face to face interviews with the responders in order to explain the question in the questionnaire to the older people who have difficulties in reading and writing. The qualitative data for this study was collected through direct observation conducted by the researcher at the health care centers. Observations were made on the physical aspect of the health centers and patients to understand the actual problems that exist. Many studies have also used the observation methods [16] [32]. The aim of the observation is to identify the real factors that affect the patients' satisfaction with the primary health care in the Old City of Jerusalem. This was done by directly observing the activities in the clinics such as consultation time, environment, and structure of the clinics [8], and by taking photos of health care centers. This additionally obtained information complemented other primary and secondary data collected by the researcher. The questionnaires were used as the primary source of data in this study and they were distributed to the patients in the Arab community in the Old City of Jerusalem. The questionnaire consists of close-ended questions, which was developed based on the previous studies that used similar factors and items. However, in the context of this study, the researcher made some modifications based on special conditions in the Old City of Jerusalem, such as political factors because the study area is still under the Israeli occupation and this is one of the few cases in the world. Therefore, apart from the usual factors, this study also includes new items and factors which can contribute to the knowledge and literature in the health and development field.The questionnaire was divided into four sections (See Table (1). The first is about demographic profiles (6 items); the second, Health and insurance (6 items); the third section is about patient's satisfaction (5 items); the last section is about the factors that affect patients’ satisfaction which include seven factors: accessibility and waiting time (5 items), cost and health insurance (5 items), physical environment (6 items), communication and equity (5 items), comprehensiveness and the quality (14 items). The questionnaire was written in Arabic language and the responses were measured by five point Likert Scale. Likert Scale was developed in an attempt to develop standards of measurement in social science research through the use of unified response categories in survey questionnaires. This scale of five points used in the questionnaire in this study asked respondents to indicate whether they are satisfied or dissatisfied with the services they received. Thus, a numerical value can be calculated from the sum of all responses. In this research, the value of the scale indicates the followings: 1= strongly satisfied, 2= satisfied, 3=not sure, 4= dissatisfied, 5= dissatisfied [29].
|
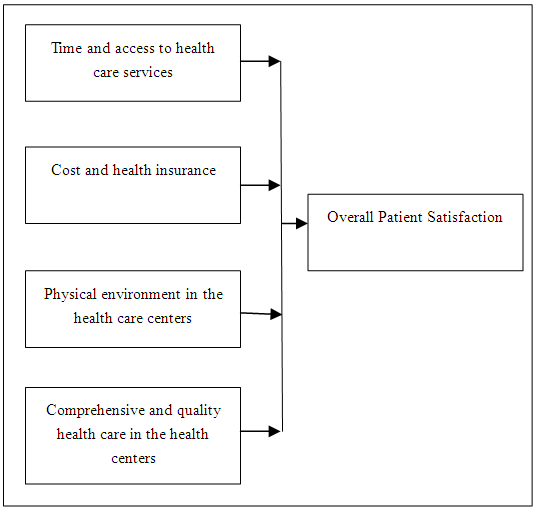 | Figure 2. Proposed Model of Patient Satisfaction with Health Care Centers |
4. Result and Discussion
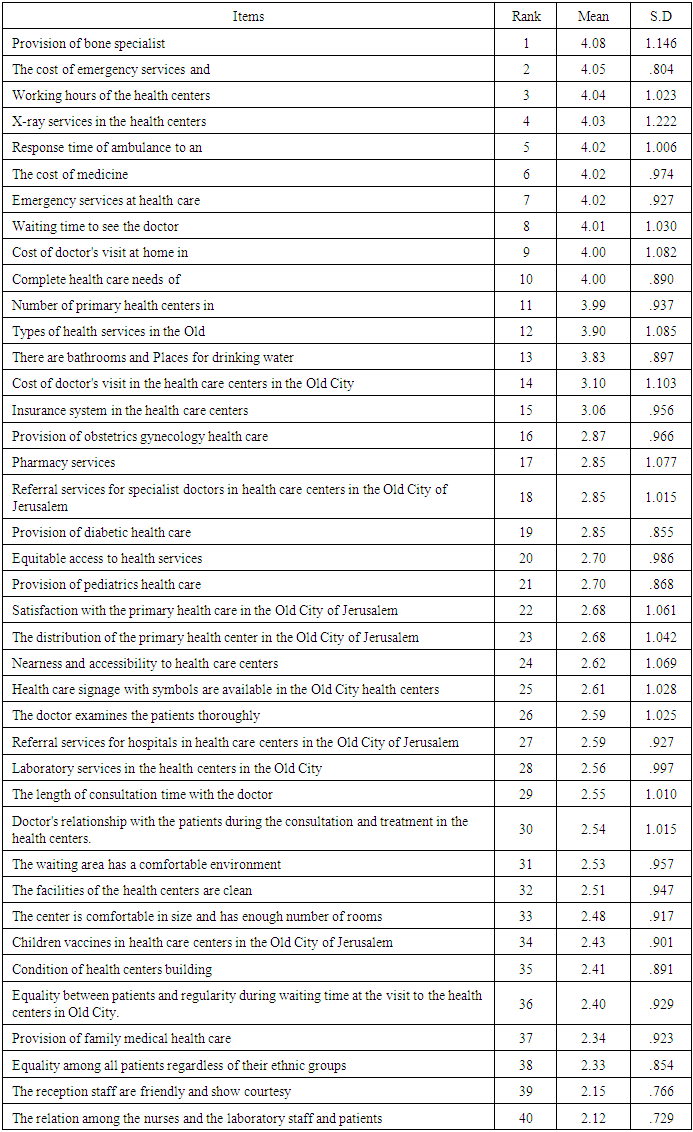
- Table 2 below shows the rank of all items that affects the patient satisfaction and it using calculation of mean score and standard deviation and followed by the discussions on the factors and problems that affect the quality of the primary health care centers in the Old City of Jerusalem.
|
5. Effect of Various Factors on Patient Satisfaction
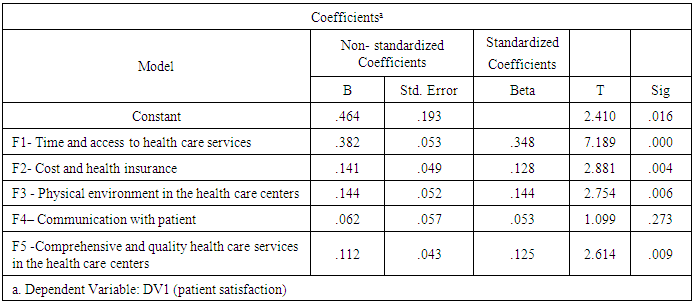
- In order to find out the effect of the factors identified in table (3) on the overall satisfaction of the patients with the health care services in Jerusalem Old City, a regression analysis was done with the five factor scores as the independent variables and patient satisfaction as a whole as the dependent variable. The significance of the F-value came out to be 0.016, which indicates that the model is statistically significant at 5 per cent level of significance. The non-standardized and the standardized beta values and the significance levels of t-tests for the significance of individual independent variables are given in table (3) As shown in the table (3), only four variables are statistically significant in the model at 5 per cent significance level. Looking at the ‘B’ values for all the variables it can be seen that only four factors are positively related to overall patient satisfaction as a dependent variable.
|
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
- Any development of the health care system has to take into account the patients’ needs based on the evaluation of patient satisfaction. This study shows a framework to understand and describe the importance of various factors that affect the patient satisfaction with health care services in the Old City of Jerusalem. Patient satisfaction reflects the quality of services. When respondents perceived performance of various dimension to be of poor quality, they were less satisfied with the health care services. The proposed model Figure (2) of patient satisfaction with health care services means that careful attention should be paid by health organization in the Old City of Jerusalem to each identified factor. As reflected in the proposed model, time and access to health care services has been assigned the greatest relative importance by the respondents. This implies that time and access to health care service that includes nearness and accessibility to health care center, response time of ambulance to an emergency location, working hours of the health care centers, waiting time to see the doctor and the length of consultation time with the doctor can reinforce or decrease the patient satisfaction level. Therefore, the health organization and health providers in the Old City of Jerusalem like Israeli health insurance, Palestinian health services and international organization should pay more attention and improve efficiency of health care centers by:1. Health care organization and policy makers have to improve the health care centers in the Old City of Jerusalem and increase the number of the health care centers to reach as many residents as possible.2. Increase the operation hours of the health centers and introduce a night shift system between medical centers in order to be available to patients even at night time.3. Develop the emergency services sector especially ambulance services in the Old City of Jerusalem with at least need one ambulance car for every health care center for urgent cases.The next important dimension was that of physical environment in the health care centers which includes variables such as condition of health centers building, the center is comfortable in size and has enough number of rooms, the waiting area has a comfortable environment, the facilities of the health care center are clean, there are bathrooms and places for drinking water and means of information and recreation are available in the Old City health centers. This implies that the decision makers at health care center at the Old City of Jerusalem should be provided with the required support to increase the patients’ satisfaction level by:1. Improving the condition of the health care centers building.2. Improving the level of the cleanliness in the health care centers.3. Improving the planning, designing, and construction of the health care facilities in the Old City of Jerusalem.Third important dimension affecting the satisfaction level of patients was cost and health insurance factor that include variables such as the cost of doctors' visit to the health care centers, cost of doctor visit at home in case of emergency, the cost of emergency services and ambulance, the cost of medicine and insurance system in the health care center. Support and improvement of these variables by health authorities are very important efforts through:1. The health care insurance has to cover a percentage of the doctor visit at home especially during emergency situation as well as to cover the cost of medicine.2. Reduce the cost of emergency services and ambulance in order to be available to all patients.Finally, in the model of patient satisfaction, the last factor affects the overall patient satisfaction that is comprehensive and the quality of health care services which include complete health care needs of citizen in the Old City, provision of family medical health, provision of pediatrics heath, provision of bone specialist, provision of obstetrics and gynecology health, pharmacy services, x-ray services, laboratory services, emergency services, childhood vaccines, referred services to specialist doctor, referred services to hospitals and the doctor examination of the patient thoroughly. This implies health care center and authorities to pay more support by:1. Provisions of specialist doctors in all fields in the Old City of Jerusalem2. The health care centers in the Old City must provide more services such as x-ray, laboratory, emergency services and pharmacy services.3. Facilitate the process of referral patient services for necessary treatment to the specialist doctors and hospitals.According to the above results and discussions, the following recommendations are suggested to improve and better develop the health care quality in the Old City of Jerusalem based on the patients' satisfactions level and index. As the Arab people in the Old City of Jerusalem is facing financial problems due to low income, health authorities especially the Israeli health system should setup a new health policy and introduce programs to help the Old City residents by reducing the medicine cost for patients such as skin and psychological medicine. On another hand, they should work hard to reduce the cost of ambulance for patients especially the elder people because the structure of the Old City hinders the easy movement to and from the health centers.The Old City of Jerusalem also has to deal with high density population of 32,952 citizens per km2 with only five health centers available in the city. Thus, the Israeli, Palestinian and International Health Organizations should open a new health center and redistribute the existing health care centers to cover all study area in order to be more accessible for all residents. The UN also needs to play a sufficient role in increasing the provision of people health care to the Palestinian people.Furthermore, the Old City of Jerusalem is still politically under unstable situation with conflicts between the Arab and Jewish people. This situation requires more health centers and more efficient emergency services by increasing the emergency rooms and centers especially around the Al-Aqsa Mosque. In addition, the Israeli Army should allow ambulance cars to pass through the area without any difficulties during emergency situation.There is also a need to increase the people’s awareness about the importance of medical services and about their rights to obtain them especially the issues that relate to health insurance as compared to the health services provided to the Jews because they are paying a part of their income equally as the Jews to the health insurance system. Setting up a new awareness program for the Arab people in the Old City of Jerusalem will be useful to improve their knowledge about the health insurance system and health services.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML