-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Public Health Research
p-ISSN: 2167-7263 e-ISSN: 2167-7247
2014; 4(5): 166-172
doi:10.5923/j.phr.20140405.03
Serum Level of Naphthalene and 1,2 Benz-anthracene and Their Effect on the Immunologic Markers of Asthma and Asthma Severity in Children-Egypt
Manal Abd El-Salam1, Amal A. Hegazy2, 3, Zeinab Ragab Adawy4, Neama Rmadan Hussein5
1Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine (for girls), Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt
2Family and Community Medicine Department, Faculty of Medicine, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
3Community and Occupational Medicine Department, Faculty of Medicine (for girls), Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt
4Chest Department, Faculty of Medicine (for girls), Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt
5Clinical pathology Department, Faculty of Medicine (for girls), Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt
Correspondence to: Amal A. Hegazy, Family and Community Medicine Department, Faculty of Medicine, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Background:The rate of asthma increases as communities adopt western lifestyles and become urbanized. Objective: Was to assess the serum level of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) naphthalene, 1,2 benz-anthracene and detect their effects on some of asthma immunologic markers in children with bronchial asthma and their relation to asthma severity. Methods:The study was carried out on 60 children with bronchial asthma. They were selected from the inpatient and outpatient clinic of Al–Zahraa hospital, Al-Azhar University. Also the study included 60 children age and sex matched served as a control group. Serum levels of naphthalene and 1,2 benz-anthracene as well as (IgE, IL13 and IL5,) were assessed in the studied groups. Results: Serum levels of naphthalene and 1,2 benz-anthracene were significantly increased in children with bronchial asthma than in controls, as their levels were (24.04±13.03ng/ml; 16.07 ±8.96 ng/ml) and (5.23 ± 3.21 ng/ml; 6.99 ± 3.90 ng/ml), respectively with (p=0.000 and 0.006 respectively)with significant positive correlation to bronchial asthma severity and significant relation to urban residence and second hand smoking . There was a significant decrease in IL5 and IL13 serum levels while there was a significant increase in eosinophils counts and serum IgE levels in children with asthma than the controls, with significant positive correlation to bronchial asthma severity. Conclusions: Exposure to PAHs (naphthalene, 1,2 benz-anthracene) appears to be associated with asthma in children with significant relation to bronchial asthma severity and significant interaction with asthma markers.
Keywords: PAHs, Environmental pollution, Childhood asthma, IL5, IL13
Cite this paper: Manal Abd El-Salam, Amal A. Hegazy, Zeinab Ragab Adawy, Neama Rmadan Hussein, Serum Level of Naphthalene and 1,2 Benz-anthracene and Their Effect on the Immunologic Markers of Asthma and Asthma Severity in Children-Egypt, Public Health Research, Vol. 4 No. 5, 2014, pp. 166-172. doi: 10.5923/j.phr.20140405.03.
1. Background
- Asthma is the commonest of all chronic diseases of childhood and estimates from developed countries suggest that it affects between 11 and 20% of all school age children. The prevalence of asthma among Egyptian children aged 3 - 15 years was estimated to be 8.2%. Of major concern is the annual increase in mortality [1].The rate of asthma increases as communities adopt western lifestyles and become urbanized. With the projected increase in the proportion of the world's urban population from 45% to 59% in 2005, there will likely be a marked increase in the number of asthmatics worldwide over the next two decades. It is estimated that there may be an additional 100 million persons with asthma by 2025 [2].The airways of asthmatics are hypersensitive to certain triggers, also known as stimuli such as environmental stimulant allergen, tobacco smoke, cold or warm air, perfume, pet dander, moist air, exercise, exertion and emotional stress. In response to exposure to these triggers, the bronchi contract into spasm “an asthma attack”. Inflammation soon follows, leading to a further narrowing of the airways and excessive mucus production; which leads to coughing and other breathing difficulties [3].Exposure to high levels of air pollution has been associated with decreased lung function, asthma, nasal symptoms, bronchitis and sensitization to inhalant allergens in both children and adults [4].Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) describe chemicals that are often found together in groups of two or more, of these naphthalene and 1,2 benz-anthracene . PAHs are created when products like coal, oil, gas, and garbage are burned but the burning process is not complete [5]. PAHs belong to the group of persistent organic pollutants (POPs). These are organic contaminants that are resistant to degradation, can remain in the environment for long periods, and have the potential to cause adverse environmental effects [6].The major sources of PAHs emissions maybe divided into four classes: stationary sources (including domestic and industrial sources), motor vehicle emissions, agriculture activities, and natural sources [7]. The burning and pyrolysis of coal, oil, gas, garbage, wood, or other organic substances are the main domestic sources. Agriculture activities as open burning of brushwood, straw, moorland heather, and stubble. Natural sources as accidental burning of forests, woodland and volcanic eruptions [8-9].Vehicles reported to have the highest PAH emission rates are diesel engines, and gasoline engines operated without catalytic converters [10-12]. In urban environments, industrial operations, waste incinerators, and residential boilers are also important sources of ambient PAH [13].Some studies implicate traffic-related emissions, largely composed of diesel exhaust particles, trace metals, volatile organic compounds, nitrogen dioxide, particulate matter, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) in the development of respiratory symptoms, asthma or the onset of allergies [14-16].Some studies reported that a significant increase in immunoglobulin E (IgE) production due to exposure to PAH from diesel exhaust particles in response to common inhaled allergens [17]. The primary inflammatory lesion of asthma consists of accumulation of CD4+ T helper type 2 (TH2) lymphocytes and eosinophils in the airway mucosa. TH2 cells orchestrate the asthmatic inflammation through the secretion of a series of cytokines, particularly IL-4, IL‑13, IL-5, and IL-9. IL-4 is the major factor regulating IgE production by B cells, and is required for optimal TH2 differentiation [18]. We hypothesized increased serum level of PAHs is associated with asthma severity and had an interaction with some of asthma immunological markers.We aimed to asses serum level of Naphthalene and 1,2 Benz-anthracene in children with bronchial asthma and detect the relation to asthma severity and their effect on some of asthma immunologic markers.
2. Subjects and Methods
- This is a case control study; it was carried out on 120 children from inpatient and the outpatient clinic of Al-Zhraa hospital, Al-Azhar University during the period from Juan 2013 to December 2013. The study included 60children with bronchial asthma, their ages ranged from 6 to 17 year. They were 39 males (65%) and 21 females (35%). Also it included 60 ages and sexes matched children served as a control group. Children diagnosed as bronchial children according to GINA 2012 [19] and they were sub classified into (mild persistent, moderate persistent and severe persistent) asthma according to GINA, 2008 [20]. Children less than 6 years and children with other causes of wheezy chest were excluded from the study. Informed consent was obtained from the participating parents in adherence with the guidelines of the ethical committee of AL-Zahraa hospital, AL-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt. All studied children were subjected to: full history taking included (complaint, residence, present history, past history, family history of asthma or atopy, second hand smoking, bronchial asthma symptoms, triggering factors), full general and local chest examination.Laboratory investigations:Blood sampling-2 ml blood was taken on EDTA vacutainer for complete blood picture with total and differential leukocytic count using Cell-Dyn 1800.-5 ml of blood was taken on venoject tube. Samples were centrifuged for 20 minutes at 3000 rpm and the serum was separated and divided into two specimens, one for (IL5, IgE and IL13) assay by ELISA and the other for measurement of (Naphthalene and 1,2 Benz-anthracene) using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with UV detector, both samples were stored at -20 till the time of the assay.Naphthalene and 1,2 Benz-anthracene assaySerum level of two polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), Naphthalene and 1,2 benz-anthracene, using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with UV detector.Sample preparation, for each sample, 0.5 ml of serum was added to 0.5 ml of methanol and vortexed for 10–20 seconds. Then, 5 ml from the mixture of 1:1 hexane: diethyl ether was added and vortexed for an additional 1 minute. It was then centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 5 minutes. Eluent 70%: 45% Acetonitrile: 55% Water [21]. Concentrations of the unknown samples were calculated as:
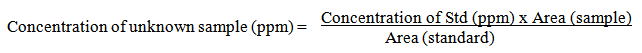 IgE, IL-5 and IL-13: were determined by using commercially available immunoassay. Quantitative Sandwich ELISA technique Bender Med systems GmbH compus Veinna. Biocenter 2A-1030 Vienna, Australia, Europe.Pulmonary function tests:It’s performed by spirometer (spirdsifts pirometry 5000 FUTUD a NANSHI).Standardization of the testing environment during spirometry was followed according to Miller et al. [22]. The child torso and head should be erect throughout testing, A nose clip was used and the mouth piece of the spirometer was put between the teeth, making a seal with the lips. After standardization of environmental conditions and removing heavy clothes of the child, he or she takes the deepest inspiration and then closes his or her mouth firmly around the mouth piece; he must blow forcibly down the tube without hesitation, without catching or holding breathing. At least three attempts are made then choosing the best result. FVC, FEV1, FEF and PEFR expressed as a percentage of predicted values [21].Statistical Analysis:Data were collected, revised, coded and entered to the Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS) version 17 and the following were done: The qualitative data were presented as number and percentages while the quantitative data were presented as mean, standard deviations and ranges. The comparison between two groups with qualitative data were done by using Chi-square test .The comparison between two groups with quantitative data were done by using independent t-test when the data were parametric and Mann-Whitney test was used in the comparison between two independent group when the data were non parametric. Comparison between more than two groups with nominal data was done by using One Way ANOVA test. Pearson and Spearman correlation coefficients were used to assess the relations between two quantitative parameters in the same group. Receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) was used to assess the best cut off point with sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (+PV) and negative predictive value (-PV).The p-value was considered significant as the following:P-value > 0.05: Non significant. P-value < 0.05: Significant.
IgE, IL-5 and IL-13: were determined by using commercially available immunoassay. Quantitative Sandwich ELISA technique Bender Med systems GmbH compus Veinna. Biocenter 2A-1030 Vienna, Australia, Europe.Pulmonary function tests:It’s performed by spirometer (spirdsifts pirometry 5000 FUTUD a NANSHI).Standardization of the testing environment during spirometry was followed according to Miller et al. [22]. The child torso and head should be erect throughout testing, A nose clip was used and the mouth piece of the spirometer was put between the teeth, making a seal with the lips. After standardization of environmental conditions and removing heavy clothes of the child, he or she takes the deepest inspiration and then closes his or her mouth firmly around the mouth piece; he must blow forcibly down the tube without hesitation, without catching or holding breathing. At least three attempts are made then choosing the best result. FVC, FEV1, FEF and PEFR expressed as a percentage of predicted values [21].Statistical Analysis:Data were collected, revised, coded and entered to the Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS) version 17 and the following were done: The qualitative data were presented as number and percentages while the quantitative data were presented as mean, standard deviations and ranges. The comparison between two groups with qualitative data were done by using Chi-square test .The comparison between two groups with quantitative data were done by using independent t-test when the data were parametric and Mann-Whitney test was used in the comparison between two independent group when the data were non parametric. Comparison between more than two groups with nominal data was done by using One Way ANOVA test. Pearson and Spearman correlation coefficients were used to assess the relations between two quantitative parameters in the same group. Receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) was used to assess the best cut off point with sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (+PV) and negative predictive value (-PV).The p-value was considered significant as the following:P-value > 0.05: Non significant. P-value < 0.05: Significant.3. Results
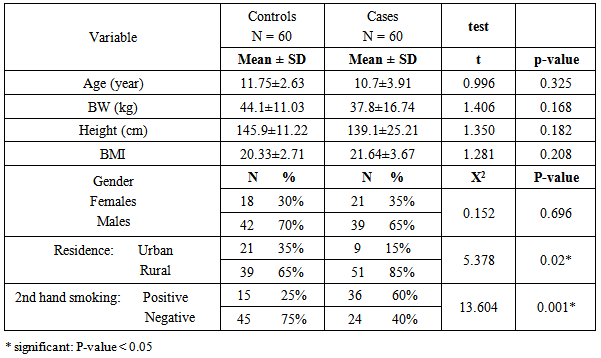
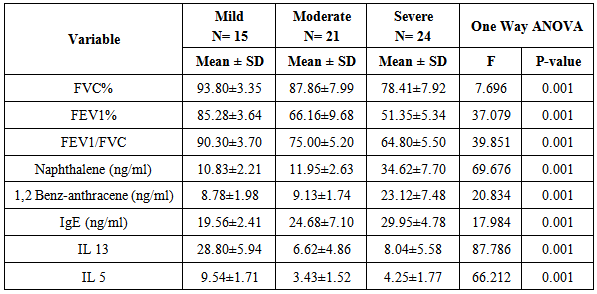
- Table 1: shows the anthropometric measurements and demographic data of the studied groups, it revealed no significant difference between both groups regarding weight, height and BMI .However there was a significant difference between both groups as regards residence (urban & rural) as the urban residence is common in cases(85.00%) than in controls (39.00%). Also there is a significant increase in the 2nd hand smoking in patients (60.00%) compared to the controls (15.00%).
|
|
|
|
|
|
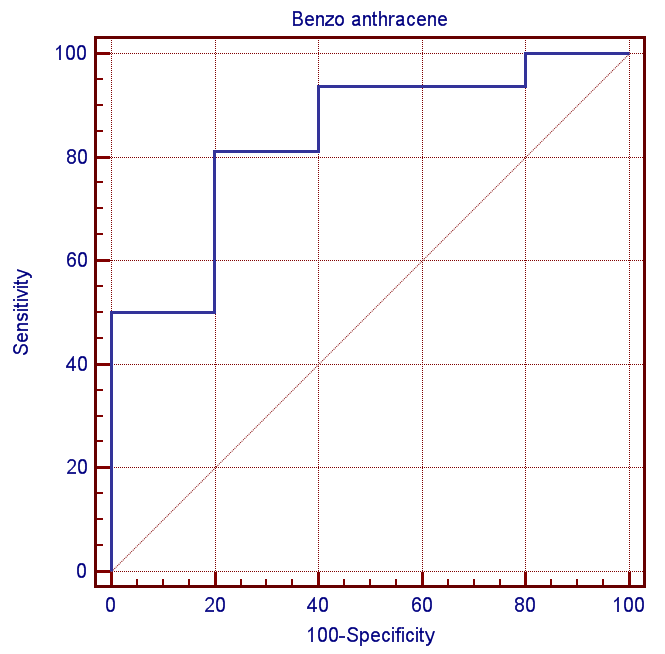 | Figure (1). ROC curve for serum level of Naphthalene between patients and the controls |
4. Discussion
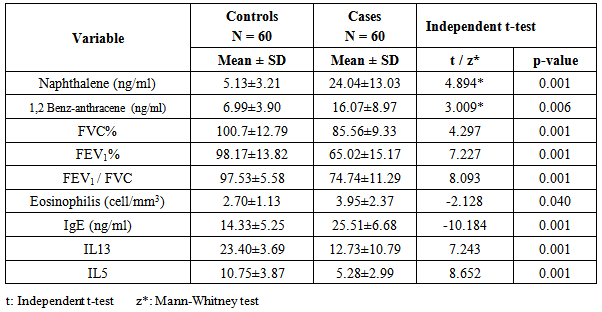
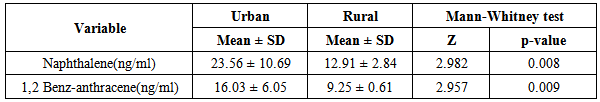
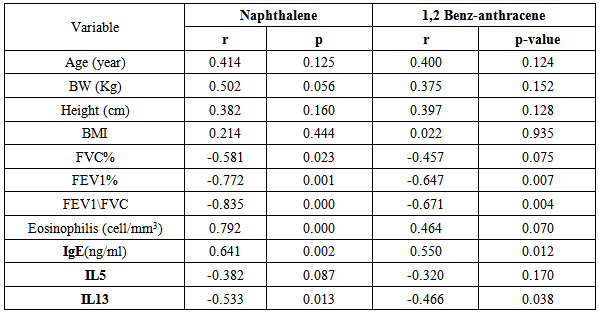
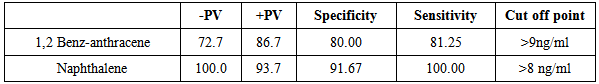
- Attacks of asthma are generated by many factors which include sudden changes in environmental temperature, exercise or exertion, or emotional stress. In children, however, the most common causes are viral infection and exposure to environmental stimulants such as dust particulates and other allergens.Our study was designed to assess serum level of some polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (naphthalene and 1,2 benz-anthracene) as well as some of bronchial asthma immunological markers to evaluate their possible association with bronchial asthma severity. There is no standard guideline or available data that determine the minimal risk level for a particular PAHs so any amount of PAHs detected in the blood sample was considered as positive in our study.In the present study there was a significant increase in the serum levels of PAHs (naphthalene and 1,2 benz-anthracene) in children with asthma than in controls. This results concord with Miller et al. who reported that early exposure to airborne PAHs and environmental tobacco smoke can lead to increased respiratory symptoms and probable asthma even as early as at the age of 12 to 24 months. Also our study is in agreement with other studies who found that significant association between exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and asthma in children [23-25]. It is not surprising to find Kids urban residents who suffer from asthma had a high level of (naphthalene and 1,2 benz-anthracene) than kids rural resident this may attributed to more air pollution and exposure to traffic-related polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban areas . Also we found that children exposed to the second hand (passive smoking) at home, or staying in the same place with a smoker, are at a higher risk of asthma. Smoking and second hand smoking are a direct contributor to PAH exposure among humans. These data conceded with the established data that asthma is more common in children exposed to second hand smoking [26-30]. Passive smoker children therefore may build up an allergic or inflammatory pulmonary response and increased DNA damage due to direct contact with PAH and environmental tobacco smoke [31-32].In our study lung functions (FVC, FEV1, FEV1/ FVC) were assessed and we noticed a significant decrease of lung functions in asthmatic children than the controls, these results were similar to the study done by Barraza-Villarreal, et al; 2014 [33] who concluded that air pollution exposure were inversely associated with lung functions. other studies reported the same effect on lung functions [34-35].In the present study it is interesting to note that interleukin-5 and 13 levels were reduced in the serum of asthma patients while it is not surprisingly to find a highly significant increase in (eosinophlis, IgE), these results are in consistent with in vitro studies that show a potent inhibitory effect of corticosteroids on gene expression and on the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines [36] as corticosteroids have several anti-inflammatory actions [37-39].Davoodi et al; 2012 [40] suggest the neutral role of IL13 in the inflammatory process and we suggest that these cytokines may be consumed at the site of inflammation and on the same line we found a negative correlation between pulmonary functions (FEV1, FEV1/ FVC) with eosinophlis and IgE levels as we suggest that the inflammatory response of airways most likely influences the decrease in lung functions, IL-13 is produced by CD4_ T cells, NK T cells, mast cells, basophils, eosinophils, and monocytes. [41-45] ,it is implicated as a central regulator in IgE synthesis, mucus hyper secretion airway hyper-responsiveness (AHR), and fibrosis [46], others such as IL-5 are essential to eosinophil hematopoiesis, activation and survival in tissue [47-51].In the present study we evaluated and compared the three studied asthma sub groups and according to our results patients with severe asthma had increased PAHs levels, decreased pulmonary functions and increased IgE with significant decrease in IL5 and IL13.ROC analysis revealed that naphthalene and 1,2 benz-anthracene value at a cut off value of 8ng/mL and 9ng/ml respectively can predict bronchial asthma development in children with high specificity and sensitivity In conclusions: exposure to PAHs (naphthalene, 1, 2 benz-anthracene) appears to be associated with asthma in children and there is a relation to bronchial asthma severity with a significant interaction with asthma immunological markers. It is essential that efforts are made to reduce pollution to avoid chest allergy.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML