-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Public Health Research
p-ISSN: 2167-7263 e-ISSN: 2167-7247
2014; 4(3): 85-91
doi:10.5923/j.phr.20140403.02
Epidemiological Analysis of the Heart Complications Related to Type 2 Diabetes mellitus in the Portuguese Hospital
Cristina Carrondo
Pulmonology Service, Hospital Central of Saint John of Oporto (RT pulmonology); Center for Research and Studies in Public Health, National School of Public Health (PhD student), Lisbon, Portugal
Correspondence to: Cristina Carrondo, Pulmonology Service, Hospital Central of Saint John of Oporto (RT pulmonology); Center for Research and Studies in Public Health, National School of Public Health (PhD student), Lisbon, Portugal.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Type 2 Diabetes mellitusis considered one of the leading causes of heart disease. The aim of this study was to characterize the major cardiac complications and their incidence in Type 2 diabetic patients throughout hospitalization. The study involved 1321 patients with Type 2 diabetes coded as “principal diagnosis” in three Central Hospitals of the Portuguese National Health System, admitted from January 1st to December 31st of 2011. Data were collected from coded discharge summaries from each hospital. We observed significant incidence of congestive heart failure in the 3 institutions. A higher incidence of diabetes heart complications was observed among women than men in St. John of Porto and North Lisbon Hospital Centers (57,9% and 62,5% for women compared to 42,1% and 37,5% respectively, for men). , associated to diabetes mellitus (DM) with renal manifestations and DM without complication, type II, unspecified, about 37.24% and 36.5%, respectively. In contrast, at the University of Coimbra Hospital Center, diabetic men had higher incidence of heart complications (55,1% vs 49,9%). , approximately 42.3% associated to DM without complication, type II, unspecified. At Saint John of Porto and North Lisbon Hospital Centers, the 71 - 80 year age-group had the highest representation of heart complications, while at the University of Coimbra Hospital Center, the highest was in the 51 -80 years group. There was high incidence of cardiac complications in diabetic women associated to DM without complications and/or renal manifestations.
Keywords: Type 2 Diabetes mellitus, Heart complications, Gender, Age
Cite this paper: Cristina Carrondo, Epidemiological Analysis of the Heart Complications Related to Type 2 Diabetes mellitus in the Portuguese Hospital, Public Health Research, Vol. 4 No. 3, 2014, pp. 85-91. doi: 10.5923/j.phr.20140403.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Diabetes mellitus(DM) is a serious public health problem globally [1], because of its high morbidity and mortality [2] reducing the average life expectancy by up to 15 years [3]. DM affects approximately 25.8 million (8.3% of the population) and is the seventh cause of death in the United States [1]. In 2011, DM affected approximately 7.9 million Portuguese (12.7% of the total population), 6.1% of males and 4.3% female [4]. Among European countries, Portugal has the highest prevalence rate of DM. In 2011, the incidence rate was 652 new cases per 100,000 inhabitants, indicating an 80%, increase in the last decade [4]. Diabetes affects more than a quarter of the Portuguese population aged 60-79 years [4].The type 2 Diabetes mellitus (T2DM), as a heterogeneous disease, is the leading cause of kidney failure (accounting for 44% of all new cases of kidney failure in 2008, 60% of non-traumatic lower limb amputation, and 28.5% of new cases of blindness among adults [3]. T2DM is considered as one of the leading causes of heart disease and stroke (60-70% of cases) in the United States [5].
1.1. Diabetes and Heart Disease
- Cardiovascular disease (CVD) significantly increases mortality due to diabetes and is the leading cause of death of diabetic patients [6]. The risk of cardiovascular death is 2 times greater in patients with T2DM than non-diabetics [7, 8, 9]. Studies have further shown that diabetics, even without prior history myocardial infarction (MI), still have a have a higher risk of cardiovascular death than patients with a clinical history of AMI but without diabetes [10, 11]. In Portugal, about 31% of patients with T2DM are admitted for AMI [4]. The T2DM increases the risk of CVD three to four times in women [12] and three times in men, after adjusting for other risk factors [13] especially younger women aged less than 65 years of age [14]. In the United States, CVD represents 77% of T2DM hospitalizations [15]. In the last decade, several studies have documented some of the most frequent cardiac complications of diabetes, namely: AMI [16, 12]; congestive heart failure (CHF) affecting about 20 to 23% of diabetic patients [17]; and, coronary heart disease (CHD) [18, 19], responsible for multiple hospital admissions [20]. Observational studies have shown that, in the presence of microvascular disease, patients with T2DM, have an increased risk of developing cardiovascular events [21].
1.2. Diabetes and Kidney Disease
- In a systematic review based on population studies, the average prevalence of chronic renal failure (CRF) was 7.2% in individuals 30 aged years or older, and it ranged from the 23.4-35.8% in patients aged over 64 years [22]. CRF and heart failure (HF), often coexist in the same patient [23]. Some studies suggest that a precautionary approach should be applied in the management of patients with CRF, in order to minimize the occurrence of episodes of AMI, HF, stroke and cardiovascular death, through proven therapies, such as: control of blood pressure, control of blood glucose levels and treatment of dyslipidemia, among others [24].Approximately 25-30% of patients with T2DM have kidney disease (KD), usually presenting as typical diabetic glomerulosclerosis, but sometimes more prominently as a vascular nephropathy [25]. Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) is the most common cause of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in developed countries, and is the leading cause of end-stage kidney disease [21], most especially amongT2DM patients of advanced age [25]. Even when the T2DM is controlled, the disease can still lead to CRF and kidney failure (21). A prevalence study of 415,910 United States Veterans with T2DM, showed that 10.7% had a renal disease in addition, but that 43.4% did not present with DN. More specifically, the prevalence of DN was approximately 4.2%-6%of patients with terminal renal failure (TRF) [26]. Due to the high degree of overlap of CVD and CRF, there has been a great interest in studying this complex bi-directional pathophysiological process that aggravates the function of both organs [27]. A large proportion of patients admitted to the hospital has varying degrees of cardiac and renal dysfunction [28]. Primary disorders of one of these two organs (heart and kidney) results, sometimes, into a secondary dysfunction or injury to the other [29].In 2011, 7% of hospital admissions in Portugal were due to diabetic patients with T2DM who had renal manifestations, among which the prevalence of CRF was 27.2%, constituting 32% of new cases of CRF hemodialysis [4]. The present study sought to describe heart complications and their incidence in hospitalized patients with type 2diabetes.
2. Methods
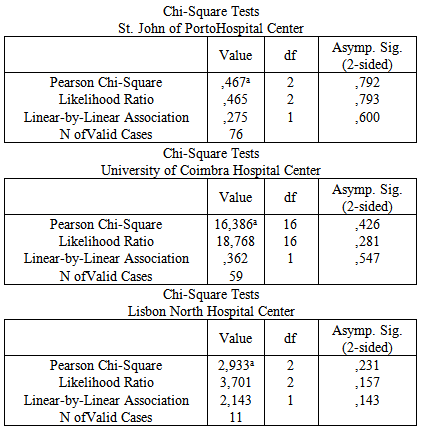
- The study was observational, descriptive and cross-sectional, involving 1321 type 2 diabetic patients admitted with T2DM as the principal diagnosis, from January 1stto December 31st of 2011. Data were collected from three public hospitals in different regions of Portugal i.e. Saint John of Porto Hospital Centre EPE, University of Coimbra Hospital Centre EPE and Lisbon North Hospital Centre EPE. The descriptive data were collected from the DRG hospital information systems database, called DREAM and SAM, with the approval of the Auditors and encoders. The principal registrycodes of diagnosis and procedures of Diabetes mellitus (DM) type II non-specified type DM was (ICD-9-CM: 250.x0 or 250.x2) were based on the classification of diagnoses and procedures according to the International Classification of Diseases 9th Revision, ICD 9 of the WHO. Therefore, the variables selected from the discharge summaries of each episode of encoded admission were: age, gender, a principal diagnosis of T2DM, and a second diagnosis of cardiac complications. The codes of heart complications included were the following: 426.13 – Atrio Ventricular Block 2º; 427.31 – Atrial Fibrillation; 427.89 – Other Specified Cardiac Arrhythmias; 428.23- Chronic Systolic Heart Failure; 428.33 – Chronic Diastolic Heart Failure; 42843 – Chronic Combined Systolic and Diastolic Heart Failure; 404.91-Hypertensive Heart disease and Chronic Renal Disease, N/C,/SPEC INSUF CARD, C/DRC EST.I-IV OR N/SPEC; 410.11- Acute Myocardial Infarction, Anterior, Initial Episode; 410.71 - Acute SubEndocardial Infarction of the Myocardium; 411.89 – Ischemic Heart Disease, Acute or Sub Acute; 411.1- Intermediate Coronary Syndrome; 413.9 - Angina Pectoris or unspecified; 426.0 – Auricular Ventricular Complete Block; 424.0 – Mitral Valve Diseases; 424.1 – Aortic Valve Diseases; and, 428.0 – Congestive Heart Failure, unspecified. Data were entered and analyzed using the statistical program Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS©) for Windows® version 18.Univariate and bivariate analysis were applied to establish relationships between distinct variables. The analysis of variables was conducted mainly through counts and frequencies. Also Chi-Square Tests with a confidence interval (CI) of 95% were carried out to verify the existence of dependency relationships between variables.
3. Ethical Considerations
- The study was approved by the ethics committees of the three hospitals The confidentiality and privacy of data collected were guaranteed in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration, using the most recently revised version of the World Medical Association.
4. Results
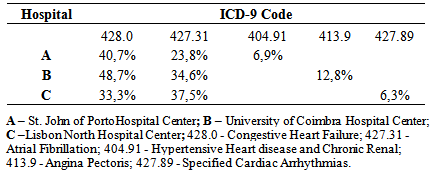
- At St. John of Porto Hospital Center, of 536 T2DM patients who attended, 54% had cardiac complications, with a significant incidence of congestive heart failure (CHF) at 40.7%, followed by atrial fibrillation (AF) with 23.79%. At the University of Coimbra Hospital Center, of the 379 who attended, 21% had cardiac complications, with a significant incidence of CHF at 48.7%, followed by AF with 34.6%. At Lisbon North Hospital Center, of 406 who attended, 24% had cardiac complications, with a significant incidence of AF at 37.5%, followed by CHF with 33.3% as shown in Table 1.
|
|
|
|
|
5. Discussion
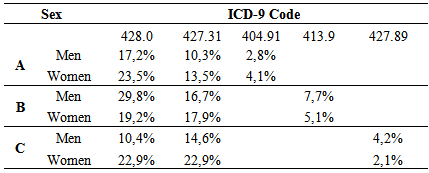
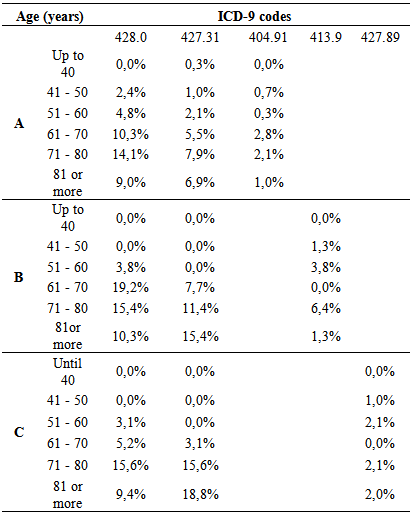
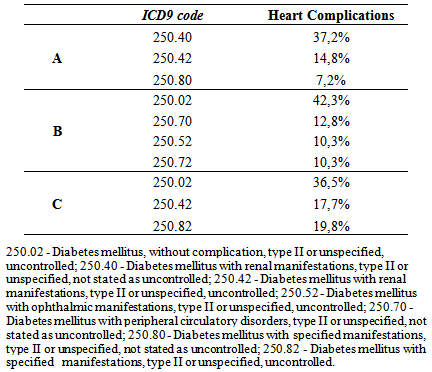
- Some authors have found that one of the most frequent cardiac complications of diabetes is the CHF, with higher incidence in diabetic women than diabetic men [17]. That finding is also upheld by the findings in this three-hospital study, which also observed that the incidence of CHF was higher in women. Its incidence was higher with advancing age, being highest between 71-80 years at St. John of Porto and North of Lisbon Hospital Centers but starting at a younger age (51 – 80 years) at the University of Coimbra Hospital Center. These results agree with the findings of Vaur et al. [17] who found that, in 4912 diabetics requiring hospitalization, the annual incidence of CHF was 1% among patients with an average age of 71 years (cautioning that they excluded diabetic patients under treatment with insulin and angiotensin system inhibitors).Another important finding of this study was to verify the coding of the typology of DM with heart complications, focusing on DM with renal manifestations and the degree of DM control. No data were found on this subject upon extensive search. However, some authors report that the incidence of kidney disease (KD) in these patients may, probably, be underestimated, since the concentration of serum creatinine in the period of hospitalization alone may not accurately reflect kidney function (KF) [30). However, renal dysfunction as a co-morbidity can be a complication of the treatment of CHF, even when it was not present at the time of admission. Between 27 and 45% of diabetics admitted for CHF can develop an acute worsening of their KD throughout hospitalization [30]. A study showed that of 1.681 patients, over the age of 65 years admitted in hospitals for CHF, 21% presented with KD, and 41% had a baseline serum creatinine level increased [31]. Similar works have noted that 18% of 11,327 in-patients in 115 hospitals had renal dysfunction associated with CHF [32]. Finally, 30% of patients hospitalized with acute heart failure had clinical history of chronic renal failure in an assessment of 105,388 episodes of hospitalization in 274 hospitals reported in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure National Registry (ADHERE) [33].Another cardiac event with high incidence observed in this study was the AF, agreeing with the result of an important meta-analysis (n = 1.686 .097) involving 108.703 cases of AF, where about 24 to 34% were diabetics with T2DM [34]. However, that review may have under-estimated the real association between DM and AF, due to the presence of other factors. For example, the body mass index and the presence of prior heart disease varied between the studies included in the analysis, making it impossible to take account of their possible impact on the association [34]. Dublin et al. [35] also observed a causal association between DM and AF. In that study, the duration of DM and the risk of incidence of AF increased over time, in such a way, that for diabetics with over 10 years of DM, the risk of developing AF was approximately 64% compared to only 7% in those with DM less than 5 years of duration [35]. Watanabe et al. [36] who did work on records of 28,449 265 patients who presented episodes of AF, led the association between glucose tolerance and the risk of developing AF. The Framingham Heart Study also found that DM, insulin resistance and glucose tolerance are associated with left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) which, itself, could be an important risk factor of AF [37]. The present study demonstrates that heart complications prevail more in females. This finding has been interpreted, analyzed and discussed in some earlier studies, albeit with some controversy. In one meta-analysis, the increased relative risk adjusted to age of coronary heart disease (CHD) was greatly reduced in female diabetics than in males. However, the same study, after allowance for the risk of more severe CVD, diabetic women presented a higher risk of developing CHD than diabetic men [38]. It concludes that gender could be a risk factor that should be considered and understood. Another explanation for this difference, for some authors, is that diabetic women are exposed to less aggressive preventive treatments than diabetic men [39]. Another important risk factor pointed out in woks is the impact of insulin resistance, differentially influenced by age, sex hormones and lifestyle [40]. Another reason, though, is the difference in the impact of risk factors, including hormone levels such as the loss of estrogens in the case of diabetes [41]. The INTERHEART study describes several risk factors which could explain the differences on gender related to CVD (such as high blood pressure, high alcohol consumption, stress, and weight gain and low physical activity) and which could have prevailed more in women than in men [42]. The improved levels of LDL cholesterol are related to CVD, in both men and women, but low levels of HDL cholesterol and increased levels of triglycerides have shown to be more intensely related to CHD in women than in men [13].
6. Conclusions
- The high incidence of CHF among the Type II diabetic (T2DM) population with renal manifestations emphasizes the need of early identification of the disease and the aggressive treatment of risk factors of CHF and KD. Evidence of renal disease in the presence of heart failure should not be ignored. Instead, it should be sought for, and renal disease prevented in all CHF case management. Finally, given the steep climb in rate of CFH from that among those below 40 years to those above 70 years, there is strong indication that younger diabetics may benefit from more intensive monitoring of CHF risk factors, such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, microalbuminuria, anemia and others.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- To Dr. Carlos Costa, Dr. Fernando Lopes, Dr. Miguel Tavares, Dra. Madalena Rocha, Dr. McCullough, Dr. Claudio Ronco and Dr. Egede.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML