-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Physical Chemistry
p-ISSN: 2167-7042 e-ISSN: 2167-7069
2015; 5(2): 39-47
doi:10.5923/j.pc.20150502.03
Novel Corrosion Inhibitor for Steel in 0.5 M H2SO4 Containing Halide Ions
O. A. Abdullatef1, B. A. Abd-El-Naby2
1Faculty of Pharmacy, Pharos University, Alexandria, Egypt
2Faculty of Science, Alexandria University, Alexandria, Egypt
Correspondence to: O. A. Abdullatef, Faculty of Pharmacy, Pharos University, Alexandria, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Silene marmarica was studied as an environmentally friendly inhibitor for steel corrosion in 0.5 M H2SO4. The effect of iodide and chloride ions on the inhibition efficiency of Silene marmarica, were studied by using potentiodynamic polarization and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy techniques. The results showed that Silene Marmarica inhibited the corrosion of steel in 0.5 M H2SO4, where the inhibition efficiency increased with the increasing concentration of Silene marmarica. The results also showed that the presence of iodide produced a synergistic effect on the inhibition efficiency while, the presence of chloride ion decreased the inhibition efficiency of Silene marmarica. The adsorption behavior of Silene marmarica in the absence and presence of iodide or chloride was studied and was found to fit both the Langumir adsorption isotherm and the Kinetic-Thermodynamic model.
Keywords: Steel, Acidic, Inhibition, Adsorption, Iodide ˃
Cite this paper: O. A. Abdullatef, B. A. Abd-El-Naby, Novel Corrosion Inhibitor for Steel in 0.5 M H2SO4 Containing Halide Ions, Physical Chemistry, Vol. 5 No. 2, 2015, pp. 39-47. doi: 10.5923/j.pc.20150502.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Mild steel is a widely used metal, that has many applications including the manufacturing of installations for petroleum, fertilizers, water treatment equipment [1-5], and different chemical industrial processes such as acid cleaning, acid descaling and pickling [6]. One of the most commonly used methods for protecting metals against corrosion, is using inhibitors [7, 8]. The common corrosion inhibitors are mostly organic compounds having hetero atoms in their aromatic ring or delocalized π – bonds [7-9]. Unfortunately, these compounds have toxic effects not only on living organisms but also on the environment [8]. Nowadays, the need for green corrosion inhibitors has become essential for the environment. This class of corrosion inhibitors is environmentally friendly and is extracted from natural products such as plant extracts [10]. Several authors carried out their studies on the inhibition of corrosion of metals by using plant extracts [11-17]. Ficus Nitida leaves was investigated as corrosion inhibitor towards general and pitting corrosion of steel, nickel and zinc in different aqueous solutions by using potentiostatic, potentiodynamic polarization and weight loss techniques [18]. Ficus Nitida leaves decreased the corrosion rates of the three tested metals in the three different corrosive media. Consequently, the inhibition efficiency of Ficus Nitida leaves increased as the extract concentration, increased. Zakvi and Mehta studied the corrosion behavior of steel in 0.1 N solutions of sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, nitric acid and phosphoric acid containing 0.5 g/L of Mahasudar shana Churna extract using the polarization resistance technique [19]. The inhibition efficiency of the plant extract in the previously mentioned acids was in the following order: phosphoric
 sulfuric
sulfuric  hydrochloric
hydrochloric  nitric. The seeds of Brassica Negra (black mustard) was studied as a corrosion inhibitor for steel and 304 stainless steel by open circuit potential and potentiodynamic polarization techniques [20]. The potentiodynamic polarization measurements showed that 0.5% of final concentration of black mustard seeds has a passivating effect. Khamis et al. [21], investigated a new category of environmentally safe corrosion inhibitors (Thyme, Coriander, Hibiscus, Anise, Black Cumin and Garden Gress) for the corrosion of steel in 0.5 M sulfuric acid by using the potentiodynamic polarization and electrochemical impedance techniques. The inhibition efficiency of these plants was attributed to their chemical constituents which are volatile oils, hydrocarbons, aromatic phenyl ring and oxygenated compounds. Silene marmarica is a small herbaceous plant found in Meditranian basin countries. It has a soft texture and green color. It is one of the oldest plants used in ancient and modern medicine. It may be used as a sanitizer or antimicropial agent. It could also be used as a scented repellent. The aim of this work is to evaluate Silene marmarica as an environmentally safe corrosion inhibitor for steel in 0.5 M sulfuric acid and to assess the effect of addition of halides on the inhibition efficiency.
nitric. The seeds of Brassica Negra (black mustard) was studied as a corrosion inhibitor for steel and 304 stainless steel by open circuit potential and potentiodynamic polarization techniques [20]. The potentiodynamic polarization measurements showed that 0.5% of final concentration of black mustard seeds has a passivating effect. Khamis et al. [21], investigated a new category of environmentally safe corrosion inhibitors (Thyme, Coriander, Hibiscus, Anise, Black Cumin and Garden Gress) for the corrosion of steel in 0.5 M sulfuric acid by using the potentiodynamic polarization and electrochemical impedance techniques. The inhibition efficiency of these plants was attributed to their chemical constituents which are volatile oils, hydrocarbons, aromatic phenyl ring and oxygenated compounds. Silene marmarica is a small herbaceous plant found in Meditranian basin countries. It has a soft texture and green color. It is one of the oldest plants used in ancient and modern medicine. It may be used as a sanitizer or antimicropial agent. It could also be used as a scented repellent. The aim of this work is to evaluate Silene marmarica as an environmentally safe corrosion inhibitor for steel in 0.5 M sulfuric acid and to assess the effect of addition of halides on the inhibition efficiency.2. Experimental
2.1. Electrochemical Tests
- Potentiodynamic polarization curves and Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy were achieved by using Gill ACM 604 Instrument. 0.01 ≤ f ≤ 3 x 104 Hz frequency range for EIS measurements with an applied potential range of ± 250 mV around the rest potential and a signal amplitude of 10 mV around the rest potential at a 20 mV/min. scan rate was used for polarization curves measurements. The data was obtained in a multi nicked cell in which graphite rod and saturated calomel electrode were used as counter and reference electrodes, respectively. Steel rods have the chemical composition (wt %): C 0.21; S 0.04; Mn 2.5; P 0.04; Si 0.35; balance Fe has been used as the working electrode. The steel samples were fixed in poly tetrafluoro ethylene (PTFE) rods by an epoxy resin in a manner that only one surface of area (0.28 cm2) was left uncovered. The exposed area was mechanically polished with a series of emery papers of different grades, the samples were then washed thoroughly with distilled water followed by A.R. ethanol and finally with distilled water, just before insertion into the cell. Measurements were done at 30°C.
2.2. Preparation of Solution
- Silene marmarica is edible, its chemical composition, which is Thujon, Borneol, Cineol and Pinene, is given in Fig. 1. Raw Silene marmarica was used in this study as a whole. Stock solution of Silene marmarica was obtained by refluxing 10 g of dry plant in 100 mL of distilled water for 60 min. The refluxed solution was filtered off to remove any contaminants.
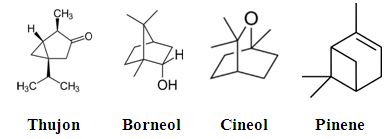 | Figure 1. Chemical composition of Silene Marmarica |
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Potentiodynamic Polarization Measurements
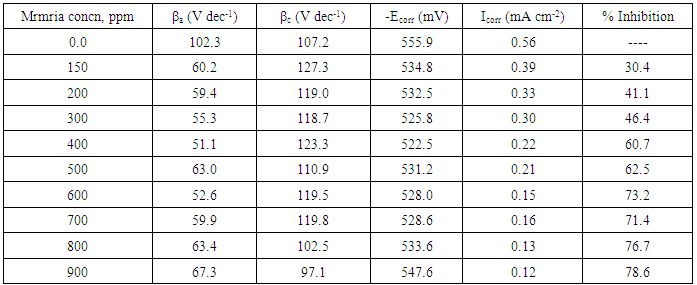
- Tafel polarization curves for steel in 0.5 M H2SO4 in absence and presence of different concentrations of Silene marmarica are shown in Fig. 2. The cathodic and the anodic parts of Tafel lines were changed simultaneously, indicating that Silene marmarica acted as mixed type inhibitor and affects both the anodic dissolution and hydrogen evolution reactions.
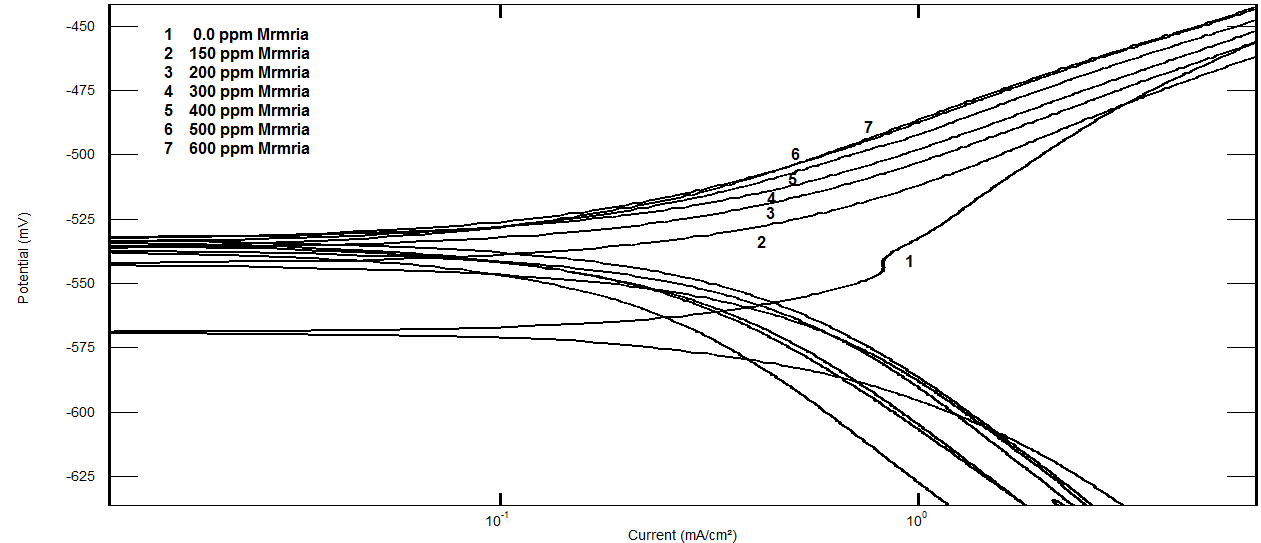 | Figure 2. Potentiodynamic polarization curves for steel in 0.5 M H2SO4 containing different concentrations of Silene marmarica at 30°C |
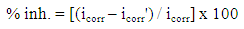 | (1) |
|
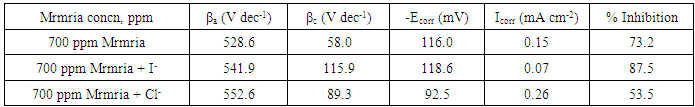
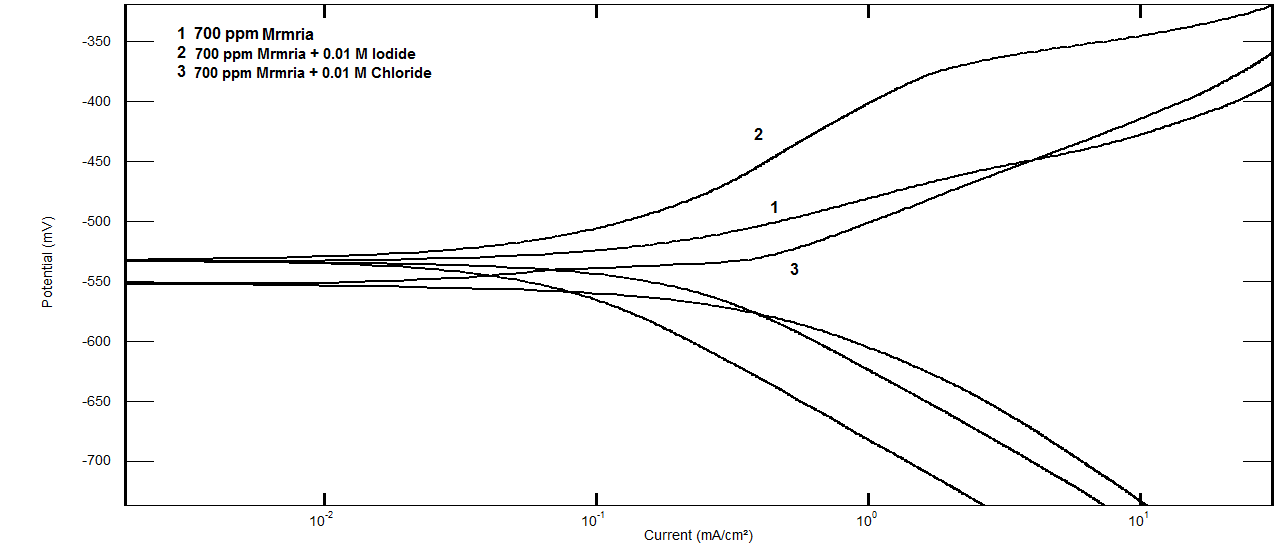 | Figure 3. Potentiodynamic polarization curves for steel in 0.5 M H2SO4 containing 700 ppm Silene marmarica in absence and presence of 0.01 M chloride or iodide ions at 30°C |
|
3.2. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) Measurements
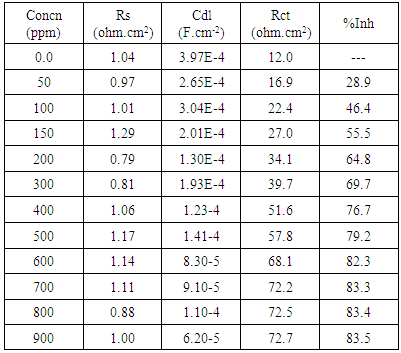
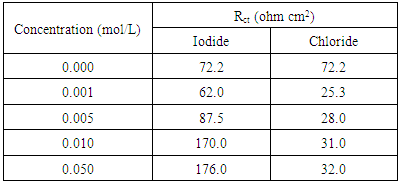
- Nyquist plots for steel in 0.5 M H2SO4 for different concentrations of silene marmarica in absence and presence of 0.01 M of both iodide or chloride ions are shown in Figs. 4, 5 and 6, respectively. Nyquist plots showed only one capacitive depressed semicircle. It is clearly seen that the diameter of the semicircle increases with increasing the concentration of the inhibitor. The impedance spectra for different Nyquist plots were analyzed by fitting the experimental data using Zsimpwin program to a simple equivalent circuit model, Fig. 7. The equivalent circuit model includes the solution resistance Rs and the circuit includes capacitor C which is placed in parallel to charge transfer resistance element Rct. The percentage of inhibition was calculated from the impedance measurements using the relation
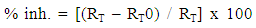 | (2) |
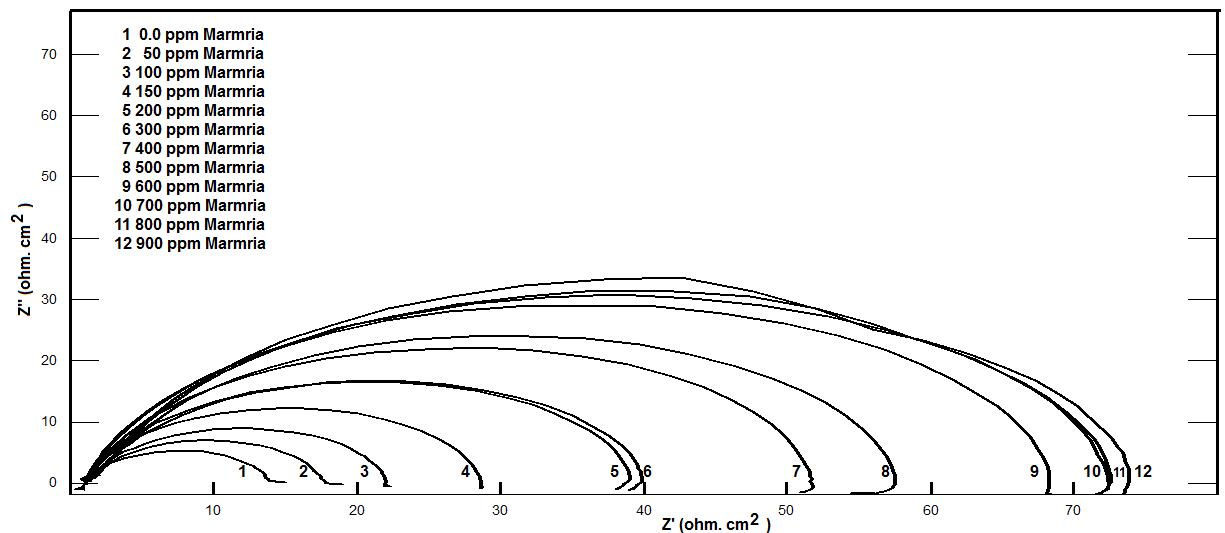 | Figure 4. Nyquist plots for steel in 0.5 M H2SO4 containing various concentrations of Silene marmarica at 30°C |
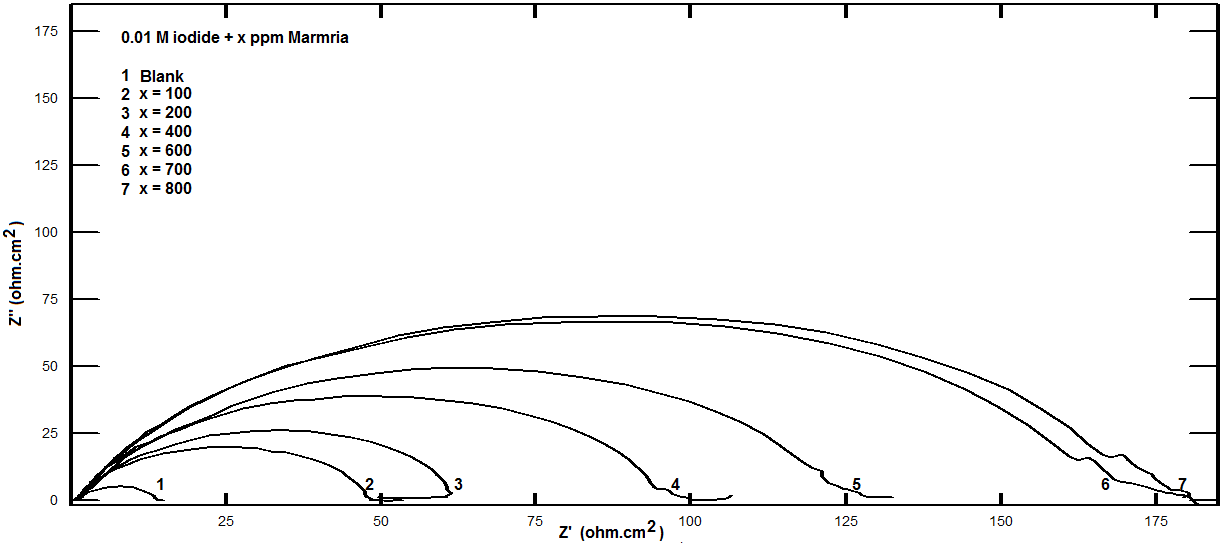 | Figure 5. Nyquist plots for steel in 0.5 M H2SO4 containing various concentrations of Silene marmarica in presence of 0.01 M Iodide ion at 30°C |
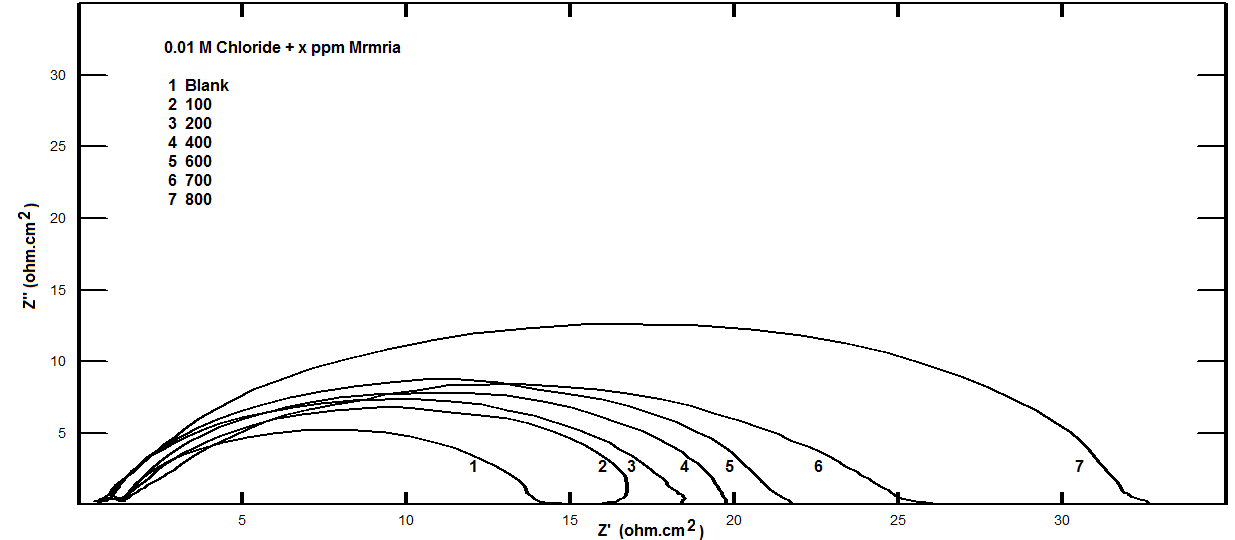 | Figure 6. Nyquist plots for steel in 0.5 M H2SO4 containing various concentrations of Silene marmarica in presence of 0.01 M Chloride ion at 30°C |
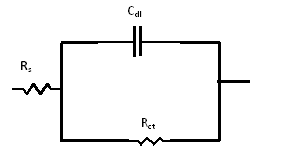 | Figure 7. The equivalent circuit model |
|
|
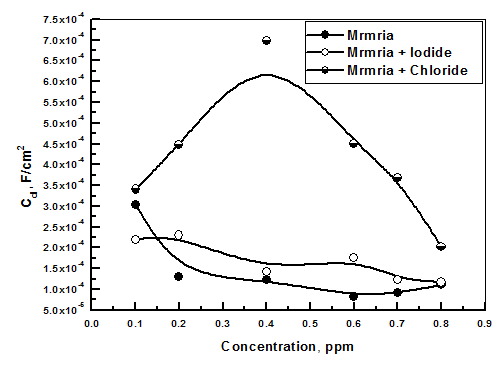 | Figure 8. The variation of Cdl with the concentrations of Silene marmarica in presence of 0.01 M Chloride and 0.01 M Iodide ions at 30°C |
3.3. Adsorption Characteristics
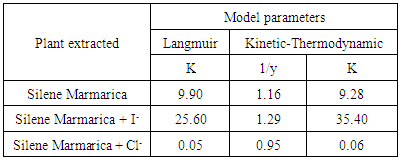
- In order to identify the nature of the adsorption between the inhibitor molecules and the metal surface; the application of different adsorption isotherm is essential. The relation between the percentage inhibition and the concentration of plant extract in absence and presence of iodide and chloride ions was shown in Fig. 9. The percentage inhibition was calculated from impedance measurements. These curves are characterized by an initial steeply rising part indicating the formation of a mono-layer adsorbate films on the steel surface until the saturation of metal surface is reached. It has been found that the presence of iodide increased the inhibition efficiency at all concentrations, in accordance with the results obtained from electrochemical measurements, while the presence of chloride decreased the inhibition efficiency at all concentrations. The experimental data was fitted to the Langumir adsorption isotherm and the Kinetic-Thermodynamic model in absence and presence of both chloride and iodide ions.
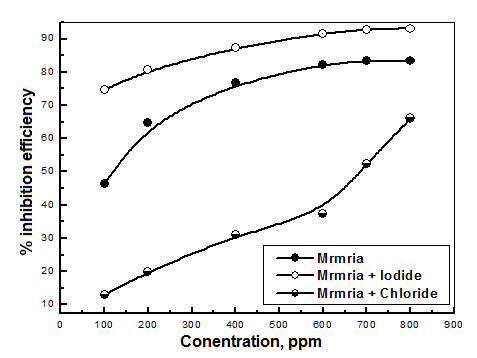 | Figure 9. Variations of percentage inhibition of the corrosion of steel in 0.5 M H2SO4 with concentration of Silene marmarica extracts in absence and presence of chloride and iodide ions |
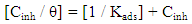 | (3) |
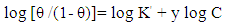 | (4) |
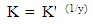 | (5) |
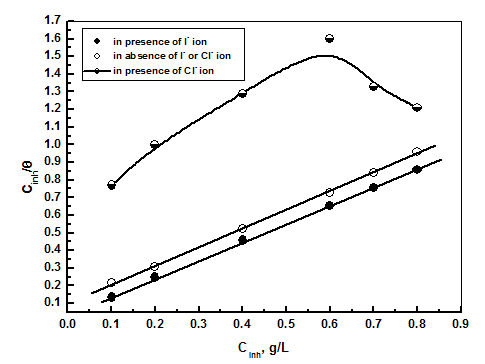 | Figure 10. Application of Langmuir model to the results of adsorption of extract on steel surface in absence and presence of iodide ion |
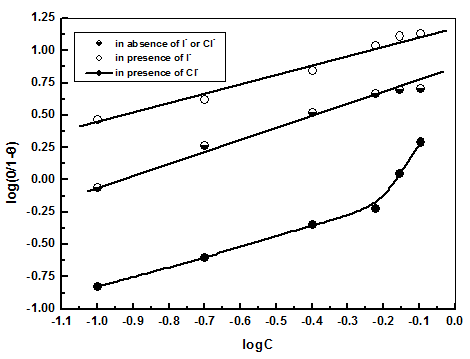 | Figure 11. Application of the Kinetic - Thermodynamic model to the results of adsorption of extract on steel surface in absence and presence of iodide or chloride ion |
|
3.4. Effect of Halide on the Inhibition Efficiency of Silene Marmarica for Steel in 0.5 M H2SO4
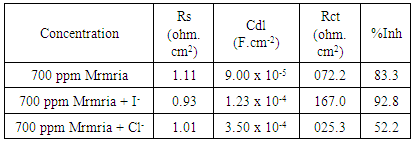
- Effect of Silene marmarica extract on the corrosion of steel in 0.5 M H2SO4 solution in absence and presence of different concentrations of iodide or chloride were examined by using potentiodynamic and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Figs. 12 and 13 show the potentiodynamic polarization curves for steel in 0.5 M H2SO4 containing 700 ppm Silane marmarica in absence and presence of different concentrations of iodide or chloride ions. The figures showed that the presence of iodide ion has an effect on both the anodic and cathodic tafel lines indicating that the iodide ion acted as mixed type inhibitor. On the other hand, the chloride ion had an acceleration effect on the potentiodynamic polarization curves.
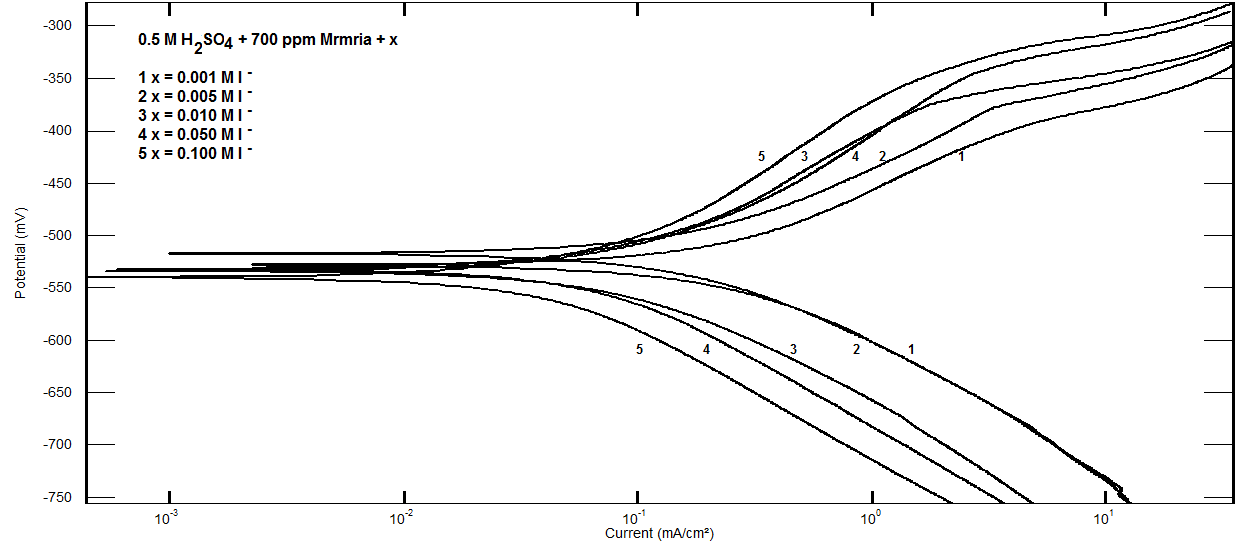 | Figure 12. Potentiodynamic polarization curves for steel in 0.5 M H2SO4 containing 700 ppm Silene marmarica in absence and presence of different concentrations of iodide ions at 30°C |
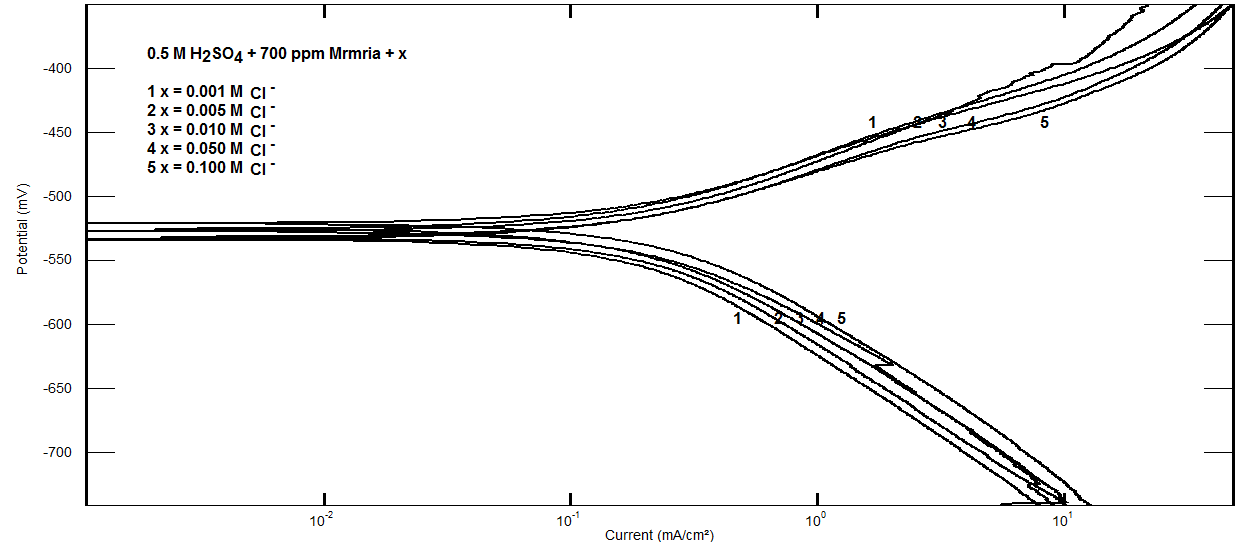 | Figure 13. Potentiodynamic polarization curves for steel in 0.5 M H2SO4 containing 700 ppm Silene marmarica in absence and presence of different concentrations of chloride ions at 30°C |
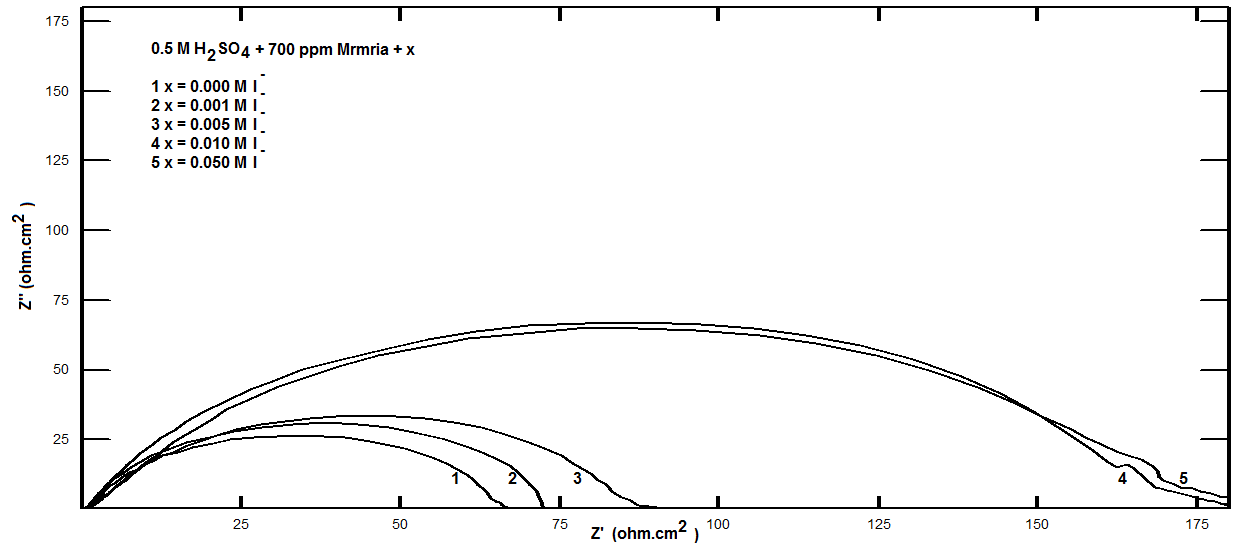 | Figure 14. Nyquist plots for steel in 0.5 M H2SO4 containing 700 ppm Silene marmarica in absence and presence of different concentrations of iodide ions at 30°C |
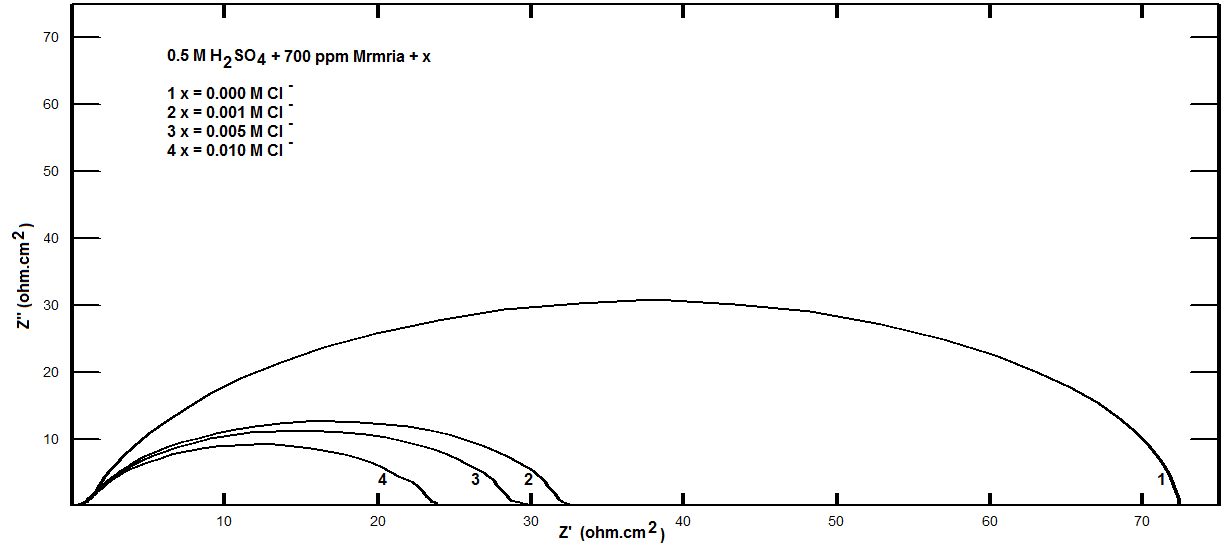 | Figure 15. Nyquist plots for steel in 0.5 M H2SO4 containing 700 ppm Silene marmarica in absence and presence of different concentrations of chloride ions at 30°C |
|
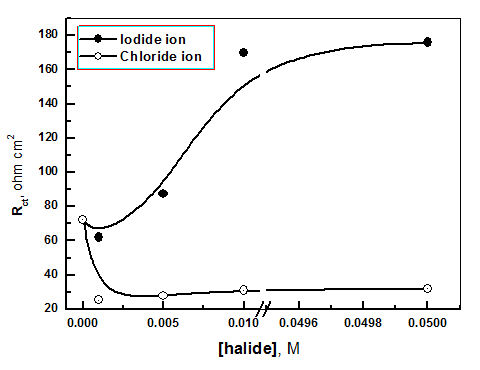 | Figure 16. The variation of Rct of solution containing 700 ppm silene marmarica with different concentrations of chloride or iodide ions |
4. Conclusions
- The extract of Silene marmarica acted as good inhibitor for the corrosion of steel in 0.5 M H2SO4. Silene marmarica extract is considered as mixed type inhibitor. The inhibition efficiency was found to increase with the increasing of extract concentration up to a maximum value. Iodide ion enhanced the inhibition efficiency of Silene marmarica while chloride ion decreased the inhibition efficiency. Langmuir adsorption isotherm is applicable to fit the data of Silene marmarica indicating the ideal behavior in the adsorption processes of these extracts on the steel surface. The Kinetic - Thermodynamic model fit the data of Silene marmarica, where higher values of the binding constant K in the presence of iodide ion was revealed, rather than in its absence were obtained indicating strong adsorption of the inhibitor in the presence of iodide compared to its decrease in absence.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- Gratitude is paid for Dr Gihan El-Batoti, Faculty of Pharmacy, Pharos University Egypt, for her support, guidance and linguistic revision.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML