-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Physical Chemistry
p-ISSN: 2167-7042 e-ISSN: 2167-7069
2013; 3(2): 29-38
doi:10.5923/j.pc.20130302.01
Methods for Qualitative Analysis of Cefazolin Sodium Raw Material and Pharmaceutical Product
Pedroso T. M., Salgado H. R. N.
Department of Drugs and Pharmaceuticals, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences of Araraquara- UNESP, Rodovia Araraquara-Jaú, km 1, CEP 14801-902, Araraquara, SP, Brazil
Correspondence to: Pedroso T. M., Department of Drugs and Pharmaceuticals, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences of Araraquara- UNESP, Rodovia Araraquara-Jaú, km 1, CEP 14801-902, Araraquara, SP, Brazil.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
In this work we studied qualitative methods for analysis and identification of cefazolin sodium, β-lactam antimicrobial for parenteral use, belonging to the group of first-generation cephalosporin, used as a therapeutic agent and for the surgical prophylaxis, in the pharmaceutical form of powder lyophilized for injectable solution. Qualitative analysis was performed by solubility, melting point, pH determination, thin layer chromatography, ultraviolet spectroscopy, infrared spectroscopy and high performance liquid chromatography, allowing the identification of sample. These methods were reproducible and quick to identify cefazolin sodium, which can be used routinely in analysis of quality control in pharmaceutical laboratories.
Keywords: Cefazolin Sodium, Cephalosporin, Analytical Method, Qualitative Analysis, Quality Control
Cite this paper: Pedroso T. M., Salgado H. R. N., Methods for Qualitative Analysis of Cefazolin Sodium Raw Material and Pharmaceutical Product, Physical Chemistry, Vol. 3 No. 2, 2013, pp. 29-38. doi: 10.5923/j.pc.20130302.01.
1. Introduction
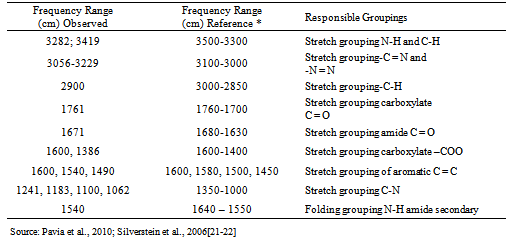
- The characterization of active substances for quality control is essential for obtaining effective and stable drugs, thus ensuring its content in the pharmaceutical specialties and its conservation throughout the period in which it is marketed. The quality in the manufacture of medicines is directly related to the promotion and maintenance of health, thereby performing analytical techniques for assessing the purity of the raw materials used in the manufacture of medicaments, quality specifications are necessary to verify that the product is suitable for use in the population. Failure to comply with these criteria can interfere with biopharmaceutical characteristics, in this sense, the analytical techniques are essential for the safe use of medicines. Cephalosporins are a class of antibiotics widely used and therapeutically important. Clinical studies have shown that cephalosporins are prophylactic and therapeutic effective agents against a broad spectrum of microbial agents; they have low toxicity and are used to treat many types of bacterial infections[1-3].number of cefalosporisnas available, it should be viable to adopt a classification system. Although the can be classified based on chemical structure, clinical pharmacology, resistance to β-lactamase or antimicrobial spectrum, the classification system is the most usual for "generations" and is divided into 5 generations: first, second, third, fourth generation and recently, the fifth generation, in which the compounds are grouped according to the general characteristics of antimicrobial activity[3-5].Cefazolin sodium is a semi synthetic antimicrobial which has no absorption orally, being found for parenteral use[6]. It shows good activity against bacteria Gram-positive and relatively moderate activity against micro-organisms, Gram-negative[3]. Its molecular formula is C14H13N8Na4S3, its molecular weight is 476.5 g/mol with a sodium content of 48.3 mg per gram of cefazolin sodium. It is identified chemically as (6R,7R)-3-[[(5-methyl-1,3,4-thia-dizol-2-yl)sulfanyl]methyl]-8-oxo-7-[(1H-tetrazol-1-yl)acetyl]amide]-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxy-late. The chemical structure of cefazolin sodium is shown in Figure 1.
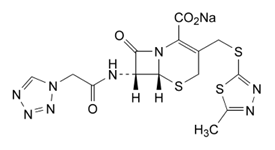 | Figure 1. Chemical structure of cefazolin sodium (CAS 27164-46-1) |
2. Chemicals
- CFZ reference substance (purity 98.2 %) and CFZ lyophilized injectable form containing 1000 mg of the active component, were kindly donated by the Laboratory ABL Antibióticos do Brasil Ltda (Cosmopolis-SP, Brazil). The vials do not present excipients. All solutions and mobile phases used in this assay were prepared from ultrapure water obtained from a Milli-Q Plus (Millipore, USA). All other chemicals were of analytical grade.
3. Methods
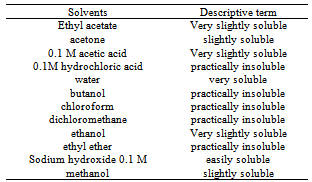
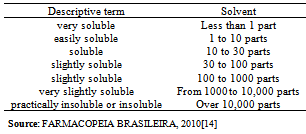
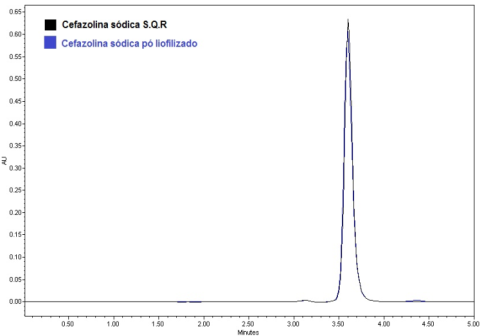
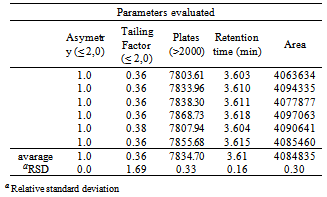
- a) Analysis of drug appearance: The appearance of the drug was assessed visually and then it was compared with official compendiums [8-12]. b) Moisture content: The moisture content was determined by Karl Fischer Orion™ model AF8, using Karl Fischer reagent free from pyridine methanol VETEC with at most 0.005% of water and sodium tartrate dihydrate (volumetric standard for standardization of Karl Fischer reagent contains 15 66 + 0.05% H2O). The method of loss on drying was carried out in infrared moisture analyser, Gehaka™ model 2000 IV- the scales with infrared radiation heating, which allows to assess the humidity of the sample.c) Solubility: The solubility test was performed at 25°C in test tubes with 25 mm diameter x 150 mm height and analytical grade solvents. The solubility was indicated according to the recommendations in official compendia designated by descriptive terms wherein the term part refer to dissolving 1g of a solid in the number of solvent milliliters, provided the number of parts.d) Determination of the melting range: the melting range was determined in capillary tubes with thickness of 1.6 mm and 7.5 cm in length, three capillaries tests being performed simultaneously inserted in automated equipment (Stuart Scientific SMP3 - Staffordshire, UK) with a heating rate of 1.0°C per minute.e) Determination of pH: The pH potentiometric determination was obtained at pH meter device model B474™ brand Micronal, previously calibrated solution of cefazolin sodium, subjecting lyophilized powder 100 mg/mL, prepared in purified water. The test was conducted in a controlled temperature of 25ºC.f) Spectrophotometry in the ultraviolet region: Ultraviolet spectra were obtained on a Shimadzu UV-Vis spectrophotometer; model UV-mini-1240, using quartz cuvettes with a 1 cm optical path. Readings were taken between 200 and 400 nm, being determined in solutions prepared in various solvents such as purified water (Milli-Q™), 0.1 M hydrochloric acid PA (Synth™), 0.1 M sodium hydroxide PA (Merck™), methanol PA (Synth™), phosphate buffer pH 6, and 1% phosphate buffer pH 8 containing 20.0 μg/mL.g) Infrared absorption spectrophotometry: The infrared spectra were obtained with a Shimadzuspectrophotometer Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrophotometer Model: IR Prestige-21 IR Affinity-1 FTIR-8400S/Kyoto - Japan, with digitization of the spectra (region 500-4000 cm-1 and 2 cm-1 interval). The tablets were prepared by mixing 1% of sample (reference substance and lyophilized powder) weighing 1.5 mg of cefazolin sodium in 150 mg KBr previously pulverized in an agate mortar and dried at 105 °C until constant weight, they were placed in special molds and then pressed under vacuum pressure of 80.000 kN to form transparent discs.h) Thin-layer chromatography: The plates used for identification of the drug were silica gel 60 F254 DC-Fertigfolien alugram™ 20 x 20 cm (Macherey-Nagel) with a thickness of 0.25 mm, purchased commercially, and activated at 105 °C for 1 h. The mobile phase was placed in a vat chromatographic until saturation. The mobile phase used was methanol or absolute ethyl alcohol: water (90:10, v/v). Aliquots of 10 µL of solutions containing cefazolin sodium (sample and reference substance) freshly prepared in purified water at a concentration of 5 mg/mL (w/v), were applied to the stationary phase consisting of silica gel impregnated in aluminum and held to the test. After the end of the 10 cm elution, the plate was removed from the glass vessel and dried under a stream of air, the spots were detected by exposing the plate in the UV (365 nm) and soon afterwards the exposure to iodine atmosphere, which were analyzed for size, shape, position and Rf values.i) High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC): The reverse phase chromatographic method was performed on Waters system consisting of binary pump gradient chromatographic Waters 1525™, manual Rheodyne injector and detector Breeze 7725i UV-Vis Waters 2487™. The analysis of the drug under study was performed isocratically on Zorbax Eclipse Plus columns 5 mm C18 (250 mm x 4.6 mm) Agilent™ and 5 mm Symmetry C18 (4.6 x 250 mm) Waters™ kept at room temperature. The mobile phase consisted of water and acetonitrile (60:40 v/v), pH was adjusted to 8 with drops of triethylamine and the test was performed at a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min using UV detector at 270 nm, the peak areas were integrated using the program Empower software™. The suitability of the chromatographic system was determined based on conformance testing of the chromatographic system (system suitability) to ensure the performance of the chromatograph for analysis performance, injecting solutions in seven working concentration of 60 μg/mL. The relative standard deviation of the parameters of asymmetry of the peak broadening factors, number of plates, retention time and peak area was analyzed as recommended by the FDA in 2004[13].
4. Results
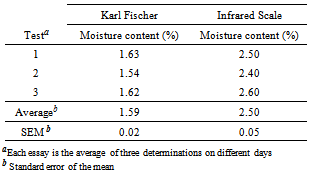
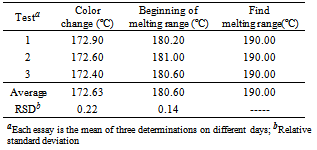
- Qualitative analyzes are essential for the identification of raw materials and securing the content of active substance in marketed pharmaceutical form; in this context, this work proposes some analytical methods to identify reproducible, reliable and easy performance.Cefazolin sodium aspect powder had presented a crystalline odorless and hygroscopic white or almost white. The physical aspects of cefazolin sodium corresponded to those described in official compendia[8-12].The moisture content by Karl Fischer presented to cefazolin sodium in lyophilized powder was 1.6%, and IR was 2.5% as shown in Table 1.
|
|
|
|
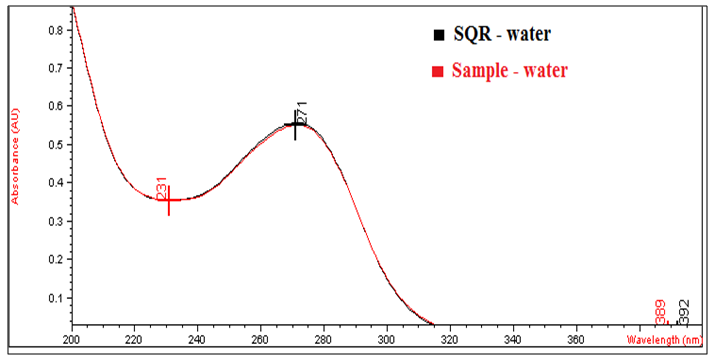 | Figure 2. Absorption spectra of aqueous solutions of cefazolin sodium RS and cefazolin sodium lyophilized powder, both with a concentration of 20.0 μg/mL in the ultraviolet region |
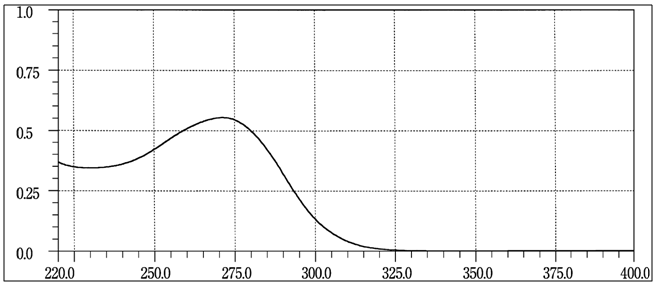 | Figure 3. Reference spectrum in the ultraviolet region for cefazolin sodium available in official compendia - Japanese Pharmacopoeia 2011 [12] |
|
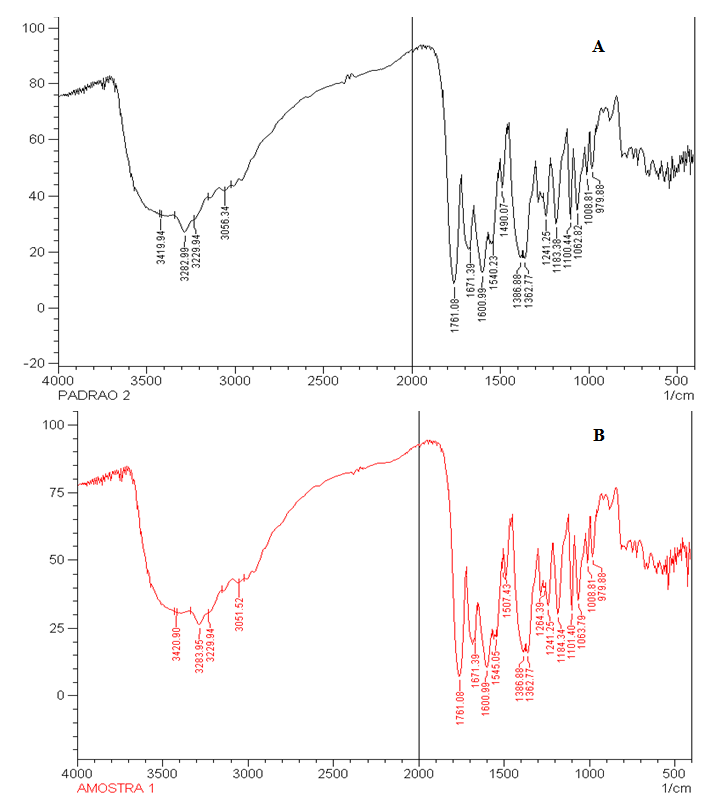 | Figure 4. Spectrum in the infrared region of cefazolin sodium RS (A) and cefazolin sample of lyophilised powder (B) in KBr pellets |
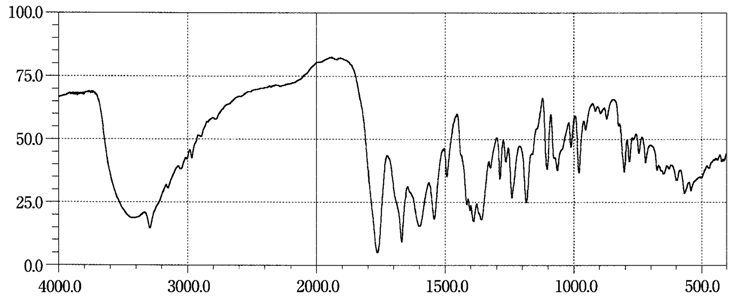 | Figure 5. Reference spectrum of cefazolin sodium available spectrum in the infrared region in official compendia - Japanese Pharmacopoeia 2011[12] |
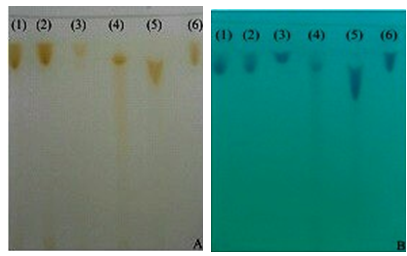
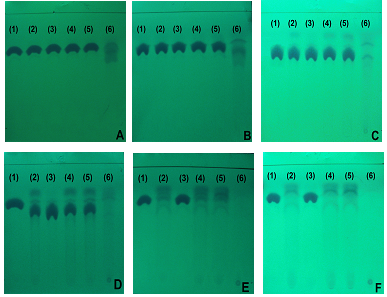
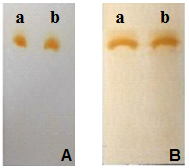 | Figure 6. Chromatograms of cefazolin sodium RS (a) and cefazolin sodium lyophilized powder (b), methanol mobile phase (A) and water: ethanol (1:9 v / v) (B) disclosed in iodine atmosphere |
|
5. Conclusions
- With globalization, technological advances occur ever faster and provide different methods daily, targeting efficiency, reproducibility, lower uptime to fit routine pharmaceutical industries, where "time is money"; however, they are often complex and costly. Qualitative analyzes made possible the rapid characterization of cefazolin sodium with the advantages of being simple, fast, reproducible and inexpensive methods and can be used routinely in analyzes of quality control. It is worth mentioning that the Farmacopeia Brasileira (2010) still does not describe methods for qualitative analysis of cefazolin sodium, being at the discretion of the pharmaceutical industry adoption of the most convenient methods to prove the quality of medicines produced.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- We thank the laboratory ABL Antibioticos do Brasil Ltda. (Cosmopolis-SP) for the kind donation of medicines and reference substance; CNPq, FAPESP and PADC-FCF for the financial support and Maria de Fatima Rodrigues for technical support.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML