Adnan Salih Al-Ithawi1, Alaa H. Ali2
1Baghdad University, College of Science for Women
2Department of Materials Research, Ministry of Science and Technology
Correspondence to: Adnan Salih Al-Ithawi, Baghdad University, College of Science for Women.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Abstract
In this study we proved experimentally that, the refractive index effected on energy of photon in medium. Also we have shown that, the model of photon as mass particle associated with wave is correct [3, 4], by analysis the energy of photon measured experimentally, with principles of new theory.
Keywords:
Photon, Mass, Energy, Particle, Wave
Cite this paper: Adnan Salih Al-Ithawi, Alaa H. Ali, Experimentally Proved that, The Refractive Index Effected on Energy of Photon in Medium, International Journal of Optics and Applications, Vol. 5 No. 5, 2015, pp. 151-154. doi: 10.5923/j.optics.20150505.02.
1. Introduction
Photons exhibit wave-particle duality meaning that photons acts in a manner consistent with wave or particle in different situations [1]. Yong’s experiment is still considered to be the most convincing proof of the wave nature of light, Feynman put forward his view that when an object behaves like a wave, it should produce interference fringes in Yong’s double slit experiment, and when behaves like a particle, it will produce no fringes in the same experiment [2].We demonstrated in our articles [3, 4], theoretical model of photon as mass particle associated with wave. In this study we try to confirm this model experimentally.
2. Experimental
A simple system was used to measure the kinetic energy of photon in medium, first we measured the (energy / second) of photons in air by using, laser beam (He = Ne, λ = 632.8µm) then we used a cell contain a water vapor, the laser beam incident perpendicular on the window of the cell transmitted (97%) from the incident light. The (energy /second) of photons was measured inside the cell, finally we measured the (energy/second) of photons outside of cell.The results in the following table (1)Table 1. Experimental results
 |
| |
|
The difference in the laser energy in air and medium is due to the absorbance, scattering, and as we think to velocity of photon. To estimated the effect of velocity on energy we shall made analysis of the parameters in table (1).
3. Simple Analysis
The laser beam incident on second window of the cell by an angle because of refraction, then (4%) from the energy will reflected from the first surface of window and (4%) from the second surface,4.37*0.04=0.1748mJ/s4.37-17.48=4.1952mJ/s4.1952*0.04=0.1678 mJ/sThe total losses for reflection is 0.1748+0.1678=0.3426 mJ/sAccording to this simple simulation, the outside energy must be:4.37-0.3426=4.0274mJ/sBut we measured the energy outside as in table (1) 4.13 mJ4.13-4.0274=0.1026mJ/sThis difference came from effect of velocity, it means that the kinetic energy of photon inside cell will decrease 0.1026mJ/s, because its velocity (v).The laser beam incident perpendicular on the window of the cell which transmitted (97%) from the incident light, so the energy of photon in medium when the photon pass throw window is:4.71-4.71*0.03=4.5687 mJ/sIf the cell transmitted 100% of incident light, then the decrease in energy of photon in medium is:4.71*0.1026/4.5687=0.1057731959=0.106 mJ/sThe kinetic energy of photon in medium is:4.71-0.106 = 4.604mJ/sThe refractive index of medium (n), can be calculate [3, 4], 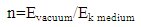 | (1) |
n=4.71*10-3/4.604*10-3n=1.023023458We summarized the analysis of experimental results in table (2), Table 2. Experiment results
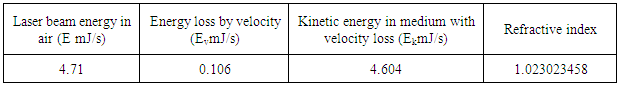 |
| |
|
The difference between (E) in air and in medium is due to the velocity of photon.
4. Number of Photons
To be sure that this result is correct, the number of photons in air and medium must be the same. The number of photons can be calculated according to this relation;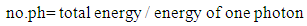 | (2) |
or no.ph=total natural mass/natural mass of one photon
4.1. In Vacuum
As in the current theories, the energy of photon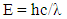 | (3) |
E = 6.626*10-34*3*108/632.8*10-9E = 0.03141276856*10-17 JWe can find the natural mass of one photon from the relation;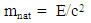 | (4) |
mnat=0.03141276856*10-17/9*1016=0.003490307628*10-33 KgTotal natural mass for laser beam from equation (4):mtot=4.71*10-3/9*1016=52.33333333*10-19 KgAccording to equation (2), the number of photons in case of energy and natural mass; no.ph for energy = 4.71*10-3/0.03141276856*10-17 = 1499390281*109 photon/sno.ph for natural mass= 52.33333333*10-19/0.003490307628 * 10-33= 1499390281*109 photon/sit is clear that, the number of photons are the same in case of energy or natural mass.
4.2. In Medium
If we want to find the energy, and relative mass of photon in medium, the current theories assumed that, there is no effect of refractive index on the energy and stay constant while the photon is mass less.According to new theory, the energy is effected by the medium and decrease according to refractive index, while the photon has natural mass in air and effective mass in medium which depend on refractive index. We can calculate the kinetic energy in medium as [3, 4]: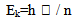 Where
Where 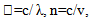 then:
then: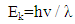 | (5) |
V=c/n=3*108 /1.023023458=2.932484076*108 m/sEk= 6.626*10-34*2.932484076*108/632.8 *10-9 = 0.03070581462*10-17JTo calculate the effective mass of one photon in medium [3, 4]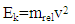 | (6) |
0.03070581462*10-17 = mrel*(2.932484076*108)2mrel = 0.0035707666579*10-33 KgThe total kinetic energy in medium:Ek = no.ph*Energy of one photonEk = 1499390281*109*0.03070581462*10-17= 4.604000001 mJ/sThis result is very close to the analysis result of experiment (Ek=4.604mJ/s) as in table (2).The very small difference between two results is due to the accuracy of detector.Total relative mass in medium from equation (6):4.604*10-3/(2.9326484076*108)2=53.53822764*10-19 KgAccording to equation (2) for energy and natural mass in medium;no.phfor energy = 4.604*10-3 /0.030706581462*10-17 = 1499390281*109photon/s,no.phfor natural mass = 53.53822764*10-19/0.003570666579*10-33 = 1499390281*109photon/sIt is clear that, the number of photons are the same in case of kinetic energy or effective mass of photon in medium and it is the same as in vacuum.The relation between natural mass and effective mass is refractive index as [3, 4],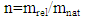 | (7) |
n=0.003570666579*10-33/003490307628*10-33 =1.023023458The result in equation (7), for refractive index is the same as in table (2).From all the results the number of photons are constant, which indicate that all calculations are correct.
5. Calculate of Wavelength
To calculate the wavelength of photon in medium, as in current theory;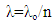 | (8) |
λ=632.8*10-9/1.023023458=618.558*10-9 mwhile in new theory (1,2)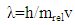 | (9) |
λ=6.626*10-34/ 2.932484076*108* 0.003570666579*10-33λ=632.8*10-9m
6. Refractive Angle
6.1. Current Theory
To found the refractive angle of the laser beam according to senll’s law, 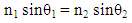 | (10) |
As in the experiment the incident angle is (90°);1=1.023023458 sinθ2sinθ2 = 0.977494692θ2=1.358239355°
6.2. New Theory
The dispersion phenomena in new theory explained according to natural mass of photon [3, 4]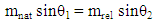 | (11) |
52.33333333*10-19 = 53.53822764*10-19sinθ2sinθ2=52.33333333*10-19/53.53822764*10-19sinθ2=0.977494691θ2=1.35823935°Which is the same result from equations (10,11).
7. Momentum of Photon in Medium
7.1. Current Theory
If the photon is wave as in The Minkowski version [5]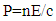 | (12) |
P = 1.023023458*0.03141276865*10-17/3*108P = .0.01071199997*10-25J.s/mIf the photon is particle as in Abraham version [6]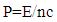 | (13) |
P = 0.03145069532*10-17/1.023023458*3*108P = 0.01023527155*10-25 J.s/mThe parameter (E) in equation (12) represent the energy in medium, which is constant in vacuum or medium.
7.2. New Theory
In new theory the momentum in medium is [3, 4]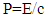 | (14) |
P=0.03141276865*10-17/3*108P=0.01047092288* 10-25 J.s/mEquation (14) represent the momentum of photon in medium, which h the same equations as in vacuum, this means that the controversy of Minkowisky and Abraham is solved.We can summarized the analytical results in table (3).Table 3. Analytical results
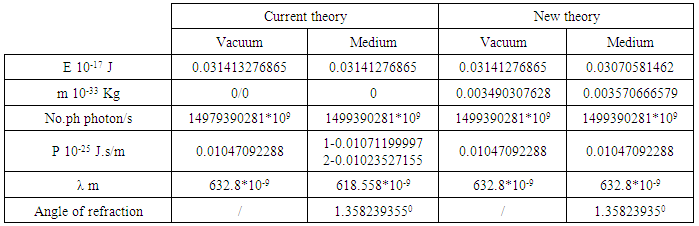 |
| |
|
8. Conclusions
In the current theories as we know that the energy of photon is constant in medium or vacuum, while the momentum is changeable according to Minkowisky and Abraham. In this study we proved that the energy of photon is decreased in medium because of the refractive index of medium and the momentum is constant.The important factor in this study which indicate that the results are correct is the number of photons which is the same number in all analytical steps.In summary, by analysis of the energy of photon measured experimentally, with principle of new theory, we have shown that, the model of photon as mass particle associated with wave [3, 4] is correct. As shown in table (3); the energy is changeable with refractive index, and the photon explained as particle has natural, and relative mass. The wavelength and momentum in medium are constant, while the dispersion phenomena was explained with mass of photon.
References
| [1] | Chitraleema Chakraborty, Nature of photon, particle or a wave, University of Rochster, Rochster, NY, 14627, U.S.A, December, 4, 2012. |
| [2] | Feynman, Leighton, Sands, Feynman lectures in physics, Addison, Wesley.vol.3, 1965. |
| [3] | Adnan Salih, Mass, Energy, and Momentum of Photon in Medium, international journal of physical sicences, 18, 21, 1192, 2013. |
| [4] | Adnan Salih Al-Ithawi, The photon as a mass particle associated with wave, international journal of optics and applications, 5(1), 22-25, 2015. |
| [5] | Minkowski, Hermann (1908), "Die Grundgleichungenfür die elektromagnetischen Vorgänge in bewegten Körpern", Nachrichten von der Gesellschaft der Wissenschaftenzu Göttingen, Mathematisch-Physikalische Klasse: 53–111. |
| [6] | Abraham, Max (1909), "Zur Elektrodynamikbewegter Körper", Rendiconti del Circolo Matematico di Palermo 28: 1–28. |

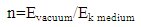
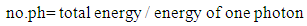
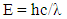
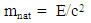
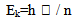 Where
Where 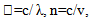 then:
then: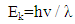
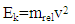
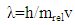
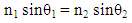
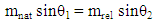
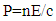
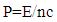
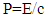
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML

