-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Optics and Applications
p-ISSN: 2168-5053 e-ISSN: 2168-5061
2015; 5(3): 51-57
doi:10.5923/j.optics.20150503.01
SNR and BER Performance Enhancement on FSO Induced by Atmospheric Turbulence Using Optical Spatial Filter
Ucuk Darusalam, Purnomo Sidi Priambodo, Eko Tjipto Rahardjo
Department of Electrical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Universitas Indonesia, Jl. Kampus Baru UI, Depok
Correspondence to: Ucuk Darusalam, Department of Electrical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Universitas Indonesia, Jl. Kampus Baru UI, Depok.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
In order to enhance signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and bit-error-rate (BER) performance on free-space optical (FSO) communications, anoptical spatial filter (OSF) is implemented at focus spot of receiver lens. Conceptually, the OSF collects fluctuation of signal intensity that is caused by beam wander and spatial noise at focus spot within a narrow region. The confinement of signal intensity fluctuation in a narrow region that goes random arround the optical axis can minimizes reception of noise into photodetector (PD). It also brings an advantage for enhancing mean value of signal intensity. Hence, PD receives optimum signal power and noise can be minimized. Those noise suppression leads to enhancement SNR performance. It means the distribution of signal power is optimally produced by PD rather than noise. Hence, higher signal intensity and narrow noise bandwidth by the OSF minimize the error distribution that gives an advantage to decrease the order of BER. From the calculations and experiment show that the OSF enhances SNR and BER performance under influenced of turbulence media. In comparison to direct detection (DD) method, the OSF with pinhole of 20 and cone reflector of 1.5 produces best performance that increases at 4.2 dB and decreases at 10-12.
Keywords: FSO, Atmospheric turbulence, Spatial noise, Beam wander, Spatial filter, Cone reflector, Pinhole
Cite this paper: Ucuk Darusalam, Purnomo Sidi Priambodo, Eko Tjipto Rahardjo, SNR and BER Performance Enhancement on FSO Induced by Atmospheric Turbulence Using Optical Spatial Filter, International Journal of Optics and Applications, Vol. 5 No. 3, 2015, pp. 51-57. doi: 10.5923/j.optics.20150503.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- FSO is a potential telecommunication platform that has achieved tremendous development on bit rate capacity, link distance, and integrated in multi-system [1-6]. It has attractive benefit such as free-licensed, low-cost, high-security, and high rate transmission [7]. It has major drawbacks that the SNR and BER performance is strongly influenced by noise modulation of atmospheric turbulence [8]. Some impacts as the results of atmospheric turbulence modulation on optical propagation are beam wander and spatial noise effects [9]. Those lead to fluctuation of amplitude and phase in optical propagation. Those also increase to scale-up with propagation path length and turbulence level on the atmosphere. Through these, signal intensity goes to fluctuation on focus spot of receiver lens randomly. Unfortunately, PD receives those impact in the form of fading, large noise bandwidth, and misalignment detection. It produces lower signal power which frequently falls below a the prescribed threshold level
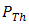 of PD and maximum noise as well. These lead to degradation of SNR. Hence, the lower SNR contributes to higher order of BER. Moreover, SNR and BER performance degrades in maximum by the presence of turbulence effects. Recently, several methods have been developed to enhance SNR and BER performance on FSO under influenced of atmospheric turbulence. Spatial-diversity (SD), time-diversity (TD), cooperative-diversity (CD), photon detection technique (PDT), amplification method, and adaptive optics (AO) have been investigated so far in order to solve turbulence effects intensively [10-15]. Those methods pay great concern to minimize degradation SNR and BER performance. Generally, those aforementioned methods implement DD for retrieving a signal without an optical treatment previously in a receiver plane. Contrary to the benefit of FSO that has low-cost implementation, those aforementioned methods are quite complex and high-cost. SD offers enhancement SNR and BER performance with multiple system of transmitter and receiver that requires complex electronics of equal gain combiner [10]. TD provides method of signal transmission in multi-periode of time that also requires complex signal processing in the receiver system [11]. CD offers smart combination of spatial- and time-diversity that also requires complex algorythm as well [12]. PDT offers higher sensitivity for lower signal while noise does not taken into account to be suppressed optically [13]. Optical amplification that uses erbium-doped fiber amplifier commonly, also does not provide optical method to enhance signal intensity with minimum noise [14]. Moreover, AO offers enhancement of signal intensity with processing of optical propagation technique but beam wander does not taken into consideration as the serious problem to be suppressed [15]. By taking into consideration that beam wander and spatial noise effects can be suppressed optically at focus spot of receiver lens, the OSF can be implemented as a detection method before signal is received by PD. Thus, implementation of the OSF for suppressing noise that is caused by turbulence effects is the motivation of this work in order to enhance SNR and BER performance.In this paper, the OSF is implemented on FSO of full-duplex transmission at wavelength of 1550 nm. It is a simple- and low-cost method for suppression of beam wander and spatial noise effects. It can be integrated with the aforementioned methods such as optical amplification or SD. It also has competitive benefit for bit rate capacity processing in comparison to TD. The characteristics of turbulence effects are random phenomena and independent process as well. Meanwhile, turbulence effects cannot be treated as a separate process in optical propagation. Thus, beam wander and spatial noise effects cannot be solved separately in order to enhance SNR and BER performance. Regarding those, the OSF is designed to suppress beam wander and spatial noise effects simultaneously. The OSF is composed of cone reflector and pinhole [16] that is installed on focus spot of receiver lens before PD. Cone reflector is designed to suppress beam wander that has random angle of focus spot through directed reflectance radially into pinhole diameter [17]. Pinhole is designed to suppress spatial noise through governing Fresnel diffraction on focus spot. Through suppression of beam wander and spatial noise effects simultaneously, fluctuation of signal intensity and noise reception into PD can be minimized. Thus, as the continuation work in [16, 17], SNR and BER performance enhancement using the OSF is reported through calculations ans experiment.
of PD and maximum noise as well. These lead to degradation of SNR. Hence, the lower SNR contributes to higher order of BER. Moreover, SNR and BER performance degrades in maximum by the presence of turbulence effects. Recently, several methods have been developed to enhance SNR and BER performance on FSO under influenced of atmospheric turbulence. Spatial-diversity (SD), time-diversity (TD), cooperative-diversity (CD), photon detection technique (PDT), amplification method, and adaptive optics (AO) have been investigated so far in order to solve turbulence effects intensively [10-15]. Those methods pay great concern to minimize degradation SNR and BER performance. Generally, those aforementioned methods implement DD for retrieving a signal without an optical treatment previously in a receiver plane. Contrary to the benefit of FSO that has low-cost implementation, those aforementioned methods are quite complex and high-cost. SD offers enhancement SNR and BER performance with multiple system of transmitter and receiver that requires complex electronics of equal gain combiner [10]. TD provides method of signal transmission in multi-periode of time that also requires complex signal processing in the receiver system [11]. CD offers smart combination of spatial- and time-diversity that also requires complex algorythm as well [12]. PDT offers higher sensitivity for lower signal while noise does not taken into account to be suppressed optically [13]. Optical amplification that uses erbium-doped fiber amplifier commonly, also does not provide optical method to enhance signal intensity with minimum noise [14]. Moreover, AO offers enhancement of signal intensity with processing of optical propagation technique but beam wander does not taken into consideration as the serious problem to be suppressed [15]. By taking into consideration that beam wander and spatial noise effects can be suppressed optically at focus spot of receiver lens, the OSF can be implemented as a detection method before signal is received by PD. Thus, implementation of the OSF for suppressing noise that is caused by turbulence effects is the motivation of this work in order to enhance SNR and BER performance.In this paper, the OSF is implemented on FSO of full-duplex transmission at wavelength of 1550 nm. It is a simple- and low-cost method for suppression of beam wander and spatial noise effects. It can be integrated with the aforementioned methods such as optical amplification or SD. It also has competitive benefit for bit rate capacity processing in comparison to TD. The characteristics of turbulence effects are random phenomena and independent process as well. Meanwhile, turbulence effects cannot be treated as a separate process in optical propagation. Thus, beam wander and spatial noise effects cannot be solved separately in order to enhance SNR and BER performance. Regarding those, the OSF is designed to suppress beam wander and spatial noise effects simultaneously. The OSF is composed of cone reflector and pinhole [16] that is installed on focus spot of receiver lens before PD. Cone reflector is designed to suppress beam wander that has random angle of focus spot through directed reflectance radially into pinhole diameter [17]. Pinhole is designed to suppress spatial noise through governing Fresnel diffraction on focus spot. Through suppression of beam wander and spatial noise effects simultaneously, fluctuation of signal intensity and noise reception into PD can be minimized. Thus, as the continuation work in [16, 17], SNR and BER performance enhancement using the OSF is reported through calculations ans experiment.2. Noise Suppression to Enhance SNR and BER Performance Using the OSF
- In Fig. 1, conceptually, the OSF [16, 17] has benefit among ideal of aperture averaging [18] and DD [19]. Technically, ideal of aperture averaging receives incident of optical propagation on receiver lens through multiple reception where
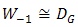 . Statistically, it produces narrowest noise bandwidth with highest probability of signal intensity. DD that has a requirement for lower diameter of receiver lens than incident of optical propagation where
. Statistically, it produces narrowest noise bandwidth with highest probability of signal intensity. DD that has a requirement for lower diameter of receiver lens than incident of optical propagation where 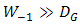 produces wider noise bandwidth and lower probability of mean irradiance. In comparison to DD, the OSF that has reception of optical propagation
produces wider noise bandwidth and lower probability of mean irradiance. In comparison to DD, the OSF that has reception of optical propagation 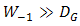 also through suppression of beam wander and spatial noise effects produces competitive probability of signal intensity with minimum noise bandwidth. However in comparison to ideal of aperture averaging, the OSF has some advantages that are simplicity for reception of optical propagation as in DD, competitive probability of signal intensity, and narrow noise bandwidth.
also through suppression of beam wander and spatial noise effects produces competitive probability of signal intensity with minimum noise bandwidth. However in comparison to ideal of aperture averaging, the OSF has some advantages that are simplicity for reception of optical propagation as in DD, competitive probability of signal intensity, and narrow noise bandwidth.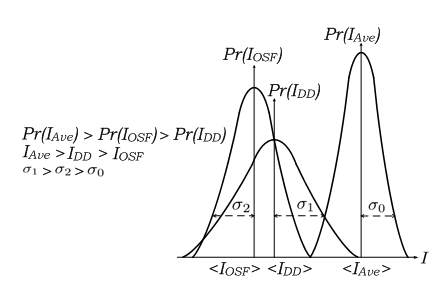 | Figure 1. The probability of mean irradiance and noise bandwidth for ideal of aperture averaging 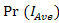 , direct detection , direct detection 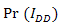 , and the OSF , and the OSF 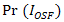 on FSO on FSO |
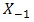 is focused onto pinhole radius
is focused onto pinhole radius 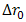 of
of 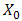 . Focus spot that coincidence on
. Focus spot that coincidence on 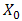 goes fading where fluctuation of signal intensity goes higher and falls below
goes fading where fluctuation of signal intensity goes higher and falls below 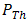 . Unfortunately, beam wander also leads misdetection into PD frequently. In order to suppress noise, The OSF governs Fresnel diffraction and reflectance of beam wander on focus spot before PD. The mean of signal intensity as the output of the OSF at
. Unfortunately, beam wander also leads misdetection into PD frequently. In order to suppress noise, The OSF governs Fresnel diffraction and reflectance of beam wander on focus spot before PD. The mean of signal intensity as the output of the OSF at 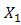 under atmospheric turbulence is given below [17],
under atmospheric turbulence is given below [17], 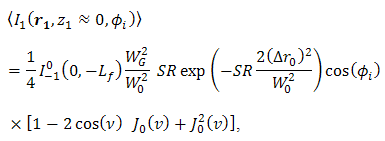 | (1) |
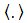 denotes mean value. In Eq. (1),
denotes mean value. In Eq. (1), 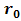 ,
, 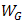 ,
, 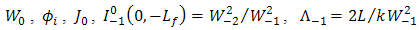
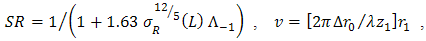
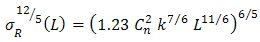 , and
, and 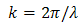 are radius coordinate at
are radius coordinate at 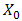 , the effective aperture radius of receiver lens on
, the effective aperture radius of receiver lens on 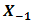 , focus spot radius, reflectance beam wander angle from cone reflector into pinhole diameter with respect to optical axiz
, focus spot radius, reflectance beam wander angle from cone reflector into pinhole diameter with respect to optical axiz 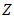 as shown in Fig. 2, Bessel function of the first kind, free-space irradiance of optical propagation that incident on receiver lens of
as shown in Fig. 2, Bessel function of the first kind, free-space irradiance of optical propagation that incident on receiver lens of 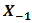 , the effective of optical propagation that incident on receiver lens for path length
, the effective of optical propagation that incident on receiver lens for path length 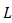 , Sthrel ratio, spatial frequency at radius
, Sthrel ratio, spatial frequency at radius 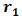 on
on 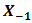 as the function of spacing distance
as the function of spacing distance 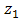 , Rytov variance for propagation path length
, Rytov variance for propagation path length 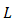 , and wave number, respectively. In Eq. (1),
, and wave number, respectively. In Eq. (1), 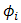 that is reflectance angle from cone reflector for incident beam wander angle
that is reflectance angle from cone reflector for incident beam wander angle 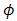 has a range of
has a range of 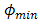 to
to 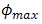 as stated below [17],
as stated below [17], 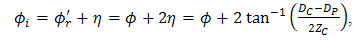 | (2) |
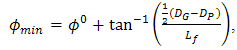 | (3) |
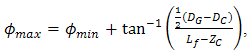 | (4) |
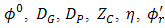 , and
, and 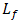 are maximum angle of focus spot from receiver lens of
are maximum angle of focus spot from receiver lens of 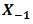 that incident at
that incident at 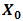 for condition of non-turbulent atmosphere, hard diameter of receiver lens, pinhole diameter, tilt angle of cone reflector, reflectance angle with respect to tilt plane of cone reflector, and length of focus spot, respectively.Turbulence effects that arise in optical propagation lead to fluctuation of signal intensity and maximum noise modulation. As shown in Eq. (1), Sthrel ratio characterizes beam wander and spatial noise on incident of optical propagation
for condition of non-turbulent atmosphere, hard diameter of receiver lens, pinhole diameter, tilt angle of cone reflector, reflectance angle with respect to tilt plane of cone reflector, and length of focus spot, respectively.Turbulence effects that arise in optical propagation lead to fluctuation of signal intensity and maximum noise modulation. As shown in Eq. (1), Sthrel ratio characterizes beam wander and spatial noise on incident of optical propagation 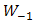 . Beam wander that arises also causes beam spreading where focus spot
. Beam wander that arises also causes beam spreading where focus spot 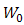 moves wider arround the optical axis
moves wider arround the optical axis 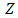 randomly. Hence, focus spot experiences long-term beam spreading. Meanwhile, short-term beam spreading or spatial noise also arises as well. The signal intensity in focus spot goes lower as stated in Eq. (1) by term of
randomly. Hence, focus spot experiences long-term beam spreading. Meanwhile, short-term beam spreading or spatial noise also arises as well. The signal intensity in focus spot goes lower as stated in Eq. (1) by term of 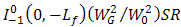 . It means signal intensity goes fading where fluctuates randomly by the presence of beam wander and spatial noise. Hence, PD produces minimum of signal power and maximum noise. The OSF which consists of pinhole with radius of
. It means signal intensity goes fading where fluctuates randomly by the presence of beam wander and spatial noise. Hence, PD produces minimum of signal power and maximum noise. The OSF which consists of pinhole with radius of 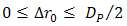 governs diffraction at
governs diffraction at 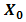 . As shown by Eq. (1), pinhole produces near-field distribution of Fresnel diffraction at
. As shown by Eq. (1), pinhole produces near-field distribution of Fresnel diffraction at  of
of  . By those mechanism, signal intensity
. By those mechanism, signal intensity 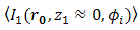 from pinhole is minimum of noise modulation.By suppression of beam wander and spatial noise effects on focus spot, PD receives fundamental component of diffraction in optimum since
from pinhole is minimum of noise modulation.By suppression of beam wander and spatial noise effects on focus spot, PD receives fundamental component of diffraction in optimum since 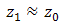 and
and 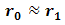 . It produces the mean of signal power
. It produces the mean of signal power 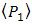 as stated below [17],
as stated below [17],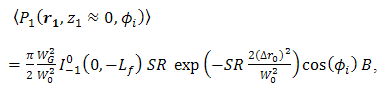 | (5) |
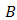 is the circular aperture function of pinhole that is given below [17],
is the circular aperture function of pinhole that is given below [17],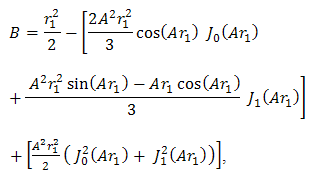 | (6) |
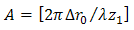 and
and 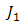 is Bessel function of second kind. In comparison to DD [18, p.459],
is Bessel function of second kind. In comparison to DD [18, p.459], 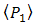 in Eq. (5) is increased by term of
in Eq. (5) is increased by term of 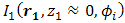 . The mean of signal power from the OSF is produced higher by PD. Term of
. The mean of signal power from the OSF is produced higher by PD. Term of 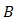 in Eq. (5) works in optimum for noise suppression where
in Eq. (5) works in optimum for noise suppression where  . Term of
. Term of 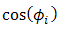 in Eq. (5) also provides suppression of beam wander in order to minimize misalignment detection that is caused by random displacement of focus spot. It means, the OSF suppresses beam wander and spatial noise effects simultaneously. Thus, PD produces optimum of signal power with minimum noise.Regarding enhancement of received signal power
in Eq. (5) also provides suppression of beam wander in order to minimize misalignment detection that is caused by random displacement of focus spot. It means, the OSF suppresses beam wander and spatial noise effects simultaneously. Thus, PD produces optimum of signal power with minimum noise.Regarding enhancement of received signal power 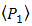 by PD in Eq. (5) as the compensation for confinement of signal intensity fluctuation in narrow region of pinhole through reflectance of cone reflector,
by PD in Eq. (5) as the compensation for confinement of signal intensity fluctuation in narrow region of pinhole through reflectance of cone reflector, 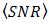 degradation can be minimized by the OSF.
degradation can be minimized by the OSF. 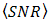 is increased by suppression of signal power ratio,
is increased by suppression of signal power ratio, 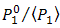 . The OSF minimizes those ratio in order to enhance
. The OSF minimizes those ratio in order to enhance 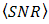 as given below [20],
as given below [20], 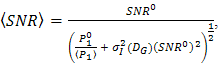 | (7) |
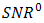 and
and 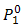 are optimum value of
are optimum value of 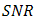 and signal power
and signal power 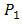 in the absence of atmospheric turbulence, respectively. In Eq. (7), the irradiance flux variance
in the absence of atmospheric turbulence, respectively. In Eq. (7), the irradiance flux variance 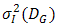 has range value of 0-1 for weak to strong turbulence level. Frequently, signal power
has range value of 0-1 for weak to strong turbulence level. Frequently, signal power 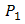 falls below
falls below 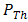 . The OSF enhances value of
. The OSF enhances value of 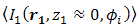 . Thus PD produces signal power
. Thus PD produces signal power 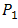 beyond
beyond 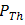 . Signal power ratio
. Signal power ratio 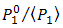 is decreased by the OSF as stated below,
is decreased by the OSF as stated below,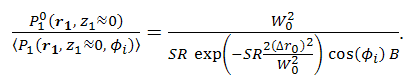 | (8) |
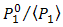 produces
produces 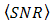 that approximate to
that approximate to 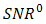 . In comparison to DD that
. In comparison to DD that 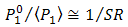 [18, p. 460], this ratio is decreased into minimum value by the OSF as shown in Eq. (8). Thus, the OSF gives advantage to minimize signal power ratio
[18, p. 460], this ratio is decreased into minimum value by the OSF as shown in Eq. (8). Thus, the OSF gives advantage to minimize signal power ratio 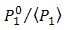 by suppressing beam wander and spatial noise effects simultaneously.Generally, probability density function uses gamma-gamma distribution
by suppressing beam wander and spatial noise effects simultaneously.Generally, probability density function uses gamma-gamma distribution 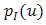 as the channel model for FSO at atmospheric turbulence [18, p. 462].
as the channel model for FSO at atmospheric turbulence [18, p. 462]. 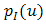 is the probability of signal unit
is the probability of signal unit 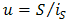 that is influenced by
that is influenced by 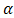 and
and 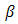 as the representations of small- and large-scale of atmospheric turbulence, respectively.
as the representations of small- and large-scale of atmospheric turbulence, respectively. 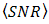 enhancement by the OSF minimizes the probability of
enhancement by the OSF minimizes the probability of 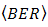 . Based on [20],
. Based on [20], 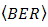 can be suppressed into lower order through
can be suppressed into lower order through 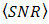 enhancement. Furthermore,
enhancement. Furthermore,  of OOK modulation method is derived from [20] with regards to integral solution in [21].
of OOK modulation method is derived from [20] with regards to integral solution in [21].  is stated below,
is stated below,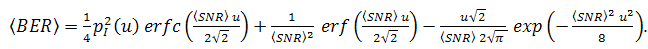 | (9) |
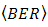 in Eq. (9) is determined by
in Eq. (9) is determined by 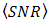 and
and 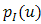 . In order to achieve lower order of
. In order to achieve lower order of 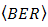 under turbulence effects,
under turbulence effects, 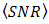 must be increased higher. Since the OSF suppresses noise, signal intensity
must be increased higher. Since the OSF suppresses noise, signal intensity 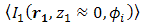 increases higher than in DD. Hence, PD produces optimum of signal power
increases higher than in DD. Hence, PD produces optimum of signal power 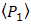 rather than noise. It means the OSF decreases the signal power ratio of
rather than noise. It means the OSF decreases the signal power ratio of 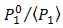 in order to enhance
in order to enhance 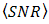 . Furthermore, by the improvement of
. Furthermore, by the improvement of 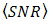 ,
, 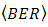 also decreases into lower order as well. In comparison to DD,
also decreases into lower order as well. In comparison to DD, 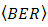 is produced lower by the OSF, since
is produced lower by the OSF, since 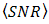 is increased by suppression of
is increased by suppression of 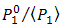 as stated in Eq. (8).
as stated in Eq. (8). 3. Experimental Set-up
- In Fig. 3, the experiment of FSO with full-duplex transmission implement wavelength,
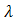 of
of 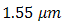 . Bit rate transmission of 1 Gbps with OOK modulation is also used. Optical propagations are separated into box of turbulence simulator (BTS). For reference, optical propagation of backward-directed from beam collimator BC-1 into receiver lens-1 is conditioned with non-turbulent media. Optical propagation of forward-directed of from beam collimator BC-2 into receiver lens-2 is induced by turbulence media in BTS. The properties of optical propagation are
. Bit rate transmission of 1 Gbps with OOK modulation is also used. Optical propagations are separated into box of turbulence simulator (BTS). For reference, optical propagation of backward-directed from beam collimator BC-1 into receiver lens-1 is conditioned with non-turbulent media. Optical propagation of forward-directed of from beam collimator BC-2 into receiver lens-2 is induced by turbulence media in BTS. The properties of optical propagation are 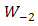 of
of 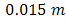 ,
, 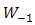 of
of 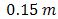 , and
, and 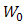 of
of 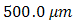 .
. 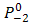 of
of 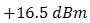 is transmitted out from BC-2 into receiver lens-2. The properties of receiver lens are
is transmitted out from BC-2 into receiver lens-2. The properties of receiver lens are 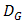 of
of 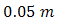 and
and 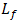 of
of 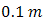 .
. 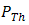 of
of 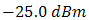 is
is 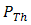 for PD-1 and PD-2. The optical power meter (OPM) and BER tester are used on experiment for
for PD-1 and PD-2. The optical power meter (OPM) and BER tester are used on experiment for 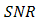 and
and 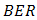 measurements, respectively.
measurements, respectively.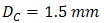 and
and 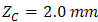 , the OSF is designed with various pinhole diameter that are
, the OSF is designed with various pinhole diameter that are 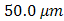 ,
, 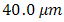 ,
, 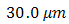 , and
, and 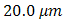 for
for 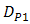 ,
, 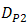 ,
, 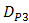 , and
, and 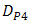 , respectively. Based on Eqs. (3) and (4) for
, respectively. Based on Eqs. (3) and (4) for 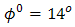 and both contant values
and both contant values 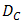 and
and 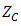 , the range of beam wander
, the range of beam wander 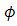 that can be received by cone reflector is
that can be received by cone reflector is 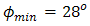 to
to 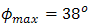 . In order to produce optimum reflection at 1.55 µm, the OSF is made from material of silver [22]. Furthermore, in order to achieve Fresnel diffraction, the OSF is installed on focus spot of receiver lens where pinhole is at
. In order to produce optimum reflection at 1.55 µm, the OSF is made from material of silver [22]. Furthermore, in order to achieve Fresnel diffraction, the OSF is installed on focus spot of receiver lens where pinhole is at 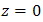 on
on 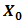 and PD is placed on
and PD is placed on 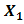 near to pinhole output of the OSF where spacing distance
near to pinhole output of the OSF where spacing distance 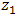 is at the order of
is at the order of 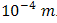 .
.4. Results and Discussion
- The calculations of
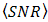 and
and 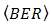 for DD and the OSF are shown in Figs. 6 and 7.
for DD and the OSF are shown in Figs. 6 and 7. 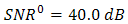 is chosen as reference for analysis. The calculations are based on values of index structure,
is chosen as reference for analysis. The calculations are based on values of index structure, 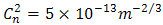 . The properties of optical propagation are set based on the experiment. Based on the
. The properties of optical propagation are set based on the experiment. Based on the 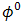 ,
, 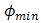 , and
, and 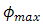 that are stated in Eqs. (3) and (4),
that are stated in Eqs. (3) and (4), 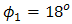 ,
, 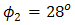 , and
, and 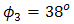 are chosen as beam wander angles.
are chosen as beam wander angles. 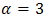 and
and 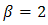 are set constant for calculations.
are set constant for calculations. 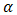 is chosen higher than
is chosen higher than 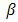 , since it is dominant factor for SNR and BER performance degradation under atmospheric turbulence.In Figs. 5 and 6, the performance of DD degrades in maximum by the presence of beam wander and spatial noise effects where
, since it is dominant factor for SNR and BER performance degradation under atmospheric turbulence.In Figs. 5 and 6, the performance of DD degrades in maximum by the presence of beam wander and spatial noise effects where 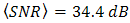 and
and 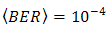 . The OSF improves
. The OSF improves 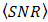 degradation that presents in DD.
degradation that presents in DD. 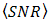 increases linear as
increases linear as 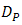 of the OSF goes lower for beam wander angles of
of the OSF goes lower for beam wander angles of 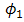 ,
, 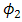 , and
, and 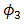 . The performance of FSO for
. The performance of FSO for 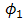 is better than at
is better than at 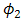 and
and  . Beam wander angle
. Beam wander angle 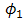 is at the range that is received by pinhole directly without reflectance of cone reflector. The range of beam wander angle for direct reception by pinhole is
is at the range that is received by pinhole directly without reflectance of cone reflector. The range of beam wander angle for direct reception by pinhole is 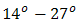 . While range of beam wander angle for reflectance by cone reflector is
. While range of beam wander angle for reflectance by cone reflector is 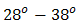 . However, for
. However, for 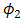 and
and 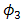 SNR and BER performance is achieved better than DD. Recalled Eq. (8),
SNR and BER performance is achieved better than DD. Recalled Eq. (8), 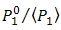 determines value of
determines value of 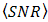 . Thus, the OSF produces lower value of
. Thus, the OSF produces lower value of 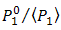 for lower
for lower 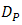 .
. 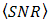 performance for the OSF is better than DD since
performance for the OSF is better than DD since 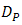 goes lower as well. The OSF improves
goes lower as well. The OSF improves 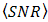 through suppression of beam wander and spatial noise effects simultaneously. It governs Fresnel diffraction as can be seen by the circular aperture function of pinhole
through suppression of beam wander and spatial noise effects simultaneously. It governs Fresnel diffraction as can be seen by the circular aperture function of pinhole 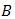 that is stated in Eq. (6). Hence the OSF minimizes
that is stated in Eq. (6). Hence the OSF minimizes 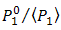 since
since 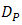 goes lower. Even for larger pinhole diameter
goes lower. Even for larger pinhole diameter 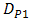 ,
, 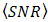 is produced higher by the OSF than DD for
is produced higher by the OSF than DD for 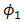 ,
, 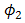 , and
, and 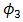 . The OSF also improves
. The OSF also improves 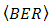 degradation as
degradation as 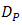 goes lower as well. It produces higher
goes lower as well. It produces higher 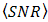 in order to achieve lower order of
in order to achieve lower order of 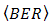 for
for 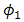 ,
, 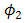 , and
, and 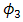 as well. Suppression of beam wander and spatial noise effects by the OSF is achieved through minimizing signal power ratio
as well. Suppression of beam wander and spatial noise effects by the OSF is achieved through minimizing signal power ratio 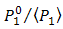 as shown by Eq. (8).
as shown by Eq. (8). | Figure 5. The calculation results where 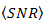 vs. vs. 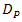 is from the OSF for is from the OSF for 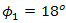 , , 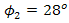 , and , and 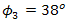 , , 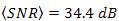 is from DD and is from DD and 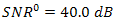 |
 | Figure 6. The calculation results where 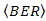 vs. vs. 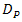 is from the OSF method for is from the OSF method for 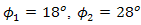 , and , and 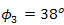 , ,  is from DD, and is from DD, and 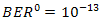 |
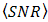 vs.
vs. 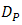 for DD and the OSF are shown.
for DD and the OSF are shown. 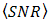 of DD is 34.9 dB. Regarding
of DD is 34.9 dB. Regarding 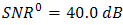 , this performance quite degrades by the presence of beam wander and spatial noise modulation that arise randomly in BTS. The OSF improves those degradation in scale of 2.5 dB, 3.5 dB, 3.8 dB, and 4.2 dB for
, this performance quite degrades by the presence of beam wander and spatial noise modulation that arise randomly in BTS. The OSF improves those degradation in scale of 2.5 dB, 3.5 dB, 3.8 dB, and 4.2 dB for 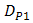 ,
, 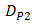 ,
, 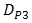 , and
, and 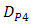 , respectively.
, respectively. 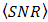 improvement by the OSF is better than DD. But
improvement by the OSF is better than DD. But 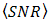 improvement by different of
improvement by different of 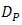 do not contribute to higher value. The OSF for each of
do not contribute to higher value. The OSF for each of 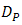 tend to produce the same value of
tend to produce the same value of 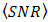 . For example,
. For example, 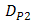 and
and 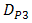 do not produce high different value of
do not produce high different value of 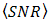 . Only
. Only 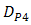 produces highest
produces highest 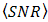 that approximates
that approximates 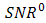 . However, the experiment result in Fig. 8 shows the same trend as the calculation in Fig. 6, that
. However, the experiment result in Fig. 8 shows the same trend as the calculation in Fig. 6, that 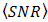 is increased by the OSF since
is increased by the OSF since 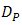 goes lower.In Fig. 8, experiment results of
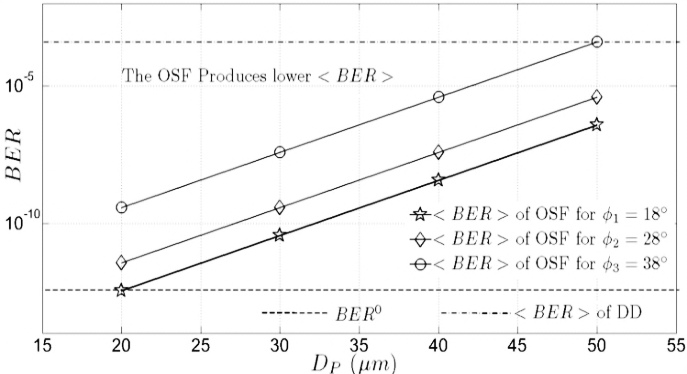
goes lower.In Fig. 8, experiment results of 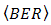 vs.
vs. 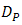 for DD and the OSF method are shown.
for DD and the OSF method are shown. 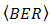 of DD is produced at 1.910-5. Regarding
of DD is produced at 1.910-5. Regarding 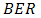 = 1.010-13 at
= 1.010-13 at 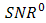 , those performance quite degrades also. The OSF improves
, those performance quite degrades also. The OSF improves 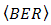 degradation in scale of 10-2, 10-4, 10-6, and 10-7 for
degradation in scale of 10-2, 10-4, 10-6, and 10-7 for 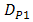 ,
, 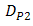 ,
, 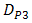 , and
, and 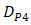 , respectively.
, respectively. 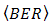 improvements by different of
improvements by different of 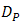 are significant. They achieve in scale range of 10-1 to 10-5 for
are significant. They achieve in scale range of 10-1 to 10-5 for 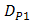 to
to 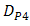 .
. 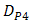 produces
produces 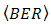 that approximate to
that approximate to 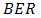 at
at 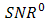 . Moreover, Fig. 8 shows the same trend as Fig. 7, that
. Moreover, Fig. 8 shows the same trend as Fig. 7, that 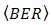 is decreased to lower order by the OSF since
is decreased to lower order by the OSF since 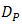 goes lower as well.
goes lower as well.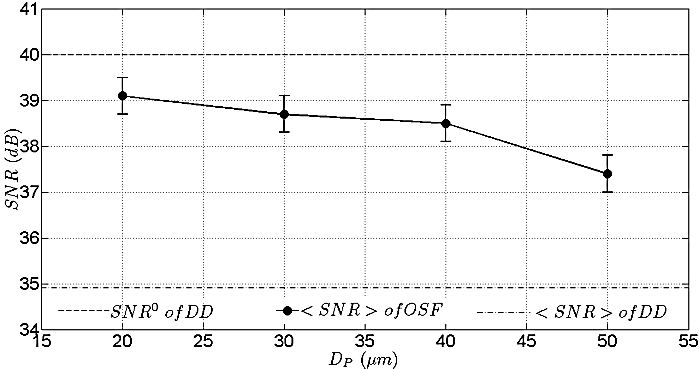 | Figure 7. The experiment results where 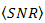 vs. vs. 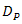 from the OSF, from the OSF, 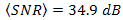 is from DD, and is from DD, and 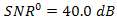 |
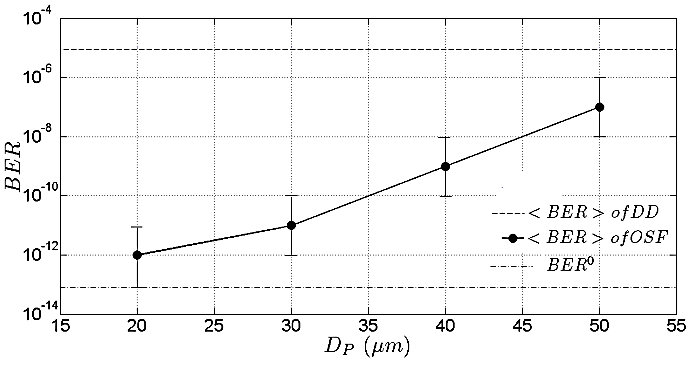 | Figure 8. The experiment results where vs. 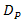 is from the OSF, is from the OSF, 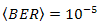 is from DD, and is from DD, and 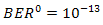 |
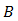 can be optimized by considering the ratio of pinhole diameter and spacing distance between the OSF and PD. Thus, term of
can be optimized by considering the ratio of pinhole diameter and spacing distance between the OSF and PD. Thus, term of 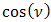 in Eq. (2),
in Eq. (2), 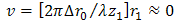 leads to
leads to 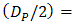
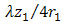 . Furthermore, for larger beam wander angle
. Furthermore, for larger beam wander angle 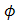 , the tilt angle of cone reflector
, the tilt angle of cone reflector 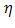 also has significant contribution to reflect random displacement of focus spot. In order to fullfill this, parameters for cone reflector must consider term of
also has significant contribution to reflect random displacement of focus spot. In order to fullfill this, parameters for cone reflector must consider term of 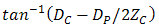 of Eq. (2). Thus, maximum tilt angle of cone reflector is
of Eq. (2). Thus, maximum tilt angle of cone reflector is 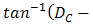
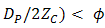 . Hence, wider range of
. Hence, wider range of 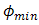 to
to 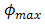 can be received by cone reflector largely. By considering those aforementioned conditions, the OSF brings some advantages such as noise suppression in optimum and fading in minimum. Moreover, misalignment of detection that is caused by larger beam wander angle can be minimized by cone reflector as well.
can be received by cone reflector largely. By considering those aforementioned conditions, the OSF brings some advantages such as noise suppression in optimum and fading in minimum. Moreover, misalignment of detection that is caused by larger beam wander angle can be minimized by cone reflector as well. 5. Conclusions
- The OSF enhances SNR and BER performance on FSO as shown by results of calculation and experiment. In comparison to DD, SNR and BER performance by the OSF is produced better. Based on both calculations and experiment,
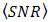 increases higher and
increases higher and 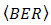 also decreases to lower order as pinhole diameter of the OSF goes lower. From the calculations, the range of beam wander angle that can be received by cone reflector of the OSF is
also decreases to lower order as pinhole diameter of the OSF goes lower. From the calculations, the range of beam wander angle that can be received by cone reflector of the OSF is 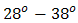 while for
while for 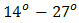 is received by pinhole directly without reflectance. Thus, the OSF receives beam wander angle in the range of
is received by pinhole directly without reflectance. Thus, the OSF receives beam wander angle in the range of 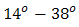 . From the experiment,
. From the experiment, 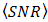 increases from 2.5 to 4.2
increases from 2.5 to 4.2 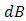 and
and 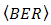 decreases from 10-7 to 10-12. The OSF suppresses noise in narrow area for minimizing fluctuation of signal intensity. Thus, PD produces optimum of signal power and minimum noise.
decreases from 10-7 to 10-12. The OSF suppresses noise in narrow area for minimizing fluctuation of signal intensity. Thus, PD produces optimum of signal power and minimum noise. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors acknowledge Mr. Surma in Opto-Electrotechnique and Laser Application of Universitas Indonesia for his contribution in Lab. facilities.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML
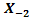 , a receiver lens plane
, a receiver lens plane 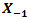 , the OSF plane
, the OSF plane 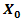 , PD plane
, PD plane 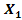 , and
, and 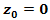 is the origin where optical propagation from laser source directs from
is the origin where optical propagation from laser source directs from 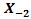 into
into  [17]
[17]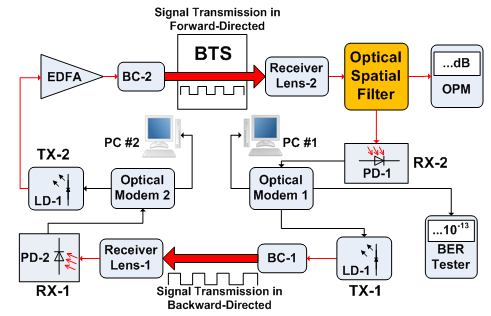
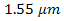 that transmitting 1 Gbps of data rate on turbulence media of BTS while for measurement of performance, OPM (Optical Power Meter) and BER tester are used
that transmitting 1 Gbps of data rate on turbulence media of BTS while for measurement of performance, OPM (Optical Power Meter) and BER tester are used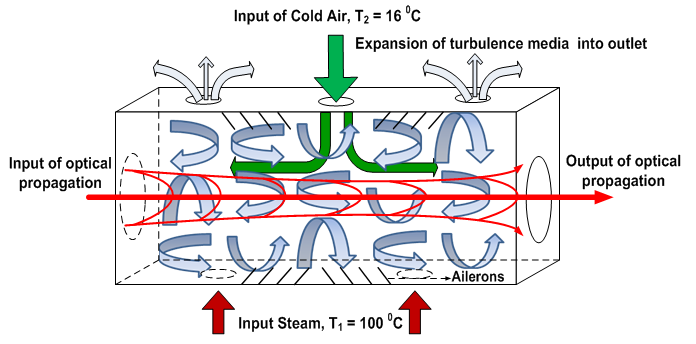
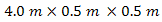 where turbulence media is constituted by the mixing flows of high temperature-gradient. The steam at
where turbulence media is constituted by the mixing flows of high temperature-gradient. The steam at 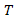 of
of  with low-speed and cold air at
with low-speed and cold air at 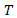 of
of 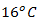 with wind-speed of
with wind-speed of 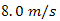 are flowed altogether along the BTS volume. Furthermore, the flows are broken-up by ailerons that is installed along the path length inside BTS [17]
are flowed altogether along the BTS volume. Furthermore, the flows are broken-up by ailerons that is installed along the path length inside BTS [17]