-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Nursing Science
p-ISSN: 2167-7441 e-ISSN: 2167-745X
2019; 9(2): 41-52
doi:10.5923/j.nursing.20190902.03

Effect of the Educational Package Based on Health Belief Model Regarding Lifestyle among Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Amira R. Said 1, Fatma K. Aly 2
1Assistant Professor of Obstetrics & Woman’s Health Nursing, Faculty of Nursing, Benha University, Egypt
2Lecturer of Obstetrics & Woman’s Health Nursing, Faculty of Nursing, Benha University, Egypt
Correspondence to: Amira R. Said , Assistant Professor of Obstetrics & Woman’s Health Nursing, Faculty of Nursing, Benha University, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Gestational diabetes mellitus is associated with potentially harmful effects on the mother and fetus. Thus the identification of gestational diabetes mellitus offers a chance to improve pregnancy outcomes and identify women to target dietary & lifestyle health promotion. Aim of this research was to examine effect of the educational package based on health belief model regarding lifestyle among women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Design: A quasi experimental design was utilized. Setting: This research was conducted in Obstetrics and Gynaecological Outpatient Clinic at Benha University Hospital. Sample: A purposive sample of (70) randomly women divided into (35) intervention group and (35) control group. Tools: Data were collected through three main tools: A self-administered questionnaire to assess women’s general characteristics and knowledge regarding gestational diabetes mellitus, health belief model scale, and health promoting lifestyle Profile II. Results: showed that the mean age in both control and study group were 27.94 ± 4.20 & 28.4 ± 4.57 years respectively. (42.9%) of control group and (45.7%) of intervention group had healthy lifestyle level toward gestational diabetes mellitus before gestational diabetes mellitus educational package implementation, compared to 4 weeks after gestational diabetes mellitus educational package implementation (45.7%) of control group and the majority (94.3%) of intervention group had healthy lifestyle level toward gestational diabetes mellitus. Conclusion: There was a positive statistically significant correlation between total knowledge score, total lifestyle score and total health belief model score before & four weeks after gestational diabetes mellitus educational package implementation (p<0.001). Recommendations: Establishing strategies to enhance the women’s understanding of healthy lifestyle by applying this model to a large sample in various obstetrics and gynecological outpatient clinics.
Keywords: Gestational diabetes, Health belief model, Health-promoting lifestyle
Cite this paper: Amira R. Said , Fatma K. Aly , Effect of the Educational Package Based on Health Belief Model Regarding Lifestyle among Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus, International Journal of Nursing Science, Vol. 9 No. 2, 2019, pp. 41-52. doi: 10.5923/j.nursing.20190902.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Globally the prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is increasing health problem, and it is considered one of the most prevalent complications of pregnancy accompanied with high health cares and significant economic costs [1]. It has increased by more than 30% within one or two decades in a number of countries including developing countries. Many developing countries are currently suffering from the increasing burden of type 2 diabetes mellitus, gestational diabetes mellitus and comorbidities which used to predominantly burden developed countries. [2]. One of the major problems with GDM is that there few symptoms and the pregnant woman is usually unaware that she has GDM until it is diagnosed at routine prenatal screening. However, despite being virtually symptom free, serious pregnancy complications are associated with GDM that include macrocosmic babies, risk of injuries during delivery, shoulder dystocia, fetal death in the uterus, respiratory distress syndrome, hypoglycaemia,, hyper bilirubinemia, cardiomyopathy, perinatal mortality due to unexplained anomalies [3]. In addition, certain symptoms such as high blood pressure, premature delivery, infectious complications, hydramnios, pre-eclampsia and higher likelihood of incidence of type II diabetes in postpartum period could involve the mother [8, 9].High prevalence rate of GDM depends on several factors, such as the high maternal age at pregnancy, obesity, multiple pregnancies, polycystic ovarian syndrome, insufficient sleep and sedentary lifestyle [10]. Lifestyle is one of the main factors that can play a key role in preventing or treating gestational diabetes. Nowadays, more than 70% of diseases are believed to be somewhat related to woman’s lifestyle. Gestational diabetes prevention strategies have recently focused on adequate information for promoting healthy lifestyles in women by encouraging physical activity and promoting healthy nutrition [11].The lifestyle for pregnant women of diabetics is severely affected and it can positively correlate with the predicted mortality rate of pregnant women with diabetes. The criterion for determining the health-related lifestyle of pregnant women with diabetes is the self-assessment of pregnant women. Healthy lifestyle incorporating the complementary components of health protecting and health promoting behavior, health protecting behavior is directed toward reducing health risks by decreasing the individuals probability of encountering illness or injury, whereas health promoting behavior is appositive approach to living directed toward sustaining or increasing the individual's level of well- being, self-actualization and personal fulfillment [7].A verity of studies, concentrate on the efficiency and effectiveness of educational interventions regarding changing preventive behaviours through educational package based on health belief model (HBM) such as increased levels of nutritional knowledge, blood glucose test, controlling the glucose, reducing the need for insulin, and reducing consumption of carbohydrates, additionally it is believed that with proper training, can be up to 80% of diabetes be prevented [4]. The educational package are designed where the learner is free to choose what, how, when and where to learn. This flexibility is an importance characteristic in open learning process. The learner is getting familiar more and more to non-formal mode of education [5]. The health belief model was developed to explain preventive health behaviours rather than behaviours in time of illness. The aim of this model is increasing the perception of individuals about a health threat and directs their behaviours towards health. This model is a comprehensive pattern which represents the association between beliefs and behaviours; it has been widely applied to various health behaviours, especially screening behaviours and plays a significant role in prevention of the disease. Therefore, understanding individuals’ viewpoints and beliefs is essential for developing the strategies of controlling diabetes [22].The health belief model assumes that health behaviours are motivated by six structures including: perceived sensitivity; a person's belief in the perception of being in a particular situation, perceived severity: the perception of the extent to which these conditions are serious, the perceived benefits; a person's opinion about the effectiveness of suggested activities to reduce the risk of the effect, perceived barriers; belief about the potential negative aspects of a particular health action, cues to action; accelerating forces that trigger a person's need for action and self-efficacy; a person's confidence in her ability to follow a behaviour [6].Significance of the research:Diabetes mellitus is a major public health concern associated with substantial morbidity, mortality, health care utilization, and costs, it is associated with potentially harmful effects on the mother and the fetus, which can seriously endanger the health of the mother and the fetus. The prevalence of gestational diabetes in the world is between 1 and 14% [12]. Women with a history of GDM have a 35-60% chance of developing type 2 diabetes with most of these women developing the disease within ten years of the diagnosis of GDM [13]. Few studies have been conducted on educational intervention based on HBM regarding lifestyle of diabetic pregnant women inspite of the high rate of pregnant women with diabetics in the country and it is effect of lifestyle on their condition. Moreover, the Health Belief Model is one of the models that widely used as a guiding framework for health behaviour interventions, especially GDM behaviour [6]. Therefore, this research was proposed to examine the effect of educational package based on HBM on knowledge, health beliefs and healthy lifestyle among women with GDM.Aim of the research:The aim of this research was to examine effect of the educational package based on HBM regarding lifestyle among women with gestational diabetes mellitus.Hypothesis:To achieve the aim of this research, the following research hypotheses were formulated: H1. Pregnant women with GDM, who will receive the educational package based on HBM, will have a better knowledge than those who don't. H2. Pregnant women with GDM, who will receive the educational package, will show higher HBM scores than those who don't. H3. Pregnant women with GDM, who will receive the educational package based on HBM, will have healthy lifestyle during pregnancy than those who don't.
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Materials
- Research design:A quasi- experimental research design was utilized to conduct the research with pre/post program. Setting: This research was conducted in obstetrics & gynecological outpatient clinic at Benha university hospital which includes one room divided into diagnostic and examination areas. As well as, waiting area for women admission where the researcher interviewed the recruited women to implement GDM educational package. This clinic provides services of obstetrics and gynaecological care, family planning counselling or for any outpatient procedures. It starts from 9.00 Am to 12.00 Pm. Sample:Sample type: A purposive sampleSample size: Seventy women among those attending the above mentioned setting. Size of the sample was completed during 6 months/three days per week. Women were randomly divided into two groups (control group = 35 women who received routine care and intervention group = 35 women who received GDM educational package). Inclusion criteria:- Pregnant women with GDM and agree to participate in the research.- Aged between 18 and 35 years.- Gestational age between 24 and 28 weeks.- Women can read and write- Women with no pregnancy complications and free from any medical disorderTools of data collection:Three main tools were used for data collection:-Tool (I). A self-administered questionnaire: It was designed by the researchers after reviewing related literature [14] [15]. And under guidance of supervisions, it was written in an Arabic language in the form of close ended questions and consisted of two parts: Ÿ Part 1- Personal characteristics of women, it consisted of (age, level of education, occupation, weight, height, and body mass index).Ÿ Part 2- Obstetrical history of women, it consisted of (gestational age, number of pregnancies, delivers, & children, and history of abortion).Ÿ Part 3- Women's knowledge regarding GDM:Women's knowledge questionnaire was adapted from [15] and was translated into Arabic language by the researchers. It was a (7) item questionnaire designed to measure knowledge of pregnant women regarding GDM. The (7) close-ended items relate to the known GDM risk factors, GDM is a risk factor for future type 2 diabetes mellitus, effects of pregnancy on DM, effects of DM on pregnancy, the long-term health consequences for the children born to GDM mothers, blood sugar test performed after delivery for GDM mothers and how long should the blood sugar test be performed after delivery.Each item was assigned a score of (2) given when the answer was completely correct, a score (1) was given when the answer was incompletely correct and a score (0) was given when the answer was don't known. The participant who checked an item (yes) was given (2), while the one who checked an item (No) was given (1) and the one who checked an item (Don't know) was given (0).Women' total knowledge score was classified as the following:- Adequate knowledge when the total score was ≥ 60% of total score- Inadequate knowledge when the total score was < 60% of total score. Tool (II). Health Belief Model Scale (HBM Scale):Health Belief Model was adapted from [16] and was translated into Arabic language by the researchers. The HBM scale designed to measure women psychological readiness to take positive action in diabetes. This scale is theoretically based on The HBM which includes perceived susceptibility/seriousness to type 2 diabetes (13 items), perceived benefits (3 items), perceived barriers to adopt healthy lifestyle behaviours (4 items) and self-efficacy to adopt healthy lifestyle behaviours (28 items). Scoring: The health belief model has a three point Likert-type scale ranging from Disagree (1), Sometimes (2), and Agree (3).Women' total HBM score was classified as the following:- Low HBM when the total score was less than 60%.- Moderate HBM when the total score was 60% to less than 75%.- High HBM when total score was 75% to 100%.Tool (III). Health-Promoting Lifestyle Profile II (HPLPII):The health-promoting lifestyle was adapted from [17] and was translated into Arabic language by the researchers. It measures the frequency of self-reported healthy behaviours focusing on four main areas including nutrition, physical activity, stress management and health responsibility. The 34 item questionnaire has four subscales which focus on different areas of lifestyle behaviours. Nutrition (1-9 items) includes the selection & consumption of a healthy diet according to guidelines of the Food Guide Pyramid which are important for health and well-being while physical activity (10-17 items) determine participation in regular activity. Another area of this tool is Stress management (18-25 items) which is the identification & implementation to control or reduce tension. while the final subscale of this tool is the health responsibility (26-34 items) which is a belief of one‘s accountability for their own health and well-being through education, attention to own health, and being informed when seeking professional assistance.Scoring: The HPLPII has a three point Likert-type scale ranging from Never (1), Sometimes (2), and Always (3). An overall score of the health promoting lifestyle is a calculation of the mean of responses from all items. In addition, subscale scores are calculated using the mean for each set of questions of the subscale. Women' total lifestyle score was classified as the following:- Unhealthy lifestyle when the total score was less than 60%.- Healthy lifestyle when the total score was 60-100%
2.2. Method
- The research was conducted according to the following steps:Approval:This research was conducted under the approval of the Faculty of Nursing Ethical Committee, Benha University. An official permission was obtained from the directors of the pre-mentioned setting to conduct the research after explaining its purpose.Tools validity:The tools of data collection were submitted to a panel of three nursing experts in the field of obstetrics and genecology to test the content validity, modification were carried out according to the panel' judgments on clarity of sentences and appropriateness of the content. Tools reliability:The reliability was done by Cronbach's Alpha coefficient test which revealed that each of the three tools consisted of relatively homogenous items as indicated by the moderate to high reliability of each tool was (0.86). Ethical considerations:Each women were given explanations about the purpose of the research and was informed that participation was voluntary and they were free to withdraw from the research at any time before the completion of it, those who agreed to complete in this research were asked to sign a consent form before starting the data collection. Confidentiality was ensured throughout the research process, and the women were assured that all data were used only for research purpose.Pilot study:The pilot study was carried out. It involved ten percent of the total sample (7 women) to test the clarity and applicability of the research tools as well as estimation of the time needed to fill the questionnaire. Women involved in the pilot not excluded from the research. The results of the pilot study:After conducting the pilot study, it was found that:- The tools were clear and applicable; however, few words were modified - Tools were relevant and valid.- No problem that interferes with the process of data collection was detected.- Following this pilot study the tools were made ready for use.Field work:To fulfil the aim of the research, the following phases were adopted. Interviewing & assessment phase, planning phase, implementation phase and evaluation phase. These phases were carried out from the beginning of April, 2018 and completed at the end of September, 2018 covering six months. The researchers visited the previously mentioned setting three days/week, (Sunday, Tuesday, Thursday), from 9.00 Am to 12.00 Pm. A. Interviewing & assessment phase: This phase encompassed interviewing both control and intervention group. Interviewing begin first with control group to avoid bias then with intervention group. At the beginning of interview the researcher greeted the woman, introduced herself to each woman included in the research, explained the purpose of the research and provided the woman with all information about the research such as (purpose, duration, & activities) and take oral consent to participate in the research. Data were collected by the researcher through administration of the tools (Self-administered questionnaire, Health Belief Model Scale, Health-Promoting Lifestyle Profile II and Women's Knowledge regarding GDM Sheet) to each woman. Average time for the completion of each woman interview was around (25-30 minutes). Average number collected was (1-3) women per day. B. Planning phase:Based on the results obtained from the intervention group during the assessment phase, the GDM educational package was developed. Sessions number and its contents, different methods of teaching, and instructional media were determined accordingly to intervention group. The general objective of the GDM educational package program was to improve essential knowledge and healthy lifestyles for women regarding GDM.C. Implementation phase:Implementation of the educational intervention for each group took (8) weeks period. Data were collected 3days /week. Pregnant women in the control group only received routine care by hospital staff while the pregnant women in the intervention group received routine care by hospital staff, in addition to participated in GDM educational package through three scheduled sessions. Sessions were implemented according to the date obtained from the women during her antenatal follow-up and each session took about (45-60) minutes. At the beginning of the first session women were oriented with the GDM educational package contents. Each woman was informed about the time of the next session at the end of session. The subsequent session started by a feedback about the previous session and the objectives of the new session, using simple Arabic language to suit women' level of understanding. At the end of each session, mothers questions were discussed to correct any miss understanding. The first session began during the women' first visit that follow the interviewing phase and included, definition, risk factors and the effect of pregnancy on DM. The second session began during the women' second visit that follow the interviewing phase and included, the effect of DM on pregnancy and long-term health consequences for the children born to GDM mothers. The third session began during the women' third visit that follow the interviewing phase and included, the role of a proper lifestyle in coping with gestational diabetes. These sessions were repeated to each subgroup of (1-3) women. Different methods of teaching were used such as discussion, demonstration, re demonstration and brainstorming. Instructional media included video contain all contents of sessions and educational package about GDM and based on mothers healthy lifestyles regarding GDM were distributed to all recruited women in the research to achieve its objectives. D. Evaluation phase:The effectiveness of the GDM educational package was evaluated 4 weeks after of implementation phase using the same format of tools which used during the assessment phase for both groups. Evaluation started first with control group then with intervention group to avoid bias. At almost time the researcher followed women via telephone. Also, according to principles of ethics in research, the women of the control group were provided by the GDM educational package that prepared by the researcher after evaluation.Statistical design:Data was collected, presented in tabular form Percentages. were calculated for qualitative data and x2 for test of significance, mean and standard deviations were calculated for quantitative data using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS version 20) for statistical analysis. Limitation of the research study:- Sometimes the sessions were protracted due to noise and other individuals' interruption.
3. Results
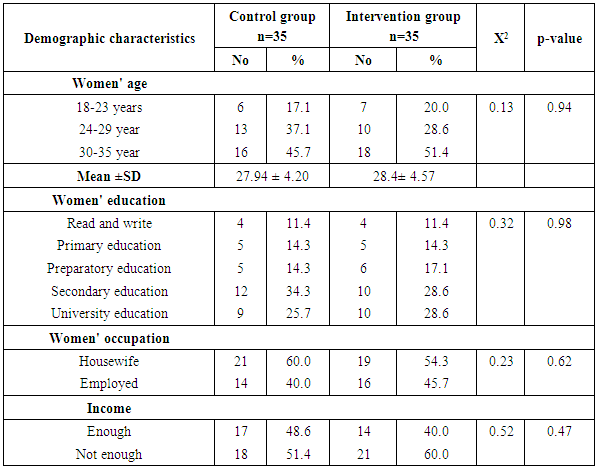
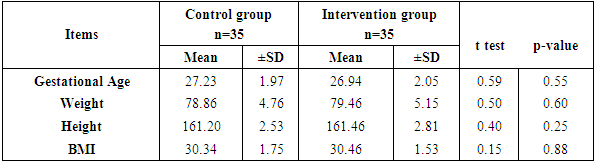
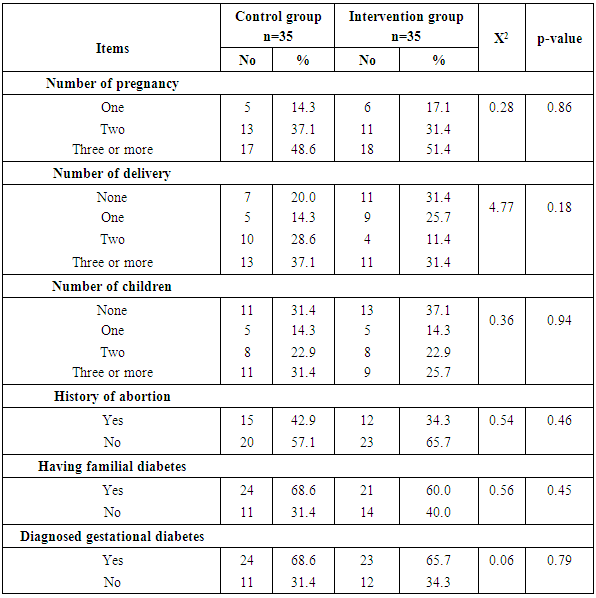
- Table (1) clarifies that 45.7% of control and 51.4% intervention groups were in age group (30-35 years) with the mean age for them 27.94 ± 4.20 & 28.4 ±4.57 years respectively. Concerning level of education, it was clear that 34.3% of control groups and 28.6% of intervention group had secondary education. (60%) of the control group and (54.3%) of the intervention group were housewife. According to the income, (51.4%) of control group and (60%) of intervention group had not enough income. That is the two groups under research homogenous.Table (2) shows that, the mean gestational age of both intervention and control groups were 26.94 ± 2.05w and 27.23 ± 1.97w respectively. The mean weight of both intervention and control groups were 79.46 ± 5.15kg and 78.86 ± 4.76kg respectively, the mean height of both intervention and control groups were 161.46 ± 2.81cm and 161.20 ± 2.53cm respectively. In addition the mean body mass index in both intervention and control groups were 30.46 ± 1.53kg / m2 and 30.34 ± 1.75kg / m2 respectively. Table (3) illustrates distribution of studied sample regarding obstetrics history. Concerning frequency of pregnancy, it was obvious that 48.6% of control group, and 51.4% of intervention group were pregnant for three times or more. Regarding number of delivery, 37.1% of control group and 31.4 of intervention group were delivered for three times or more. Concerning number of children, it was clear that 31.4 of control group compared to 37.1% of intervention group hadn’t have children. As regards history of abortion, it was found that; 57.1% of control group and 65.7% of intervention group hadn’t have history of abortion. 68.6% of control group and 60.0% of intervention group had familial diabetes. Moreover, 68.6% of control group compared to 56.7% of intervention group were previously diagnosed with GDM.Table (4) clarifies that in the intervention group there was a highly statistically significant difference regarding all knowledge items before and 4 weeks after GDM educational package implementation (P< 0.000). Meanwhile in control group there was no statistically significant difference regarding all knowledge items before and 4 weeks after GDM educational package implementation.Figure (1) Displays that, (14.3%) of control group and (22.9%) of intervention group had adequate knowledge level toward GDM before GDM educational package implementation, compared to four weeks after GDM educational package implementation (22.9%) of control group and (88.6%) of study group had adequate knowledge level toward GDM.Table (5) demonstrates that in the intervention group there was a highly statistically significant difference regarding all items of health belief model (total perceived seriousness, total perceived benefits, total perceived barriers and total self-efficacy) before and four weeks after GDM educational package implementation (P< 0.000). While in control group there was no statistically significant difference regarding all items of health belief model before and four weeks after GDM educational package implementation.Figure (2) shows that (11.4%) of control group and (8.6%) of intervention group had high HBM scores toward GDM before GDM educational package implementation, compared to (14.3%) of control group and (62.9%) of intervention group had high HBM scores toward GDM four weeks after GDM educational package implementation.Table (6) shows that, in the intervention group there was a highly statistically significant difference in relation to all items of women’s lifestyle regarding GDM (nutrition, physical activity, stress management and health responsibility) before and four weeks after GDM educational package implementation (P < 0.001). On the other hand in control group there was no statistically significant difference in relation to all items of women’s lifestyle regarding GDM before and four weeks after GDM educational package implementation.Figure (3) reveals that, (42.9%) of control group and (45.7%) of intervention group had healthy lifestyle level toward GDM before GDM educational package implementation, compared to (45.7%) of control group and the majority (94.3%) of intervention group had healthy lifestyle level toward GDM four weeks after GDM educational package implementation.Table (7) illustrates that, before GDM educational package implementation there was a positive statistically significant correlation between total knowledge and total lifestyle scores as well as there was no statistically significant correlation between total knowledge and total HBM scores in both control and intervention group. Meanwhile, 4 weeks after GDM educational package implementation, there was a positive statistically significant correlation between total lifestyle score as well as total HBM score and total knowledge score.
|
|
|
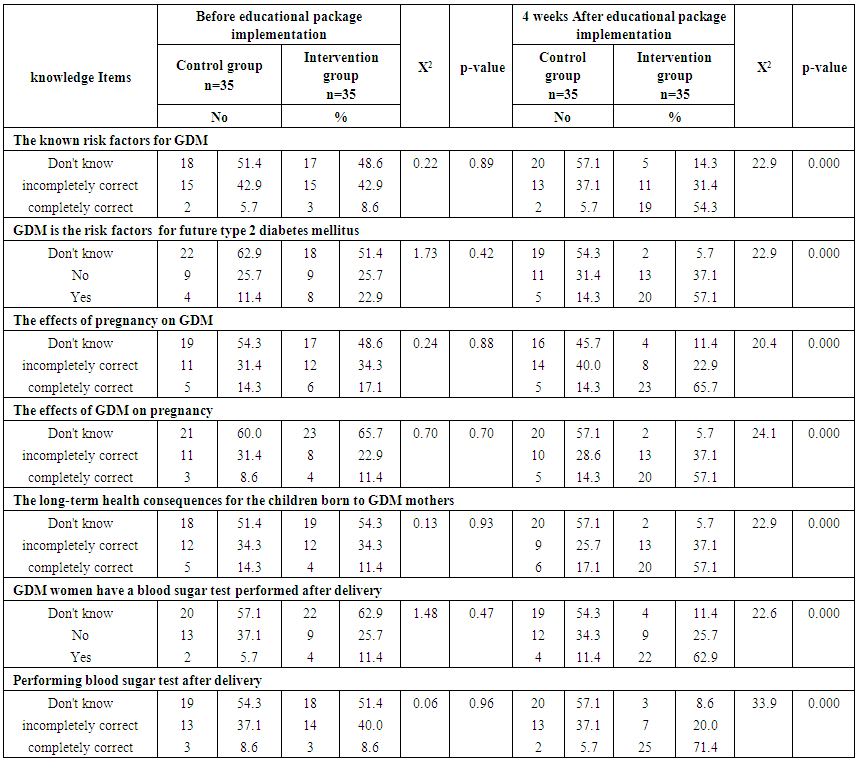 | Table (4). Relation of studied sample regarding their knowledge before and 4 weeks after GDM educational package implementation (n=70) |
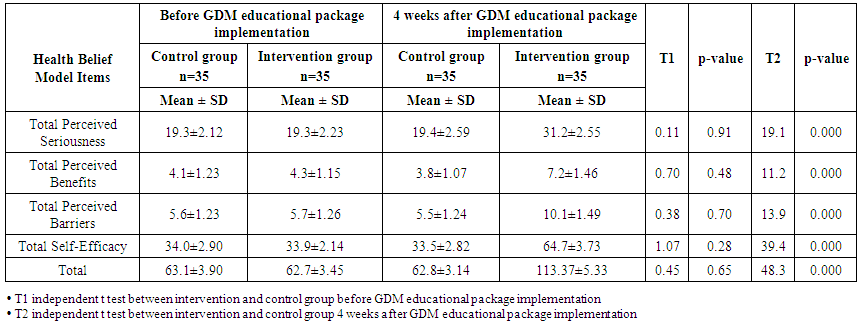 | Table (5). Mean and standard deviation of studied sample regarding their health belief model before and 4 weeks after GDM educational package implementation (n=70) |
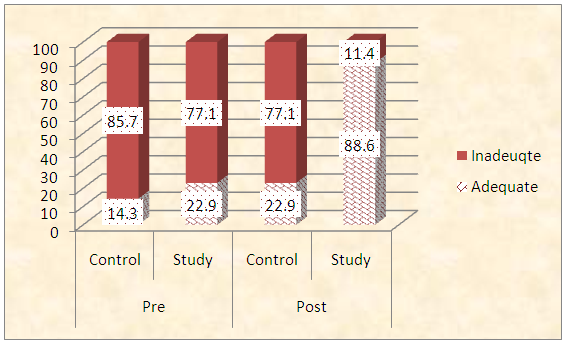 | Figure (1). Frequency distribution of studied sample regarding total knowledge score before and 4 weeks after GDM educational package implementation (n=70) |
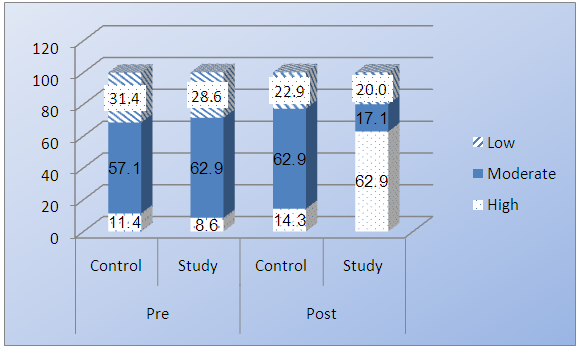 | Figure (2). Frequency distribution of studied sample regarding total HBM scores before and 4 weeks after GDM educational package implementation (n=70) |
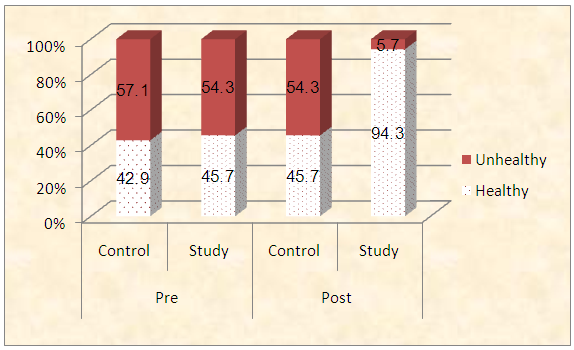 | Figure (3). Frequency distribution of studied sample regarding total lifestyle scores before and 4 weeks after GDM educational package implementation (n=70) |
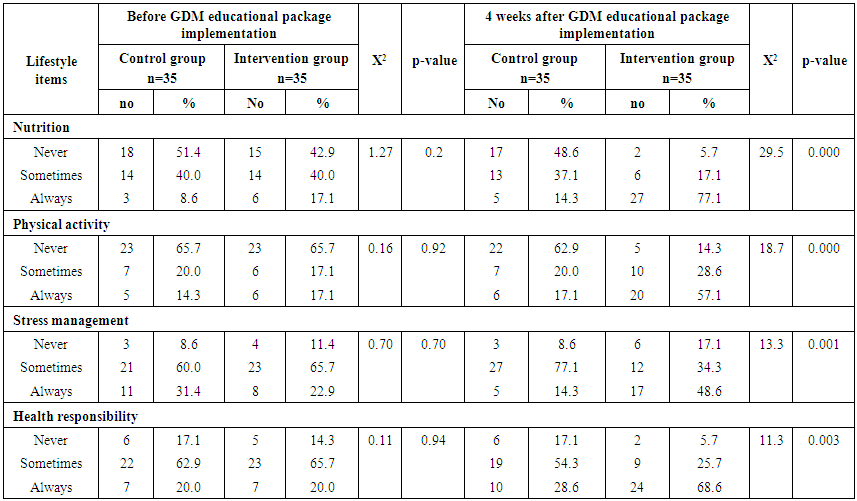 | Table (6). Relation of studied groups regarding their lifestyle before and 4 weeks after GDM educational package implementation (n=70) |
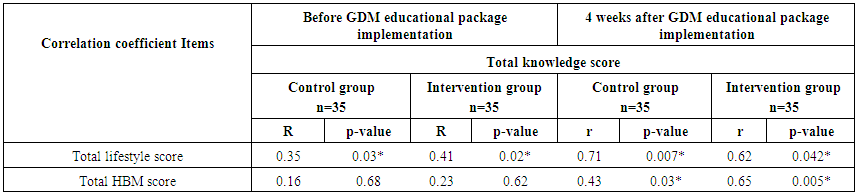 | Table (7). Correlation coefficient between total knowledge, lifestyle, and HBM before and 4 weeks after GDM educational package implementation (n=70) |
4. Discussion
- In this research the researchers attempted to examine the effect of educational package based on health belief model regarding lifestyle among women with GDM. The findings of this research study were approved the research hypotheses.Regarding demographic characteristics of the studied sample, the results revealed that; 45.7% of control and 51.4% intervention groups were in age group (30-35 years) with the mean age for them 27.94 ± 4.20 and 28.4 ±4.57 years respectively. Concerning level of education, it was clear that 34.3% of control groups and 28.6% of intervention group had secondary education. (60%) of the control group and (54.3%) of the intervention group were housewife. According to the income, (51.4%) of control group and (60%) of intervention group had not enough income. These finding matched with [14], who compares lifestyles of women with gestational diabetes and healthy pregnant women and concluded that the mean age of both control and study group were 27.8 ± 4.56 and 28.68 ±3.83 years respectively. The results of the present research showed that there was no statistically significant difference regarding gestational age, weight, height, and body mass index between the intervention and the control group. These results agreed with [18] who studied the educational intervention on preventive behaviours on gestational diabetes in pregnant women and found that there was no significant difference in gestational age, weight, and body mass index in both control and intervention groups.Regarding obstetrics history of the studied sample, the results of this research showed that concerning frequency of pregnancy, it was obvious that 48.6% of control group, and 51.4% of intervention group were pregnant for three times or more. Regarding number of delivery, 37.1% of control group and 31.4 of intervention group were delivered for three times or more. Concerning number of children, it was clear that 31.4 of control group compared to 37.1% of intervention group hadn’t have children. As regards history of abortion, it was found that; 57.1% of control group and 65.7% of intervention group hadn’t have history of abortion. 68.6% of control group and 60.0% of intervention group had familial diabetes. Moreover, 68.6% of control group compared to 56.7% of intervention group were previously diagnosed with GDM. These finding is supported by [27] who study the effect of self-care education program based on "Orem Self Care Model" on quality of life in women with gestational diabetes mellitus and found that 65% of studied women already had a family history of diabetes.Results indicated that, there was a highly statistically significant difference regarding all knowledge items before and 4 weeks after GDM educational package implementation (P< 0.000). Meanwhile in control group there was no statistically significant difference regarding all knowledge items before and 4 weeks after GDM educational package implementation. This improvement in the intervention group's knowledge might be due to pregnant women's active participation and good communication with the researchers who helped them to acquire knowledge. Besides, educational package plays a very important role in helping pregnant women to acquire knowledge regarding GDM. These results agreed with [18] who studied “impact of education on nutrition and exercise on the level of knowledge and metabolic control indicators of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Patients " who reported that the mean level of knowledge increased significantly after training intervention. Moreover, these findings congruent with [19] that studied women’s experiences of living with gestational diabetes in Australia and emphasized on the importance of health professional support to provide insight into the challenges and opportunities for future diabetes risk reduction.In relation to mean and standard deviation of studied groups regarding their health belief model before and 4 weeks after GDM educational package implementation, the results revealed that, there was a highly statistically significant difference regarding all items of health belief model (total perceived seriousness, total perceived benefits, total perceived barriers and total self-efficacy) before and 4 weeks after GDM educational package implementation. These findings are at the same line with [20] who studied “effectiveness of nutrition education based on health belief model during pregnancy on knowledge and attitude of women and showed that there were a significant increase in the mean scores of perceived susceptibility and severity in the intervention group compared to the control group after the intervention.Also, these findings are matched with [21] who studied the effect of an instructional program based on health belief model in decreasing caesarean rate among primiparous pregnant mothers and found that Perceived benefits and improving preventive behaviours have a strong correlation and a better perception of the benefits of a behaviour way to provide an appropriate action. In addition, these results is in accordance with [19] who studied the effect of educational intervention on Preventive behaviours on gestational diabetes in pregnant women: Application of Health Belief Model, who found that the mean scores of all constructs of health belief model in intervention group, three months after intervention, were significantly higher compared with the control group (P<0.05). Moreover, this finding supported by [22] who studied the effect of educational intervention based on the Health Belief Model on quality of life among women with gestational diabetes and showed that after educational programme, the mean scores of knowledge, benefits, barriers, perceived susceptibility and severity, performance, cues to action, and behaviour increased significantly in the intervention group. This may be due to education based on health belief model has a positive effect on the lifestyle of diabetic pregnant women.The results of the present research showed that, there was a highly statistically significant difference in relation to all items of women’s lifestyle regarding GDM (nutrition, physical activity, stress management and health responsibility) before and 4 weeks after GDM educational package implementation in the intervention group, meanwhile, there was no statistically significant difference in relation to all items of women’s lifestyle regarding GDM before and 4 weeks after GDM educational package implementation in the control group. These findings are in agreement with [23] who studied the impact of a self-care education programme on patients with type 2 diabetes and concluded that, continuous monitoring and raising awareness through educational programs can promote behaviours such as exercise, proper diet, etc., and thereby improve the disease.Also, these results agreed with [24] who studied barriers and coping strategies of women with gestational diabetes to follow dietary advice and reported that quick adaptation to dietary management in a short time period created challenges for women with GDM. Stress and anxiety were reported when women talked about following dietary advice. Tailored educational consultation with consideration of the barriers may promote dietary compliance and overall better health.On regard to the total lifestyle score before and 4 weeks after GDM educational package implementation; the current research findings illustrated that, the majority of intervention group had healthy lifestyle level toward GDM before GDM educational package implementation compared to 4 weeks after GDM educational package implementation. This might be due to proper education can increase awareness, improve healthy lifestyle behaviours and decrease potential complications of GDM. These findings consistent with [26] who studied the impact of self-care education on life quality of diabetic patients and showed the positive effect of self-care educational program on quality of life in the intervention group after two months of completion of the intervention. As well as, [27] who studied the effect of a health literacy approach to counselling on the lifestyle of women with gestational diabetes, who reported significant differences in the mean scores of lifestyle and health literacy between the two groups immediately and three weeks after the intervention. Comparing the means showed a higher increase in the mean scores in the intervention group (P<0.001).The present research revealed that before GDM educational package implementation there was a positive statistically significant correlation between total knowledge and total lifestyle scores as well as there was no statistically significant correlation between total knowledge and total HBM scores in both control and intervention group. Meanwhile, 4 weeks after GDM educational package implementation, there was a positive statistically significant correlation between total lifestyle score as well as total HBM score and total knowledge score. This reflected that improvement in knowledge resulted in lifestyle improvement. These results are in agreement with [25], who studied the effect of education on healthy lifestyle behaviours and self-efficacy and proved that the educational approach has a potential to improve quality of life in women with GDM. this may be due to need for consistent education of women, using variety of educational models, as an essential part of diabetes care program that will result in the improvement of women’s life style.
5. Conclusions
- Based on the findings of the current research; the research concluded that research hypotheses are supported and the HBM had a significant effect on improvement of women's life style. There was a positive statistically significant correlation between total knowledge score, total lifestyle score and total health belief model score before and 4 weeks after GDM educational package implementation.
6. Recommendations
- Based on the research findings, the following was recommended:1. Increasing awareness among mothers about importance of healthy lifestyle to reduce complications of GDM 2. Health Believe Model should be an essential part of GDM management.3. Establishing strategies to enhance the women’s understanding of healthy lifestyle by applying this model to a large sample in various obstetrics and gynaecological outpatient clinics.Future researches:1. All nurses in obstetrics & gynaecological outpatient clinic should be informed with the vital Health believe model information about GDM to improve their knowledge and practices toward GDM.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML