-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Nursing Science
p-ISSN: 2167-7441 e-ISSN: 2167-745X
2019; 9(2): 30-40
doi:10.5923/j.nursing.20190902.02

Assess Direction and Satisfaction of Medical, Surgical Nursing Students in the First Year towards Using Social Media for Communication & Study
Abeer Yahia Mahdy1, Mageda A. S. Arafat2, Heba A. Ali1, Zeinab I. Ismael2
1Medical Surgical Nursing Department, Faculty of Nursing, Benha University, Egypt
2Nursing Administration, Faculty of Nursing, Benha University, Egypt
Correspondence to: Abeer Yahia Mahdy, Medical Surgical Nursing Department, Faculty of Nursing, Benha University, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Background: nowadays increasing use of Social media within the nursing study and practice the students should realize its use is attractive in the educational setting. The aim of the study: This study was aimed to assess direction and satisfaction of medical, surgical nursing students in the first year towards using social media for communication & study Subjects and methods: descriptive design utilized to conduct this study. Sitting: The study was held in the medical, surgical department faculty of nursing (1st year) in which student start studying nursing to verify no any factor affecting them. Tools for data collection: The constructed study tools tested, and piloted by the investigator to collect data through two electronic tools. The first tool:- include two parts, part (1) student personnel data and part (2) the direction of students towards social media. The second tool, student satisfaction about using social media in nursing studying. Results: the result showed that most of the students prefer using of social media in their learning and they have positive direction toward using it, positively agreement of most of the students in using the social media in interactivity with peers and the agreement for most of them which refer to satisfaction by using it in academic learning and most of students were satisfied toward using of social media in their learning. Conclusion: Social media is a rising scope within nursing practice, and students can find its use engaging in the educational setting. The current study concluded that most of the students were agree and they satisfied to use of social media in their learning, interactivity with peers, teachers, and they agree of easy use and usefulness of it. In the same time, they prefer the presence of teachers.
Keywords: Nursing students, Social media, Communication, Satisfaction
Cite this paper: Abeer Yahia Mahdy, Mageda A. S. Arafat, Heba A. Ali, Zeinab I. Ismael, Assess Direction and Satisfaction of Medical, Surgical Nursing Students in the First Year towards Using Social Media for Communication & Study, International Journal of Nursing Science, Vol. 9 No. 2, 2019, pp. 30-40. doi: 10.5923/j.nursing.20190902.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Health care professionals use social media to increase virtual communities to share domain knowledge. [46].From vital element in nursing in all areas of activity is Communication, including prevention, treatment, rehabilitation, education, and health promotion [25]. In current years social media has become the most important methods of communication. neglected the distance between people; it provides communication to share ideas and data easily, [34] also it share personal experiences, images, files, send and receive messages, videos and perform conversation and accessing health information [8], Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (AHPRA), 2014, [4, 9]. It is a type of communication electronically through which users inspire online groups to participate in news, information, thoughts and particular messages [29]. It is also defined as the use of web-based tools which link people and qualify them to share information, pictures, videos, and so on [31].Social media as (Facebook, Instagram, and You-Tube, Twitter etc..) facilitate interaction and communication among colleagues and friends. Since the development of Web 2.0, it has become a common component of 21st-century life, which allowed for interactive online interfaces. The broad term of social media comprises several specific types of Web 2.0 technologies including but not limited to wikis (ie, Wikipedia), microblogs (ie, Twitter), blogs, that permit users to join with other individuals and share information [13].Social media has been grown in the last five years, where social media platforms offer reasonable adjuncts to curriculum delivery millennial nursing student, to meet expectation of efficiency and immediate feedback, [51]. Social media has become urgent for the new generation especially undergraduates [16, 52]. The study by [43] assured that this new generation has an internet addiction in general, and particularly with social media [17]. This due to regular use of social media by higher education student in different forms. As shown in the study by [49], about three quadrants (70.1%) of students having been used it nearly an hour per day on social media. Also, Stainbank and Gurr (2016) has told that more than (52.3%) used it one to four times per day and over 40% of them used social media over five times daily [50], While [32] found that 88% of students get them daily, 70.3% used it daily, while 18.1% used it occasionally, only 0.7% never used it [12].As noted by [54] sometimes several students may poor skills and lack of interesting by using any social media in learning, use of social media affected by some barriers and ease of use was essential to students who found it academically beneficial [5]. As suggested by [11, 21], it is essential interference of social media in nursing education. Using social media for deffrent reasons as communication among friends or for share news, but using it in nursing education is insufficient [42]. Learners have a chance to manage their learning environments using social media, and thus become more independent lifelong [45].In recent years the usage of social media by American has risen to 70%. Of the various social media sites, Facebook has recorded more than double the number of subscribers as its nearest competitor, Twitter, with 79% percent of Americans utilizing its services [37]. As stated by [47] about nine in ten of Australians (87%) using Internet daily, more than two thirds 69% of them using social networking website such as Facebook and Twitter daily to shared or sent photos or links. from Advantages of using it for the nursing student, Hopkins (2018) include some benefits of using it, interests include; interaction among students and permit communication with professionals, it easy way to communicate with a team during team projects, easy to search for information, ability to sharing of contents, encourage search and direct the learning process [18].Otherwise the students usage of social media has some negatives; disruptions due to too much use is the most challenging part to the students, and need too many hours, this effect on human relationships; some students post false and inappropriate information which not useful for their reputation as well as the organization as they're a part of trusting excessive on social media, many advantages and disadvantages in healthcare. It is useful tool for cooperation. It provides chances for professionals to interact with their peers [9]. Nurses student can discuss patients care with peers who have similar concerns through online information interchange about options of care on a wide range [26, 39]. Social media program have an impact on nursing educational expertise [26]. It provides clinical education to healthcare professionals; patients can participate in practical seminars and take healthcare support also patients given an opportunity to connect into the discussion, and they can share their own experiences with others [9, 26]. Social media has other disadvantages as; lack of validity of information online, incomplete, informal or not supported by the references, social peer stress, students may fail in the ability of face to face communication [35]. The use of new technology may lead to confusion for nurses during the working time [39]. Social media technologies have become a common method for producing and conserving social relationships [48]. Even though it is supposed that most the nursing students remarkably use social media, the role of it in nursing education has not been thoroughly investigated [55]. So that it is necessary to use social media to decrease stress among nursing student, in first year or first semester, their aged (20 and 24 years) because they do not have experience in health specialties, it is very important to reduce student load and the academic activities, and providing training of nursing students with the reality of their future profession. [27] Education load of Nursing involves practical and theoretical, the mastery of fundamental clinical skills is an essential component of courses leading to registration [44].
1.1. The Aim of the Study
- This study aimed to assess direction and satisfaction of medical, surgical nursing students in the first year towards using social media for communication & study.
1.2. Research Questions
- 1- are the nursing students have access for social media and using technology?2- are there positive students direction toward using it?3- is the nursing student satisfied with it?4- is there a positive correlation among personal data and student direction and satisfaction?
1.3. The Significance of the Study
- The strategy of old clinical nursing teaching is not standardized to theoretical and clinical competency especially nowadays in case of transportation methods, wares, sit in, and political demonstration, and clinical reasoning skills. Acquisition of critical thinking and problem-solving skills among nursing students are difficult to manage with large groups of students. So the new direction for social learning to use social media in learning is important [11].
2. Subjects and Methods
2.1. Research Design
- Descriptive design utilized to conduct this study.
2.2. Study Setting
- The study was done in the medical, surgical department faculty of nursing (1st year), Benha University in which students start studying nursing to verify that no factor affecting them.
2.3. Subjects
- First-year medical-surgical nursing students enrolled in the academic year (2018-2019) in the faculty of nursing, Benha University. With the exclusion of all students who regain the first year and student included in the pilot study the total number included in the study (n=190).
2.4. Tools for Data Collection
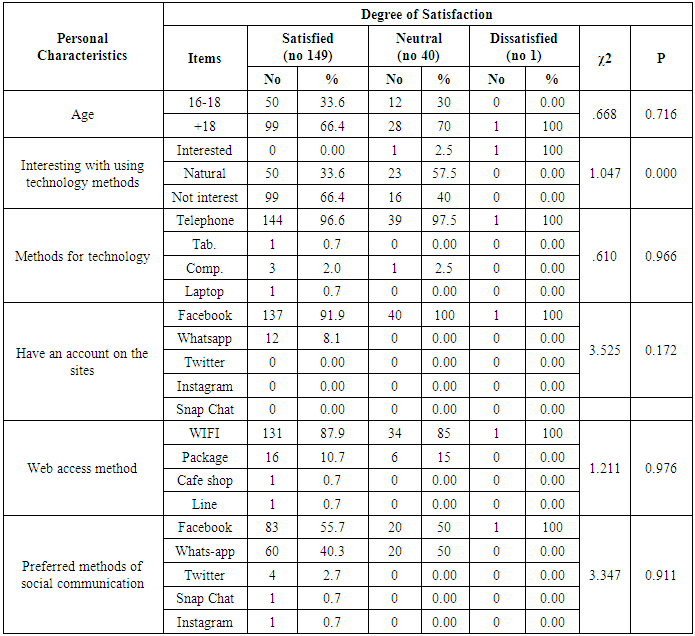
- The constructed study tools tested and piloted by the investigator to collect data through two electronic tools.The first tool:- include two parts; Part (1) student personal data. Which include: (sex, Marital status, Interesting with Using technology Methods, Have a method for tech, have an account on the sites, Web access method, preferred methods of social communication. Part (2) the direction of students towards the social media it include (Student attitudes towards social networking sites and the need to learn them 7 items, evaluation of students' level themselves in the use of social networking sites 8 items, methods used by the student to develop their skills in social networking through the web 8 items, the different options offered by the college to develop the use of technology 10 items.The second tool, student satisfaction about using social media in nursing studying include (using the social media in Interactivity with peers five items, using social media perceived ease of using six items, using social media perceived usefulness ten items, students' satisfaction nine items.
2.5. Pilot Study
- Pilot study conducted on 10% of total study participants (Medical surgical 1 st year nursing students at the faculty of nursing, Benha University, to judge the feasibility of doing the study, it's objectivity and ability of the tool to elicit the desired information, appropriateness, to estimate time needed for data collection, and to identify obstacles and problems that may encounter in data collection, needed modifications will be done according to these subject's responses from the study.
2.6. Content Validity
- It is done based on the result of pilot study and expertise advice after making a jury by five medical, surgical and teaching expertise.
2.7. Fieldwork
- After verifying that the medical-surgical student (the first year not effective use social media in their communication & study. this was known by staff researchers teaching these student. After that reviewing all available literature to develop the tools for data collection construct background about social media connection and its benefit in nursing studying. The researchers take permission from the supervisor of the first year. After that put the tools in electronic form in Google drive (G.mail). The researchers have explained the aim of the study to a students in first-year and explain the method of filling tool to the students and how to verifying the student filled it. This after confirm that all student have registered in first year group on, to answer student questions and give them instruction about time of tool which was about not more than 10 minutes, after that give advising for using social media in communication and study nursing, this through researchers and first-year supervisor. This done through academic advising after that the data collected in one week. After that researcher not receive any answered tool, the tool by the Arabic language because of new terminology in social media and also to facilitate student understanding, data collected at the end of the first term.
2.8. Legal Aspects of Ethical Considerations
- 1. Informed consent from participants to participate in the study and confidentialities will be assured.2. All rights of participants will be secured as the right to withdraw from the research at any time.3. The participant's opinions will be kept secret and will be used only for the study.4. No any harmful for a student.
2.9. Statistical Design
- After data collection, by electronic method Data was analysed electronically through frequent distribution only. after that it organized it by the researcher in the table to show correlation and p-Value the statistical package for social science (SPSS) program is used. It was also expressed as frequency and percentage, the probability of errors (p-value) test was used to examine the relationship between qualitative variables.The significance of results was as the following:1. When p>0.05 there was no statistically significant differences.2. When p <0.05 there were statistically significant differences.3. When p<0.01 there were statistically significant differences.4. When p<0.001 there was a highly statistically significant difference.
3. Results
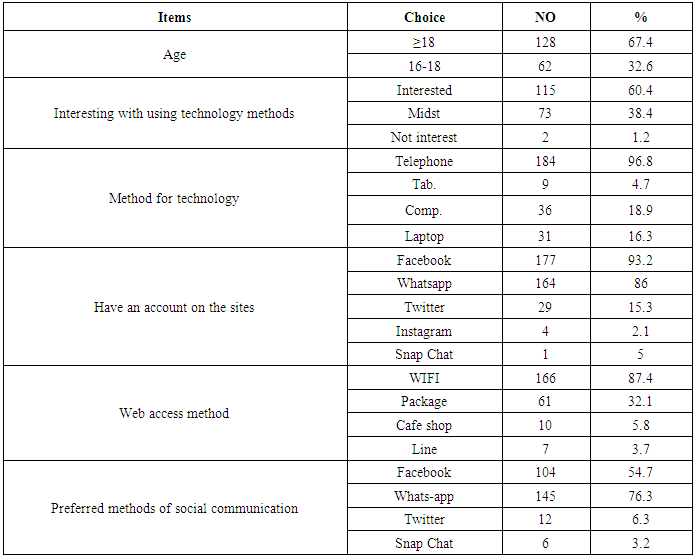
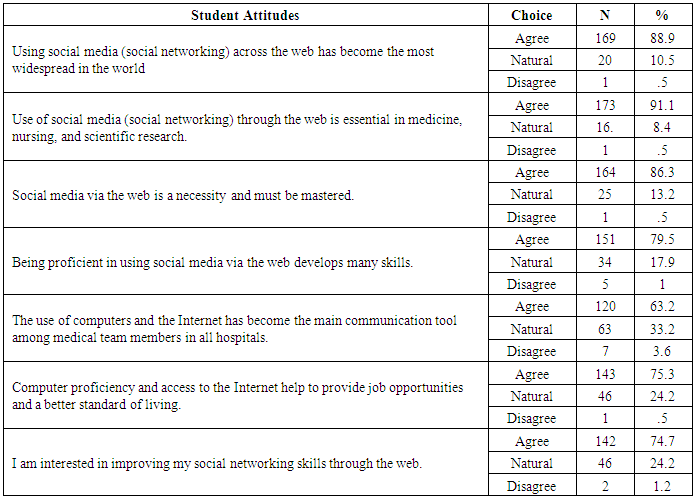
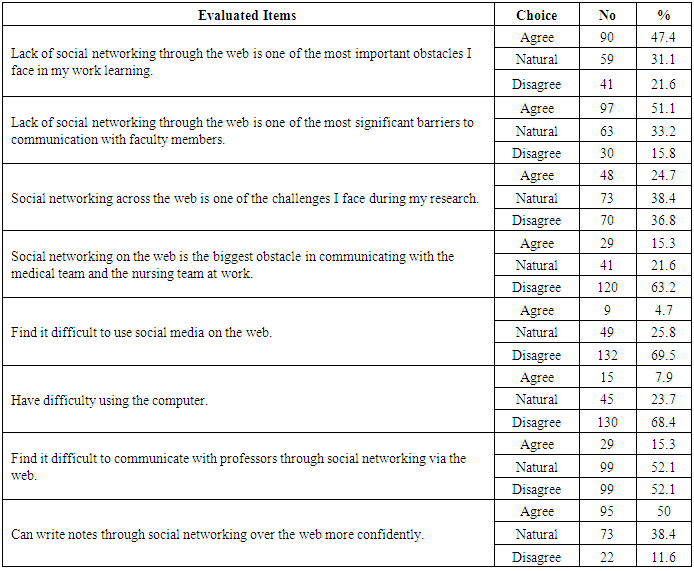
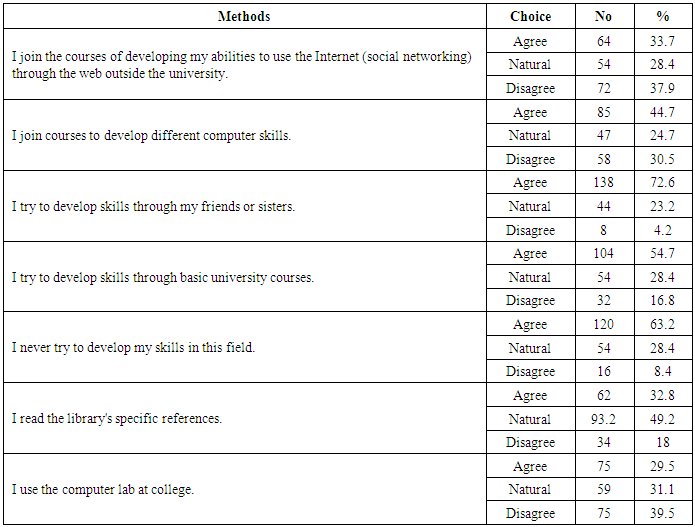
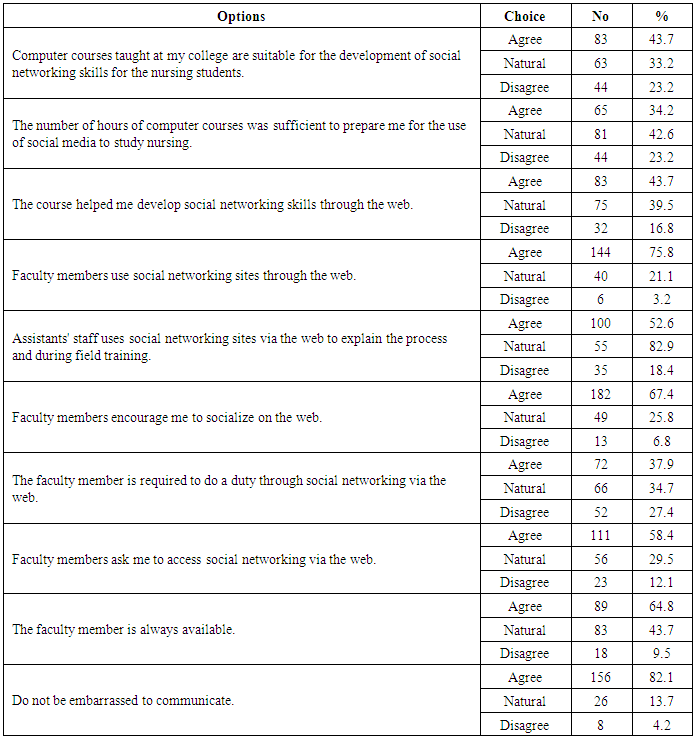
- Table (1) showed that, more than two thirds of the studied subjects (67.4%) their age≤18, (60.4%) of them are interesting with using technology methods, most of them (96.8%) are having telephone, and the large percentage (93.2%) are having Facebook account, (87.4%) were accessed to internet by WIFI and about three quarters of them (76.3% preferred the whats-app in social communication. As regard to the direction of students towards social media communication (Table 2) demonstrated that large percentage of first-year nursing students have a positive direction toward social media and the need to learn them. The results clarified that, the large proportion of students agreed of all items (as; using social media and social networking across the web has become the most widespread in the world, it is essential in medicine, nursing and scientific research, etc.….) and they agree that being proficient in using social media via the web develops many skills, and computer proficiency is essential. It is evident in Table (3) that, about half (51.1%) of students were agreed that lack of social networking through the web is one of the most important obstacles they face in their learning, and it is one of the important barriers to communication with faculty members or with professors, but more than two thirds (63.2%) of them were disagreed when they asked about if social networking on the web is the biggest obstacle in communicating with the medical team and the nursing team at work, or they find it difficult to use social media on the web (69.5%) disagreed. It was noted that (Table 4), the most of students agreed that they develop their skills in social networking through joining courses (44.7%), helping their friends or family members (72.6%), engaged in the basic university courses (54.7%) and (63.2%) of them never try to develop their skills in this field. In relation to frequency distribution of the methods used by the student to develop their skills in social networking through the web, moreover, (37.9%) of students not accepted to join courses outside the university, (29.5%) use the computer lab at college only. The most of students agreed that the college offered different options to develop the use of technology and faculty members assist them, available all time and encourage them to use of technology and socialize on the web (Table 5). As regard to students 'opinions about the use of social media, it was presented in (Figure 2) the positive agreement of most of the students in using the social media perceived the usefulness.Concerning to students satisfaction among using of social media (Figure 1) and (Table 3), the result displayed that most of first year medical surgical nursing students (78%) were satisfied with by using it in academic learning and most of them their age above 18 years while they not interested with using technology methods, (96.6%) having telephone, using Facebook account and prefer using it as the most preferred methods of social communication.Part (1) Personnel data electronic questioner sheet
|
|
|
|
|
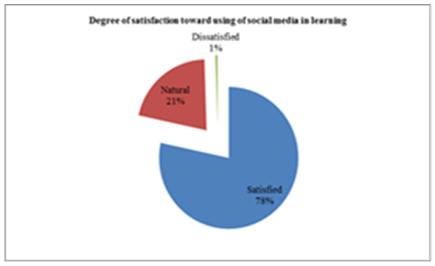 | Figure 1 |
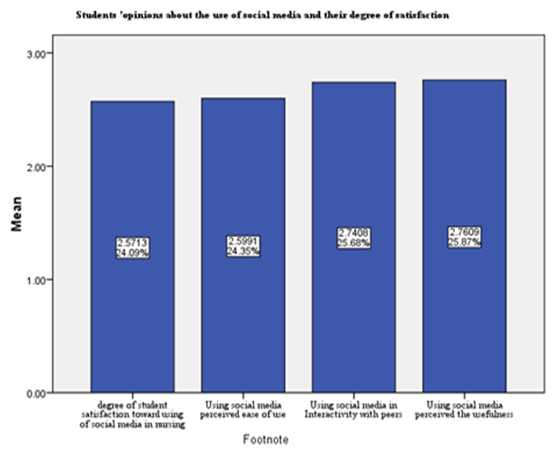 | Figure 2 |
|
4. Discussion
- The present study aimed to first; advising medical, surgical nursing students in the first year towards using social media in communication & study. Second; assess students satisfaction about using social media in nursing communication and study. As shown in the present result (60.4%) of medical, surgical first-year nursing students are interesting with using technology methods, may be due to the new generation of students was became aware to understand that new technology and social media are useful in their learning. Likewise, a meta-analysis of medical students in seven countries discovered that 60-75% using social media, 20% of them used for sharing academic information [14]. These findings supported by [36] study about social media in nursing education, who reported that above 80% of nursing students see technology as part of their everyday life. In the same direction [3, 1] evidenced that all over the world, the application of social media and internet became a fundamental part of lives of young people especially in adolescents, undergraduates, and high school students. As shown in the present study, 96.8% of students have a telephone while 4.7% only have Tap, this may be due to the low economic level of most of them and also may be due to the portability of mobile device due to its size and it is possible to everyone to learn how to use the essential functions of the invention. In agreement with the present finding [10] confirmed that the use of mobile technology is a significant surge in higher education to enhance communication and connection between, students and educators.In school, mobile devices are not only used as a tool to foster information, encourage and emphasis engagement but it moreover strong the transmission of the course content [22]. The large percent 93.2% and 86% have an account on Facebook while Snap chat 3.2% and Twitter 6.3%, may be due to the easy using of WhatsApp and Facebook and also most of the friends use this method of communication, in addition, Twitter is comparatively new teaching, and learning tool in higher education and evidence supporting its use is limited. This finding is similar to previous studies [6, 7] and [56]. Facebook was a popular educational site for students. In similarly the study by [30] mentioned that among the different social media platforms, Facebook was the most commonly used social media networking site. The study was carried out in Nepal on health science students appeared a higher percentage (80.8%) of them realized the role of Facebook in gaining information [20]. In disagreement with the present finding [15] revealed that Twitter had been the most popular platform reported in the literature.Social media use has risen within all age group through the last ten years [23] and [37]. In concurrence, [57], 66% of the world's, about 7.5 billion people hold a mobile phone. 50% of international people are online, 37% of internet users are particularly at least one social network, 2.459 billion people or 34% of people worldwide oncoming social media from a mobile apparatus. Concerning [22] displayed the highest sectional social media users are in North American, with around sixty –six percent of them linked through social networks, fifty-eight percent of them work consequently from a mobile apparatus. Approximately 89% of adults in the United States are online now with 72% of smartphone proprietorship [39]. In contrast when the Pew Research Center began to follow up on social media use in 2005, 5% only of Americans used asocial network, while in January 2017, around 79% of adults in United States use of Facebook, 28% use Instagram, 26% use of Pinterest, 25% use LinkedIn, and 21% use Twitter [36, 37].The results of the present study showed that a significant percentage of first-year nursing students have a positive direction toward social media and the need to learn them. This finding was supported by the study in Jordan [2] on undergraduate student nurses' attitudes towards using social media websites, who confirmed the same result that a significant proportion of nursing students attending both public and private universities have a positive attitude toward using social media for academic purposes. The results clarified that the large proportion of students agreed on all items (as; using social media and social networking across the web has become the most widespread in the world, it is essential in medicine, nursing and scientific research, is a necessity and must be mastered, etc.….) and they agree that being proficient in using social media via the web develops many skills, and computer proficiency is essential. This support that social media can help nurse education and it enhance communication and engagement. Furthermore, the development of social media guidelines or policies in nursing education is significant [56]. As suggested by [21] Learning activities involving social media could be included in nursing education to develop digital professionalism.The present finding found that near than half of students were agreed that lack of social networking through the web is one of the most critical obstacles they face in their learning and it is one of the significant barriers to communication with faculty members or with professors. This confirms the need to provide further education and support for students and faculty in using technology appropriately for communication [24]. Fifty percent of them were agreed that they could write notes through social networking over the web more confidently, this return to that they had excellent computer skills and they frequently use it. But more than two thirds (63.2%) of them disagreed when they asked about if social networking on the web is the biggest obstacle in communicating with the medical team and the nursing team at work, this is due to they rarely communicate with medical or nursing staff electronically but they communicate mainly with them directly in clinical setting, or they find it difficult to use social media on the web (69.5%) disagreed and (68.4%) of them were disagreed when they asked about if they had difficulty in using the computer this is due to the Millennium Generation use the computer skilfully.It was noted that, the most of students agreed that they develop their skills in social networking through joining courses (44.7%), helping their friends or family members (72.6%), engaged in the basic university courses (54.7%) and (63.2%) of them never try to develop their skills in this field.Moreover, (37.9%) of students not accepted to join courses outside the university, (29.5%) use the computer lab at college only. This may be due to that they are new students with little experience and having less time to join outside courses, also may be returned to they don't have enough financial resources and availability to go outside the college. Similarly, the study by [41] proved that using social media is limited in low-and-middle- income countries. Likewise, Mathieson and Leafman’s (2014) study reported that, when they asked about their readiness to use social media outside of the college, most of the students mentioned that they are not having enough time.Most of the students agreed that the college offered different options to develop the use of technology and faculty members assist them, available all time and encourage them to use technology and socialize on the web [28]. This is true because the new students may need guidance and support about how to filter information effectively and lectures may need to address this. The large percent (82.1%) of students reported that they did not embarrassed to communicate. The fact that technology is freely used may mean that the students were familiar with differed learning strategies. This findings supported by [21] assured that study students were not forced to use social media, but this could create disparity amongst student when used in the assessment.As regard to students 'opinions about the use of social media, the present result pointed to the positive agreement of most of the students in using social media in interactivity with peers, may be due to young students prefer this methods of communication, their peers in the same age, class and in the same educational level. In the agreement with this finding, the study by [2] reported that almost two thirds (64%) of studied students use of social media to discuss the academic problems with their peers and also with the academic staff. In the same respect [53] said that social media had been seen as an instrument for peer support, learning and increasing the student's engagement in learning. In respect to easy of using social media, the study finding revealed that the great proportion of students agreed that use of social media made simply to integrate into their lectures, reach peers, reach teachers, worth time and they enjoy studying by social media. Consider the usefulness of social media; the result assured that, using social media is useful in all items which asked students this appear from their answers that showed the agreement. This finding was supported by Price, et al., [42] who suggested that the students benefited from their communication and sharing information with others.Concerning to students satisfaction among users of social media, the result displayed the agreement for most of them which refer to satisfaction by using it in academic learning, most of them (71.1%) agree that using of social media can increase their motivation, about two thirds (66.8%) were satisfied with social media using in their learning and (64.2%) of them prefer use of social media in education and large percentage (87.9%) of them dissatisfied with the traditional methods of learning and also (77.4%) encourage their friends to use social media; this may contribute to they are the technology generation, prefer using of new technology in every -day life, they paid attention to the future and hoped to get jobs as soon as possible after graduation and nowadays the using of technology widespread in any job. In the same line, [51] noted that to "meet the generational needs of this, the millennial students and to engage them in learning, it is imperative for the educator to adapt teaching and learning methods that will optimize the probability of success. While they prefer the presence of teachers with them through more than three quadrants (78.4%) of them agree about physical appearance of the teacher is very essential for learning; this is true because the direct contact between themselves and their teachers is an essential part of the teaching process for guidance from their teachers and to discuss academic problems, researchers think that; should train students to use social networks as tool more than what they have in the class, but not substitutes for teachers. Educators can help student nurses use social media effectively [33]. These findings supported by [19] who suggested that nurses and nursing students need guidance as well as opportunities to practice professional behaviour online. In congruence with, [42], expressed that some students were aware of the dangers associated with social media, and the need for professional and university guidance.
5. Conclusions
- Social media is a rising scope within nursing practice, and students can find its use engaging in the educational setting. The present study concluded that most of the students were agree and they satisfied to use of social media in their learning, interactivity with peers, teachers, and they decide of easy use and usefulness of it. In the same time, they prefer the presence of teachers.
6. Recommendations
- From the present findings the researchers recommended the following:1. Providing the web & technology devices to students2. Integrating the social networking technologies in the formal curriculum.3. Explore opportunities for comprehensive undergraduate education developing social media in university learning, particularly in the first year.4. Further researches to evaluate the effect of using social media in learning on the students' academic achievements.5. Well- I have designed survey studies to identify preferences and barriers to the use of social media in nursing education.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML