-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Nursing Science
p-ISSN: 2167-7441 e-ISSN: 2167-745X
2013; 3(1): 22-32
doi:10.5923/j.nursing.20130301.04
Predictive Validity of NYHA and ACC/AHA Classifications of Physical and Cognitive Functioning in Heart Failure
Ponrathi Athilingam1, Rita D’aoust2, Cheryl Zambroski3, Susan C. McMillan4, Frances Sahebzemani5
1ACNP, FAANP, College of Nursing, University of South Florida, Tampa, Florida 33612
2ANP-BC, CNE, FAANP, FNAP, College of Nursing, University of South Florida
3RN, College of Nursing, University of South Florida
4ARNP, FAAN, College of Nursing, University of South Florida
5ARNP, FAANP, University of South Florida
Correspondence to: Ponrathi Athilingam, ACNP, FAANP, College of Nursing, University of South Florida, Tampa, Florida 33612.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
In clinical and research settings, heart failure (HF) is typically assessed using the New York Heart Association Classification (NYHA class) criteria and/or the American College of Cardiology/ American Heart Association (ACC/ AHA) Stages of HF criteria to assess severity and functional capacity of HF patients. Recent evidence suggests that there may be inconsistencies between the two classification schemes relative to correlations between physical function and cognitive function in HF patients. As cognitive function has been identified as a significant risk factor for patient outcomes, these inconsistencies between classification systems may limit the generalizability of the use of each assessment for research purposes. Therefore, the predictive validity of these two classification schemas were examined for their association with physical ability measured by six-minute walk test (6MWT) and cognitive function screened using the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) in a published study of 90 patients with HF. The results revealed both the NYHA class (RS = -0.232, p= 0.028) and ACC/AHA stages of HF (RS = -0.258, p=0.014) have good predictive validity for determining cognitive function indicating the need to include assessment of cognitive impairment as an at-risk factor among HF patients. The NYHA class revealed an inverse association with functional status measured by 6MWT (RS = -.298, p= 0.004), with no association to ACC/AHA stage of HF that indicates structural damage to the heart (RS = -.178; p= .093). Results support the impact of HF on functional status and cognitive function that are two important sequellae for considerations in staging severity and caring for patients with HF.
Keywords: NYHA Class, Heart Failure Stages, Cognitive Impairment, Functional Impairment, Montreal Cognitive Assessment, Six-minute Walk Test
Cite this paper: Ponrathi Athilingam, Rita D’aoust, Cheryl Zambroski, Susan C. McMillan, Frances Sahebzemani, Predictive Validity of NYHA and ACC/AHA Classifications of Physical and Cognitive Functioning in Heart Failure, International Journal of Nursing Science, Vol. 3 No. 1, 2013, pp. 22-32. doi: 10.5923/j.nursing.20130301.04.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
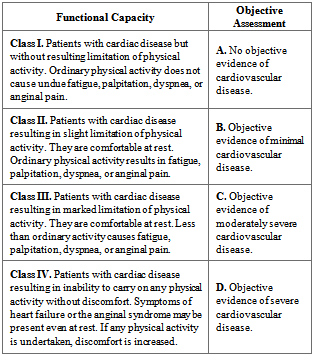
- Heart failure (HF) is a progressive disease requiring ongoing assessment of illness severity as individuals move through an unpredictable trajectory. In order to do this, clinicians require valid assessment schemes to determine HF severity to manage according to national clinical practice guidelines[1]. Clinicians typically assess HF severity using the New York Heart Association functional classification (NYHA class) or the American College of Cardiology/ American Heart Association (ACC/ AHA) stages of HF[2]. Determination of the NYHA class is based on patient symptoms (Table 1), while the specific ACC/ AHA stages of HF(Table 2) is based on the extent of damage to the heart[2]. Clinicians might use NYHA class or the ACC/AHA stage of HF exclusively and/or use both together to make clinical treatment decisions. Pathophysiologic impairments underlying HF and the impact of HF on functional status and cognitive function are two important sequellae for considerations in staging severity and caring for patients with HF[3]. However, there is conflicting evidence regarding whether the ACC/AHA stages of HF and NYHA classes are correlated to physical and cognitive function[4, 5]. This paper aims to examine the validity of these two classification schemas on their association with physical ability and cognitive function in a study of 90 patients with HF.Each of these classification systems have strengths and limitations based on the underlying conceptual approach to staging and/or classifying. The NYHA class is an indicator of cardiac symptoms, cardiac status, and functional capacity[6]. In recent years, the NYHA classes have progressed from a clinical tool to assess HF severity, to an entry criterion and an efficacy outcome measure in clinical trials[7]. In contrast, the ACC/AHA stages of HF reflect disease progression, identify high-risk conditions and enable initiation of appropriate preventive measures before symptom manifestation[3]. The ACC/AHA stages of HF have not been utilized considerably in clinical trials, since the stages are progressive, and patients who improve are not recatogerized to a less severe stage[3]. The ACC/AHA stages of HFdo not supplant the NYHA class assessment, but rather complement it by addressing the importance of the progressive nature of HF (Figure1)Although most providers are experienced in assigning a NYHA class, the method of assignment is not standardized and the reproducibility and consistency of determining NYHA class have never been established[8]. There is evidence of uncertainty in the management of patients admitted in advanced stages of HF whose symptoms improve, oreven reverse,after treatment[9]. This change or improvement often creates a dilemma for clinicians in determining what NYHA class therapies from the guidelines to prescribe, resulting in undertreatment and readmissions [9].In addition, an inter-rater variability showed only a 54% concordance between four cardiologists who assessed the same patients on the same day; indicating that assessment of NYHA class was not reproducible and reliable to predict self-reported walking distance or exercisetolerance of the patients with HF[5]. Inconsistencies in the use of NYHA class and ACC/AHA stages of HF were reported in a large retrospective study[10].These findings suggest poor understanding and inconsistent assessment of the NYHA class and ACC/AHA staging of HF, and place limitations on utilizing these measures for research and clinical practice [10,11]. Examining the validity and utility of both these measures may assist clinicians in appropriate assessment and management of persons with HF.
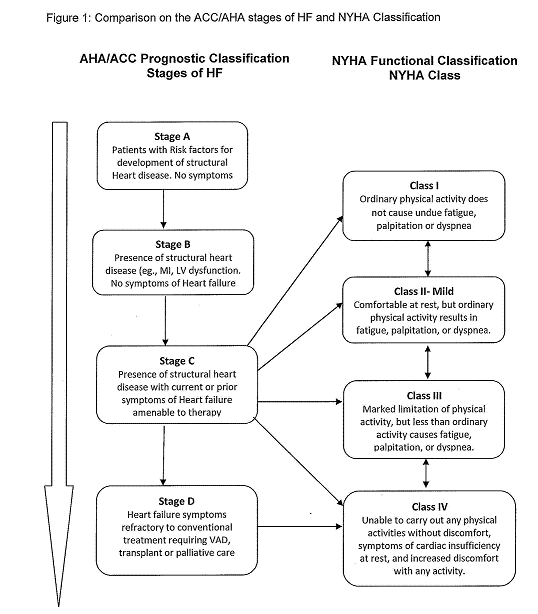 | Figure 1. Comparison on the ACC/AHA stages of HF and NYHA Classification |
2. Review of Literature
- Evidence from earlier studies indicated that the severity of HF assessed by NYHA class was associated with functional ability in HF[18,19]. However, there are concerns and inconsistencies in the reproducibility, and validity of the NYHA classification system, and “it is prudent to refrain from using the NYHA class as the sole outcome measure of changes in function in research studies” (p. 262)[11].The cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) is the gold standard for measuring functional ability in persons with cardiac disease[20]. Nonetheless,the 6MWT is being used increasingly as an alternative to CPET due to its wide availability, security, and ease of implementation[21,22].The discriminative ability of the 6MWT was similar to that of treadmill exercise capacity for predicting cardiovascular events (C statistics for both 0.72; P = .29)[23].Distance walked in six-minute was significantly correlated with the peak VO2 (p= .01) with a correlation coefficient of 0.78[24]. Although the 6MWT is considered a submaximal exercise, it best reflects the activities of daily living and is generally well tolerated by persons with HF[25]. Distance walked during the 6MWT was moderately inversely related (r = -0.43, p =.001) to NYHA class in a previous study with an interclass correlation coefficient of 0.88-91[15]. Yet, participants in NYHA class II had a significantly higher peak oxygen (VO2) uptake (16.1 ± 4.6 vs. 13.0 ± 4.2 ml/kg/min) and a longer duration of exercise (11.0 ± 3.9 versus 8.0 ± 3.4 minutes) than participants in NYHA class III/IV[26]. The multicenter HF-ACTION study (N=2331) reported an improvement by one NYHA class among 30% of the exercise-training cohort (p= .03)[19]. The ACC/AHA stages of HF are based on structural damage to the heart and the assessment doesn’t involve functional ability, hence there is scant evidence available that compared functional ability with stages of HF.The 6 MWT was a better predictor of mortality in HF (HR= 2.38; 95% CI 2.02 to 57.6; p= .005); the mortality was 11.5% among participants in NYHA class II compared to 58.8% in NYHA class III(p= .001), indicating that worse NYHA class was associated with increased mortality[27]. Increased mortality was found among participants (n=188) who received cardiac resynchronization therapy (p= .001), of whom 74% were in NYHA class III[28]. In addition, another study found that the 6MWT (distance ≤200 meter) was the strongest predictor of mortality (HR=2.14; 95% CI 1.20 to 3.81; p= .01) and HF rehospitalization (HR= 1.62; 95% CI, 1.10 to 2.39; p = .02)[29]. NYHA class III/IV has been negatively associated with the 6MWT (t -2.86; p=.005) and the distance walked in six minutes progressively decreased with worsening HF[30]. The distance walked in 6MWT was also associated with mortality rate[31]. Collectively, these studies support that worse NYHA class is associated with poor functional ability measured by 6MWT and HF readmissions.Similarly to the effect of HF on the decline in functional ability, cognitive impairment is increasingly recognized as a common adverse consequence of HF, which increases as heart function decreases[4]. Across studies, the point prevalence of cognitive impairment among patients with HF ranged from 25% to as high as 74%[32]. In a sample of 249 community-dwelling individuals with HF, those in NYHA class I/II performed significantly better on cognitive tests measuring memory, visuo-spatial ability, psychomotor speed, and executive function (p= <0.05 for all) compared to patients with NYHA class III to IV[17]. Similar linear associations with cognitive impairment have been reported on NYHA class[33] and ACC/AHA stage ‘D’ HF[34].In addition, distance walked inthe 6MWT was strongly associated with cognitive scores measured by Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE) among 80 individuals with HF (R2 = .53; p= .0001) after adjusting for demographic parameters[30]. A case control study reported that individuals with HF incur a 4-fold risk for cognitive impairment (odds ratio 4.47, CI 1.75 -11.43; p=.002) compared with matched community controls; butreported no association of cognitive impairment with NYHA class and physical functioning (p= .08)[35]. However, community- dwelling seniors with no prior history of cognitive impairment, but whohad a history of HF, revealed an increased risk(HR 1.84 & 1.80) of developing mild cognitive impairment over a five-year period[36]. Similarly, in a cross-sectional study of (N=57), 53% of persons with HFNYHA class II–IIIscored below 24 on the MMSE indicating mild cognitive impairment[37]. Feola et al. (2006) reported otherwise, finding no association between MMSE score and NYHA class (r= .01; p=.37)[38]. A recent study of 70 % of participants with HF scored less than the cut of score on the MoCA (≤ 26) indicating mild cognitive impairment. In addition, the MoCA score was strongly associated with NYHA class; among those in NYHA Class III/IV, 91% were classified as cognitively impaired compared to 52% in NYHA Class I/II[16].
3. Aims and Hypothesis
- Although NYHA class and ACC/AHA stages of HF are used exclusively or together to determine the algorithm for HF management, these measures are inconsistent in classifying HF severity and have not been examined thoroughly for validity. The purpose of this secondary analysis is to examine the predictive validity of the NYHA class and ACC/AHA stages of HF utilizing the related variables of physical and cognitive ability. In addition, we examined the concurrent validity of the two measures, the NYHA class and ACC/AHA stages of HF that measures the same construct, which is the severity of HF. In light of the evidence from the literature review, we hypothesized that: 1) The NYHA class and ACC/AHA stages of HF will be moderately, negatively correlated to physical ability measured by the 6MWT;2) The NYHA class and ACC/AHA stages of HF will be moderately, negatively correlated to cognitive function measured by the MoCA; and 3) The NYHA class will be positively correlated with ACC/AHA stages of HF.
4. Methods and Variables
- This is a secondary analysis of a cross-sectional correlation study that enrolled ninety community-dwelling adults with HF from outpatient cardiology offices[39]. Inclusion Criteria were the original study were: (1) clinical diagnosis of HF as defined by the ICD-9-CM; (2) community dwelling adults residing at home; (3) 50 years of age or older, because the incidence of HF among the US population increases sharply with age, affecting about 6% of people in their 60s and 10% of people in their 80s[40]. Persons were excluded if they were (1) on continuous oxygen; (2) listed for heart transplant with United Network for Organ Sharing as status 1A or 1B, (3) supported by ventricular assist device or home inotropic therapy; (4) enrolled in a palliative or hospice care program; (5) diagnosed with dementia or Alzheimer’s disease; or (6) a clinical history of stroke.
4.1. Ethical Consideration
- The study was approved by the Research Subject Review Board of the University. Participants were recruited over a four-month period in 2007 from cardiology offices affiliated with the University Hospital. Participants were identified with a code number.
4.2. The NYHA Classification
- The NYHA functional classes on the study participants were determined by a cardiology nurse practitioner on the day of data collection based on the individuals’ HF symptoms and 6MWT. NYHA class provides a simple way of classifying patients in one of four grading categories (I, II, III, &IV) with higher class indicating more severe HF symptoms[41]. Grading is based on the individual clinicians’ judgment partly based on cardiac functional ability and objective cardiac assessment (Table 1, grading criteria). Functional ability is an estimate of what the patient's heart will allow them to do physical activities. This ability is not influenced by the character or structural damage to the heart[41].
|
4.3. The ACC/AHA stages of HF
- Ultrasound techniques such as the 2D/3D echocardiogram, cardiac magnetic resonance, and cardiac angiogram permit a comprehensive assessment of morphology, function, and the extent of structural damage to the heart and have been the accepted norms in determining the ACC/AHA stages of HF[2, 42]. Therefore, the ACC/AHA stages of HF on the study participants were extracted from medical records based on an objective cardiac assessment within past 6 months (Table 2, grading criteria).
|
4.4. Functional Ability
- Functional ability in this study was measured using the 6MWT[21]. The reported correlation coefficient of 6MWT with peak VO2 was 0.68 (p < 0.001)[43]. The 6MWT was given according to the guidelines provided by the American Thoracic Society (ATS) Pulmonary Function Standards Committee[44,45]. Participants were told to walk at their own pace in a straight plane of the research unit corridor and the laps were counted and measured in meters walked in 6 minutes; each lap was 120 meters. The primary measurement was the total distance walked in meters over six minutes. Among healthy and sedentary subjects (122), age and BMI was a strong (r= 0.97) and significant (p= .001) predictor for distance walked in 6 minutes[46]. Therefore, predicted distance walked and the percent completed by the individual was compared in the manner described by Enright & Sherrill (1998); which was calculated using the formula based on age, gender, height, and weight of the participants (Table 3)[47].
|
4.5. Cognitive Impairment
- Participants were screened for cognitive impairment using the MoCA[49]. The MoCA is a one page; paper-and-pencil test that consists of 8 cognitive domains (i.e., visuo-spatial, naming animals, memory, attention, language, abstraction, delayed recall, and orientation) that test 13 items[49].The MoCA is administered by an interviewer and takes about 10-12 minutes to complete. The scoresrange from 0 to 30.A score above 26 is considered normal, score 22 to 26 suggests mild cognitive impairment, 17 to 21 suggests moderate cognitive impairment, and less than 17 suggests dementia[49]. The validity and reliability of the MoCA was originally tested on 94 participants with mild cognitive impairment, 93 with Alzheimer’s disease, and 90 healthy elderly controls. The MMSE revealed a sensitivity of 78%, whereas the MoCA was 100% sensitive;MMSE had a specificity of 100% and the MoCA was 87%. Test-retest reliability had less than one point variation (r = 0.92, p < .001). The internal consistency of the MoCA on the standardized items was a Cronbach’s alpha of 0.83. The MoCA had been approved as a screening tool for mild cognitive impairment in the Canadian Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Dementia[50]. The MoCA was identified as a sensitive cognitive screening tool among patients with HF[51,52]; high-risk populations with cardiovascular diseases[53]; and stroke[54]. To minimize the effects of education, one point is added to the score as a correction factor for subjects with less than high school education[49].
4.6. Control Variables
- Demographic variables included were age, education, race, and socioeconomic status. These data were collected using a demographic and clinical questionnaire created for the study to examine as covariates[51]. Data on co-morbidities was assessed using the modified version of Cumulative Illness Rating Scale,which included 14 organ systems and considered the hematopoietic system separately from the vascular system with an intra-class correlation of 0.78[55].
5. Data Analysis
- The aim of the secondary data analysis was to use the Spearman Rho correlation coefficients statistics to examine the predictive validity of both NYHA class and ACC/AHA stages of HF using the related variable of cognitive screening scores (MoCA score) and functional ability score (6MWT).
|
|
|
6. Results
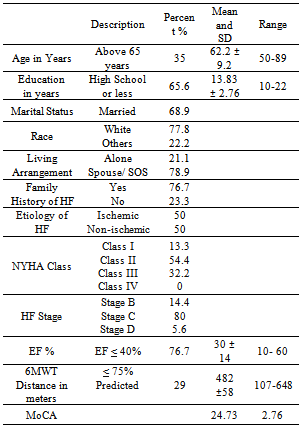
- Participants (N=90) were predominantly men (66%), Caucasian (79%), and aged 50-89, with mean age 62 ± 9 years. Ejection fraction refers to the percentage of blood that's pumped out of a filled ventricle with each heartbeat with 55 to 70% considered normal. Mean ejection fraction of the participants was 30% with SD ± 14, ranged from 10 to 60%; 77% of them having ejection fraction below 40% indicating systolic heart failure due to insufficient contraction. Ejection fraction above 40% is known as diastolic heart failure due to insufficient relaxation[39]. More than 50% of the participants were in NYHA class II and 32% were in class III, none in class IV. Almost 80% of the participants were in ACC/AHA stage ‘C’ HF, and 14% of patients in stage B were misclassified as NYHA class III.The mean MoCA score was 24.73 SD ± 2.76. The MoCA identified 54% of the participants with mild cognitive impairment. The mean distance walked in six-minute was 482 meters, SD ±58. Table 4 provides details on the demographic and clinical variables.
6.1. Test for PredictiveValidity of NYHA Class and ACC/AHA stages of HF
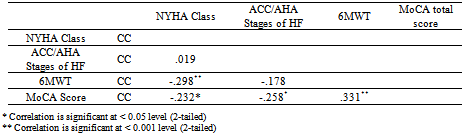
- As indicated in the correlation matrix (Table 5),predictive validity was examined by Spearman Rho correlation coefficients between NYHA class and ACC/AHA stages of HF with MoCA score and 6 MWT. Both the NYHA class (RS= -0.232, p= 0.028) and ACC/AHA Stages of HF (RS=-0.258, p=0.014) revealed significant inverse association with MoCA score. The NYHA class revealed a statistically significant inverse association with functional status measured by the 6MWT (RS = -.298, p= 0.004). ACC/AHA stage of HF showed no association with the 6MWT (RS = -.178; p= .093).
6.2. Concurrent Validity of NYHA Class and ACC/AHA Stages of HF
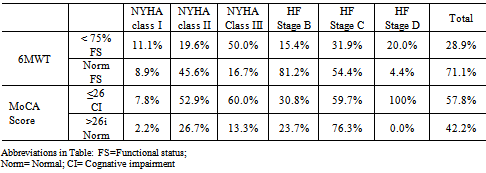
- Spearman Rho correlation coefficients were calculated to examine association between NYHA Class and ACC/AHA stages of HF. Although both measure HF severity, the result indicated that they are not significantly related to each other (RS = 0.02, p=0.86). A cross tabulation with a Pearson Chi-square analysis (Table 6) showed that the 6MWT score ≤75% of predicted distance walked, which indicates poor functional status, was associated with NYHA class (X 2 (2)10.03; p =.001) but not associated with ACC/AHA stages of HF (X 2 (2)2.03; p = .09). A dichotomized MoCA score <26, indicating Mild Cognitive Impairment,was associated with both NYHA class (X 2 (2)6.67; p = .001) and ACC/AHA stages of HF (X 2 (2)7.65; p = .001).
7. Discussion
- The predictive validity of NYHA class and ACC/AHA Stages of HF was supported by their relationship with the cognitive screening scores ofthe MoCA. Both measures showed inverse associations with the MoCA score indicating similar predictive validity on the cognitive measure. These findings of association between NYHA class and cognitive function are consistent with current literature[16,17]. Similar findings of association have been reported between stage ‘D’ ACC/AHA stages of HF and cognitive impairment in mental processing speed, verbal and visual memory function deficits[34]. On the other hand, an older study showed that patients with previous myocardial infarction (MI) in NYHA class III/IV performed similar in memory function tests (p=>0.05 in all) compared to similar MI patients who had no HF[56]. The result of our study confirms the findings of more recent HF research on the association between NYHA class and ACC/AHA stages of HFand cognitive impairment, and provides validity data for both classification strategies. Predictive validity of the NYHA class for functional ability was supported by its correlation with the 6MWT (p=0.007). Similar findings of association between NYHA class and functional ability have been reported in HF literature[26,57,58]. The rate of ischemic cerebrovascular events increased from 6.7% in patients with no HF to 9.2% in patients ofNYHA functional class I,and 9.7% for patients with NYHA functional classes II and III, which was significantly associated with poor functional ability (P < .001)[59]. Major clinical intervention studies have used NYHA class as a measure of change in functional status over time including, OPTIMIZE-CHF[60]; CARE-HF[61]; COPERNICUS[62]; and COMPANION[63]. The work of these large intervention studies supports the association of NYHA class with functional status. However, the predictive validity of ACC/AHA stages of HF was not supported for functional ability measured by the 6MWT confirming that the ACC/AHA stages of HF is based on extent of damage to the heart not functional ability. The NYHA class measures functional ability that fluctuates based on patients self-reported HF symptoms, whereas the ACC/AHA stages of HF progresses in one direction only and is not influenced by patients’ symptoms[10]. There is also lack of evidence in the literature that supports association between ACC/AHA stages of HF and functional ability.We found no significant association between NYHA class and ACC/AHA stages of HFto support the concurrent validity (p=0.86). Our findings support that the NYHA class measures functional ability that fluctuates based on HF symptoms, whereas the ACC/AHA stages of HF progresses in one direction only and is not influenced by patients’ symptoms, hence are not similarin identifying severity of HF[10]. In our study, 14% of participants were classified as ACC/AHA stage ‘B’ HF(high risk, with no HF symptoms); the same were classified as NYHA class II/III(with HF symptoms). This inconsistency in the classification could also possible explain the non-association found in this study. The ACC/AHA Stage ‘B’ HF is defined by the ACC/AHA guidelines as patients with structural heart disease but no current or prior symptoms of HFto alert providers to plan treatment protocol to minimize remodeling of the heart. Once a patient experiences symptom ofHF, they advance to stage C even if they later become asymptomatic[9]. Wang and colleagues (2003) found that more than half of all patients with impaired systolic function (34% to 92% of patients) had been characterized asasymptomatic stage ‘B’ HF[64]. This was also found in a cross sectional study (N= 424), where persons in the early asymptomatic HF stages ‘B’showed significantly lower scores on physical and mental function, suggesting inconsistency in the classification of HF symptom in persons with stage ‘B’ HF[65]. Thus, evidence supports our findings on the non-association between NYHA class and ACC/AHA stages of HFare potentially due to inconsistency in HF symptom classification.
8. Limitation
- This is a secondary analysis of a published study that compared the NYHA class that was determined on the date of data collection based on participants reported HF symptoms by one cardiology nurse practitioner. Whereas, cardiologist clinical reports based on an objective assessment of echocardiogram within 6 months was used to determine ACC/AHA Stages of HF. Thus comparing a current functional class with a past 6 months data on structural damage may be a reason for the non-significance; hence the result should be viewed with caution.
9. Summary and Relevance to Clinical Practice
- Results from this study indicate that both NYHA class and ACC/AHA stages of HF have good predictive validity for determining cognitive impairment screened using the MoCA indicating the need to include early assessment of at-risk for cognitive impairment among HF patients. This result supports the evidence both the ACC/AHA and Heart Failure Society of America (HFSA) guidelines that encourage providers to use both measures. The AHA and HFSA guidelines warrant providers to use ACC/AHA stages of HF to determine initiation of HF therapies based on evidence from clinical trials for high-risk patients with structural damage to heart who have no HF symptoms supporting the management goal of prevention of HF progression by remodeling of the structure of the heart[3, 6]. Results from our study indicate possibility of adding cognitive impairment as an at-risk factor in HF. Patients with HF are expected to perform regular maintenance tasks such as monitoring weight and responding to water retention related to weight gain, edema, dyspnea, and being adherent to multiple medications, following a sodium-restricted diet, as well as engaging in moderate physical activity[66]. Cognitive impairment may contribute to self-care deficit through problems with decision-making and executive function in complex situations such as early recognition and interpretation of HF symptoms, thus increasing patients’ risk for non-compliance and increased readmission rates forde compensation[67].The NYHA classes showed good predictive validity for functional status measured by 6MWT; while the ACC/AHA stage of HF that is based on structural damage to the heart showed no association to 6MWT suggesting NYHA class is a better predictor of functional ability than ACC/AHA stages of HF. This notion supports the 2010 HFSA guideline recommendation to use the 6MWT in addition to HF symptoms in the assessment of NYHA class and provide step-by-step management strategies to determine progress after treatment implementation[3]. Similarly, the Canadian Cardiovascular Society’s consensus model for the management of HF used only NYHA class as a basis for HF treatment determinations[68].In summary, the ACC/AHA stages of HF complement NYHA class by addressing the importance of the progressive nature of HF. Findings from this study add to the evidence the need for assessing at-risk that includes physical and cognitive ability among patients with HF. Results support the impact of HF on functional status and cognitive function that are two important sequellae for considerations in staging severity and caring for patients with HF. The guidelines warrant the providers to use both classifications schemes in order to have consistency n assessing at-risk and progress in the management of patients with HF. Appropriate use of both measures is vital in the management of HF.What this Paper Adds● Both the NYHA class and ACC/AHA stages of HF have good predictive validity for determining cognitive function. However, cognitive impairment is currently not an at-risk factor among HF patients that warrant screening.● The NYHA classes showed good predictive validity for functional status measured by 6MWT and should be used by clinicians in determining NYHA functional class.● Results support the impact of HF on functional status and cognitive function that are two important sequellae for considerations in staging severity and caring for patients with HF. ● The ACC/AHA stages of HF do not supplant the NYHA class assessment, but rather complement it by addressing the importance of the progressive nature of HF. Findings from this study add to the evidence the need for assessing at-risk factors that includes physical and cognitive ability among patients with HF.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML