-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Nursing Science
p-ISSN: 2167-7441 e-ISSN: 2167-745X
2012; 2(4): 38-46
doi: 10.5923/j.nursing.20120204.03
A Comparison of Vinegar Compresses vs. Cold Water& Water with Vinegar for treating of Fever at Tropical Hospitals
Fathia Attia Mohammed 1, Elsayeda Ibrahim Ahmed 2
1Lecture of Medical Surgical Nursing, Faculty of Nursing Zagazig University
2Lecture of Nursing Administration, Faculty of Nursing Zagazig University
Correspondence to: Fathia Attia Mohammed , Lecture of Medical Surgical Nursing, Faculty of Nursing Zagazig University.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Fever is a common encounter in hospitalized patients & its management is integral aspects of nursing care. Research aimed to assess and compare the efficacy of vinegar,, cold water and cold water with vinegar compresses in the treatment of fever. This was a quasi-experimental study conducted in the Tropical Hospitals at Sharqia Governorate. The study was carried on 45 patients; divided to three group15 patient in each group, all of them were suffering from fever & suspected to have typhoid fever for investigation & administered the same drug management. We used vinegar compresses with the first group, cold water compresses with second group & water with vinegar compresses with third one. A compress was done at the same time & locations. Body temperature was measured after one &two hours orally by using mercury thermometer. Both compresses methods were effective in decreasing body temperature and vinegar was found to be more effective than cold water and cold water with Vinegar compresses (P ≤ 0.001). Vinegar compresses can be used in the treatment of fever when we needs to rapidly lowering patient temperature.
Keywords: Vinegar, Medical Uses of Vinegar, Fever, Cold Compress, Typhoid Fever
Cite this paper: Fathia Attia Mohammed , Elsayeda Ibrahim Ahmed , "A Comparison of Vinegar Compresses vs. Cold Water& Water with Vinegar for treating of Fever at Tropical Hospitals", International Journal of Nursing Science, Vol. 2 No. 4, 2012, pp. 38-46. doi: 10.5923/j.nursing.20120204.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Vinegar is a liquid substance consisting mainly of acetic acid and water, the acetic acid being produced through the fermentation of ethanol by acetic acid bacteria.[1]. Vinegar, from the French vinegar, meaning “sour wine,” can be made from almost any fermentable carbohydrate source, including wine, molasses, dates, sorghum, apples, pears, grapes, berries, melons, coconut, honey, beer, maple syrup, potatoes, beets, malt, grains, and whey. Initially, yeasts ferment the natural food sugars to alcohol. Next, acetic acid bacteria (Acetobacter) convert the alcohol to acetic acid[2]Not sure this is relevantWhite vinegar comes about by the process of oxidization of any alcohol. There are several types of vinegars that are found like apple cider vinegar or balsamic vinegar and each of them provides several health benefits. It has been known to increase therefore leading to a stronger immune system [3].Relevance? as it is being used as compress not for ingestion. The Islamic Prophet Muhammad is reported to have said, "The best of condiments or condiment is vinegar."[4] Avicenna, in his famous book "The Canon of Medicine",mentioned several beneficial medicinal uses for vinegar: it is a powerful clotting agent, it heals burns and skin inflammations, and it relieves headaches caused by heat. This is a really interesting reference but it would be important to reference scientific sources to support this. He also considers vinegar a good digestive supplement [4] .Bin Qayyim Al-Jawziyya also mentions the merits of vinegar in his book, Al Tabb al Nabawi (The Prophetic Medicine). In this book, he mentions that wine vinegar helps against gastric inflammation and bile, and prevents the effects of toxic medications and poisonous mushrooms. He also notes that vinegar quenches thirst, acts as an appetite stimulant, and prevents tumours' from occurring as well as helps in the digestion process (5). This is a really interesting reference but it would be important to reference scientific sources to support this.One of the main white vinegar health benefits is that it helps in the absorption of calcium and other important minerals from the varied foods that are eaten. This is because vinegar contains acetic acid which has the ability of helping the body absorb the required minerals and calcium (reference at the end ). It therefore not only helps in digestion, but also in making the bones stronger and thereby preventing osteoporosis. It has to be kept in mind that due to its acid content, vinegar must always be diluted before ingestion or it can cause heart burn. White vinegar uses are several and these include medicinal uses as well. Here are some of them: 1-It can be used as a form of treatment for minor infections and skin burns. Dab a cloth in white vinegar and cover it over the infected area for a cooling effect and soothing of sunburned skin and therefore helps in providing effective skin care.2-For infections, rashes, insect bites, dabbing of white vinegar with the help of a cotton swab can help clean the area and prevent further infections to the skin.3-It is used as an effective remedy for sore throat. Adding a tsp of white vinegar to 8 ounces of water and then gargling with it followed by swallowing the mixture will help rid a person of throat problems.4-Using white vinegar in an inhaler and taking a steam of the same can be used as a decongestant for a blocked chest.5-One of the main white vinegar skin benefits is that it helps to treat extremely dry skin. Using 2 tabs of vinegar in bath water will help moisturize the skin naturally and help in curing itchy skin as well.6-White vinegar can also cure dandruff. After a regular bath, simply pour a mixture of half cup vinegar diluted in 2 cups water.7-White vinegar also helps in curing toenail fungus. Rub a cotton swab dipped in white vinegar over the infection many times in a day.8-Soaking ones feet in vinegar helps in curing athletes foot, as well as an equal mixture of alcohol and vinegar helps to combat swimmer's ears [3 & 6].Fever is a common encounter in hospitalized patients and can cause morbidity and mortality in critically ill patients & its management is integral aspects of nursing care [7].. About 5% of people who go to an emergency room have a fever [8]. Fever (also known as pyrexia is a common medical sign characterized by an elevation of temperature above the normal range of 36.5–37.5 °C (98–100 °F) due to an increase in the body temperature regulatory set-point. This increase in set-point triggers increased muscle tone and shivering. [9]A wide range for normal temperatures has been found. Fever is generally agreed to be present if the elevated temperature is caused by a raised set point and: Rectum temperature is at or over 37.5–38.3 °C (99.5–100.9 °F) [9,].Temperature measured through mouth is at or over 37.7 °C (99.9 °F) &Temperature measured under axillaries or thought otic route at or over 37.2 °C (99.0 °F) [10]A fever can be caused by many different conditions ranging from benign to potentially serious. There are arguments for and against the usefulness of fever, and the issue is controversial.[11] With the exception of very high temperatures, treatment to reduce fever is often not necessary; however, antipyretic medications can be effective at lowering the temperature, which may improve the affected person's comfort. Infections are the most common cause of fevers, however as the temperature raises other causes become more common.[12]The regulation of body temperature involves a complex series of physiological responses. Temperature is ultimately regulated in the hypothalamus. A trigger of the fever, called pyrogens, causes a release of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). PGE2 then in turn acts on the hypothalamus, which generates a systemic response back to the rest of the body, causing heat-creating effects to match a new temperature level. In many respects, the hypothalamus works like a thermostat. When the set point is raised, the body increases its temperature through both active generations of heat and retaining heat. Vasoconstriction both reduces heat loss through the skin and causes the person to feel cold. If these measures are insufficient to make the blood temperature in the brain match the new setting in the hypothalamus, then shivering begins in order to use muscle movements to produce more heat. When the fever stops, and the hypothalamic setting is set lower; the reverse of these processes (vasodilatation, end of shivering and no shivering heat production) and sweating are used to cool the body to the new, lower setting. [13] When taken from a source each sentence should reference the sourcePyrogens are a substance that induces fever. These can be either internal (endogenous) or external (exogenous) to the body. The bacterial substance lip polysaccharide (LPS), present in the cell wall of some bacteria, is an example of exogenous pyrogens. Pyrogenicity can vary: In extreme examples, some bacterial pyrogens known as super antigens can cause rapid and dangerous fevers. Depyrogenation may be achieved through filtration, distillation, chromatography, or inactivation [14]. When taken from a source each sentence should reference the sourceTypes of Fever- Prolonged fever lasting longer than about 10-14 days-Chronic Fever that lasts longer than three to four days; some researchers consider intermittent fevers that recur over months to years as "chronic" fevers-Intermittent: Fevers that either varies from normal to fever levels during a single day or may occur one day and recur in about one to three days - Remittent: Fevers that come and go at regular intervals -Constant: Also termed continuous; usually low grade and does not change by much (by about 1 degree F over 24 hours)In continuous fever, temperature remains above normal throughout the day and does not fluctuate more than 1 °C in 24 hours, e.g. lobar pneumonia, typhoid, urinary tract infection, brucellosis, or typhus. A fever is usually accompanied by sickness behavior, which consists of lethargy, depression, anorexia, sleepiness, hyperalgesia, and the inability to concentrate.[15]There are arguments for and against the usefulness of fever, and the issue is controversial. Theoretically fever can aid in host defense.[11] .Fever in children is believed to train the immune system and prevent asthma. White blood cells also rapidly proliferate due to the suitable environment and can also help fight off the harmful pathogens and microbes that invaded the body. [16]Research has demonstrated that fever assists the healing process in several important ways: Increased mobility of leukocytes, Enhanced leukocytes phagocytosis ,Endotoxin effects decreased ,Increased proliferation of T cells[16,17]Fever should not necessarily be treated.[18] Most people recover without specific medical attention.[19] Although it is unpleasant, fever rarely rises to a dangerous level even if untreated. Damage to the brain generally does not occur until temperatures reach 42 °C (107.6 °F), and it is rare for an untreated fever to exceed 105 °F (41 °C).[18] Some limited evidence supports sponging or bathing feverish children with tepid water.[20] The use of a fan or air conditioning may reduce the temperature and increase comfort. If the temperature reaches the extremely high level of hyperpyrexia, aggressive cooling is required.[12] In general, people are advised to keep adequately hydrated.[21] Whether increased fluid intake improves symptoms or shortens respiratory illnesses such as the common cold is not known.[22]Cold causes vasoconstriction (shrinkage of blood vessels), decreasing blood flow to an area, and slowing the body’s metabolism and its demand for oxygenA tepid sponge bath is a bath with water below body temperature, between 80_F and 95_F (26.6_C to 35_C). This type of bath may be ordered to reduce a client’s elevated temperature. The first effect of this water on the skin is blood vessel constriction. Sources of cold include ice packs, ice bags, cold collars, or commercial cold packs. If the client’s systemic temperature is elevated, cooling blankets or cooling tepid sponge baths can be used. [23]Typhoid fever is a systemic infection, caused mainly by Salmonella typhi found only in man. It is characterized by a continuous fever for 3-4 weeks, relative bradycardia, with involvement of lymphoid tissue and considerable constitutional symptoms. Each year, world over, there are at least 13-17 million cases of typhoid fever, resulting in 600,000 deaths. [24] With an estimated 16–33 million cases of annually resulting in 216,000 deaths in endemic areas, the World Health Organization identifies typhoid as a serious public health problem. Its incidence is highest in children and young adults between 5 and 19 years old. [25]Infection caused by S. typhus remains an important public health problem, particularly in developing countries. Morbidity and mortality attributable to typhoid fever are once again increasing with the emergence and worldwide spread of S. typhi strains that are resistant to most previously useful antibiotics.The clinical presentation of typhoid fever varies from a mild illness with low-grade fever, malaise, and slight dry cough to a severe clinical picture with abdominal discomfort and multiple complications. [26]. TF is characterized by the sudden onset of sustained fever, severe headache, nausea, abdominal pains and loss of appetite, constipation or sometimes diarrhea [25]Humans are the only natural host and reservoir. The infection is transmitted by ingestion of food or water contaminated with faces. Ice cream is recognized as a significant risk factor for the transmission of typhoid fever. Shellfish taken from contaminated water, and raw fruit and vegetables fertilized with sewage, have been sources of past outbreaks. The highest incidence occurs where water supplies serving large populations are contaminated with faces. [27, 28]People can transmit TF as long as the bacteria remain in their body; most people are infectious prior to and during the first week of convalescence, but 10% of untreated patients will discharge bacteria for up to 3 months. In addition, 2–5% of untreated patients will become permanent, lifelong carriers of the bacteria in their gall-bladder. [25]The definitive diagnosis of typhoid fever depends on the isolation of S. typhi from blood, bone marrow or a specific anatomical lesion. The presence of clinical symptoms characteristic of typhoid fever or the detection of a specific antibody response is suggestive of typhoid fever but not definitive. Blood culture is the mainstay of the diagnosis of this disease. [29] The major routes of transmission of typhoid fever are through drinking water or eating food contaminated with Salmonella typhi. Prevention is based on ensuring access to safe water and by promoting safe food handling practices. Health education is paramount to raise public awareness and induce behavior change.Supportive measures are important in the management of typhoid fever, such as oral or intravenous hydration, the use of antipyretics, and appropriate nutrition and blood transfusions if indicated. More than 90% of patients can be managed at howith oral antibiotics, reliable care and close medical follow-up for complications or failure to respond to therapy. However, patients with persistent vomiting, severe diarrhea and abdominal distension may require hospitalization and parenteral antibiotic therapy. [30, 31]There are two vaccines currently recommended by the World Health Organization for the prevention of typhoid: these are the live, oral Ty21a vaccine (sold as ''Vivotif Berna'') and the injectable Typhoid polysaccharide vaccine (sold as ''Typhim Vi'' by Sanofi Pasteur and ''Typherix'' by GlaxoSmithKline). Both are providing 50% to 80% protective and are recommended for travellers' to areas where typhoid is endemic. Boosters are recommended every 5 years for the oral vaccine and every 2 years for the injectable form. [32]
2. Objective
- To assess and compare the efficacy of vinegar compresses versus tape water & tape water with vinegar as hypothermic compresses \ agent
2.1. Research Question
- The main research question was what are the best compresses methods is more effective in reducing patient body temperature?
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Research Design
- This was a quasi-experimental study. We conducted the study in 45 subjects between Jun 2011 and October 2011
3.2. Sitting
- Tropical Hospital at Zagazig & Hehia city, Sharqia governorate, the tow mentioned hospitals are under the supervision of Ministry of Health at Egypt
3.3. Subject
- All admitted patients to the mentioned hospitals in the time of research application .The inclusion criteria for selected subject were only patients admitting suffer from high fever with a classic manifestation of typhoid fever in the first day before administer drug therapy& suspected medical diagnosis is typhoid fever for investigation. All patients have under the same management strategies according to typhoid protocol management'. All patients haven’t past chronic illness' including both male & female patient in variety of age
3.4. Intervention
- 45 patients divided into 3 groups, each group included 15 patients. White vinegar, cold water & cold water with vinegar half to half compresses followed by measuring body temperature within first & second hours orally by using mercury thermometer & documented in flow sheet for each patient. All compresses were applied for Pt., under axillaries, above the forearm &under the Knee. When applied forehead compresses most of the patients were suffered from vinegar orders so, we excluded from all application in three groups.
3.5. Administrative Design
- The written permission was obtained before conducting the study from hospital directors. The research objective was illustrated either for patients or their family & orally consent was obtained
4. Result
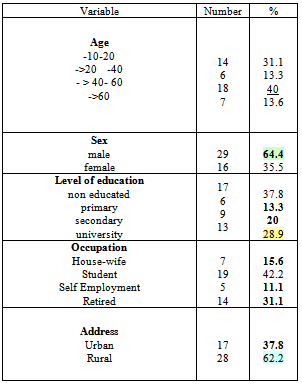
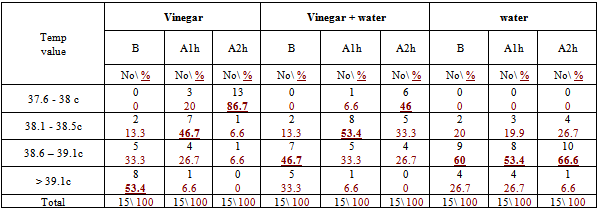
- The subjects characteristics are shown in table 1 indicates to the majority of subject age was either below than 20 or 40 year, nearly two third were male , more one third were uneducated while nearly half were student and nearly tow third were lived in rural area.Percentage distribution of subjects body temp before & after compresses in three method was illustrated in table 2 indicates that more than half have body temp more than 39 0C , nearly half have body temp in between 38.1- 39.1 & 60% have body temp in between 38.1- 39.1 before vinegar , vinegar with water & water compresses application respectively.
|
|
|
|
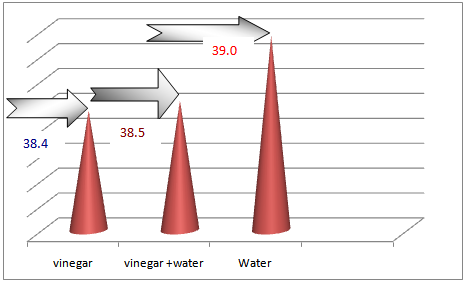 | Figure 1. Represent the Mean Temp after Application of Compresses by Hour |
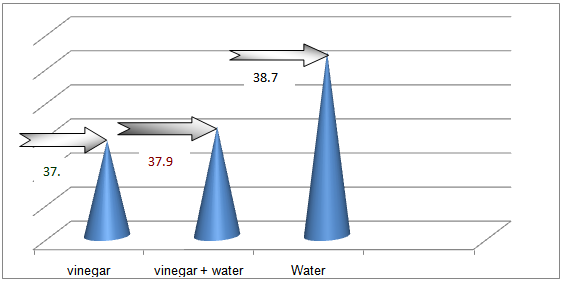 | Figure 2. Represent the Mean Temp after Application of Compresses by 2 Hours |
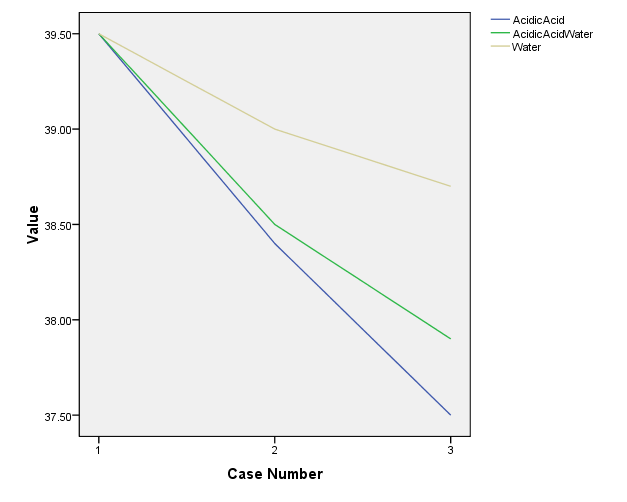 | Figure 3. Histogram represents the degrees of Temp changes After Application of Compresses |
5. Discussion
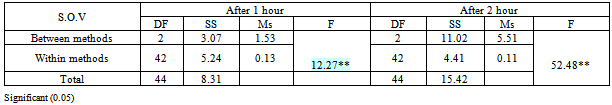
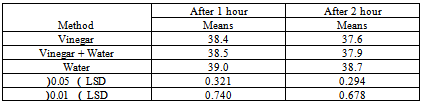
- We writing in methodology that the PT coming to tropical hospital suffer the same clinical manifestation of typhoid fever according to physician view & already send samples to lab to assure & start the same medical management sterategies One of the major weaknesses was not discussed here. The abstract states “suspected to have typhoid fever” It is very important to understand that diagnosis of he organism is very important to the reliability of this study. Different organisms have different fever patters. There is an evidence that using antipyretic drugs or external cooling helps recovery, and as the review by Carey indicates they can cause discomfort and delay recovery, therefore their routine use should be discouraged. Larger studies are needed to establish the effects (or lack of them) of the impact of antipyretic drugs and external cooling (alone or in combination) on short-term recovery from illness and short- to medium term morbidity. Available evidence does not support routine administration of antipyretics to reduce duration of fever or illness (33).Several methods have been recommended to reduce fever in children, which include tepid sponging, fanning, alcohol sponging and antipyretics. However, controversy surrounds the use of tepid sponge for reduction of fever. The effectiveness of tepid sponging as a treatment alongside antipyretic varies between studies, with some finding that it is of no benefit and others suggesting that it is helpful (34)Numerous non-pharmacological interventions for management of fever were detailed including environmental changes (e.g. removing blankets, turning down thermostat, opening windows), physical cooling measures (e.g. ice packs, cooling blanket, bathing) and other interventions (e.g. mobilization, incentive Spiro meter use). Furthermore, many interventions seen as useful by some participants (e.g. ice packs, cooling blankets, fans, etc.) were seen as problematic by others. The hypothermia blanket is used cautiously to treat uncontrollable hyperthermia. Risk occurs because the cold interferes with the normal febrile (fever) response. Fever-producing pathogens cause the body’s temperature regulatory centre (the hypothalamus) to produce a new body temperature set point in the body’s effort to fight off the pathogen’s negative effects. Using a hypothermia blanket during this response decreases the actual body temperature, moving it further away from the set point. This may cause an even more severe febrile reaction. In addition, fever sometimes is helpful, because it has the effect of destroying pathogens (35).Cold causes vasoconstriction (shrinkage of blood vessels), decreasing blood flow to an area, and slowing the body’s metabolism and its demand for oxygen.A cloth (padded gauze) is immersed in cold water and applied in area where we get large superficial vessels E.g. axilla and groin .Change the cloth when it becomes warm &applied for 15-20 min (36)Regardless of practice setting, interventions chosen by nurses were frequently based on trial and error or individual conventions – ‘what works’– rather than evidence-based practice. Some nurses’ accounts indicated use of interventions that were clearly contraindicated by the literature. Fever management is often left to the discretion of the individual practitioner because evidence-based guidelines are not explicit (37) Recent studies reveal wide variation in nursing practice and barriers to evidence-based fever management. In studies conducted separately in three different countries (US, Sweden and Australia), all authors noted a lack of consistency in the way nurses described fever and the management of fever (38). The gap between available evidence from patient outcomes research and data on bedside practice for fever management is a striking, widespread problem.Their participants reported using interventions not supported by literature such as alcohol, ice packs to the groin and opening the windows in the intensive care unit to treat fever. During the chill phase of fever, use of ice packs is likely to lead to increased shivering as the temperature set point has been raised and the body is working to increase the temperature to the new threshold (39). This concern is magnified when the ice is applied to the groin area which contains a large number of heat sensitive neurons. The use of alcohol to reduce fever is unclear efficiency. While Polderman suggests that a combination spray is efficacious (40) there is little published evidence to support its use. Moreover, alcohol can be drying to skin, and alcohol toxicity has been reported with the use of 100% isopropyl or ethyl alcohol for sponge baths in both children and older adults (41), there is a need for research to evaluate the use of the alcohol and water sprays in fever management. A tepid sponge bath is a bath with water below body temperature, between 80_F and 95_F (26.6_C to 35_C). This type of bath may be ordered to reduce a client’s elevated temperature. The first effect of this water on the skin is blood vessel constriction. Administration of cold water for fever has been practiced for years. Formally and informally, healthcare personnel have voiced opinion for and against the practice of cold water and questioned its relative effectiveness compared to other methods. Several methods have been recommended to reduce fever in children, which include tepid sponging, fanning, alcohol sponging and antipyretics. However, controversy surrounds the use of tepid sponge for reduction of fever. The effectiveness of tepid sponging as a treatment alongside antipyretic varies between studies, with some finding that it is of no benefit and others suggesting that it is helpful (42).Best practices in fever management are then essential to optimizing patient outcomes. Yet the topic of best nursing practices for fever management is largely ignored in the clinical and research literature, which can complicate the achievement of best practices.( 43)We observed that administration of vinegar compresses resulted in rapid temperature reduction in the initial 30-60 minutes as compared to water alone or combined with vinegar half to half ; however, by the end of 2 hours both groups had reduce degree of temperature in different range. There was a difference in ultimate reduction of temperature between the three groups. Client with the vinegar compresses group had a higher reduction of body temp than only water or water with vinegar group's figure (3).There wasn't other studies that support or to compare the present result with them In spit of many research encounter to use vinegar as a hypoglycaemic & as an anti-inflammatory.
6. Summary& Conclusions
6.1. Main Outcome Measures
- Reduction of body temperature was effective within used vinegar compress compared to other methods used. Results: The reduction of body temperature in the vinegar compress faster than cold water & cold water with vinegar half to half compress, however, by the end of 2 hours
6.2. Conclusions
- Using of vinegar compresses is more effective in reduction of body temperature for patient who suffer from fever
6.3. Recommendation
- - Applications vinegar compresses for patients who suffer from fever in all health institutions especially when needs to lower patient body temp fasting . - Further work needs to be conducted, particularly with regard to assess using of vinegar in management fever in health institution - Reapplication of our results using other samples would be helpful in ensuring the validity of these findings.- Further work needs to be conducted to illustrate which effect of vinegar on skin surface are as a vasodilators or evaporated or both
6.4. Limitations
- - The study was undertaken at tropical hospitals only.- There aren't similar studies to support & compare with our study
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML