-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Nanoscience and Nanotechnology
p-ISSN: 2163-257X e-ISSN: 2163-2588
2025; 14(1): 1-8
doi:10.5923/j.nn.20251401.01
Received: May 22, 2025; Accepted: Jun. 20, 2025; Published: Jul. 3, 2025

Effects of Varying Growth Temperature on Optical and Structural Properties of Iron-doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles
Ayabei Shadrack1, Sharon Kiprotich1, John Njagi1, Jatani Ungula2
1Department of Physical and Biological Sciences, Murang’a University of Technology, Murang’a, Kenya
2Department of Pure and Applied Sciences, Kenya Methodist University, Meru, Kenya
Correspondence to: Sharon Kiprotich, Department of Physical and Biological Sciences, Murang’a University of Technology, Murang’a, Kenya.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

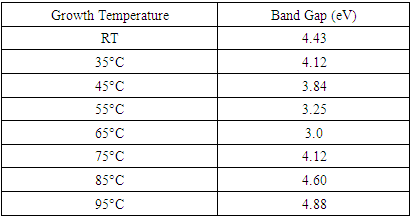
Iron-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles (Fe: ZnO NPs) have gained attention in biomedical fields due to their tunable optical properties and potential as biomedical agents. However, the influence of growth temperature on their structural integrity and luminescence performance remains unexplored. This study investigated the effect of varying growth temperature on the structural and optical properties of Fe: ZnO NPs to optimize their performance for potential bioimaging applications. Fe: ZnO NPs were synthesized using the sol-gel technique at different growth temperatures room temperature (RT), 35°C, 45°C, 55°C, 65°C, 75°C, 85°C, 95°C) and their structural and optical characterization was carried out using X-ray diffractometer (XRD), photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy, and Ultraviolet-Visible spectrometer (UV- Vis). XRD results confirmed the retention of a single-phase hexagonal wurtzite structure, and the slight shift in peaks showed the successful incorporation of Fe. Optical properties showed systematic absorbance modulation, a blue shift, and reduced optical bandgap (3.0 eV) at 65°C. PL revealed strong UV emission peaks in the 410-470 nm region, indicating enhanced near-band-edge (NBE) emission, which was optimized at 65°C and quenched at higher growth temperatures. Growth temperature at 65°C yields optimum optical and structural properties, therefore not only addressing the existing knowledge gap on temperature-dependent optimization of Fe: ZnO NPs for bioimaging but also establishing a foundation for future nanomedical applications of these NPs.
Keywords: Bioimaging, Fe: ZnO NPs, Sol gel synthesis, Temperature, Band gap
Cite this paper: Ayabei Shadrack, Sharon Kiprotich, John Njagi, Jatani Ungula, Effects of Varying Growth Temperature on Optical and Structural Properties of Iron-doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles, Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, Vol. 14 No. 1, 2025, pp. 1-8. doi: 10.5923/j.nn.20251401.01.
1. Introduction
- Among several promising options for bioimaging, iron-doped zinc oxide Fe:ZnO NPshave emerged asremarkable due to their unique optical and magnetic properties [1]. The above properties render them very promising as non-invasive biomedical imaging agents, especially fluorescence imaging and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), where materials that are highly luminescent and also biocompatible are needed [2]. To achieve their full potential in real-world applications, however, their optical and structural properties need to be finely tuned with regard to controlled synthesis conditions. The sol–gel synthesis method presents a flexible and cost-effective approach to making these nanoparticles, which can be easily fine-tuned for their structural and functional properties. This key factor that can affect the properties of Fe:ZnO nanoparticles, such as morphology and crystallinity, is the growth temperature that significantly impacts the usability of these materials towards biomedical applications. Although there is an increasing interest in Fe:ZnO NPs, the effect of growth temperature on the structural integrity and luminescent performance of these nanostructures, which are essential parameters defining the consistency of bioimaging functionality remains scanty. Numerous research papers have been conducted on synthesizing and characterizing Fe:ZnO nanoparticles for biomedical applications. For example, the work by [3] used a modified sol–gel approach to synthesize Fe-doped ZnO nanoparticles and study their structural properties. However, the effect of synthesis temperature on the nanoparticles was not considered in the investigation, leaving this as an open question for their effectiveness in bioimaging applications. Moreover, [3] identified the structural, optical, and magnetic properties of Fe-doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized through a polymeric precursor method. They observed that tweaking the synthesis process may alter iron ions’ oxidation state in the nanoparticles, hence perturbing their magnetic properties. However, the research did not study the systematic effect of growth temperature on the properties of nanoparticles, emphasizing the need for further investigation in this field. The work by [4] focused on how iron-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles possess superior biocompatibility and multifunctional potential in various fields. Although the study outlined the biomedical application of these nanoparticles, it did not explore the role of growth temperature in influencing their biocompatibility and functional properties. These findings emphasize the crucial role of synthesis conditions in determining the intrinsic properties of Fe:ZnO nanoparticles. However, there are still few studies that investigate the correlation between synthesis temperatures and the properties of iron-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles, specifically in the context of bioimaging. In order to seal this gap, this study systematically examines how changes in growth temperature alter the structural and optical properties of Fe:ZnO NPs prepared by sol--gel method with a view of determining the conditions that would maximize their use in bioimaging applications. This study aims to fill the above gap by providing a detailed analysis of the structural and optical properties of Fe:ZnO nanoparticles as synthesized at different temperatures ranging from ambient to 95°C. In the sol–gel process, a liquid suspension called the “sol” turns into a semi-solid “gel” structure. This approach helps in synthesizing nanoparticles that are stable in terms of size and shape, as well as uniformity [5]. Although other synthesis techniques likethe hydrothermal method are efficient at producing well-crystallized ZnO nanomaterials, the fact that it can employ long reaction periods and high temperatures leads to non-uniform particle sizes and inconsistent morphologies [6]. These limitations make it challenging to acquire nanoparticles that are uniform enough for reliable bioimaging applications. Co-precipitation is singled out as a simple and low-cost technique. However, it is limited by the application of aqueous solvents, which may hinder the accuracy in the control of particle size and shape [7]. Moreover, the process may build nanoparticles with lower crystallinity, and it’s prone to aggregation, which may weaken their crucial optical and structural properties that are important for the purposes of bioimaging applications [7]. Varying growth temperature during sol-gel processing can have a profound impact on the physical and chemical properties of the nanoparticles produced. Raising the temperature of synthesis typically leads to enhanced crystallinity and reduced defect density, which makes the optical properties required for bioimaging optimal [8]. Alternatively, lowering the synthesis temperature may result in nanoparticles that display enhanced surface area and different shapes, which may change their performance when interacting with biological entities [9]. The incorporation of iron in ZnO nanoparticles improves their capacity to react magnetically, qualifying them for use in the context of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) [4]. By incorporating Fe ions into the bandgap of ZnO, it is possible to optimize its optical characteristics to address specific imaging requirements. The interactions between the growth temperature and iron doping concentration are complex, modifying the general characteristics of the nanoparticles with their joint action [10]. Research also shows that modifying the growth temperature directly influences the size, morphology, and particle dispersion of Fe:ZnO nanoparticles, hence with implications in their luminescence and magnetic responses [4]. This work seeks to understand the essence of how differences in temperatures affect the properties of Fe:ZnO nanoparticles, destined to enhance their functionality in the areas of bioimaging.
2. Methodology
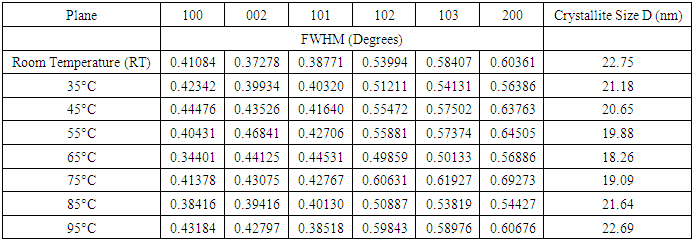
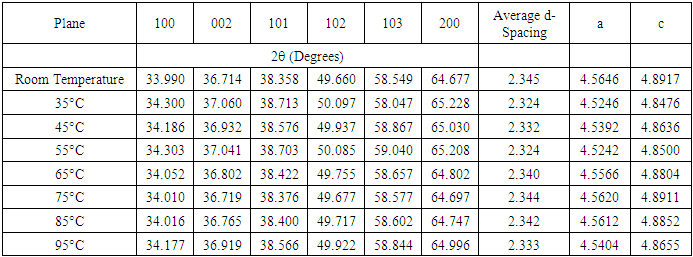
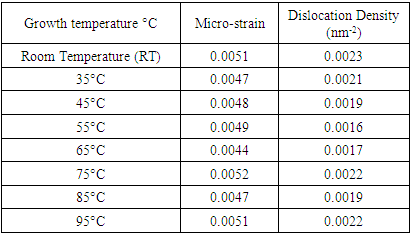
- ChemicalsZinc acetate dihydrate Zn (CH3COO)2• • H2O of purity 99.9%, as a metal precursor, Diethanolamine (DEA) C4H11NO2 of 99.3% purity as a complexing agent, Ethanol C2H5OH of 99.9% purity as a solvent for the precursor. Iron (III) nitrate nanohydrate Fe (NO3)3•9H2O of 98% purity, as the source of iron, Deionized water (DI) (H2O), all supplied by Sigma Aldrich. All reagents were of analytical grade and were directly used without any special treatment.Experimental procedureSol-gel technique was adopted from [11] to synthesize Fe: ZnO NPs by adding 4.4g of Zn (CH3COO)2•(H2O) to 100 ml of ethanol in a clean beaker on a magnetic stirrer at room temperature. 2 mL of DEA was added after 15 minutes, and stirring continued until a transparent solution was formed. 0.45% Fe was added, and stirring was continued for another 30 minutes. 1.6M NaOH was added dropwise using a burette to adjust the pH to 11 with the aid of a pH meter. The contents were then transferred to a hot magnetic stirrer set at RT as the first growth temperature, and heating took place for 2hrs where a gel-like solution was formed. The solution was covered in a clean foil and left to age overnight. The gel was rinsed several times with DI before drying in an oven at 100°C for 2hr to eliminate residual solvents and finally annealed in a muffle furnace at 500°C for 1 hour. The sample was ground into fine NPs and kept in a sample holder for further analysis. The procedure was repeated for other growth temperatures (35°C, 45°C, 55°C, 65°C, 75°C, 85°C, 95°C).Characterization TechniquesX-ray diffraction analysis was done using an X-ray diffractometer model ARL EQUINOX 100 with Cu-Kα radiation (λ=1.5406Å) to determine the phase purity, crystalline structure, and crystallite size of synthesized Fe: ZnO NPs. Photoluminescence spectroscopy (PL) model Infitek SPLF97 Fluorescence spectrometer was used to determine the optical emission properties and defect states of the synthesized Fe: ZnO NPs. The measurements were performed at room temperature with an excitation wavelength of 300nm. Ultra Visible spectrophotometer was used to obtain the absorbance spectra at room temperature at the wavelength range of (200-800 nm).XRD AnalysisThe X-ray diffraction pattern obtained, as shown in Figure 1, was compared with the standard reference data from the Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards (JCPDS), specifically card No. 01-070-8072. All samples were synthesized from 0.45% Fe, and the growth temperature varied from room temperature (RT), 35°C, 45°C, 55°C…….95°C, all exhibited distinct diffraction peaks corresponding to the hexagonal wurtzite phase of ZnO with no secondary phases detected. This indicates the successful incorporation of Fe3+ on the ZnO lattice without phase segregation.
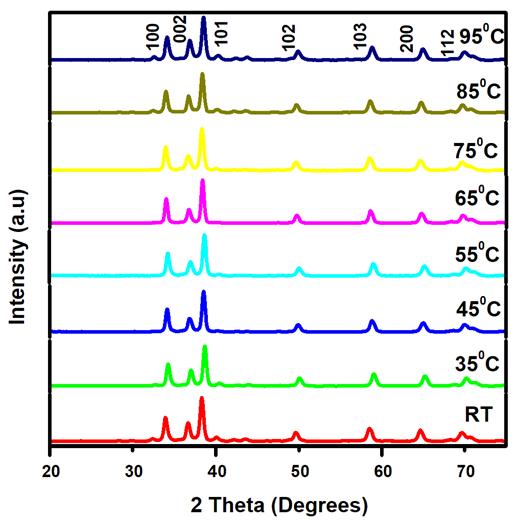 | Figure 1. XRD pattern showing diffraction peaks of Fe: ZnO NPs at different growth temperatures |
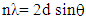 | (1) |
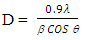 | (2) |
|
|
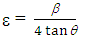 | (3) |
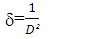 | (4) |
|
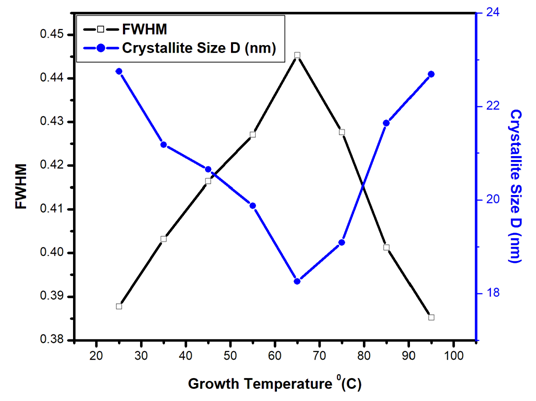 | Figure 2. Variation of FWHM and Crystallite size D (nm) of Fe: ZnO NPs at varying growth temperatures |
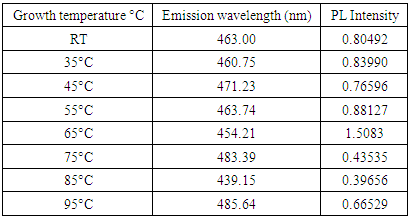
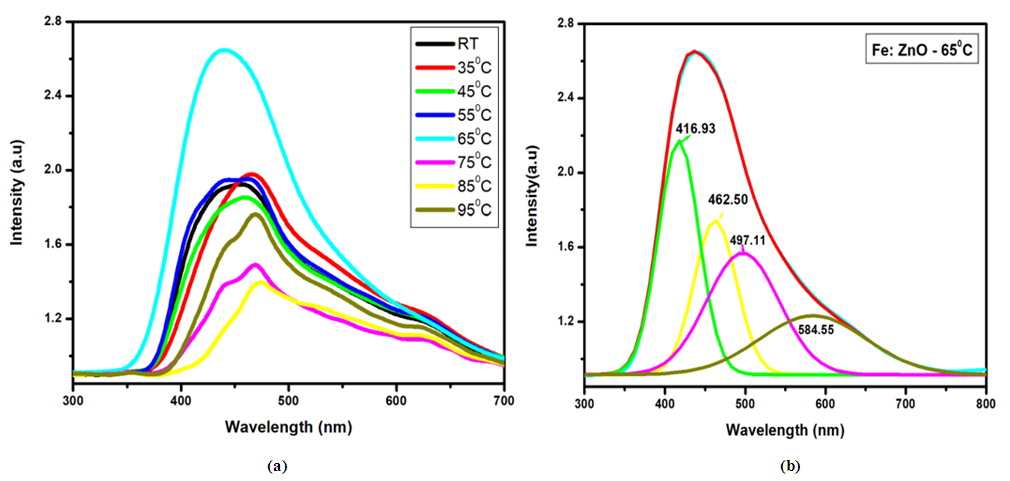 | Figure 3. (a) Photoluminescence spectra (PL) of Fe: ZnO NPs at different growth temperatures and (b) Deconvolution of Fe: ZnOat 65°C |
|
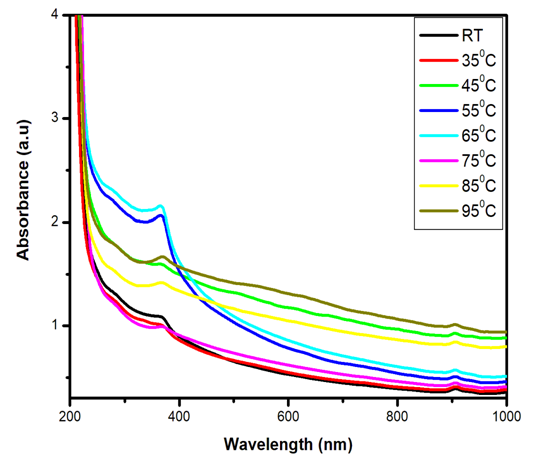 | Figure 4. Ultra Violet Visible (UV Vis) absorbance spectra of Fe: ZnO NPs at varying growth temperatures |
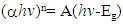 | (5) |
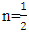 for direct allowed transitions, while n = 2 for indirect allowed transitions. Since ZnO is a direct bandgap semiconductor,
for direct allowed transitions, while n = 2 for indirect allowed transitions. Since ZnO is a direct bandgap semiconductor, 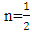 was used. The Tauc plot was obtained by plotting (αhv)2 against photon energy (hv), and the optical band gap was obtained by extrapolating the linear portion of the curve to the x-axis where (αhv)2 = 0. Figure 5 shows the optical band gaps obtained through extrapolation and summarized in Table 5.
was used. The Tauc plot was obtained by plotting (αhv)2 against photon energy (hv), and the optical band gap was obtained by extrapolating the linear portion of the curve to the x-axis where (αhv)2 = 0. Figure 5 shows the optical band gaps obtained through extrapolation and summarized in Table 5.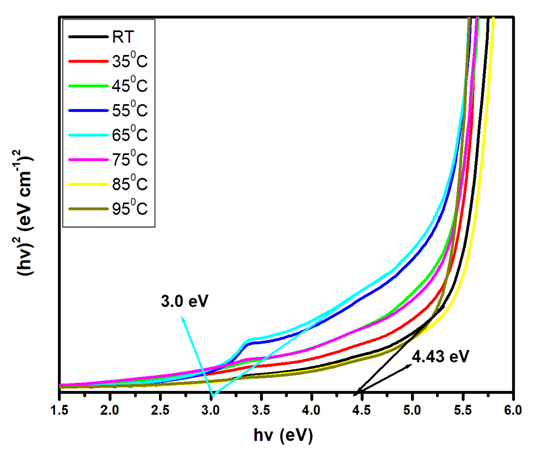 | Figure 5. Tauc plot showing extrapolated band gaps of Fe: ZnO NPs at different growth temperatures |
|
3. Conclusions
- Herein, Fe: ZnO NPs at varying growth temperatures were successfully synthesized via the sol-gel technique, which offered a cost-effective and simple controllable route for tuning the structural and optical properties. XRD analysis confirmed the presence of the hexagonal wurtzite structure of ZnO with no secondary phases. The average crystallite size estimated using the Debye-Scherrer formula decreased from 22.75 nm at RT to 18.26 nm at 65°C. PL investigation revealed 65°C with the highest intensity at 1.51 a.u and the emission wavelength shifted to 454.21 nm, indicating that the crystallinity increased and non-radiative defects were minimized. UV- Vis absorption analysis and Tauc plots confirmed that the bandgap can be tuned through variation of the growth temperature. Optical bandgap analyzed for all samples was found to decrease initially from 4.43 eV at RT to as low as 3.0 eV at 65°C and then increased slightly for higher growth temperatures due to the Burstein-Moss effect. By addressing the research gaps identified in earlier studies, the findings of this study enhance the understanding of how optimizing growth temperature, the synthesis can effectively be used to tailor Fe:ZnO nanoparticles towards biocompatibility and specificity. These findings offer a strong foundation for developing modified advanced nanoparticles for non-invasive, high-resolution bioimaging.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors wish to thank Murang’a University of Technology for offering access to various synthesis and characterization techniques for this research.
Conflict of Interest
- The authors declare no conflict of interest.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML