-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Nanoscience and Nanotechnology
p-ISSN: 2163-257X e-ISSN: 2163-2588
2018; 8(1): 1-6
doi:10.5923/j.nn.20180801.01

Evaluation of Microcrystalline Cellulose from Groundnut Shell for the Removal of Crystal Violet and Methylene Blue
Zakariyya Uba Zango1, Saifullahi Shehu Imam2
1Department of Chemistry, Al-Qalam University Katsina, Katsina, Nigeria
2Department of Pure and Industrial Chemistry, Bayero University, Kano, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Zakariyya Uba Zango, Department of Chemistry, Al-Qalam University Katsina, Katsina, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2018 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), a fine, white, odorless, crystalline powder is extracted from groundnut shell. Purity test carried out on the crystalline powder have shown red coloration which indicated that the prepared MCC is pure. The isolated MCC demonstrated adsorption capacity towards the removal of Crystal Violet (CV) and Methylene Blue (MB) dyes. Equilibrium is gradually achieved within 240 mins for the CV, while for the MB it is achieved within 220 mins with equilibrium adsorption capacity (qe) values of 65 mg/g and 79 mg/g respectively. Increasing the stirring speed from 100 rpm to 400 rpm has little or no influence on the adsorption capacity. 0.5 g of the adsorbent is found to be sufficient for 100% removal for both the CV and MB. Alkaline medium proved to be effective for the adsorption of both CV and MB where a maximum removal of MB is recorded at a pH of 8 while that of CV is recorded at pH 10. Good adsorbent is the one which can be easily regenerated and reused. Groundnut shell MCC shows high adsorption capacity as up to 6 cycles of re-used with percentage removal of 62 and 84 for the CV and MB respectively.
Keywords: Adsorbent, Crystal Violet (CV), Methylene Blue (MB), Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC)
Cite this paper: Zakariyya Uba Zango, Saifullahi Shehu Imam, Evaluation of Microcrystalline Cellulose from Groundnut Shell for the Removal of Crystal Violet and Methylene Blue, Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, Vol. 8 No. 1, 2018, pp. 1-6. doi: 10.5923/j.nn.20180801.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Many chemical industries such as pharmaceutical, textile, polymers, refineries, plastic, and leather use diverse classes of synthetic dyes. Usually, these industrial processes discharge 30–40% of the dyes which remain in the wastewaters [1]. These organic contaminants are carcinogenic, hazardous and highly-toxic and may cause harmful effect not only for human health but also for marine life even at low concentrations [2, 3]. They are biologically non-degradable due to their aromatic structure and their synthetic Origin. Methylene Blue (MB) and CV are typical examples of widely used industrial dyes which has relevant toxic effect. Methylene blue (MB) is common cationic dye which readily aggregates and highly soluble in solutions even at micro molar concentrations causing harmful effects. Additionally, it was reported to cause breathing difficulties, eyes burn, vomiting, nausea, and mental bewilderment [4, 5] while contact with Crystal Violet is said to resulted in the skin diseases and said to causes oral ulcerelation [6].It is difficult to degrade dye materials because they are very stable to light and oxidation [7]. For their removal from contaminated water, several methods such as physical, chemical and biological methods have been investigated [8, 9]. Among the proposed methods, removal of dyes by adsorption technologies is regarded as one of the competitive methods because adsorption does not need a high operation temperature and several coloring materials can be removed simultaneously [10]. Researchers have studied adsorption of dyes using natural low-cost adsorbents due to its effectiveness and environmental friendly; Example include oil palm fronds [11], corn cob [12], sugarcane bagasse [13] and saw-dust [14]. M.H. Hussin et al reported on the adsorption of methylene blue microcrystalline cellulose obtained from oil palm fronds [15]. Cellulose is the world’s most ubiquitous and abundant natural occurring polymer which is produced by plants, as well as by microorganism [16]. In nature, cellulose is the substance that makes up most of a plant's cell walls. In chemistry, it is a poly disperse polymer of high molecular weight and comprised long chains of D-glucose units joined together by β-1, 4-glucosidic bonds [17] which is insoluble in water but degradable by microbial and fungal enzymes [18] The use of cellulose in high added value applications is still rare due to its insolubility in water and most organic solvents, hygroscopic character and no melting. Meanwhile, the interest in nano cellulose has sharply increased lately due to the specific chemical and physical properties of such material [19]. In nature, the cellulose molecular chains are biosynthesized and self-assembled into microfibrils, which are composed of crystalline and amorphous domains [20]. Crystalline cellulose was impenetrable by water while amorphous cellulose swelled in water due to disruption of inter-molecular hydrogen bonds [21].Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) is a fine, white, odorless, crystalline powder, and a biodegradable material, which can be isolated from cellulose and used as a suspension stabilizer and a water retainer, in the cosmetics, food, and pharmaceuticals industries and in environmental remediation of industrial pollutants [22, 23]. This work is aimed at isolation of Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC) from groundnut shell for the adsorption of Crystal violet and Methylene blue dyes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
- Groundnut shell was collected from Dawanau Market, one of the largest cereals market in Kano Nigeria. Crystal violet (Molecular Formula C25N3H30Cl, MW 407.979 g/mol and Density: 1.19 g/cm3) and Methylene blue (Molecular Formula C16) were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (USA). All chemicals used in this work are of high purity and of analytical reagent (AR) grade and were used as received. Double Distilled Water (DDW) was used throughout the study.
2.2. Pulping and Bleaching
- The groundnut shell was grinded into crystalline powder and dried in the dark for a period of one week. It was then sieved to obtain finely grinded powder. A cartridge containing 50g of dried groundnut shell was placed in a Soxhlet equipped with 1000 mL round bottom flask. The sample was first subjected to extraction at 85°C with 600 mL ethanol/toluene (2/1 (v/v)) mixture during 24 h [24]. The pulping process was performed under atmospheric pressure. The dried Alfa stems were kept for 4 h at 85°C in a 500 mL round bottom flask containing 300 mL of NaOH (1 mol/L), equipped with a reflux condenser and a magnetic stirrer. The obtained mixture was then immediately filtered. The residue was successively washed with 350 mL of NaClO solution (40 wt%) for 18 h at 30°C, 250 mL of ethanol for 2 h at 30°C and 250 mL of diethyl ether for 2 h at ordinary temperature [25]. After this treatment, the cellulose pulp was washed with distilled water until pH of 7 was reached. At last, the residue obtained was dried for 24 h at 60°C.
2.3. Preparation of Microcrystalline Cellulose
- Micro crystalline cellulose was isolated from the pulp using a method described by Chuayjuljit et al., [23]. Based on original procedures described by Battista [26]. In the preparation, 100 mL HCl solution was taken in a 250 mL flask and kept it in a heating mental. The temperature of heating mental was kept constant at 85°C and stirring of HCl solution started. After getting the 85°C temperature of HCl solution, 100 g of the groundnut shell pulp were added in the solution slowly with continuous stirring. After complete addition of the powder, the mixture was kept under continuous stirring for one and half hours. After confirming the complete depolymerization of the powder, the heating and stirring was stopped and the mixture was kept for cooling.After getting the mixture at room temperature, it was neutralized with water to get the neutral pH. Then this mixture was filtered with the Watmann 42 filter paper separating microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) and neutral water. Then this microcrystalline cellulose was again washed with acetone to remove traces of water present. Again filtration was done to separate acetone and microcrystalline cellulose. After filtration, the microcrystalline cellulose was kept for natural drying. After complete drying, the microcrystalline cellulose was weighted.
2.4. Purity Test
- Purity test of MCC was done by taking 1 mg of sample in 1 mL of phosphoric acid and it was heated on a water bath for 30 minutes. Then 4 mL of 0.2% (w/v) solution of Catechol in phosphoric acid was added and it was again heated for further 30 minutes.
2.5. Identification Test
- Identification test was done to determine the presence of starch and dextrin in the crystalline powder. In the experiment, 0.1 g of MCC was mixed with 5 mL of water. The mixture was shaken vigorously and three drops of iodine solution was added to the mixture. It was allowed to stand for 5 minutes.
2.6. Preparation of Adsorbate
- The adsorbates, Crystal Violet (CV) and Methylene Blue (MB) dye solutions were prepared by measuring 100 mg of each dye powder and dissolved into 20 mL of distilled water. The solution was then transferred into 1000 ml volumetric flask and distilled water was added till the mark. The concentrations of the resulting solutions were 100 mg L−1 respectively. The solutions of different concentrations used in various experiments were obtained by dilution of the stock solutions. The stock solution was prepared every day. All of the solution was prepared with distilled water.
2.7. Dye Adsorption Experiment
- Batch adsorption experiments were conducted on both the CV and MB. In the experiment, 100 mL of the dye is transferred into an Erlenmeyer flask containing 0.1 g of the adsorbent. The mixtures are subjected to an isothermal shaking at 30°C with a speed of 200 rpm until equilibrium is attained. The samples were collected and centrifuged. The initial and final concentrations of the CV and MB in the solutions were determined by visible spectrophotometer ((Varian CARY 50 probe)) fitted with a quartz cell with a path length of 1.0 cm. Absorbance measurements were made at 590 nm for CV and 670 nm for MB respectively. A calibration curve was constructed with dye concentrations ranging from 1.0 to 15.0 mg/L.The removal percentage (%R, %), the amount of the dye adsorbed at time t (qt, mg g−1), and the adsorption capacity of the dyes at equilibrium (qe, mg g−1) were calculated by applying Equations (1), (2) and (3), respectively [27, 28]
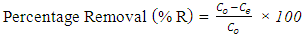 | (1) |
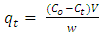 | (2) |
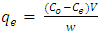 | (3) |
2.8. Effect of Stirring Rate
- Rate at the adsorbent and adsorbate interact is one of the important feature in adsorption study. The effect of stirring rate was studied by conducting adsorption experiment at different stirring speed between 100 to 400 rpm with an initial dye concentration 100 mg/L and the adsorbent dosage of 0.1 g.
2.9. Effect of Absorbent Dosage
- The dependence of the adsorption of dye on the amount of adsorbent was studied by varying the adsorbent dosage from 0.1 g – 0.7 g with a constant CV and MB concentrations of 100 mL at room temperature and constant stirring rate and of 200 rpm.
2.10. Effect of pH
- Solution pH affects adsorption process of dye molecules by affecting both aqueous chemistry and surface binding-sites of the adsorbent. The effect of pH in the range 3 – 12 with a constant shaking time of 240 min for the removing of dyes was investigated. The pH of solutions was adjusted using 0.1M HCl or NaOH. Initial dye concentration fixed at 100 mL. The pH values were measured by using a pH-meter model HI 8014, Hanna Instruments (Italy).
2.11. Regeneration and Reusability Test
- The regeneration and reusability of adsorbents are very important parameters to be considered for industrial applicability. In order to study the reusability of the groundnut shell MCC, adsorption experiment was conducted with initial CV dye concentration of 100 mg/L and adsorbent dosage of 0.5 g at room temperature and stirring rate of 200 rpm. The adsorbent was recovered by centrifugation, followed by filtered and washing with 0.1 M NaOH solution and then with distilled water to remove all the traces of the dye. The experiments were repeated 6 times with both CV and MC times using the same procedure.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Purity and Identification Analysis
- Purity test is done to ascertain the quality of the MCC formed. After the analysis was carried out, the crystalline formed was found to be red in colour which shows that prepared MCC is pure.When the MCC was mixed with water and iodine was added in drops, brownish-red color was formed. The formation of the brownish-red coloration confirmed the presence of starch and dextrin in prepared MCC.
3.2. Effect of Contact Time
- The contact time between adsorbent and adsorbate is an important factor when doing adsorption study. It is shown in figure 1 that the adsorption capacity of CV and MB increase with increasing the contact time. At the beginning, rapid adsorption is recorded for both the dyes because the adsorption sites are not fully occupied. The dyes get attached to the adsorption sites very easily [29]. However, as the times goes the adsorption of the dyes became slowly which is as a result of the increased of the concentration of the dyes in the adsorption sites. An equilibrium is gradually reached within the within 240 mins for the CV with an equilibrium adsorption capacity (qe) value of 65 mg/g. While for the MB, the equilibrium is observed at 220 mins with qe value of 79 mg/g. Figure 1: Spectra for the adsorption of (a) CV and (b) MB onto groundnut shell MCC
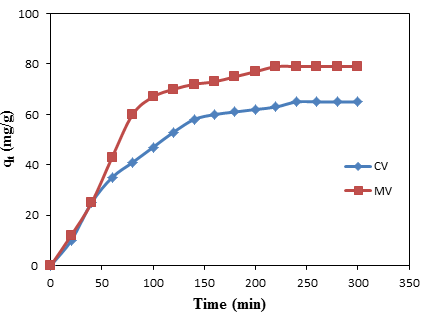 | Figure 1. Adsorption of CV and MB onto groundnut shell MCC |
3.3. Effect of Stirring Speed on Adsorption Process
- Effects of stirring speed on the adsorption capacity and removal efficiency as shown in Figure 2. It is observed that no considerable increase in the removal efficiency of dyes when the stirring speed was increased from 100 to 400 rpm. In other words, diffusion CV and MB from solution to surface of the groundnut shell MCC is constant, regardless of the increased in the stirring rate.
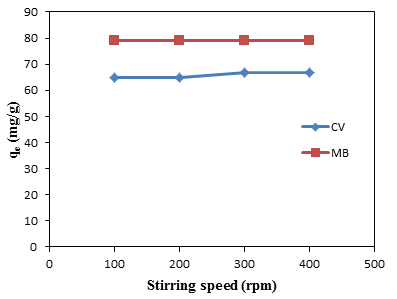 | Figure 2. Effect of stirring speed for the adsorption of CV and MB by groundnut shell MCC |
3.4. Effect of the Amount of Adsorbent
- A promising adsorbent material has to be able to remove considerable amounts of adsorbate at low doses. This feature is paramount to reduce operational costs and minimize the risks related to the secondary pollution [30]. Under the experimental conditions, qe is found to decreases as the dosage increases (figure 3). The decrease in the adsorption capacity value at equilibrium is said to be as a result of a greater availability of the exchangeable sites on surface area at a higher concentration of the adsorbent [31, 32]. However, in contrast, the %R value increases, 100% removal is achieved at a dosage of 0.5 g. for both CV and MB dyes (Figure 4). The removal efficiency is said to increase with the dosage because the larger amount of adsorbent provides a greater surface area and more active adsorption sites which makes penetration of the dye molecules to the removal site of the adsorbent much easier. Also attractive interaction increases between ions and adsorbent surface [33].
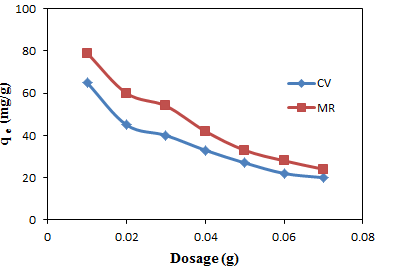 | Figure 3. Equilibrium adsorption capacity against adsorbent dosage for the adsorption of CV and MB onto groundnut shell MCC |
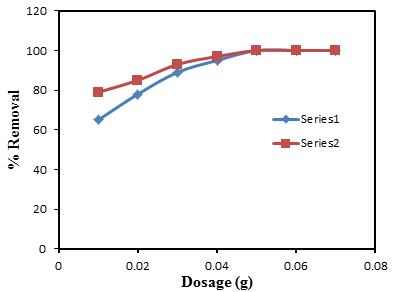 | Figure 4. Removal efficiency against adsorbent dosage for the adsorption of CV and MB onto groundnut shell MCC |
3.5. Effect of pH
- The pH of an aqueous medium is an important factor that may influence the uptake of the adsorbate. The chemical characteristics of both adsorbate and adsorbent vary with pH [34]. Figure 5 shows low adsorption of dyes at lower pH values of 2-4 for both CV and MB. The minimum adsorption observed at low pH could be related to the higher concentration and mobility of H+ ions, which is favored by high solubility of the dyes in acid medium [24]. Also it is partly because hydrogen ions themselves are strongly competing with dye molecules for the adsorption sites in the acidic medium. Thus, in acidic medium the positively charged surface of sorbent tends to oppose the adsorption of the cationic adsorbate [35]. With increase in pH of the solution, the amount of removal is found to increase. The maximum MB removal was observed at pH 8 while that of CV was found to be at pH 10. The basic dyes give positively charged ions when dissolved in water. When pH of dye solution is increased the surface acquires a negative charge, there by resulting in an increased adsorption of MB and CV due to an increase in the electrostatic attraction between positively charged dye and negatively charged adsorbent [36, 37].
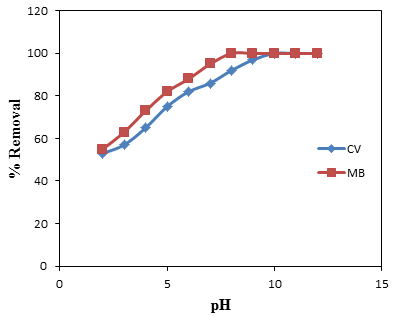 | Figure 5. Removal efficiency against pH for the adsorption of CV and MB onto groundnut shell MCC |
3.6. Reusability of the Adsorbent
- Regeneration is very important aspect of the adsorption from economy and environmental point of view. The disposal of adsorbent is one of the problems associated with the adsorption processes. The reusability of adsorbent is a crucial factor for the application in industrial wastewater treatment since it significantly affects the operational cost. Due to economic consideration, regeneration of adsorbent is necessary especially for expensive adsorbents [38]. The regeneration is vital for way to replace the need of new adsorbent and also to tackle the problem of excessive adsorbent disposal. As shown in Figure 6, six consecutive cycles, the removal efficiency of CV is found to be 62% while that of MB is 84%. This demonstrated the high regeneration capability of groundnut shell MCC and its good reusability for CV and MB removal.
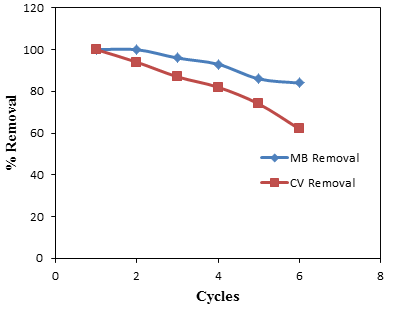 | Figure 6. Regeneration of groundnut shell MCC adsorbent for the adsorption of CV and MB |
4. Conclusions
- Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) was isolated from groundnut shell. Batch adsorption experiments were conducted for the removal of Crystal Violet (CV) and Methylene Blue (MB) onto the prepared MCC. Equilibrium of adsorption is gradually reached within the within 240 mins for the CV with an equilibrium adsorption capacity (qe) value of 65 mg/g. While for the MB, the equilibrium is reached within 220 mins with qe value of 79 mg/g. 100% removal is achieved at a dosage of 0.5 g. for both CV and MB dyes. However, qe is values found to decreases as the dosage increased which is attributed to a greater availability of the exchangeable sites on surface area at a higher concentration of the adsorbent. Alkaline medium is found to favor the adsorption of both the CV and MB in which the maximum removal of CV is observed at pH 10 while that of MB is observed at pH 8. High removal efficiency is observed even at 6 cycles with 62% and 84% removals for CV and MB respectively. As such MCC obtained from groundnut shell is considered to be effective adsorbent for the removal of environmentally pollutant dyes.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors wish to thanks Department of Chemistry, Al-Qalam University Katsina for providing funds and atmosphere to conduct the research. Also wish to acknowledge the efforts of Professor Muhammad Bashir Ibrahim of Bayero University Kano, Nigeria for making all the necessary corrections and suggestions towards the success of the work.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML