-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Nanoscience and Nanotechnology
p-ISSN: 2163-257X e-ISSN: 2163-2588
2017; 7(1): 21-25
doi:10.5923/j.nn.20170701.05

Synthesis of Nanoparticles through Flame Spray Pyrolysis: Experimental Apparatus and Preliminary Results
Giulio Solero
Politecnico di Milano, Campus Bovisa, Dipartimento di Energia, Milano, Italy
Correspondence to: Giulio Solero, Politecnico di Milano, Campus Bovisa, Dipartimento di Energia, Milano, Italy.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Nanostructured materials represent nowadays a wide, and probably still largely unexplored, field of potential applications. In fact, this is a research topic in high and rapid development, both at a basic level and under the point of view of possible practical applications, leaving large space for a thorough scientific analysis, which requires with no doubt long time for ultimate conclusions. This paper deals with the preliminary work performed in the field of FSP (Flame Spray Pyrolysis) synthesis for nanoparticles, using an external mixing gas assisted nozzle. Particularly, an experimental apparatus has been designed, realized and characterized for the controlled synthesis of nanoparticles by the flame spray pyrolysis technique. The apparatus consists of a gas-assisted spray for droplet generation and dispersion in a secondary pilot flame. By dissolving suitable precursors in a liquid fuel, different types of nanoparticles have been produced. In the preliminary tests SiO2 and TiO2 have been synthesized and characterized by TEM analysis and XRD, respectively, as a function of the main operating conditions (for instance, precursor concentration) of the experimental apparatus. The designed set-up shows good stability and reproducibility of the reaction flame and, therefore, of the material produced and the obtained results, even if preliminary, encourage the use of the experimental apparatus for the controlled synthesis of nanostructured materials.
Keywords: Nanomaterials synthesis, Flame spray pyrolysis, Combustion
Cite this paper: Giulio Solero, Synthesis of Nanoparticles through Flame Spray Pyrolysis: Experimental Apparatus and Preliminary Results, Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, Vol. 7 No. 1, 2017, pp. 21-25. doi: 10.5923/j.nn.20170701.05.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Nanostructured materials represent nowadays a wide, and probably still largely unexplored, field of potential applications. In fact, this is a research topic in high and rapid development, both at a basic level and under the point of view of possible practical applications, leaving large space for a thorough scientific analysis, which requires with no doubt long time for ultimate conclusions.The potential application fields of nanoparticles are very wide and, probably, not yet fully understood: from energetics (sensors, propulsion, reduction of environmental impact) to chemistry (catalysis, additives) to medicine (diagnostics) and of course to material science. For instance, recent studies [1, 2] put into evidence that inert nano-additives can influence combustion features of Diesel sprays with possible important effects on propulsion systems. In the field of rocket propulsion the use of nanoparticles can enhance the engine performance under the point of view of specific thrust [3]. Also the problem of nanoparticles impact on human health is a rather unexplored field. The same can be said about the study of the different methodologies for controlled synthesis of nanoparticles. In fact, numerous processes are utilized for the synthesis of nanostructured materials and in particular for nanoparticle production. These processes can be divided in three main categories [4]. The mechanical methods obtain a reduction of the particle dimensions through mechanical systems such as the “ball milling” technique. The liquid-chemical methods rely on the precipitation of a solid in a solution or the chemical conversion of colloidal dispersions in a gel (“sol-gel technique”). The high temperature methods for the synthesis are numerous and include evaporation/condensation techniques, aerosol techniques and flame synthesis [5]. The high temperature synthesis offers several advantages for nanoparticle production in terms of both purity of materials and size control of the particles. For the flame synthesis process there are two main ways to inject the precursor in the flame: in homogenous phase, through an evaporation system at controlled temperature, or through a spray system, in liquid phase (FSP: Flame Spray Pyrolysis). This last methodology offers a greater flexibility in terms of type of precursors to be used and flow control determining the amount of produced material. The advantage of the Flame Spray Pyrolysis technique (FSP) is the use of a wide variety of possible low cost precursors (mainly in the field of metal oxides such as TiO2, Al2O3), obtaining a final product with high purity and relatively narrow size distribution [6, 7]. FSP seems to be a versatile process allowing a strict control of the produced nanomaterial, particularly product size and morphology strictly depend on precursor concentration and dispersion gas flow rate [8, 9]. Moreover, also inorganic nanorods can be synthesized through this technique [10]. A typical experimental set-up [11, 12] is constituted by a unit for droplets generation and dispersion (usually a gas-assisted spray), a heat source for droplets evaporation and ignition and an oxidant for combustion. The simplest way to generate micron size droplets is the use of an assisted atomizer, which presents also optimal features under the point of view of homogeneity of droplets size. Obviously, due to the complexity of the physical and chemical phenomena involved in the controlled synthesis by FSP, investigation should be performed about the influence of the operating conditions of the spray (flow field, dimensional distribution, precursor typology and physical properties, gas to liquid mass ratio, oxidant typology) on the final product, that is on the morphological and structural properties of the derived nanoparticles.
2. The Experimenyal Set-up
- This paper deals with the preliminary work performed in the field of FSP synthesis, using an external mixing gas assisted nozzle, presented in Fig. 1.
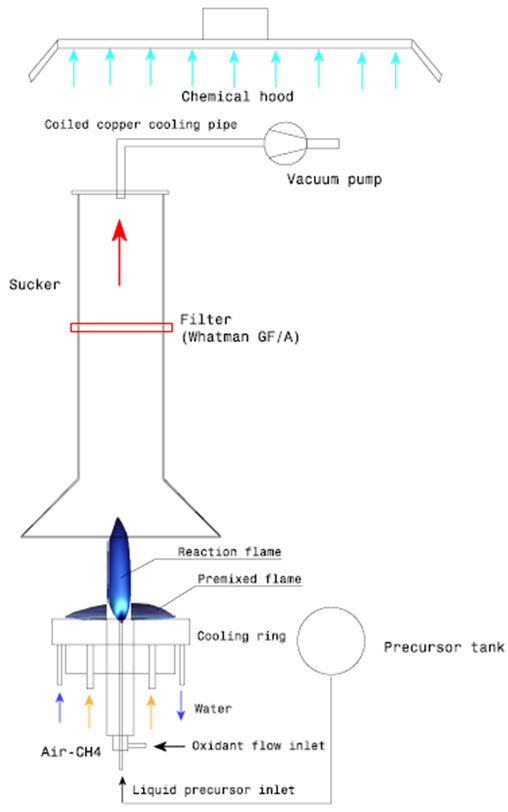 | Figure 1. Schematic view of the experimental set-up |
3. Experimental Results
- As outlined in the Introduction, the main features of the nanoparticles (especially under the point of view of size distribution and morphology) to be synthesized in the combustion process depend on the structure of the spray. It is important to achieve a constant range of droplet size as a function of different operating conditions. In order to investigate the dimensional distribution of the generated droplets as a function of dispersion gas flow rate and gas to liquid mass ratio, the behaviour of the spray jet has been initially characterised in isothermal (cold) conditions, both through visualizations for qualitative analysis and PDA (Phase Doppler Anemometry) for quantitative measurement of mean droplets size. Figure 2 shows a typical isothermal water spray as obtained by our nozzle. The general morphology of the spray seems quite homogeneous, the big spots are falling droplets after condensation in the ambient air.
 | Figure 2. Image of the water spray |
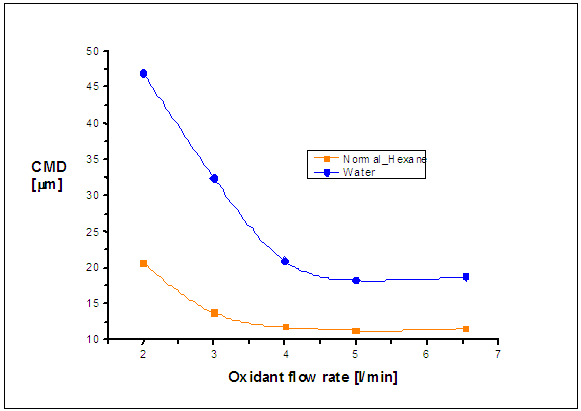 | Figure 3. Comparison of the counter mean diameter (CMD) for water and n-hexane spray at 5 mm from the exit nozzle |
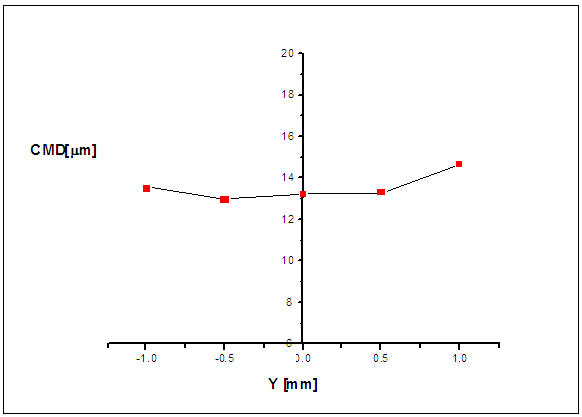 | Figure 4. Radial profile of the CMD for the water spray at 50 mm from the exit nozzle |
 | Figure 5. n-hexane spray flame |
 | Figure 6. n-hexane with TEOS precursor spray flame |
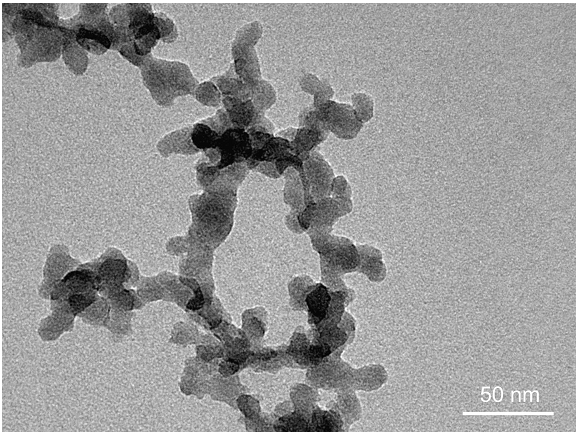 | Figure 7. SiO2 nanoparticles synthesized in the spray flame: 0.5 molar solution of TEOS, 1 ml/min |
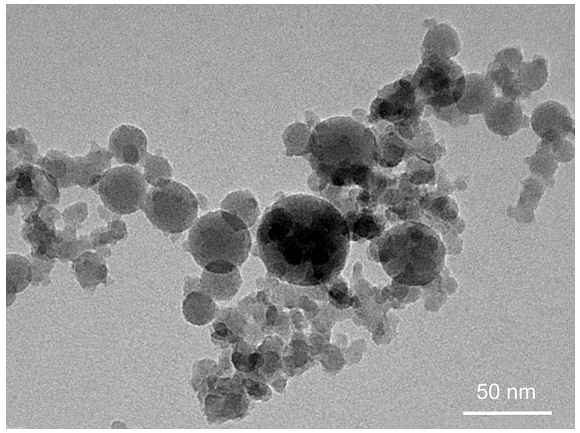 | Figure 8. SiO2 nanoparticles synthesized in the spray flame: 1 molar solution of TEOS, 3 ml/min |
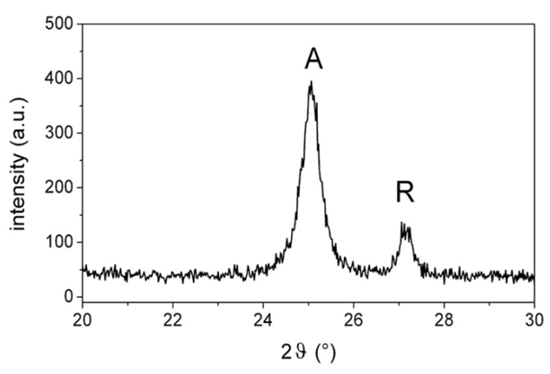 | Figure 9. Main peaks of the XRD spectrum of synthesized titania nanoparticles (A = anatase, R = rutile) |
4. Conclusions and Future Work
- An experimental apparatus has been designed, realized and characterized for the synthesis of nanoparticles by the flame spray pyrolysis method. The apparatus consists of a gas-assisted spray for droplets generation and dispersion in a secondary pilot flame. By dissolving suitable precursors in a liquid fuel, different types of nanoparticles have been produced. In the preliminary tests SiO2 and TiO2 have been synthesized and characterized by TEM analysis and XRD, respectively. The experimental set-up shows good stability and reproducibility of the reaction flame and, therefore, of the material produced. The influence of operating conditions of the synthesis apparatus (mainly, the precursor concentration and flow rate) upon the morphology of the nanostructured material has been preliminarily investigated. The titania nanoparticles generated by the FSP apparatus show (through XRD analysis) a crystal structure (≈86% anatase) suitable for practical appliances in the field of photocatalysis.The obtained results, even if preliminary, are anyway promising and encourage the use of the designed experimental apparatus for future work in the field of controlled nanomaterials synthesis through FSP. Particularly, further analysis will be devoted to the following aspects:- sensitivity analysis of the experimental set-up through a detailed study of the influence of the spray operating conditions (for instance: precursor typology and concentration, oxydant and fuel flow rates) upon the structure of the nanomaterials synthesized (TEM and XRD analysis are useful instruments for this purpose);- improvement of the collection system of the generated nanopowders, for instance by an automatic mechanism: this can provide useful informations about the degree of conversion of the chemical reactions involved in the synthesis process;- use of the FSP apparatus for the synthesis of other types of nanoparticles, varying the precursor. Moreover, the results that will be obtained in the near future through the designed experimental set-up can be useful for the tuning and validation of theoretical models about nanomaterials synthesis mechanisms.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The author thanks Dr. F. Cignoli, Dr. R. Dondè and Dr. S. Maffi (CNR-Ieni Institute in Milano) for the help and technical support provided during the experimental analysis, especially for the use of PDA, TEM and XRD techniques.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML