-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Nanoscience and Nanotechnology
p-ISSN: 2163-257X e-ISSN: 2163-2588
2017; 7(1): 4-8
doi:10.5923/j.nn.20170701.02

Internet of Nano Things (IoNT): Next Evolutionary Step in Nanotechnology
Anand Nayyar1, Vikram Puri2, Dac-Nhuong Le3
1Department of Computer Applications & IT, KCL Institute of Management and Technology, Jalandhar, India
2M. Tech (ECE), Guru Nanak Dev University (Regional Campus), Jalandhar, India
3Faculty of Information Technology, Haiphong University, Haiphong, Vietnam
Correspondence to: Anand Nayyar, Department of Computer Applications & IT, KCL Institute of Management and Technology, Jalandhar, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Nanotechnology, since its inception has provided enhanced and efficient solutions to various applications in biomedical, industry, agriculture and military applications. Nanotechnology has led to the evolution of nano-machines which are tiny components comprising of arranged set of molecules performing pre-determined tasks. The interconnection of nanosensors and nanodevices with Internet has led to development of next generation standard based on IoT called “Internet of Nano Things” (IoNT). The main objective behind this paper is to provide in-depth view of Internet of Nano Things (IoNT)- Architecture, Application areas and Challenges to make researchers aware of IoNT standard for overcoming existing challenges and making use of IoNT in diverse areas in near future for rapid deployment.
Keywords: Nanotechnology, Internet of Things (IoT), Internet of Nano Things (IoNT), Nanosensors, Nano-machines, Sensors, Body Sensor Networks, Nano Communication, Wireless Networks
Cite this paper: Anand Nayyar, Vikram Puri, Dac-Nhuong Le, Internet of Nano Things (IoNT): Next Evolutionary Step in Nanotechnology, Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, Vol. 7 No. 1, 2017, pp. 4-8. doi: 10.5923/j.nn.20170701.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The next revolution in the area of computing will be totally outside the realm of traditional desktop. The Internet of Things (IoT) [1, 2] is regarded as new revolution that is picking up huge popularity in the world of modern wireless telecommunications. The backbone behind Internet of Things (IoT) is the pervasive presence of wide range of things or objects like RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags, sensors, actuators, mobile technology, NFC (Near Field Communication), Smart Phones, Tablets etc. having unique addressing schemes to interact and communicate among each other to attain desired objectives. IoT concept, today being a reality, was proposed by Ashton [3] in 1999 and is linked to new concept of RFID regarding its usage in supply chain. IoT, day by day is gaining the ubiquity of Internet by integrating every object for interaction via embedded systems, making it a highly distributed network of devices communicating both ways with humans and even with devices. The concept of IoT marks high impact on various aspects of everyone’s life as wide range of devices and communication protocols are under rapid development process by industries and researchers in diverse fields like e-health, e-agriculture, e-industry, smart cities, e-military etc. I nternet of Things (IoT) [18] produces tons of data which has to be properly stored, processed and presented in efficient manner-for that various other computing technologies like Cloud Computing provides a virtual infrastructure for such utilities which integrates monitoring devices, storage of data, data analytics tools and client based data delivery models. With growing trend of 4G Networks, LTE and WiMAX, the vision towards IoT is also evolving. Internet of Things (IoT) requires [4]: shared understanding of situation of users and devices; software architectures and pervasive networks to present contextual information; and high performance data analytical tools depicting smart technology.Internet of Things, no doubt has transformed the use of Internet and Device to Device communications in which devices, sensors and objects interact with one another and exchange data and has also given birth to several other domains like Wireless Body Sensor Networks (WBAN), Internet of Nanotechnology-Nano Things (IoNT) and everything is leading to one combined terminology i.e. Internet of Everything (IoE).The basic definition of Nanotechnology is “Nanotechnology is the engineering of functional systems at the molecular scale. In its original sense, “Nanotechnology” refers to the projected ability to construct items from the bottom up, using techniques and tools being developed today to make complete, high performance products. Nanotechnology [7, 8] has provided various High grade solutions to many real world application areas like Biotechnology, Biomedical, Industry, Agriculture, Military applications as it is developing devices in scale of one to few hundred nanometres. In order to power nanotechnology, the backbone is Nanomachine. A Nanomachine is defined as the basic functional unit integrated via nano-components to perform basic tasks like sensing or actuating. Effective cooperation and coordination among nano machines expands variety of applications in terms of complexity and operations. In nutshell, the integration of nanoscale devices with exiting traditional communication networks with High Speed Internet has led to new evolution which is termed as “Internet of Nano-Things(IoNT)” [5, 6]. With the advent of Internet of Nanotechnology (IoNT), research in the area of Nano communication has also increased ten times with an objective to create new standards for Nano devices to communicate among each other and should also be deployed in diverse applications. Internet of Nano-Things (IoNT) will comprise of miniature sensors connected to each other via Nano networks to obtain data from objects. So, in turn Internet of Nano things will open new doors of research in the area of Nano Sensors, Nano communication and Nano Devices. The concept of Internet of Nano Things (IoNT) was proposed by Ian Akyildiz and Josep Jornet [6] in the paper “The Internet of Nano-Things” and stated a new networking paradigm and state of art electromagnetic communication among nano scale devices and also presented major research challenges in terms of channel modelling, information encoding and protocols for Nano networks and proposed “Internet of Nano-Things”.The objective of this paper is to present a Comprehensive Review of Internet of Nano-Things (IoNT)- Architecture, Applications, Challenges cum research directions.
2. Overview of Nano Technology and Nano Machines [9]
2.1. Brief Introduction
- The concept of Nanotechnology was stated by “Richard Feynman”-A Physicist Nobel Laureate in 1965 in his famous speech titled “There’s Plenty of Room at the Bottom” in December 1959 [10]. The main idea behind his speech was to highlight the area of Miniaturization and future of creating powerful and tinier devices. The concept of “Nanotechnology” was first quoted by N. Taniguchi [11] as “Nanotechnology mainly comprise of processing of, separation, consolidation, and deformation of materials by one atom or by one molecule. The basic ideology behind development and usage of Nanotechnology is miniaturization and fabrication of devices in scale of 1 to 100 nano meters. Mihail Roco [12] from US National Nanotechnology has defined four generation of nanotechnology development. The current era, as per Roco, is Passive Nanostructures i.e. Materials designed to perform one task. The second phase includes “Active Nanostructures” for multitasking which involves development of highly efficient sensors, actuators and drug delivery devices. The third generation includes “Feature Nano systems” comprising of thousands of interacting components.
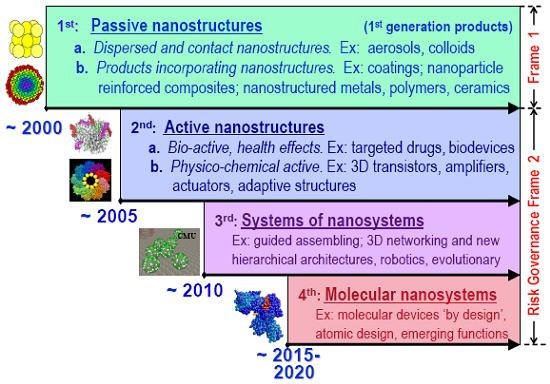 | Figure 1. Nanotechnology Generations- As Depecited by Mike Roco of US. National Nanotechnology Institute [12] |
2.2. Nano Machines
- With miniaturization and fabrication of devices via Nanotechnology techniques, the ultimate end product which is developed is termed as “Nano-Machines”. Nano-machine [13] is regarded as tiny components comprised of arranged set of molecules to perform simple computational, sensing and actuating tasks. Nano-machines can be further used as foundation for development of nano-bots, nano-processors, nano-memory and nano-clocks. A Nano-Machine [14] is defined “An Artificial Eutatic mechanical device that relies on nanometre-scale components”. Nano-machine, in simple terms can be defined as, “A Mechanical device that performs a useful function using components of nanometre-scale and defined molecular structure which includes both artificial nano-machines and naturally occurring devices found in biological systems”.In order to develop Nano-Machines, there are various approaches- Top down approach, Bottom-up approach and Bio Hybrid Approach. [9]Top Down Approach: Focussed on downscaling existing microelectronic and micro-electro-mechanical technologies without atomic level control. Example: Micro-contact printing and development of Nano-machines like Nano-electromechanical systems (NEMS). Bottom Up Approach: Focussed on design of nano-machines using individual molecules. This approach is also known as molecular manufacturing. Example: Nano machines like molecular switches, molecular shuttles etc.Bio-hybrid Approach: Focussed on design of new nano-machines also known as biological nano-machines based on molecular signalling. Example: Bio-nano robots, nano-biosensors, biological storing components etc.
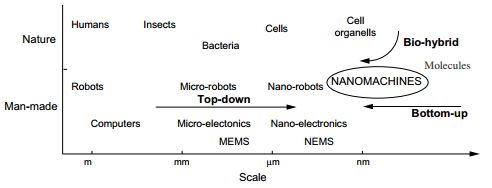 | Figure 2. Nano-Machines Development Approaches [9] |
2.3. Nano-Machine Architecture
- Nano-machine comprise of one or more components integrated with each other in varied levels of complexity and range from simple miniaturization machine to high end and sophisticated nano-robotics. The following are the components which make up a Nano-Machine:a. Control Unit: Control unit functions as the heart and central nervous system for nano-machine and does the task for executing all the instructions to perform the desired task. Control unit also controls all other components of nano-machine and also act as storage unit for saving all the data from nano-machine to be used by users.b.Communication Unit: This unit does the task of sending and receiving of information at nano-level. c. Reproduction Unit: Reproduction unit performs fabrication of each component of nano-machine using external elements and assemble them effectively to make up the nano-machine.d. Power Unit: It does the task of powering all the components of nano-machine. It collects energy from various external sources like temperature, light etc. for next task of consumption and distribution.Sensors and Actuators: Sensors and Actuators acts as bridge between nano-machine and environment. Sensors used in nano-machines are of varied types like Temperature, Chemical, clamps, motor etc.
3. Internet of Nano Things (IoNT) [5-7]
- The basic building block of Internet of Nano Things (IoNT) is Nanotechnology. The IoNT is comprised of nano scale network of physical objects which exchange information among each other powered by Nano Communication. The concept was developed by Ian F. Akyildiz and Josep Miguel Jornet from Georgia Institute of Technology and defined IoNT as follows:The Interconnection of nanoscale devices with existing communication networks and ultimately the Internet, defines a new networking paradigm called “Internet of Nano-Things”.As per the recent market research reports by analysts, IoNT market is expected to grow from $4.26 billion in 2016 to $9.69 billion by 2020, at an estimated Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 22.81% from 2016 to 2020.Internet of Nano Things (IoNT) infrastructure can be deployed by mixing nano devices and several other technologies like IoT, Sensors Network, Cloud Computing, Big Data Analytics etc. The IoNT infrastructure depends on the area of operation and required bandwidth required by particular application. The enhancement and wide range adoption of IoNT depends on processing capabilities, large storage at low costs, smart antennas and Smart RFID tag technology. Some of the major players in the IoNT market are Intel Corporation, Cisco Systems Inc., Qualcomm Incorporated, Juniper Networks and IBM Corporation in U.S., Schneider Electric and Alcatel-Lucent S.A. in France, and SAP S.E. and Siemens AG in Germany among others.Even having high future adoptability prospects, the growth of the IoNT market faces a few challenges due to privacy and security issues. Since critical data is communicated between devices over the internet, concerns related to security of the data have risen. Another factor which hinders the growth of IoNT market is the huge capital investment required for the development of nanotechnology.IoNT uses two broad areas of communication:• Electromagnetic Nano-Communication [8, 15]: It is regarded as transmission and receiving of electromagnetic (EM) radiation from components based on nanomaterials.• Molecular Communication [6, 7]: It is regarded as transmission and receiving of information encoded in molecules.
3.1. Network Architecture of Internet of Nano Things
- Internet of Nano Things (IoNT) is picking up the pace in rapid areas. Regardless of the application areas, the following components are the trump part of Architecture of Internet of Nano Things:1. Nano-Nodes: Nano-nodes are regarded as the smallest and simplest nano machines which perform various tasks like computation and transmission if the data over short distances and have less memory. Considering Body Sensor Networks, Biological sensors fitted in Human Body are considered as Nano-Nodes.2. Nano-Routers: Nano-routers have large computational power as compared to nano nodes and they act as aggregators of information coming from nano-nodes. Nano-routers also play crucial role in controlling nano-nodes by exchange control commands.3. Nano-Micro interface devices: These devices perform the task of aggregation of information coming from nano-routers and transmit it to the microscale and vice versa. They act as hybrid devices to communicate in nanoscale using Nano communication techniques and also with traditional communication networks with classical network protocols.4. Gateway: It enables the remote control of entire nano things network over the Internet. Example: Considering Body Sensor Network- With the use of Gateway all the sensor data from the Human Body can be accessed anywhere and everywhere via doctors over Internet.
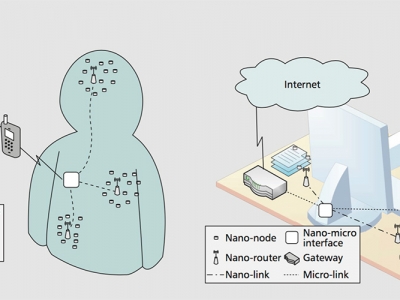 | Figure 3. Typical Architecture and Common Components making up Internet of Nano Things (IoNT) |
3.2. Applications
- The most sophisticated and advanced methodologies are used by IoNT for data collection, which enables IoNT to extend its base from existing applications to wide range of new and advanced applications as compared to IoT. In the Figure 3. Typical Architecture and Common Components making up Internet of Nano Things (IoNT) is highlighted.Health Care Monitoring/Nano-Sensor Based Body Sensor Network [5, 16]: The First and the foremost application where IoNT can be seen these days in real world is Body Sensor Network (BSN) comprising of in-body nano sensors playing a crucial role in collecting and monitoring patient’s biological activity and other details. Nano sensors being used in BSN provides real time data on a wearable device being used by the doctor for getting timely information regarding patient’s health.Environmental Monitoring: With the use of nano sensors in Environmental monitoring via deployment in public locations like Railway Stations, Bus Stops, Airports, Hotels and Restaurants and other Public places, live and real time monitoring of Traffic, Air Pollution, Temperature Monitoring is done more efficiently.Precision Agriculture [18]: The use of IoNT in agriculture will lead to development of several precision farming applications and with the live implementation of Nano-Sensors based Nano devices will lead to efficient environment monitoring, crop growth and even animal monitoring. With the development of Wireless Nano Sensor Network (WNSN) various agriculture activities can be performed like Grass Monitoring, Animal Health and Feed Management, Agriculture Field Condition Monitoring and Effective monitoring of usage of Pesticides and Insecticides in the Agriculture field.Other Possible Applications in Real World: Considering IoNT advantages, in the near future IoNT can also be applied by Military for Battlefield Monitoring, Development of Nano-Robotics and Nano-Drones, Space Based Applications, Industry Production and many more.
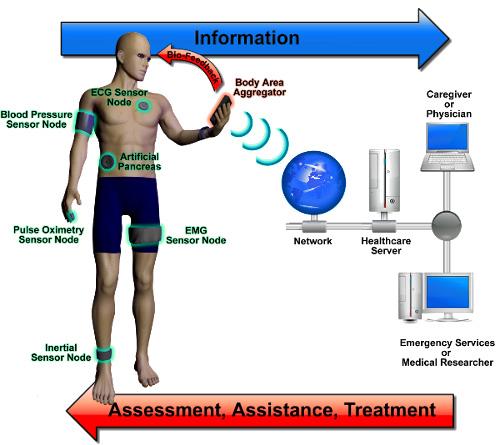 | Figure 4. Health Monitoring via Nano Sensors comprising Real Time Health Monitoring Internet of Nano Things (IoNT) |
4. Issues/Challenges of Internet of Nano Things (IoNT)
- IoNT is regarded as the most miniaturized nano sensor networks having huge potential to be as such adoptable in real time applications in diverse fields. But even though of having tons of advanced advantages, IoNT also suffers with some issues and challenges which needs to be addressed so that IoNT can become indispensable part of mankind in near future without any hiccup. Researchers must address the issues regarding context management, security and privacy, service composition and discovery.Apart from working on researching on various application areas and development of Nanotechnology based IoNT devices, new security and privacy mechanisms needs to be addressed with regard to the data being collected by nano sensors. Services should also be enhanced and new service-oriented architectures needs to be proposed to make nano sensors and nano networks compatible to hold tons of large varieties of data.
5. Conclusions and Future Scope
- The development of Nanotechnologies, nano machines, Internet of Things (IoT), Internet of Nano Things (IoNT) will have a great impact on advanced development in almost every field in near future. Researchers are currently working in development of nano machines comprising IoNT for live deployment in varied areas in near future. In this paper, in depth review with regard to Internet of Nano Thing (IoNT) is presented which is regarded as next evolutionary step in world of nanotechnology in addition to nano machines, applications and research areas.
Future Scope
- In the near future, work would be done on developing own IoNT based Nano Sensor Network for Industry or Agriculture for various monitoring activities.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML