-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Nanoscience and Nanotechnology
p-ISSN: 2163-257X e-ISSN: 2163-2588
2011; 1(2): 48-53
doi:10.5923/j.nn.20110102.09
Phagocytosis of Simulated Nano-wear Debris by Osteoblasts
1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Rehabilitation Medicine, SUNY Downstate Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY 11203, USA
2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio, TX 78229
Correspondence to: Mrinal K Musib, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Rehabilitation Medicine, SUNY Downstate Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY 11203, USA.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
In this study I have used well characterized simulated wear-nano-particles of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) of known size and shape to study particulate phagocytosis by MG63 osteoblast-like cells. The particles were treated to decrease their propensity to form aggregates in aqueous suspension and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was performed to image them as individual particles on 0.01 µm pore size polycarbonate filter membranes. These images were further subjected to morphometric analysis of the particles using ASTM F1877 descriptors [equivalent circle diameter (ECD in μm), aspect ratio (AR), elongation (E), roundness (R), and formfactor (FF)]. The mean (±SD) ECD of the particles were 0.056±0.03 µm. They were subsequently introduced to confluent MG63 cells at particle:cell ratio of 100:1 and incubated for 24 h. Transmission electron micrography (TEM) showed the nanoparticles inside the cytosol. No time dependent response was observed beyond 24 h. The nanoparticles seemed to re-agglomerate once inside the cell. The damage to the cells was evident from the compromised cell membrane. This study will help further our knowledge of the wear-mediated osteolytic process.
Keywords: Nanoparticles, Phagocytosis, Osteoblasts, SEM, TEM, Orthopedic Wear Debris
Cite this paper: Mrinal K Musib, Phagocytosis of Simulated Nano-wear Debris by Osteoblasts, Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, Vol. 1 No. 2, 2011, pp. 48-53. doi: 10.5923/j.nn.20110102.09.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Wear debris, primarily of UHMWPE are continually released at the articulating surfaces of most orthopedic total joints. Cellular response to the debris is the primary cause that limits the longevity of such implants[1-9]. Various cell lineages phagocytose/endocytose such non-biodegradable particulates resulting in the release of chemical entities, which has been hypothesized as one of the fundamental events that occur when wear-debris come in contact with surrounding cells[10-15]. But evidence showing UHMWPE particle phagocytosis, particularly the nanoparticles <100 nm by MG63 osteoblast-like cells (which is widely used as a model to study in vitro cellular response) is lacking. This may be attributed among other things to difficulties associated in handling UHMWPE nanoparticles. Furthermore size and shape are important attributes that dictate rate and extent of phagocytosis[16-20]. Figure 1 (a-c) shows the various steps/scenarios involved in phagocytosis. The cells initially identify the target and the particles adhere to the cell surface, followed by its internalization (a). Theprocess continues till the cell gets saturated with particles and can no longer phagocytose more particles (b), which may be referred to as the “phagocytotic capacity” of that particular cell type. It can be calculated using images/dimensions of the particles including its length, width and thickness. There may also be large non phagocytosable particles (c) and some studies hypothesize the limiting size of such wear particles to be about 10 µm for most cell types although there is no clear consensus in this regard.Cells tend to attach to the particle surface and wrap around the particle[10] prior to internalizing the particle. Engulfment of a particle involves the following critical steps: cell-particle interaction and subsequent adhesion, cell activation and projection of membrane-bound cytoplasm around the particle, and membrane fusion to include the particle[21,22]. The number of phagocytosed particles depends on several factors: cell type and morphometry, cell growth environment, chemical composition of the particle, surface property of the particle, and size and shape of the particle. The phagocytotic capacity (% volume of cell occupied by particles) will depend on the various size-shape descriptors as mentioned before like ECD, AR and R[12,23,24].Previous investigators have studied the role of size in phagocytosis, both biological and theoretical[25]. Simon et al, studied the phagocytosis of polystyrene microspheres (0.5-8.0 µm) by human blood neutrophils and found that phagocytosis decreased with increasing particle size[20]. Neale et al, investigated phagocytosis of polymeric and metallic biomaterials (0.5-3.0 µm) and found that all particles were phagocytosed resulting in inhibition of cellular functions[11]. Okafor et al, used cpTi particles (0.519±0.125 µm) to study endocytosis by human mesenchymal stem cells and found the particles to be cytotoxic once they are internalized[12]. They identified using SEM and confocal microscopy that the particles are localized in the cytoplasm. Wang et al, used latex particles (0.1-10.0 µm) and identified them in human and rat osteocasts in as little as 2 h[13]. Thus it seems that attachment followed by internalization of particles is an innate property of most cell types that dictate their subsequent response and biological behavior.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Particle Suspensions
- The method used to fractionate and characterize the particles has been explained elsewhere[28]. In short, 1 mg/1 ml of GUR 1050 resin (Ticona) was suspended in acidified water (pH 5.5) containing 2000 ppm of surfactant Pluronic F127 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog #P2443-250G). Suspensions were vortexed for 5 minutes, sonicated for 120 minutes and filtered through appropriate pore size filter to remove larger particles.The nano-fraction particles were collected on 0.01 µm pore size polycarbonate filters (Osmonics). All filter membranes were washed with 1 ml of dd H2O to dissolve any salt crystals that may be present and to further disperse the particles throughout the membrane to facilitate viewing of individual particles.One of the particulate-containing 0.01 µm filter was air dried, adhesive-fixed onto a SEM stub and sputter coated with Au-Pd (25 nm). Eight to ten images were obtained at varying magnifications using an SEM. Using the images, a morphometric analysis of 300 particles was performed using the 5 size-shape descriptors as mentioned in the Particle Morphology Analysis (PMA) program described in ASTM standard F1877[29-31].
2.2. Preparation of 10% FBS Media Containing Particles for Cell Response Studies
- The number of particles in a unit volume of the original suspension was quantified (from the SEM images) using the ‘UTHSCSA Image’ program and the results were extrapolated to calculate the number of nano-particles in 1 mg of the original suspension. Particles present on the unprocessed filter membranes were tested for the presence of endotoxin using an E-TOXATE kit (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog #ET0100) and were found to be endotoxin negative and subsequently resuspended in DMEM containing 10% FBS. This stock suspension containing a known number of the nano-particles per unit volume was further sonicated for 5 min and stored at 4ºC for 7 days before being used in cell response studies.
2.3. MG63 Osteoblast like Cells
- The MG63 cell line was obtained from the American Type Culture collection (Rockville, MD). It was originally isolated from a human osteosarcoma and showed numerous osteoblastic traits and is transformed. MG63 cells are clonal (one cell type) and do not form a calcifiable matrix. They are considered a model of an immature osteoblast because they respond to 1, 25-(OH)2 vitamin D3 and parathyroid hormone by increasing alkaline phosphatase specific activity. Cells were plated at 9300 cells/cm2 in Dulbecco’s modified eagle medium (DMEM) containing 10% FBS and 0.5% antibiotics. They were cultured in an atmosphere of 100% humidity, 5% CO2 and 37ºC and allowed to confluence.
2.4. Particles Used
- Prior to removing an aliquot of the media containing a known number of particles per unit volume of the suspension the tube was vortexed for 5 seconds to resuspend the particles uniformly. Particles at the ratio of 100 per cell were introduced to the culture and the cells were allowed to be in contact with the particles for 24 h in an incubator. The control had no particles but fresh media. The volume of the particle-containing media used was just enough to cover the surface of the cells and the media was shaken occasionally to facilitate the interaction of cells and particles.At harvest, experimental media was removed from cultures and cell layers were washed three times with PBS. The cell layers were removed by trypsinisation. The cells were centrifuged (500g, 10min) and pellets post-fixed in 1% OsO4. The samples were embedded in Epon and 90 nm sections cut with a diamond knife, mounted on copper grids, stained with 1% uranyl acetate and lead citrate and examined with a TEM (Philips, Leicester, UK) at 60 kV.
3. Results
3.1. Particle Characterization
- ASTM F1877 descriptors were used to perform morphometric analysis of the particles. Table 1 shows the results of the size-shape analysis and other statistical parameters for 300 UHMWPE particles.
|
3.2. Phagocytosis
- TEM analysis was performed after 24 h of incubation and confirmed the internalization of the UHMWPE particles, most cells having internalized several particles. Although most of the particles were in the cytosol, some particles were attached to the cell membrane. MG63 cells cultured without particles had a round or oblong nucleus with one or two nucleoli (Figure 3). The cell membrane was intact and other organelles including the Golgi apparatus and mitochondria were discernable under the TEM. Following exposure to particles, MG63 cells showed a marked change in their morphology.
 | Figure 2. Representative SEM micrographs of the nanofraction particles collected on a 0.01 µm pore filter. Magnification is a) 16,000X (top) and b) 75,000X |
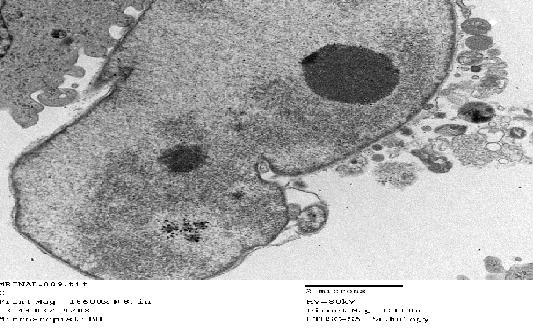 | Figure 3. TEM image of representative MG63 cells that have not been treated with particles (control) |
4. Discussion
- With the introduction of improved wear resistant materials (like highly cross-linked UHMWPE) to fabricate total joint components, there has been a decrease in wear debris volume, but has led to increased generation of nano-debris32. Although a well corroborated mechanism as to how cells respond to nano-wear-debris is presently elusive, even these smaller nano-size particles (like their larger counterparts) are phagocytosed by cells prior to eliciting a biological response. As evident from the results of this study, cells phagocytosed the nanoparticles resulting in damaged cell membrane. Further research needs to be initiated to investigate the exact mechanism (selective phagocytosis or endocytosis) involved in the process of particular intake and also the fate of even smaller particles (< 50 nm).According to my knowledge, this is the first study showing the presence of nanoparticles (<100 nm) of UHMWPE inside MG63 cells. Previous investigators have also identified larger particles inside a plethora of cell types. Phagocytosis seems to be an inherent property of most cell types and this phenomenon involving non-biodegradable wear-debris results in the release of various chemical entities including inflammatory mediators, cytokines and chemokines by cells eventually leading to implant failure. In this investigation we have identified smaller particles, some as small as few tens of nanometers, inside the cytoplasm of osteoblasts. The resulting damage to the cell membrane is evident, and accompanied by the cell’s frustration in not being able to degrade/digest/expel these particles may be responsible for eventual cellular toxicity and death. Furthermore it is an interesting observation that the smaller particles tend to form agglomerates when inside the cytosol, the exact repurcations of which is not very clear. Previous investigators have hypothesized that smaller submicron sized particles may be internalized by cells by the phenomenon of pinocytosis, thus minimizing cellular damage, if any. This is in contradiction to the observations/results of this study, wherein we see extensive damage to cell membrane due to phagocytosis of the nanoparticles.There are very few specific studies involving usage of TEM and well characterized particles of UHMWPE to study cellular phagocytosis. Among other reasons it may be attributed to difficulties associated in handling these particles. As compared to other electron microscopic techniques, TEM may be better suited for such studies as the electron dense particles may be easily identified/distinguished as dark structures amongst the cellular organelles.The present work enhances our understanding of the size-shape dependent phagocytosis of nano-particles. Cells seem to identify their targets based on their size and topography/morphology. Eventually only a certain volume fraction of the cell may be occupied (phagocytotic limit) which we hypothesize would be distinct for individual cell types, beyond which cells will lose the affinity and ability to internalize more particles. Moreover cells seem to favor internalization of spherical particles (particles with higher ‘R’ and lower ‘AR’ and ‘E’ values), which has also been shown by other researchers[10]. This innate property of cells may have immense bearing in the field of drug delivery. Another striking observation was the presence of membrane ruffles, which are dynamic actin filaments and are assumed to be associated with actin-dependent internalization process during phagocytosis. Further investigations are needed to properly understand the creation and involvement of these filaments/ruffles in response to varying size and shape of the target particles.This study may also point to the importance and relevance of one of the most fundamental features of target molecules/particles, their size and shape, in the size-shape-dependent phagocytotic process. Non-usage of clinically relevant, well characterized, non-spherical particles as may be present in situ in an actual in vivo situation, which has been a shortcoming of previous studies, has been addressed in this investigation. Preliminary investigations also show a size dependent response with significantly (p<0.01) greater number of nanoparticles being phagocytosed as compared to larger particles.Limitations of this work includes usage of simulated wear particles (although clinically relevant) and not actual wear-debris. The volume of the media containing the particles should be just sufficient to cover the surface of the container and be occasionally shaken to facilitate proper cell-particle interaction. Future work will include isolation, identification, fractionation and characterization of wear-debris from patients and performing in vitro and in vivo studies. Further research needs to be undertaken to study cellular response to even smaller particles, < 50 nm.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML
