-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Research in Neuroscience
p-ISSN: 2326-1226 e-ISSN: 2326-1234
2018; 7(1): 14-30
doi:10.5923/j.neuroscience.20180701.03

Regulation of miRNA-124, Nuclear Factor-Kappa B and β-Catenin Expression in Response to Novel Therapeutic Protocol in LPS Induced Alzheimer’s Disease in Rats
Mai M. Anwar1, Ola S. M. Ali2, Laila Ahmed R.3, Badawi A. M.1, Nadia A. Eltablawy1
1Department of Biochemistry, National Organization for Drug Control and Research (NODCAR), Egypt
2Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy, Al-Azhar University, Egypt
3Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University, Egypt
Correspondence to: Mai M. Anwar, Department of Biochemistry, National Organization for Drug Control and Research (NODCAR), Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

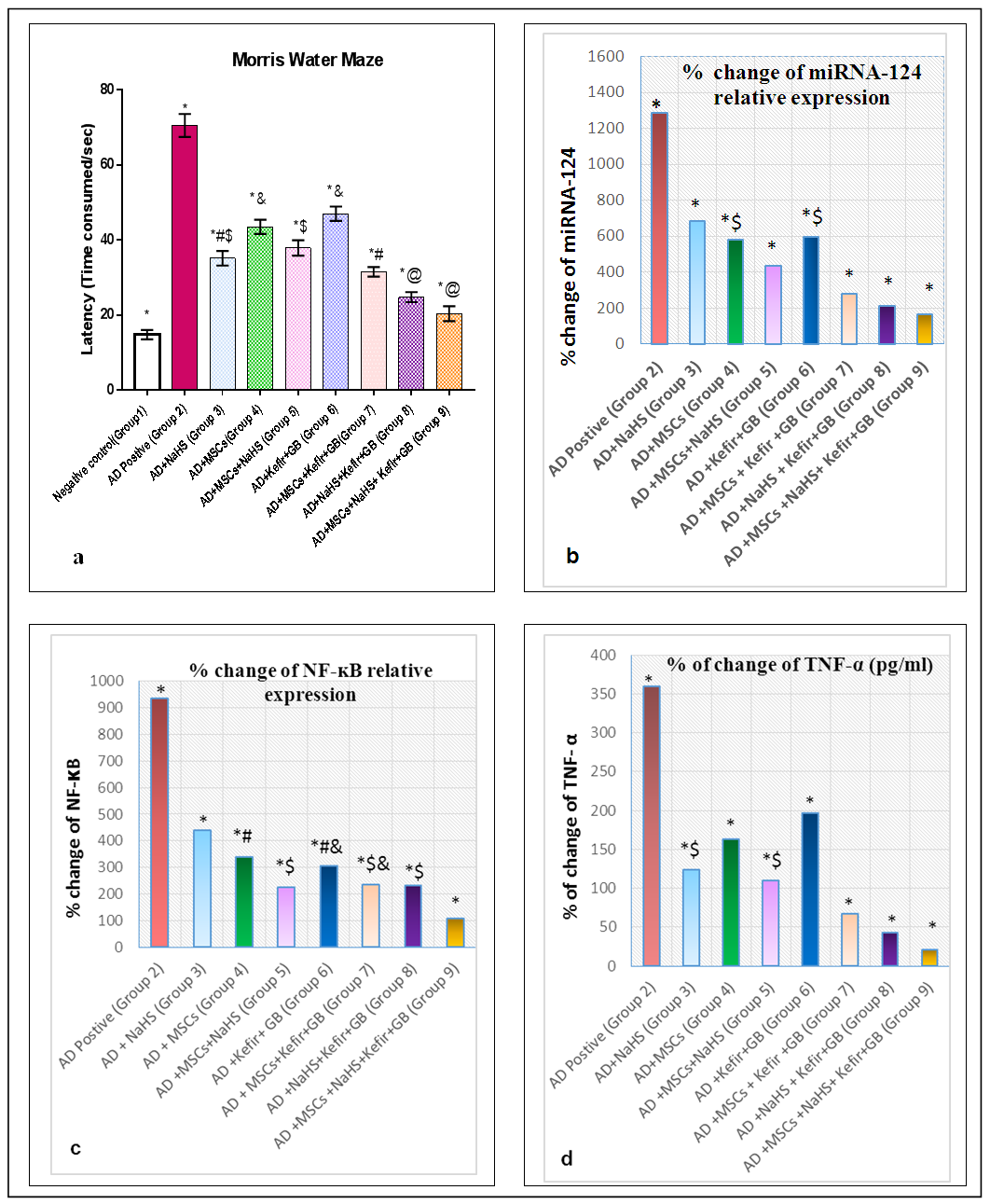
The severity of neurons loss with specific targeted protein dysfunction deposited and localized within brain tissues, are the main drawbacks of the unbalanced disturbances in the whole physiological and immunological body system accompanying Alzheimer’s disease (AD). This study is aimed to demonstrate the role played by microglia and numerous inflammatory signalling pathways involved in AD pathogenesis in addition to investigating the potential therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) not only when given individually in a unique method of administration but also when taken in a combination with exogenous hydrogen sulphide donor (NaHS), Kefir and Gingko Biloba (GB) that all do play a vital different role as a neuroprotective therapy. Materials and Methods: rats were divided into nine equal groups: (Group 1) negative control; (Group 2) rats were directly injected with lipopolysaccharide (LPS); (Group 3) AD rats received NaHS; (Group 4) AD rats received MSCs intracerebrally; (Group 5) AD rats received MSCs with NaHS; (Group 6) AD rats received kefir with GB; (Group 7): AD rats received MSCs followed by kefir with GB; (Group 8) AD rats received NaHS followed by kefir with GB; (Group 9) AD rats received MSCs with NaHS followed by kefir with GB. Results: Among the inflammatory drawbacks of AD induction by LPS, overexpression of miRNA-124, NF-κB and TNF-α was recorded accompanied with a reciprocal cross-regulatory effect on β-Catenin level resulting in its suppression. The combination of NaHS, kefir and GB with MSCs can function as a potent immune-modulator preventing the underlying pathological successive brain damage cascade in addition to protecting rats against LPS induced AD toxic aggregation therefore our proposed therapeutic strategy may be used as a subject of clinical interest.
Keywords: AD, miRNA-124, NF-κB, β-Catenin, MSCs intracerebrally, NaHS, Kefir
Cite this paper: Mai M. Anwar, Ola S. M. Ali, Laila Ahmed R., Badawi A. M., Nadia A. Eltablawy, Regulation of miRNA-124, Nuclear Factor-Kappa B and β-Catenin Expression in Response to Novel Therapeutic Protocol in LPS Induced Alzheimer’s Disease in Rats, Research in Neuroscience , Vol. 7 No. 1, 2018, pp. 14-30. doi: 10.5923/j.neuroscience.20180701.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Alzheimer’s disease (AD) can be ideally described as a two way progressive reversible -irreversible immunological and aggressive inflammatory disorders originally located in the central nervous system (CNS) with a huge tremendous impact reaching a wide range of population [1-3]. The initiation and progression of AD in varies brain areas can be literally attributed first to a serious of several intra/extra-cellular physiological factors such as brain cell secreted inflammatory cytokines and ending with protein aggregates hallmark formation including Aβ-42 deposited protein peptides which upon accumulation aid in the accumulation of numerous small neurotoxic oligomers aggregations and filaments of sticky twisty hyperphosphorylated tau protein forming neurofibrillary tangles deposited within neurons [3-6], leading to disturbances in the whole innate-adaptive body type immune responses with stimulation of various inflammatory drawbacks [7, 8].Inflammation is a process of combating pathogenic microorganisms and repairing tissue types damages whether through stimulation of innate immune responses by the help of pathogenic inflammatory recognition derived cells including macrophages, dendritic cells and natural killer cells or through stimulation of adaptive immune responses in case of severe inflammatory conditions mainly by the help of T and B-lymphocytes which have been actually derived from previously stimulated innate immune type through lymph nodes and various lymphoid organs [8-10]. Binding of pathogenic associated molecular patterns (PAMPS) to pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) through cell surface receptors, such as Toll-like receptors (TLRs) leads to the initiation of inflammatory cascade events and the excitation of reactive oxygen species with enhancing macrophage phagocytic activity aiming to achieve either positive or negative immunological regulatory defensive events depending on the biological status of body [11].Alzheimer’s disease can be considered as the main precipitating factor of CNS direct causative injury with the probability of being also provoked by systemic body tissue injuries [12-14]. Once inflammation occurred in the brain, the neural immune system responses involve various healing/ protective mechanisms such as activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signalling pathway which is a vital antiapoptotic pathway playing a crucial biological role in controlling cell apoptosis, survival, and proliferation [15, 16] in addition to its vital role in regulating miRNAs different brain types, β-catenin, Bcl-2, glycogen synthase kinase 3(GSK-3), nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-κB), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and mitogen activated protein kinases (MAPK) expression which in turn stimulate lymph node to release aggressive microglia responsible for phagocytising AD aggregates [15, 16].In this study, we attempted to study the effect of LPS association with AD perciptation ascertaining its relation with neural cells damage and AD plaques formation by direct single intraperitoneal (IP) injection. Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) is a potent endotoxin outer membrane component of gram negative bacteria producing several persistent inflammatory cytokines leading to neural death [17-19]. Following the administration of LPS, various symptoms termed “sickness behaviour” may be observed on rats subjected to clinical trial in gradual manner including loss of interest depression like symptoms, hypersomnia, loss of appetite, impaired cognitive function, decreased social interaction and observed reduction in rat’s exploration interest [20, 21]. Action of LPS on CNS starts by direct penetration to brain's different areas, tissues and organs mainly noticed through nerve transduction, circumventricular organs (CVOs) and area postrema (AP) or can be even through hypothalamus activating serious of inflammatory cascades accompanied with exaggerated oxidative stress production and upregulation of AD specific pathogenic enzyme known as beta-secretase enzyme (BACE 1) [17-19].Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) are precursors like multipotent and self-renewal characteristic cells located in the bone marrow with the ability to differentiate into hematopoietic cells and nonhematopoietic cell types including neurons, myoblasts and adipocytes with the ability to secrete cytokines and growth factors potentiating their abilities to work as a successful transplantation therapy in neurodegenerative disease [22, 23]. The advantages of MSCs for being transplanted in brain over any other types of cell are their availability and capability to penetrate the blood-brain barrier (BBB) without disrupting the host brain structure in addition to their efficiency to differentiate into Purkinje neurons or cells plus enhancing neurogenesis, angiogenesis, and synapsis regeneration in damaged brain sites. Mesenchymal stem cells may directly be introduced into the localized injured area intracerebrally or via circulation route intravenously [23-25].Hydrogen sulphide (H2S), is considered as the third most abundant endogenous neuromodulator gas transmitter following nitric oxide and carbon monoxide mainly produced endogenously from L-Cysteine by cystathionine β-synthase (CBS) abundantly expressed in the central nervous system. It was also found that modulation of H2S level in brain tissue has been highly associated with AD pathogenesis characterized by dysfunction and severe suppression of CBS enzyme level in the brain. Therefore, the present study was undertaken to assert the crucial beneficial effects of NaHS as an alternative exogenous H2S donor, on the underlying neural cell damage and over all cerebral dysfunctions as a result of AD through its rapid strategic declared anti-inflammatory, vasomodulation and antioxidant effects [26-28].Healthy nutrition and diet are the main target for the scientists and entire population world-wide due to their ability to treat, manage and prevent immunity related disorders such as neurodegenerative disease, cancer and inflammation. Microbiota disturbance is a dynamic mechanism to be considered as a main initiative of these disorders in the past decades [29]. Recent researches indicate strong association between cognitive alterations and microbiota so probiotics were used to modulate these alterations including memory and learning where their beneficial effects are related to the microbiological components and other nutritional composition. Kefir differ from any other probiotic products by being produced from grains composed of mixture of lactic acid, acetic acid bacteria, lactose fermenting and non-fermenting yeast. Kefir grains when inoculated in milk, producing acidified carbonated fermented milk type containing several bioactive peptides, exopolysaccharides and bacteriocins [17, 29-31].Ginkgo Biloba (GB) is a traditional herbal medicine that has been used for decades in treating numerous disorders. The main neuroprotective pharmacological actions of GB can be related to the presence of two main components flavonol glycosides and terpenoids through their direct ability to slowdown, treat, maintain and prevent mental cognitive disorders by enhancing cerebral blood flow and protecting neurons from oxidative damage as a result of anti-inflammatory and antioxidant related actions [32-34]. The main aim of this study is to establish applicable moneywise therapeutics with novel methods of administration that do have a potent neuroprotective actions against AD hallmark not only by multi-targeting the pathological and major contributing factors of the disease but also by acting as a key targeting therapy treatment.
2. Materials and Methods
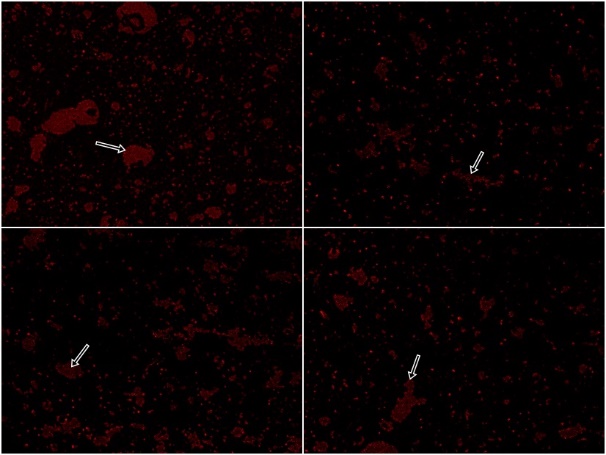
- MaterialsLipopolysaccharides and NaHS were purchased from (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO), GB pure extract was obtained from Pharaonia Pharmaceuticals Egypt, Kefir grains were purchased from Cultures for Health (17978 S, Grasle Rd. Ore. City OR 97045, United States), Dulbecco’s Modiefied Eagle’s Medium (DMEM) (Lonza), RNeasy lysis buffer (RLT) (QIAGEN) and Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (Lonza).Preparation of milk Kefir grains:Dried kefir grains (20 mg) were directly inoculated in 100 ml of pasteurized milk and incubated at 20°C for 24 h. The milk was filtered to remove kefir grains at the end of fermentation [17, 35].Preparation of Ginko Biloba (GB):Rats received GB were administrated 100mg/kg as a single daily dose by oral gavage for 15 days with slight dose modifications [36].Preparation of exogenous hydrogen sulphide (NaHS):Rats were administered NaHS (IP) at a dose of 5 mg/kg dissolved in deionized water once daily for 15 days with slight dose modification [37].Preparation of Bone Marrow (BM) derived MSCs:Mesenchymal stem cell were isolated from five adult male albino rats by flushing the tibia and femur with DMEM. Nucleated cells were isolated in accordance with density gradient [Ficoll/Paque (Pharmacia)] followed by resuspension in complete culture medium supplemented with 1% penicillin-streptomycin and 10% fetal bovine serum. Cells were respectively incubated at 37°C in 5% humidified CO2 for 12–14 days upon formation of large colonies followed by washing twice times with PBS (pH7). Cells were then trypsinized with 0.25% trypsin in 1mM EDTA for 5 min at 37°C and centrifuged followed by incubation in 50 cm2 culture flasks. The resulting cultures were referred to as first passage cultures according to the method of [38]. MSCs were characterized by adhesiveness, characteristic fusiform shape and their power to differentiate into osteocytes and chondrocytes [39]. After the first passage, the morphological characters of MSC were analyzed for the expression of cell surface molecules using flow cytometry procedures for CD45-ve, CD 90+ve, and CD105+ve.Identification and labeling of BM-MSCsBone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells prior to transplantation were labeled with PKH26 red fluorescence cell linker kit according to the manufacturer’s specific recommendations (Sigma, Saint Louis, Missouri, USA). Cells were centrifuged and washed twice in special serum free medium then pelleted and suspended in PKH26 dye solution. One month post transplantation, MSCs labeled with PKH26 were tracked and visualized in brain tissue using a fluorescence microscope (Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louis, USA). AnimalsSeventy-two male albino rats, weighing 200-250 g were purchased from the experimental animal unit, Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University. Purchased rats were maintained in temperature-controlled sterile pathogen free animal house at 22°C in a 12-h light/dark cycle with free access to water and semi-purified diet that contained (g/kg): 100 g casein, 750 g sucrose, 50 g cellulose, 50 g fat blends, 10 g vitamin mix, and 40g mineral mix. All the ethical protocols for animal treatment were undertaken in accordance with the ethical standards of animal facilities, Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University with the approval from the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee.Induction of AD lipopolysaccharideAlzheimer’s disease was induced among all rats in the successive eight groups subjected to study treatment protocol by (IP) injection with 0.56 mg / kg body weight of (LPS) dissolved in 1 ml of sterile PBS (pH7) to induce AD as a modified single dose [40].Experimental designHealthy male albino rats (200 to 250 g) were randomly divided into nine equal groups (eight rats each), rats were fed on a semi purified diet for a period of time one week before the study get started. The experiment was designed as follow:Ÿ Group 1 (control): Eight healthy rats as negative control group.Ÿ Group 2 (AD): Rats were injected (IP) with 0.56 mg / kg body weight of LPS dissolved in 1 ml of sterile PBS to induce AD as a modified single dose [40].Ÿ Group 3 (AD+NaHS): AD induced rats received (NaHS) (IP) at a single daily dose of 5 mg/kg dissolved in deionized water for 15 days with dose modification [37].Ÿ Group 4 (AD+MSCs): AD induced rats received (MSCs) in a single intracerebral administration protocol at a dose of 5μl (5×105) in 10% PBS after being anesthetized with ketamine hydrochloride 80 mg/kg, where rats were injected with 1 ml of solution per kg of body weight intramuscularly with slight modifications [41]. The site of intracerebral injection is approximately half way between the eye, ear and just off the midline [42-44].Ÿ Group 5 (AD+MSCs+NaHS): AD induced rats received (MSCs) in a single intracerebral dose of 5μl (5 × 105) in 10% PBS with slight modifications [41] with a daily (IP) administration of NaHS at a dose of 5 mg/kg dissolved in deionized water once daily for 15 days with slight dose modification [37].Ÿ Group 6 (AD+kefir+GB): AD induced rats received 4ml/kg body weight of kefir by oral gavage once daily for a month with slight dose modification [17, 36] accompanied with concurrent administration of GB 100mg/kg a single oral daily dose for 15 days with slight dose modification [36].Ÿ Group 7 (AD+MSCs+kefir+GB): AD induced rats received (MSCs) intracerebrally followed by a daily oral dose of kefir for a month with a concurrent daily administration of GB for 15 days.Ÿ Group 8 (AD+NaHS+kefir+GB): AD induced rats received (NaHS) (IP) at a single dose for 15 days followed by a daily oral dose of kefir for a month with a concurrent daily administration of GB for 15 days.Ÿ Group 9 (AD+MSCs+NaHS+kefir+GB): AD induced rats received (MSCs) intracerebrally with a subsequent receiving of (NaHS) (IP) at a single dose for 15 days followed by a daily oral administration of kefir for a month with a concurrent daily administration of GB for 15 days.Morris Water Maze (MWM)After one month of applying treatment protocol, rats were assigned to perform Morris Water Maze (MWM) in order to study the effect of given treatments on rat’s deteriorated memory as a result of inducing AD which will be reflected on rat's performance in maze. Rats were placed in a blue circular pool (6 feet in diameter) filled with water (26 ± 2°C). A circular escape platform was placed in the middle of the target quadrant 2 cm below the water surface where during training it can be exposed about 1 inch above the water to teach the rats that there is a way to be rescued. Rats were trained to perform four trials per day with an interval of 20 min where each trial lasts 60 seconds for 4 consecutive days. On the fifth day, a trial was performed where time taken by each rate to reach the platform (latency time) was recorded considering behaviour changes, and histopathological brain damage among groups. Blood sampling and preparation:After performing Morris test and before decapitation, venous blood was collected from the retro-orbital vein of rats left to clot for 30 minutes separated by centrifugation at 10,000xg for 20 minutes. Serum was kept frozen till analysis of TNF-α serum level which was estimated using the ELISA technique according to (Cusabio Biotech, China) manufacture’s instruction. Animals were then anesthetized with sodium phentobarbital (60mg/kg) and killed by decapitation followed by brain tissue extraction.Tissue sampling and preparation:Brains were rapidly removed and cut into three transverse symmetrical halves by midline incision. One half was fixed in 10% formalin for histopathological studies in addition to MSCs labelling with PKH26 red fluorescence cell linker kit, and the other two halves were lysed in a specific different manners. One was prepared to perform tissue estimation of miRNA-124, and NF-κB relative expression using Quantitative Reverse Transcription polymerase chain reaction (QRT PCR), while the other half was prepared to perform brain tissue estimation of β-catenin by western blotting.Detection of miRNA-124 relative expression by QRT PCR: Purification and extraction of total RNA from brain tissue using miRNeasy Kit QIAGEN (GmbH, Hilden, Germany) was done by brain tissue homogenization using 5 volumes Qiazol lysis reagent and chloroform followed by incubation at room temperature for 2–3 minutes and centrifugation for 15 minutes at 12,000xg 4°C. The extracted RNA was reversely transcribed into complementary DNA (cDNA) using TaqMan® MicroRNA Reverse Transcription Kit (QIAGEN GmbH, Hilden, Germany). For each 15μL RT reaction, add 7μL master mix, 3μL primer especially designed with Gene Runner Software (Hasting Software, Inc., Hasting, NY) from RNA sequences gene bank (Table 1) then incubate the tube in ice for 5 minutes. The results were expressed by 2ΔΔCq method.Detection of NF-κB relative expression by QRT PCR:Purification and extraction of total RNA from brain tissue using EZ-10 Spin Column Total RNA Mini-Preps kit (Bio Basic Inc., ON, Canada) was done by brain tissue homogenization using RLT lysis buffer and ethanol followed by centrifugation at 12,000xg for 30 sec at room temperature. The extracted RNA was respectively reverse transcribed into complementary DNA (cDNA) using a QuantiTect® Reverse Transcription Kit (QIAGEN). Primers were designed with Gene Runner Software (Hasting Software Incorporation, New York) from RNA sequences assigned from gene bank (Table 1). The relative expression of NF-κB was calculated using the comparative Ct method using 2-ΔΔCq. All values were normalized to the β-actin gene and reported as fold change over background levels detected in Alzheimer’s disease.
|
3. Statistical Analysis
- The results were expressed as the mean ± standard error (mean± SE) for eight animals per each group. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to compare group variables. The pairwise comparisons were conducted using Mann-Whitney U test. Values at p < 0.05 were considered significant. Correlations were assessed using Pearson correlation coefficient. Data were statistically analysed using the statistical package for social sciences18 software (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA).
4. Results
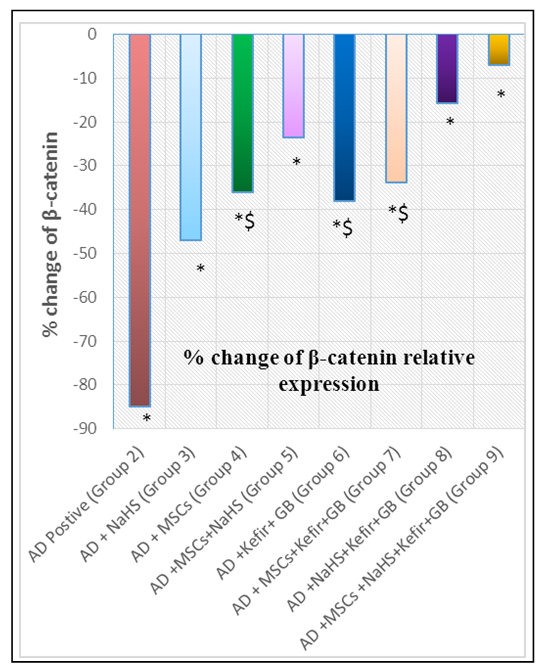
- Our previous work demonstrated that induction of AD by LPS is a process of inflammatory cascade hypothesis resulted in upregulation of Bax relative expression and TNF-α brain tissue observed level accompanied with downregulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), antioxidants and overall immunological body defensive statues including seladin-1, Bcl-2 and IL-10 against exaggerated various inflammatory stimuli. Where all resulted in the disruption of normally balanced homeostasis between (Th1/Th2) T helper cells towards Th1 type which can be considered as one of the most precipitating factor for AD leading to the stimulation of apoptotic regulation factors as a drawback of AD hallmarks deposition including amyloid β and tau protein [17]. Meanwhile the administration of MSCs intravenously and/or milk kefir grains attenuated the drawbacks of AD induction by LPS.Behavioral Tests through time consumed in MWM inflammatory induced memory impairment:The aim of establishment MWM behavior test is to assure the induction of AD by LPS along with identifying the degree of mental and memory impairment associated with AD progression which was reflected on rat's behavior through time consumed to reach the platform (latency time) in water maze. Interestingly, the maze was also performed to observe the degree of improvement regarding restoring memory function and rat's exploration behavior in the maze following treatment with our suggested therapeutic protocol. Our results revealed that AD induced rats (Group 2) spent the longest time in MWM when statistically compared with control untreated group (Group 1) and other examined treatment groups in our study protocol as shown in figure 1(a). The obtained results also revealed the role of NaHS as an exogenous H2S donor in improving the impaired memory of LPS challenged rats whether administrated alone or in combination with Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and/or concurrent administration of Kefir and Ginko Biloba. Intracerebral injection of MSCs when given individually and/or simultaneously with Kefir and GB combination therapy, displayed a marked decrease in the latency time as shown in figure 1(a). While the best marked improvement regarding memory dysfunction abilities was observed in group of rats administrated all the examined material in our study protocol as shown in figure 1(a).miRNA-124 and NF-κB brain mediated expression by progressive serum TNF-α up regulation as a result of LPS inducing AD disposition with impaired neuronal induction of β-catenin expression level.It was clearly assessed that induction of AD knocked-up miRNA-124 brain tissue relative expression which has the main regulatory modulating role on LPS/TLR-4 signalling pathway with an exaggerated production in TNF-α serum level (pg/ml) followed by an elevation in NF-κB brain tissue expression (p<0.05) accompanied as well with marked decrease in β-catenin brain tissue expression (p<0.05) indicating the intimate and direct crosslink between the given parameters as shown in figure 1(b,c&d) and 2(a).
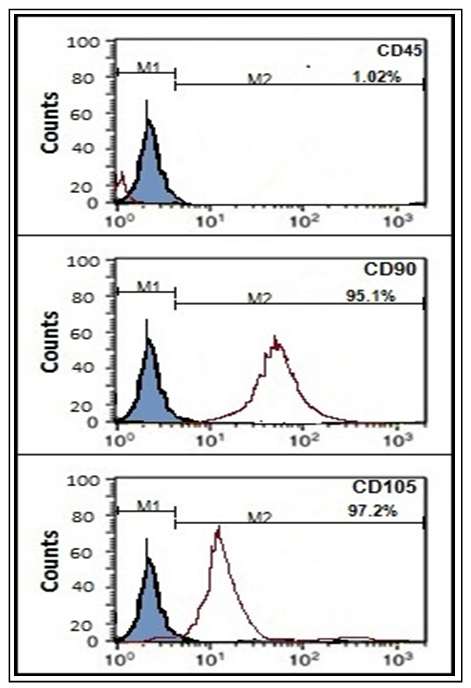 | Figure (2b). Characteristics of BM-MSCs. Cells were stained with CD45-ve (A), CD90 +ve (B) and CD105+ve (C) antibody using flow cytometry |
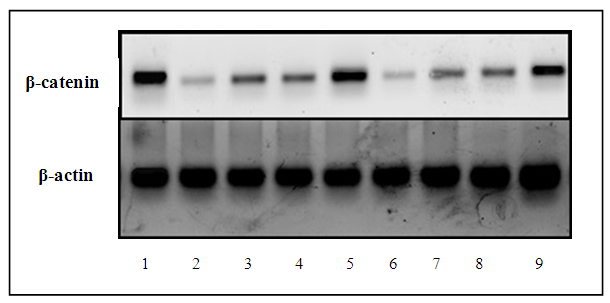 | Figure (2c). Representing the protein expression level of β-catenin analysed by western blot for the nine successive groups against β-actin used as reference housekeeping gene |
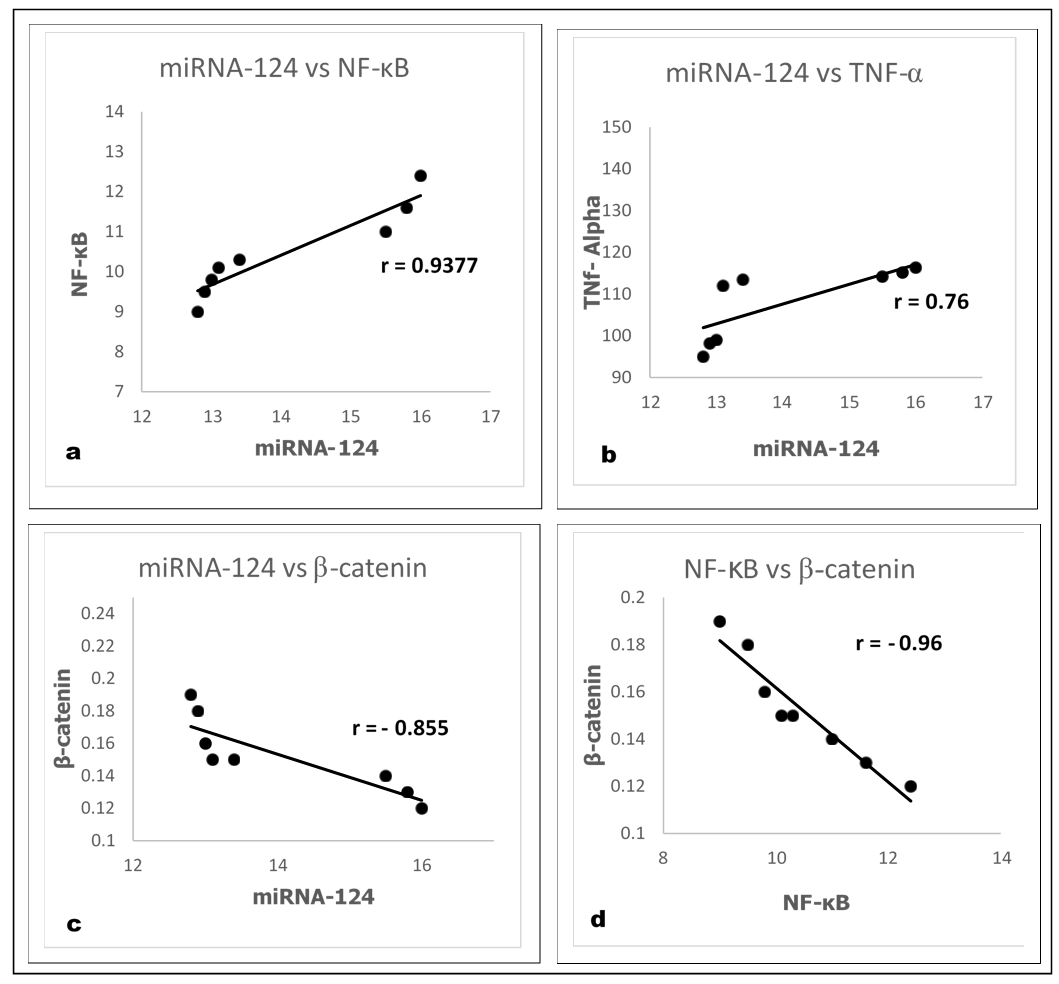 | Figure (3). Pearson’s correlation among different parameters in LPS induced AD group (Group 2) |
5. Discussion
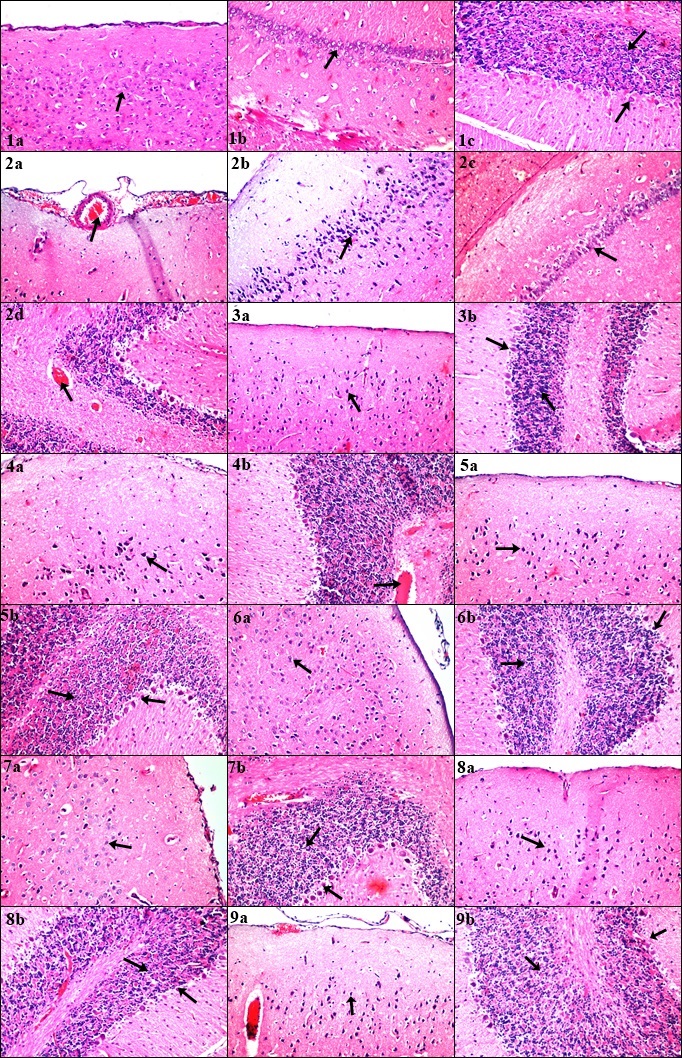
- In our previous study, we demonstrated the unique suggested relation between amyloid clusters protein deposition and a serious of inflammatory reaction triggering cascades including activation of aggressive microglia brain type and oxidative stress elevation with impaired brain function [17, 46-47]. miRNA-124 and NF-κB brain expression with TNF-α serum level can be considered as vital conserved pathways playing a vital role in regulating a wide range of crucial biological processes ranging from inflammation to learning and memory loss via knocking-up/down series of protein expressions such as β-catenin. MicroRNAs are tiny small non-coding RNA molecules crucially involved in vital physiological and pathological processes, including neurons dysfunction [48-51].One type of miRNA which can be considered as the most abundantly brain type miRNA specifically expressed in nervous system is miRNA-124 contributing to various neurological processes including memory storage, memory-related synaptic plasticity and neurogenesis. Neurons are highly enriched with miRNA-124 and its expression can be up/down regulated proportionally to the brain tissue statues. We attempted to study major aberrations in miRNA-124 together with NF-κB brain tissue level which is transcriptional factor that regulates a large number of genes controlling the regulation of varies inflammatory cytokines before and after the induction of AD with a coherent study of TNF-α serum level acting as a main inducer of apoptosis and brain injuries in many neurological diseases in addition to playing a crucial role in brain development, circadian rhythm and behaviour control [48-51]. Studying the complexity of triple successive reciprocal regulation on β-catenin signalling was also the aim of this study which is a vital multifunctional protein being identified as a crucial component of cell–cell adhesion system acting as a potential link between various brain inflammatory disorders [52, 53]. In accordance with our result, [54-59] reported a significant increase in TNF-α serum level, miRNA-124 and NF-κB brain tissue relative expression with a simultaneous marked decrease in β-catenin brain tissue expression following induction of AD by LPS (Group 2).Action of LPS on CNS can be initiated first by penetrating brain tissues barriers inducing (LPS)/TLR4 endotoxin cascade followed by recognition of inflammatory pathogen by pattern recognition receptor (PRR) leading to various cytokines expression and activation of brain type aggressive macrophages via LPS/TLR4 stimulation [18, 19]. Binding protein patterns then consequently attach with LPS pathogenic monomer aiming to be linked with CD14 which deliver LPS to the anchor site of TLR4 through their accessory protein Lymphocyte antigen 96 (LY96) leading to direct recruitment of intracellular adaptor proteins containing toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain in order to start on the Myeloid Differentiation Primary Response Gene 88 (MyD88) pathway where together with TIR Domain-containing Adaptor Protein (TIRAP) [18, 19, 60-61] regulating NF-κβ excessive activation with successive induction of Transforming growth factor β-Activated Kinase 1 (TAK1), MAPK and IκB Kinase (IKK) respectively by triggering TNF-α transcription level [58-60]. Also the vital phosphoinositide3-kinase(PI3K)/Akt might be suggested to be activated by TLR4 which is known as an intracellular crucial regulatory growth modulator and responsible for the proliferation of neural stem cells with playing a significant biological functions in neurons cell apoptosis, survival, proliferation, synaptic plasticity and neurotransmission but when only being regulated in optimal normal rate [62]. There are numerous bridging factors that literally can affect the suggested reciprocal cross-regulation relationship between miRNA-124, NF-κB and β-catenin brain tissue expression with the induced TNF-α serum level (pg/ml). Based on our present study, induction of AD resulted in overexpression of miRNA-124 with activation of destructive M1 brain type microglia/macrophages as a result of suggested immune responses drawbacks hindering neurogenesis, synaptic plasticity, axonal regeneration and aggravating severe neurological inflammatory defects such as sustained overactivation of neuronal PI3k/Akt pathway ending with over expression of NF-κB, MAPK, Tau protein, Bax and TNF-α with simultaneous suppression in β-catenin, Bcl-2, Seladin-1 and IL-10 expression leading to apoptotic brain tissue loss with impaired memory function ending with complete brain dysfunction on the long run [63-67].Results also show that glycogen synthase kinase-3(GSK3) not only regulates β-catenin but also regulates NF-κB as well, where GSK3 is mainly involved in many cellular processes including main transcriptional regulation processes, and protein tissue turnover. The level of GSK3 can directly be linked with β-catenin expression, whereas the suppression of β-catenin level indicates GSK3 extreme upregulation explaining complexity of action with mentioning the ability of GSK3 to act as extreme potent inducer of NF-κB and TNFα direct apoptotic effect with depleting β-catenin expression which plays an important role in maintaining neural and synaptic transmission with mentioning that downregulation of β-catenin results in knocking-up of NF-κB and TNF-α level [68, 69].miRNAs-124 are suggested mainly to be involved in eliminating and downregulating serious of inflammatory responses through targeting important signalling regulators leading to the activation of M2 microglia polarization in order to resolve AD pathological hallmarks. The M2 microglia brain-type usually maintains neurological restorative process through promoting neurogenesis, direct axonal regeneration, and synaptic plasticity with relieving congested blood vessels through the expression of Th2-derived cell cytokines via regulating T and B lymphocytes types stimulating the expression of inflammatory suppressor factors such as IL-10 [70-72]. Exogenous administration of hydrogen sulphide donor (NaHS) to AD induced rats resulted in a decrease in brain tissue relative expression level of miRNA-124 which can be contributed to its M2 activated microglia anti-inflammatory actions decreasing the expression of major pro-inflammatory factors including TNF-α and caspase-3 with direct inhibition of MAPK and NF-κB via restoring PI3K/AKt to its normal optimal level with inducing the release of anti-inflammatory cytokines including IL-10 and Bcl-2. Maintaining the PI3K/Akt pathway in normal rate can be considered as an important regulatory domain through acting as a potent negative regulator of TLR inflammatory cascade, MAPK, TNF-α and NF-κB expression via activating Protein kinase B (PKB) which can considered to be positively regulated by PI3K [73, 74].In accordance with our results, [75, 76] reported an increase in β-catenin expression as a drawback of treating AD induced rats with NaHS. This observed increase in β-catenin expression can be directly related to a simultaneous observed increase in PI3K/AKt activity which in turn directly inhabits GSK3 by phosphorylating serine at position 9 causing GSK3 distorted function at neurons whereas the increase in β-catenin level indicates GSK3 inhibition. Also β-catenin can initially supresses NF-κB related activity level via knocking-down Fas expression, playing an important dual role in brain tissue [77].An observable decrease in miRNA-124 relative expression previously elevated in LPS induced AD in rats, was observed after intracerebral local administration of MSCs [78]. It was also observed that not only miRNAs that play a vital role in increasing the activity and differentiation of MSCs in brain but it was also found that TLR4/LPS agonist enables bone marrow MSCs to enhance programmed CD34+ cell related activation, proliferation and differentiation through immunomodulation, tissue repair and regeneration of damaged brain areas’ by activating microglia phenotype M2 and enhancing phagocytosis to the LPS induced AD hallmarks brain tissue deposition inhibiting NF-κB activated pathway accompanied with a decrease in TNF-α due to neuron cells recovering shift from a classically activated phenotype M1 towards an inflammatory-resolving brain phenotype M2 [79]. [80] observed downregulation of the inflammatory expression level of NF‑κB activated PI3K signalling pathway as a result of administration of MSCs intracerebrally while activated AKt resulted in suppression of GSK3 by phosphorylation at position 9 which in turn knock-up β-catenin and Bcl-2 level accompanied with a decrease in Bax expression resulting in a unique polarization shift towards activated brain type microglia M2 which can be considered as anti-inflammatory phenotype pathway [17, 81-82]. Regarding the marked observed decrease in miRNA-124 and NF-κB with a simultaneous increase in β-catenin brain tissue relative expression level and a remarkable decrease in TNF-α serum level following the administration of MSCs intracerebrally with NaHS, can be related to the synergistic neuromodulation, and anti-apoptotic effects resulting in recovery of damaged neuron cells as a drawback of AD with an observed improvement in memory impairment behaviour.A relevant decrease in miRNA-124 and NF-κB with a simultaneous augmentation in β-catenin brain tissue expression level was observed following the administration of kefir concurrently with GB which can be accessed via recovered inflammatory microglia conditions in the brain with anti-inflammatory effects including immune modulatory, antiapoptotic and antioxidant actions. Gink Biloba (GB) exerts its Aβ aggregation engulfing effect initially by suppressing the M1 microglia brain type with upregulating the M2 type or even approaching the vital haemostatic balance between M1-M2. Direct suppression of TLR4/NF-κB signalling pathway leading to a decrease in the production of important inflammatory cytokines such as serum TNF-α which was also achieved by administrating GB. The inhibition of NF-kB brain relative expression was also obtained by preventing IkBa phosphorylation and degradation step, where the expressions of TNF-α especially in macrophages has been proven to be dependent on NF-kB activity [83-85]. [86], reported an induction in Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway following systemic administration of GB which can be reflected in the form of increase in the brain tissue relative expression of β-catenin by direct phosphorylation /inhibition of GSK3 which in turn prevents β-catenin from phosphorylation and being degraded. Direct phosphorylation of GSK3 can be initiated by activating PIk3/AKt in addition to the antioxidant and scavenging suggested activity of GB [86, 87].Also our previous study [17], has proven the efficacy of kefir as an antioxidant, anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory actions by increasing the secretion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) with suppressing the antiproliferative cytokines including TNF-α through their immune modulating and anti-inflammatory actions where all played an important role in decreasing the elevated miRNA-124 and NF-κB brain tissue relative expression level previously related to AD induction by LPS as a result of neurotoxic amyloid-β (Aβ) aggregated plaques accumulation by attenuating TLR4 expression associated with MAPK ,TNF-α and NF-κB regulation [17, 88-89]. [90], also reported the ability of probiotics to increase β-catenin by direct phosphorylation of GSK3 via activating PI3k/AKt level accompanied with observed downregulating of Bax and TNF-α expression with an observed increase in Bcl2 regulating expression resulting in keeping β-catenin in continues active unphosphorylated form [17, 90]. The good microorganism’s resident in kefir play an important role when taken together with Gink Biloba by their synergistic immune modulating and antioxidant effects which was reflected on the observed improvement in rat’s brain motor functions and behaviour.It was also observed that administrating the combination therapy of kefir and GB together with MSCs intracerebrally and/or NaHS demonstrated a better suppression in miRNA-124, TNF-α and NF-κB with an increased triggering effect on β-catenin brain tissue expression than administrating each alone as a multiple therapy resulting in a better anti-inflammatory and apoptotic relieving actions but with unnoticeable difference between the effect of administrating kefir and GB together with MSCs intracerebrally or NaHS on NF-κB expression as their effect is nearly similar. While the administration of suggested medical therapy composed of MSCs, NaHS and combination therapy composed of kefir and GB revealed the best augmenting effect on improving brain function abilities through reversing and relieving AD pathological drawbacks especially when early diagnosed as a result of synergistic anti-inflammatory and onset apoptotic eliminating actions mainly via engulfing amyloid-β (Aβ) plaques aggregations and associated accumulated oligomers by suppressing the M1 microglia brain type with a simultaneous upgrading towards M2 brain type leading to a suggested increase in PI3K/AKt activity level accompanied with a remarkable decrease in production of inflammatory cytokines including TLR4 /TNF-α and NF-kB brain expression ending with a marked complete recovery of damaged neuron cells as observed on rats behaviour in MWM and study obtained result’s.Concerning the histological examination of our study, an improvement in plaques formation with severe attenuation in nuclear pyknosis, and congestion was observed within different brain areas including the cerebral cortex, hippocampus (subiculum, fascia dentate & hilus), striatum and cerebellum among the suggested treatment groups in different rate, variations and patterns revealing the efficacy of the examined materials as a suggested novel therapy for AD in our recent study protocol.Conclusion: the present study provides a clear evidence indicating the efficacy of administrating NaHS, intracerebral MSCs transplantation and a combination therapy composed of kefir and GB in single, multiple, triple or quaternary successive alternative manner in relieving the pathological hallmarks of AD including Aβ aggregates and tau protein with restoring mental and behaviour abnormalities via attenuating pro-inflammatory cytokine production, decreasing microglia M1 polarization, suppressing miRNA-124, NF-κB and TNF-α expression with increasing β-catenin expression. Meanwhile it is recommended for AD to be early diagnosed before being irreversibly characterized type where long time plaques accumulation and deposition lead to injuries and damage to different brain areas that somehow hard to be healed and recovered to the initial brain state. It is also highly recommended to administrate the quaternary suggested medical therapy protocol together but in a longer duration of time to ensure the complete recovery and restoration of AD drawbacks previously affected brain patterns including neurons and synapse in addition to being a protective and prophylactic moneywise recommended therapy with a minimum or even unnoticeable major or minor side effects leading to an increase in patient compliance.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- This study was conducted by personal funding of corresponding author.Ethical approval: all procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of animal facilities, Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University with the approval of the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee.Contributions: Authors are very grateful for Dr. Adel M. Bakeer professor of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University for his contributions to the histopathological findings in this study.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML