-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Research in Neuroscience
p-ISSN: 2326-1226 e-ISSN: 2326-1234
2018; 7(1): 6-13
doi:10.5923/j.neuroscience.20180701.02

Evaluation of the Anticonvulsant Effect of Pennisetum glaucum Supplement in Some Laboratory Animal Seizure Models
Muhammad H. D.1, Dawud F. A.1, Yau J.2, Abdulrauf R. A.1
1Department of Human Physiology, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria
2Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Muhammad H. D., Department of Human Physiology, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Pennisetum glaucum has been pharmacologically studied for various activities like antidiabetic, anti-microbial and anti-tumor activities. The present study was aimed at investigating the anti-convulsant effect of Pennisetum glaucum supplement in some laboratory animals. Quantitative phytochemical test was carried on Pennisetum glaucum using standard laboratory techniques. In PTZ-induced seizures in mice, 20 swill albino mice were group into 4 negative control which received normal saline, 25% Pennisetum glaucum supplemental group, 50% Pennisetum glaucum supplemental group and diazepam (2 mg/kg) treated group. All the 4 groups received their respective interventions for 14 day. Thirty minutes after the 14th administration freshly prepared PTZ (85 mg/kg) was subcutaneously injected to all the mice and observed for seizure onset, seizure duration, percentage seizure protection and percentage mortality protection for 30 minute post PTZ injection. Induction of PTZ kindling seizures in wistar rats involves the grouping of 20 rats into 4 (normal saline, 25% Pennisetum glaucum supplemental group, 50% Pennisetum glaucum supplemental group and 200 mg/kg valporic treated group) with each group receiving PTZ (35 mg/kg) on every alternate day for 30 days. Thirty minutes after each PTZ injection rats were observed for the presence/absence of seizures and seizure severity which were evaluated using Racine scale. In Maximal electroshock study, 20 chicks were equally grouped into 4: negative control, 25% Pennisetum glaucum supplemental group, 50% Pennisetum glaucum supplemental group and phenytoin (20 mg/kg) treated group. Maximal electroshock seizures in chicks was induced. Seizure duration, recovery from seizure, seizure protection and mortality protection were the parameters recorded. The results of the study showed a high presence of flavonoids, saponins, tannins, phytate with the least of alkaloids. Also, protein, Magnesium and Phosphorus were revealed. Pennisetum glaucum at 50% supplement offered 40% protection from death and significantly (p≤0.05) decrease the duration of seizure (41.20 ± 3.34vs 137.00 ± 13.13 seconds) whereas diazepam a standard anticonvulsant proved more effective in delaying seizure onset (182.00 ± 10.00vs 72.80 ± 1.32 seconds), offering 60% protection from death and decreasing seizure duration (72.20±19.98vs 137.00 ± 13.13 seconds) in mice. The supplement was able to suppress the progression of seizure to most severe stages 4.4 reached by the control by retarding seizure severity to only stage 3.8 and 2.5 at 25% and 50% Pennisetum glaucum supplemental groups respectively in wistar rats. The supplement also, offered 40% vs 20% protection from seizure when compared to the control. However, phenytoin a standard anticonvulsant offered 100% seizure protection in chicks.
Keywords: PTZ-Pentylenetetrazole, Epilepsy, Seizure, PG-Pennisetum glaucum, MES-Maximal electroshock, Anticonvulsant
Cite this paper: Muhammad H. D., Dawud F. A., Yau J., Abdulrauf R. A., Evaluation of the Anticonvulsant Effect of Pennisetum glaucum Supplement in Some Laboratory Animal Seizure Models, Research in Neuroscience , Vol. 7 No. 1, 2018, pp. 6-13. doi: 10.5923/j.neuroscience.20180701.02.
1. Introduction
- Epilepsy is one of the most prevalent non communicable brain disorders characterized by recurrent unprovoked seizures that result from excessive disorderly discharge of cerebral neurons either due to over excitation of glutamatergic or under inhibition of GABAergic neurons resulting to disability and mortality [1].In Nigeria, the prevalence of epilepsy varies from 5.3 to 37/1000 [2] and major causes are attributed to meningitis, tumours and trauma sustained from automobile traffic accidents [3] which unfortunately is persistently increasing day by day. Also, parasitic infestations such as Onchocerca volvulus, Taenia solium and Toxoplasma gondii are believed to increase the risk of epilepsy and these infections are common in most parts of Sub-Saharan Africa [4].Pennisetum glaucum popularly known as pearl millet in English, gero in Hausa, oka in Yoruba is a member of the grass family (poaceae) [5] that is widely grown around the world especially in tropical semi-arid regions for fodder and food [6]. It is rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids, flavonoids and gluten free [7] which are beneficial in the treatment of epilepsy.Experimental animalsTwenty swiss albino mice (weighing 18-29g), twenty wistar rats and forty chicks.Drugs and TreatmentPentylenetetrazole (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, USA), Diazepam (Laborate Pharmaceutical, India) and Phenytoin (Dilantin) (Parke – Davis, Mumbai, India). Both drugs and chemical were prepared (fresh each time) in normal saline to the desired concentration.Plant materialPennisetum glaucum were purchased from Market in April (2016) and identified as such by a taxonomist where it was given the voucher number 1824. Preparation of supplementPennisetum glaucum were soaked in water for 12 hours, grounded into paste using grinding machine, sieved into another container using muslin cloth and the residue were discarded while the filtrate were allowed to settle down in the container. The water floating on top of the sediment were then decanted in order to concentrate the sample which were put into muslin cloth and allowed to drain completely and thereafter dried under the sun into powder [6]. A portion of the powder were collected for the assessment of phytochemicals while the remaining part were weighed and added to pellets grower mash (feed for mice) obtained from vital feeds Plateau state at 25% and 50% respectively. Quantitative Determination of Phytochemical of Pennisetum glaucumAlkaloid [8], Flavonoid [9], Tannin [10], Saponin [11] and Phytate [12].Pentylenetetrazole induced seizures in miceThis was done according to the method described by Swinyard et al., 1989 [13]. Twenty mice were divided into 4 groups of 5 mice eachGroup 1- Standard feed + Normal Saline (orally)Group 2- Diet containing 25% Pennisetum glaucum (Tornekar et al., 2009) [14].Group 3- Diet containing 50% Pennisetum glaucum Group 4- Standard feed + Diazepam 2mg/kg (orally) (Umokoro et al., 2007) [15].Mice were pre-treated for 14 days, 30 minutes after the 14th administrations all mice received freshly prepared pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) 85mg/kg subcutaneously and were observed for a 30minutes period for onset, duration, quantal protection and death protection (Swinyard, 1989) [16]. An episode of clonic spasm of at least 5 seconds was considered as seizure while Lack of threshold convulsion during 30 minutes of observation was regarded as protection.Pentylenetetrazole induced kindling seizures in wistar ratsTwenty wistar rats were divided into 4 groups of 5 each and given various interventions as shown below. On every alternate day, 30 minutes after receiving their interventions they were injected sub-convulsant dose of PTZ (35mg/kg) [17] and observed for 30 minutes for the presence or absence of seizure and seizure severity for 30 days.Group 1- Standard feed + Normal Saline (orally) + PTZ 35mg/kg (Ip)Group 2- Diet containing 25% Pennisetum glaucum [14] + PTZ 35mg/kg (Ip)Group 3- Diet containing 50% Pennisetum glaucum + PTZ 35mg/kg (Ip)Group 4- Sodium valpoarate 200mg/kg (orally) + PTZ 35mg/kg (Ip).Seizure behaviour was evaluated using the Racine scale of 0-5 with stage 5 showing the most severe seizure activity.Score 0-rats show no responseScore 1-hyperactivity, vibrissae twitchingScore 2-head nodding, head clonus and myoclonic jerkScore 3-unilateral shaking of fore limbs Score 4-rearing with bilateral shaking of fore limbsScore 5-generalized tonic-clonic seizures with loss of righting reflex (Racine, 1972) [18].Rats were considered fully kindled when they showed stages 4 and 5 on two consecutive trials which happened on 15 administration of PTZ (30th day of the experiment). Maximal electroshock induced seizure in chicks The method described by Swinyard and Kupferberg, 1985 [19] as modified by Sayyah et al. (2002) [20] was used in the study. Forty day old chicks were divided into 4 groups of 10 each as indicated below:Group 1- Standard feed +Normal Saline (Ip)Group 2- Diet containing 25% Pennisetum glaucum [14]Group 3- Diet containing 50% Pennisetum glaucumGroup 4- Standard feed + Phenytoin 20mg/kg (Ip) [21]Administrations were done for a day. Thirty minutes after the administrations an electrical stimulus was applied to induce seizure to the chicks using Ugo Basile electroconvulsive machine connected to Claude Lyons stabilizer with corneal electrodes placed on the upper eyelids. The shock duration, frequency, current and pulse width were set and maintained at 0.8 seconds, 100 pulse/sec, 80mA and 0.6 ms respectively. Seizure was manifested as tonic hind limb extension. Parameters observed were duration of seizure, seizure protection, recovery time from seizure and percentage mortality.The ability of Pennisetum glaucum supplement to prevent seizures or prolong the latency and/or onset was considered as an indication of anticonvulsant activity.Statistical AnalysisData obtained from Pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures in mice and MES in chicks were statistically analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s multiple comparison post hoc tests while data from Pentylenetetrazole induced Kindling in wistar ratswere analysed with Kruskall Wallis test (to assess the presence or absence of seizure and the severity of seizure) followed by Mann-Whitney U-test (to compare between 25%, 50% Pennisetum glaucum supplemental groups and valporic treated group) using SPSS version 20.0. Values of P ≤ 0.05 were considered significant.
2. Result
- Quantitative phytochemical screening and proximate analysis of Pennisetum glaucumQuantitative phytochemical screening of Pennisetum glaucum has revealed high flavonnoids (63.77%), saponins (7%), tannins (0.95%), phytate (0.28%) and least alkaloids (0.08%).Quantitative proximate analysis of Pennisetum glaucum showed a high presence of carbohydrates (65.92%), crude protein (12.03%), moisture (10.20%), crude fibre (7.40%), lipids (2.00%), magnesium (0.025%) and phosphorus (0.028%).Effect of Pennisetum glaucum supplement against Pentylenetrazole-induced seizure in swiss albino miceThe results showed that 25% and 50% Pennisetum glaucum supplemental groups showed significant (P ≤ 0.05) decrease in seizure onset (66.40 ± 3.17 and 81.80 ± 2.11 seconds) respectively when compared to diazepam treated group (182.00 ± 10.00 seconds). However, no significant difference was observed between Pennisetum glaucum supplemental groups when compared to the negative control (72.80 ± 1.32 seconds) (figure 1).
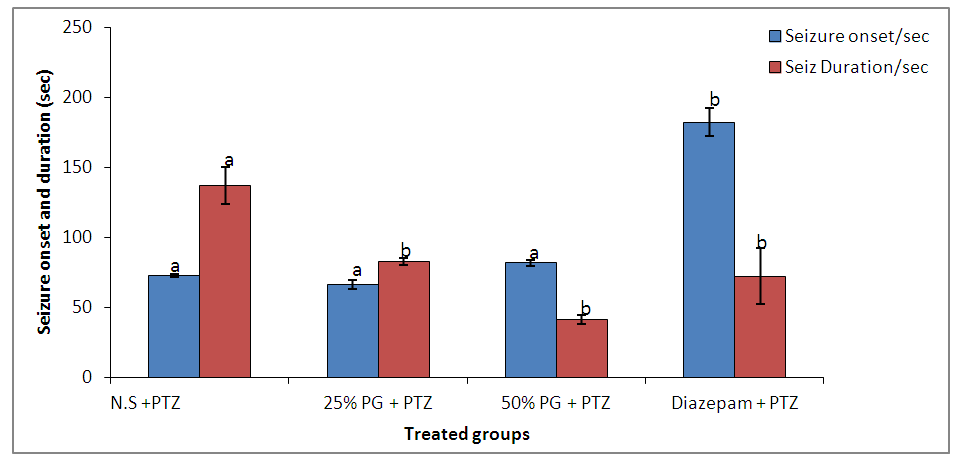 | Figure 1. Effect of Pennisetum glaucum supplement on seizure onset and duration against pentylenetetrazole induced seizures in mice |
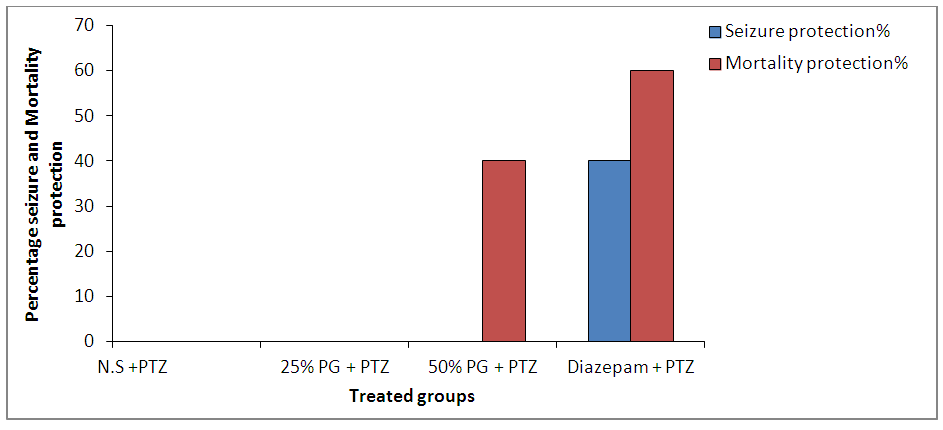 | Figure 2. Effect of Pennisetum glaucum supplement on seizure and mortality protection against pentylenetetrazole induced seizures in mice |
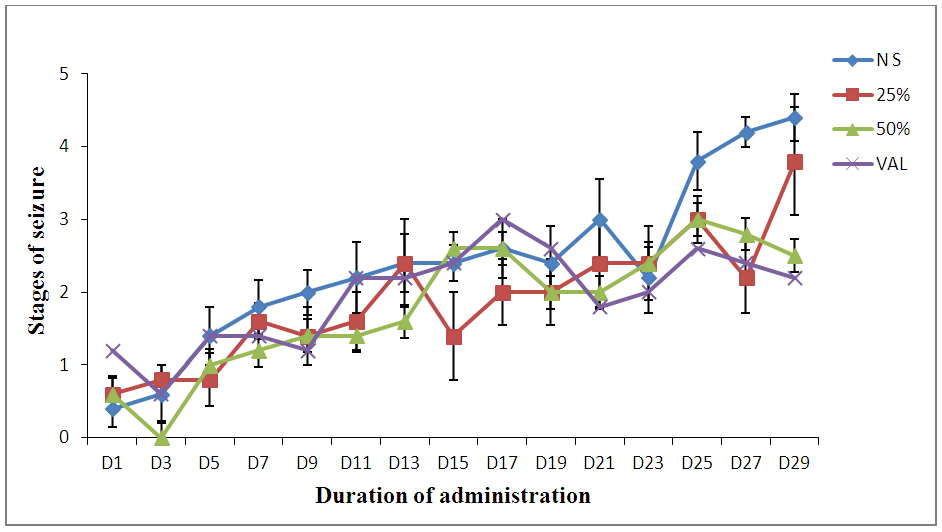 | Figure 3. Effect of Pennisetum glaucum supplement against Pentylenetetrazole induced Kindling in wistar rats |
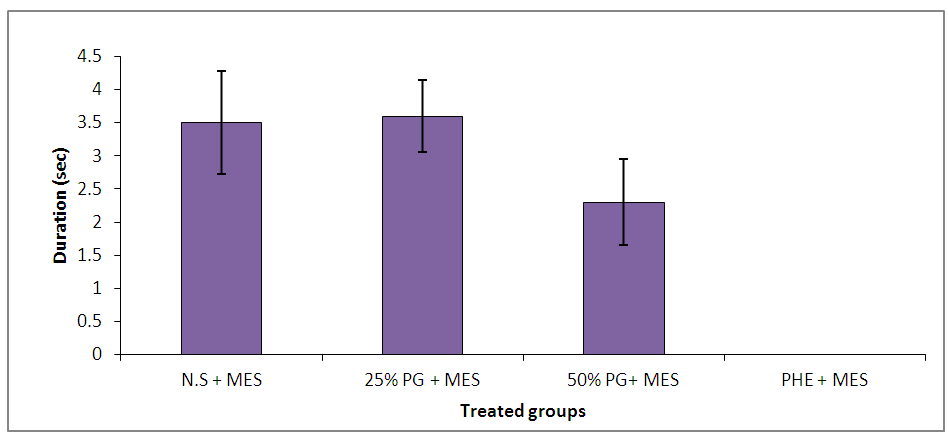 | Figure 4. Effect of Pennisetum glaucum supplement on seizure duration against maximal electroshock-induced seizures in chicks |
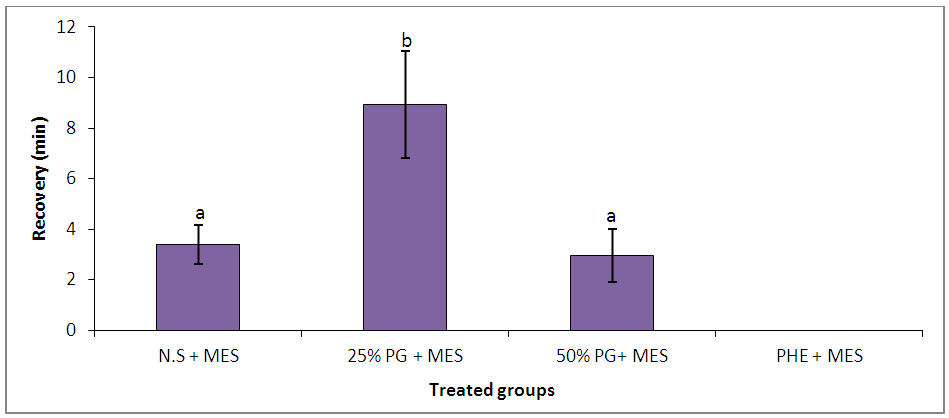 | Figure 5. Effect of Pennisetum glaucum supplement on time of recovery from seizure against maximal electroshock-induced seizures in chicks |
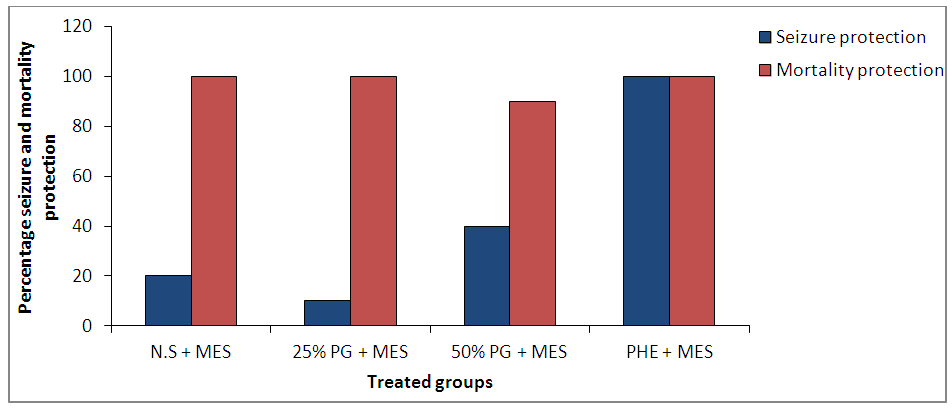 | Figure 6. Effect of Pennisetum glaucum supplement on seizure and mortality protection against maximal electroshock-induced seizures in chicks |
3. Discussion
- Pentylenetetrazole is a known convulsant that induces seizure similar to the symptoms observed with the human condition (absence seizure) [22] and also drugs that are useful in absence seizures are found to suppress PTZ-induced seizures [23]. Pentylenetetrazole produces convulsions by blocking GABA-A receptors thereby impairing GABA-mediated inhibitory neurotransmission [24]. Hence, AEDs such as diazepam and phenobarbitone are thought to produce their effect by enhancing GABA-mediated inhibition in the brain [25]. In addition, activation of NMDA receptor system appears to be involved in the initiation and propagation of PTZ-induced seizure [26]. Anticonvulsant activity of subcutaneous PTZ test identifies compound that raises seizure threshold in the brain [27].Hence, the ability of Pennisetum glaucum at 50% to decrease seizure duration and offer protection from death in mice suggests its possible interaction with GABAergic neurotransmission and blockade of glutamatergic neurotransmission mediated by NMDA receptor in system in the brain. To produce anticonvulsant activity against absence or myoclonic seizures [28]. Since anticonvulsant activity of a novel compound is not measured only by its ability to prevent convulsions but also to delay the onset of seizures or to reduce death rate and/or decrease the frequency of the episodes [29].Phytoconstituents such as flavonoids, tannins and saponins have been shown to modulate central nervous system (CNS) activities. It is found that many flavonoids could act as benzodiazepine- like molecules in the CNS and modulate GABA-generated chloride currents in animal models of anxiety, sedation and convulsion [30]. Also, flavonoids have overall health promoting functions with particular importance in the prevention of diseases associated with oxidative damage of membrane, proteins and DNA [31]. Flavonoids and tannins have been shown to interact with various voltage gated ion channel which are targets of synthetic AEDs [32]. Hence, Modulation of the activity of ligand gated and voltage gated ion channels by these secondary metabolite of Pennisetum glaucum is likely to be an explanatory basis for the seen anticonvulsant effect.Also, Saponins in plants are believed to have sedative potential as well as the ability to inhibit spontaneous motor activity in mice [33]. Thus, their presence in high concentrations in Pennisetum glaucum supplement may be responsible for the observed effect.Kindling is an established model of abnormal plasticity that leads to prolonged seizure and epilepsy [34]. Pentylenetetrazole induced kindling seizureinvolves repeated administration of a subconvulsive dose of PTZ (35mg/kg) in wistar rats which produces a progressive increase in convulsant activity concluding to generalized seizure [35]. The generalized tonic clonic seizure in this model resembles that of epilepsy in humans [36]. The results obtained from this study demonstrated a trend towards improvement in seizure management in 25 and 50% Pennisetum glaucum supplement treated groups as seizure progression to classical convulsive stages (stages 4.4) were suppressed reaching only to stages 3.8 and 2.5 respectively. This was also described by Malami et al. (2015) who demonstrated that 3-synthesized dichloro-substituted phenylpropanalmides retarded seizure progression from reaching most severe stages of 4 and 5.Since, PTZ induces seizure by blocking the major inhibitory pathways mediated by GABA at all levels of the CNS [37], this study further suggests the potentials of Pennisetum glaucum supplement in enhancing GABA transmission or inhibit seizure generation following kindling.Also, seizure activity leads to mitochondrial dysfunction causing decrease ATP level needed for cellular metabolism, collapse in brain energy level resulting to abnormal neuronal excitability. Hence, the presence of Phosphorus which is an essential component of adenosine triphosphate. (ATP) in addition to high carbohydrate content in Pennisetum glaucum supplement may help in boosting brain energy level thereby counteracting abnormal neuronal excitability. The Magnesium in Pennisetum glaucum supplement may also have contributed to it anticonvulsant activity since it is known to slow the spread of electrical discharge from one area of the brain to another and it deficiency has been shown to decrease seizure thresholds which were reversed by it supplementation [38].Maximal electroshock (MES) causes several changes at the cellular level which can interrupt neuronal transduction causing cellular damage. One of the mechanisms by which MES causes this damage is via facilitation of large amount of calcium ions Ca2+ entry into the cells thereby prolonging seizure duration [39]. Facilitation of other positive ions including Na+ influx has also been reported in MES and it blockade prevent MES-induced tonic hind limb extension in animal models [40]. Potentiation of GABA receptors are also reported to protect against MES-induced seizure [41] and currently available AEDs like phenytoin and sodium valproate act by modulating these ion channels [42].MES assay is used primarily as indication for compounds that are effective in the treatment of generalized tonic clonic seizure [43] Protection against THLE from MEST suggest anticonvulsant effect that prevent the spread of seizure activity from a focus [44].It has been suggested that seizure induction by electroshock machine is through inhibitory current breakdown and voltage-dependent Na-channel in these electrically induced stimuli [45] hence, MES seizure can be prevented by sodium channel blockers like phenytoin, felbamate, valpoarate and lamotrigine which limit repetitive firing of action potential by slowing the rate of recovery of voltage activated sodium channels from inactivation [46] or agent that block glutamatergic transmission mediated by NMDA receptors [47] thereby suppressing tonic hind limb extension in chicks.The protein content in Pennisetum glaucum is high and consists of all varieties of essential amino acids including Tryptophan [6] which can raise serotonin level and helps in stress reduction which is implicated in the pathophysiology of epilepsy.Also, the lipid content of Pennisetum glaucum which was reported to contain phospholipids including omega 3 and decosahexanoic acid (DHA) [48] which plays a vital role in management of stress, behavioural disorders, strengthen the brain and ensure smooth brain function [49] thereby reducing seizures might have also contributed to its anticonvulsant activity. Despite showing lesser efficacy than the commonly used anticonvulsants used in this study Pennisetum glaucum supplement at 25% and 50% offers several advantages over anticonvulsants due to its lack of rapid initiation and relatively low cost and serves dual purposes (food and drug).
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML