-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Research in Neuroscience
p-ISSN: 2326-1226 e-ISSN: 2326-1234
2017; 6(1): 5-10
doi:10.5923/j.neuroscience.20170601.02

Haematological and Immunohistochemical Effects of Gongronema latifolium on the Hippocampus of Albino Wistar Rats
Aquaisua N. Aquaisua, Innocent A. Edagha
Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Basic Medical Sciences, University of Uyo, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Innocent A. Edagha, Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Basic Medical Sciences, University of Uyo, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Different parts of Gongronema latifolium (Gl) has been reportedly used in herbal medicine for the treatment of various health conditions; diabetes, malaria, and hypertension and possess antioxidant properties. Varying doses of Gl ethanolic leaf extract was investigated on haematological indices, and possible histomorphological changes in hippocampal CA1 region. Twenty albino Wistar rats was randomized into four groups of five rats each; group 1 (control), groups 2, 3 and 4 received (100, 200 and 300 mg of Gl per kilogram body weight of the rats). Administration of the extract was for 14 days via orogavage, after which rats were fasted overnight and humanely sacrificed under chloroform inhalation in a dessicator. Results for haematological indices reveals that the white blood cell counts was significantly (p<0.05) increased in test group at a dose dependent concentration compared to the control. Histologically, the hippocampal brain sections showed very mild hydropic vacuolations at the 300 mg dose concentration of the extract with mild to moderate neuronal swellings. Neurotoxicity marker for astrogliosis via glial fibrillary acidic protein expression indicated that it was down regulated in the test groups compared to control. In conclusion, ethanolic leaf extract of Gongronema latifolium does not have deleterious effect on haematological induces although the white blood cell count was significantly raised as a result of normal physiologic response, but caused mild to modreate swelling of hippocampal neurons, with no attendant increase in GFAP expression in albino Wistar rats.
Keywords: Gongronema latifolium, Haematoxicity, Hippocampus, Reactive astrogliosis
Cite this paper: Aquaisua N. Aquaisua, Innocent A. Edagha, Haematological and Immunohistochemical Effects of Gongronema latifolium on the Hippocampus of Albino Wistar Rats, Research in Neuroscience , Vol. 6 No. 1, 2017, pp. 5-10. doi: 10.5923/j.neuroscience.20170601.02.
1. Introduction
- Medicinal plants are rich sources of novel drugs that form the elements in traditional systems of medicine, modern medicines, nutraceuticals, food supplements, folk medicines, pharmaceutical intermediates, bioactive principles and main compounds in synthetic drugs. Plants have long served as a useful and natural source of therapeutic agents. Almost all plants have medicinal values and their uses differ from place to place. One of such plant is Gongronema latifolium which has been used in traditional medicine for treating diabetes, malaria and hypertension and as laxative. It is also used as a spice and vegetable [1]. Gongronema latifolium is locally called “utazi by Igbos, “arokeke” by Yorubas, and Utasi” by the Efiks and Ibiobios in Nigeria. It belongs to the family of Asclepiadacae. It is an edible rainforest plant native to the South East part of Nigeria, commonly eaten in soups and has widely been used in folk medicine [2]. It is an herbaceous shrub with yellow flowers and the stem that yields characteristic milky exudates when cut. Some phytochemicals such as β – sistosterol, lupenyl esters, Pregnance ester, glucosides, essential oils and saponins, alkaloids, flavonoids, phytic acids, tannins and phenols are associated with different parts of this herb [3]. Scientific studies have established the hypoglycaemic, hypolipidaemic and antioxidant effects of extract of G. latifolium [4-8]. G. latifolium at 200, 400, and 800 mg/kg of aqueous leaf extracts and fractions reportedly reduced the glucose level in alloxan diabetic rats (Akah et al., 2011) [9]. 200 and 400 mg of G. latifolium ethanolic extracts reportedly possess hypoglycemic effect; improved lipid profile in diabetic rats and beneficially affected integrity and function of the liver and pancreas (Mafulul et al., 2013) [10].Phytochemical evaluation of the leaves of the plant has shown that it is rich in essential oils, saponins and pregnanes, alkaloids, tannins, phytates, flavonoids and oligosaccharides [7]. The medicinal and nutraceutical benefit of this plant is attributed to the different phytochemical components in the plant individually or collectively [11]. Hippocampal CA1 neurons are exceptionally sensitive to oxygen deprivation, and the hippocampal pyramidal cells are among first to be affected in a variety of conditions that lead to loss of memory and intellectual functions [12]. We therefore investigated the effects of G. latifolium ethanolic leaf extract on haematological indices, histomorphological and immunohistochemical changes in the hippocampal CA 1 region of albino Wistar rats.
2. Materials and Method
- Plant Extract The flesh leaves of G. latifolium were collected from the medicinal farm of the Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Uyo, Uyo during the month of August, 2015. The Plant sample was exposed to dry at room temperature for 7 days. The plant was identified in the Botany Department, Faculty of Science, University of Uyo, Nigeria and specimen no. UUPH/9 deposited. The dried leaves were ground into powder. The powdered sample, weighing 350 g, was extracted 80% ethanol according to the method used by [13]. Extraction in ethanol gave a percentage yield of 30 and was stored in refrigerator (Thermocool Nig. Ltd), for use during the experiment. Stock solution was prepared by dissolving 1 gram of ethanolic extract in 10 ml DMSO to give a concentration of 100 mg/ml respectively. Experimental Animals Twenty albino Wistar rats of average weight of 200 grams were purchased from the Animal House, College of Health Sciences, University of Uyo and were housed in standard cages with 5 animals per cage. The rats were allowed free access to feed and water ad libitum. The rats were allowed to acclimatize in the laboratory for 7 days under 14 hours light and 10 hours dark per day. Experimental DesignThe 20 albino Wistar rats were randomly selected into 4 groups with 5 animals per group. Group 1 served as the control while Groups 2, 3 and 4 were orally administered 100mg, 200mg and 300mg of Gongronema latifolium leaves extract per kilogram body weight of the animals respectively being an approximate estimate for 10%, 20% and 30% of acute toxicity via intraperitoneal route in mice. Individual animals were dosed base on the body weight of the animal and the administration of the extract lasted for 14 days. Stock solution from which individual dosage was taken from was prepared daily. At the end of 14 days, the rats were fasted overnight and then sacrificed under chloroform anaesthesia. Brain tissues were excised, cleaned by blotting with filter paper and fixed in 10% buffered formalin for histological examination. Whole blood was collected by cardiac puncture with sterile needles, placed into EDTA containing sample tube for haematological studies.Haematological StudiesHaematological parameters were determined using automated haematological analyzer (Sysmex® Analyzer KX-21N, Sysmex Corporation, Japan). RBC, HGB, HCT, WBC and Platelets count were estimated in whole blood using this analyser. RBC constant; MCV, MCH and MCHC were calculated from the values of RBC, HGB, HCT.Histological StudiesParaffin embedded brains were sectioned to reveal the hippocampal CA region and processed for light microscopy [14], and likewise same embedded tissue sectioned at 5 microns thick was processed to reveal glial fibrillary acidic protein expression [15]. Statistical analysisThe results are presented as mean ± standard error of mean (SEM) and were analyzed for statistical significance by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Student’s t test. The values with p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Graphs were developed using Microsoft Excel Tools.
3. Results
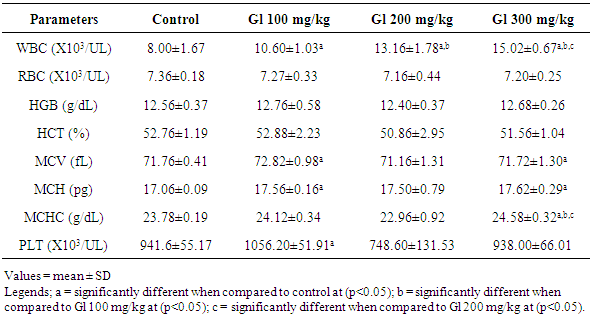
- The result of the effect of ethanolic leaves extract of Gongronema latifolium on haematological parameters is presented in Table 1. The white blood cell count (WBC) was significantly different between the treatment groups and the control. A dose dependent increase in the WBC count was observed across the treatments. The red blood cell counts (RBC), hemoglobin concentrations (HGB) and hematocrit (HCT) remained relatively unperturbed throughout the study groups. The mean corpuscular volume (MCV) and mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) were significantly different in groups treated with Gl 100mg/kg and Gl 300mg/kg when compared to the control, while the mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) was only significantly increased in group treated with Gl 300mg/kg when compared to other groups. Platelet count (PLT) increased significantly in group treated with Gl 100mg/kg compared to the control. All comparison was carried out at P < 0.05. The graphical representations (line graph) of this result are shown in Figures 1 and 2.In Figure 1 (A-D) is shown the paraffin embedded section stained with haematoxylin and eosin of the hippocampus CA1. In 2A is the control with normal cytoarchitecture (not affected); 2B shows normal cellular morphology and density (not affected); 2C had few hydropic vacuolations (mildly affected); 2D has more prominent hydropic vacuolations (mildly affected). In Figure 2 (A-D) is shown the immunolabeling marker for neuroinflammation and neurotoxicity via the expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). 2A shows normal expression of GFAP in a control hippocampal CA1 section with the absence of dendritic thickening or astrocytic cell body swellings (+ mildly expressed); 2B shows hippocampus did not express GFAP (not expressed); 2C shows little or no immunopositivity (not expressed); 2D shows very weak stain intensity for GFAP (not expressed).
|
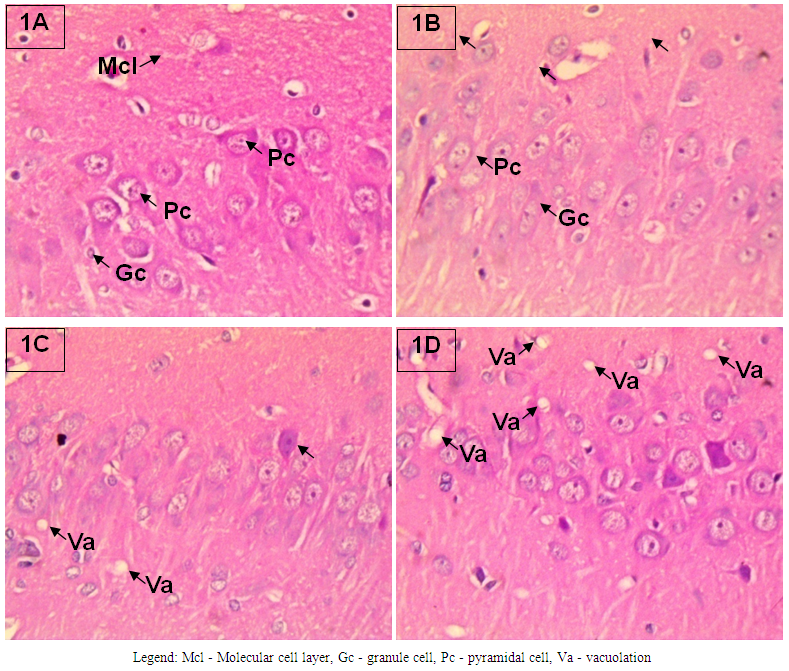 | Figure 1A-D. Histomorphological Effect of ethanolic extract of Gongronema latifolium on the Hippocampus of adult Wistar rat H&E at x400 magnification |
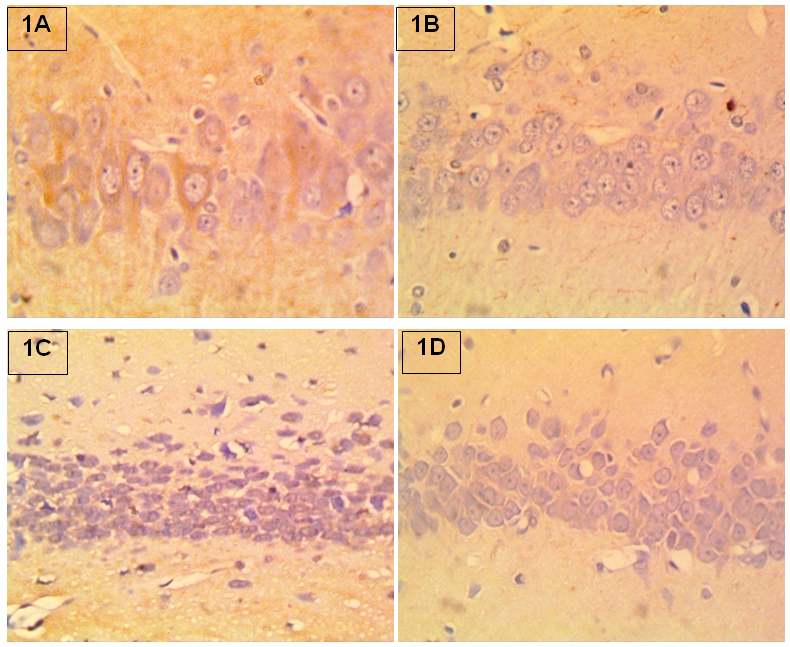 | Figure 2A-D. Neuroinflammatory effect of ethanolic extract of Gongronema latifolium on the Hippocampus of Wistar rat GFAP stained at x400 magnification |
4. Discussion
- The plant kingdom has become a very useful resource for man in his desire and search for beneficial products for nutritional and or medicinal purposes. Gongronema latifolium has been extensively studied and utilized for its medicinal potentials. It has been proven to have antidiabetic properties [16] and is used locally by diabetics. Studies have also reported that it can also protect the liver and kidney against injury or ameliorate injuries inflicted on these organs [17, 18]. The antioxidant and antibacterial/antimicrobial properties of G. latifolium have also been studied likewise antimalarial and antipyretic potentials of the plant [19-22]. Indeed, the plant has enormous medicinal potential in addition to its nutritional benefits. However, there is little information on the hematological effect of this plant. Blood serve as a medium through which all substances are transported in the system and therefore susceptible to alterations – detrimental or beneficiary to these substances. This alteration can be used to explain blood selected functions of chemicals/plant extract [23]. The leaf extract of the plant has been reported to reverse alterations in hematological indices and weight loss in diabetic rats [24]. The result of this study shows a dose dependent significant increase in the white blood cell count of the experimental rats. White blood cells have been known to increase in cases of infections or assault to organs and tissues and as response to incoming xenobiotics or foreign bodies to the system. The observed increase in this study is as a response to the presence of the extract in the system. This collaborated with the study by [24]. Interestingly, the plant extract did not induce any significant deleterious perturbation on the hemoglobin concentration, hematocrit and red blood cell counts of the experimental animals. Some plant extract have been known to cause haemolysis and reduce red blood cell count, however, Gongronema latifolium do not cause any harm to these parameters as shown in this study. Platelet play a role in blood clotting and the result of this study showed a significant increase only in group treated with Gl 100mg//kg while other treatments showed insignificant decrease in the platelet count when compared to the control. Report by [24] also collaborate with this study. It can be said then that at low concentration, the extract has the potential to induce platelet synthesis while at higher doses, the effect is otherwise. Histomorphological distortions were not prominent in the test groups compared to the control, as shown in Figure 1 (A-D), however early onset of vacuolations and mild neuronal shrinkage was observed in the 300 mg group alongside foci neuronal swellings. This may be an early and recognizable indicator of neuronal degeneration in the hippocampus [25]. CA1 neurons are highly sensitive to oxygen deprivation and can easily undergo neurodegeneration [12]. Also, GFAP expression is regarded as a sensitive and reliable marker to label reactive astrocytes that are responding to CNS injuries [26]. However, GFAP expression in this study was not markedly changed in the test groups compared to control as seen in Figure 2 (A-D). In conclusion, the ethanolic leaf extract of Gongronema latifolium does not have a deleterious effect on haematological indices, but caused mild to moderate swelling of hippocampal neurons, with no attendant increase in GFAP expression in albino Wistar rats.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML