-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Research in Neuroscience
p-ISSN: 2326-1226 e-ISSN: 2326-1234
2015; 4(1): 10-15
doi:10.5923/j.neuroscience.20150401.02

Effect of annona muricata Seed Extract on Blood Glucose, Total and Differential White Cell Count after Repeated Exposure to Clozapine
Agbai E. O.1, Mounmbegna P. P. E.2, Njoku C. J.3, Nwanegwo C. O.4, Awemu G. A.5, Iwuji S. C.6
1Department of Human Physiology, Madonna University Nigeria
2Department of Biochemistry, Madonna University Nigeria
3Department of Pharmacology, Niger Delta University, Wilberforce Island, Nigeria
4Department of Physiology, Imo State University Owerri, Nigeria
5Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Madonna University Nigeria
6Department of Biomedical Technology, Federal University of Technology, Owerri, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Agbai E. O., Department of Human Physiology, Madonna University Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The use clozapine as antipsychotic agent poses high risk of developing agranulocytosis and hyperglycemia. We investigated the ameliorative effects of annona muricata seed on blood glucose, total and differential white cell count after repeated exposure of rats to 20mg/kg of clozapine. Twenty male albino wistar rats were divided into group A (control) and B (experimental). Group B was administered 20mg/kg of clozapine daily. Clozapine was administered repetitively in group B rats at different periods of one week (group B1), 3 hours after one week (group B2), and three hours following the last three hours (group B3). After the last of administration of clozapine (group B3), the rats were randomly subdivided into group C and D and received 600 and 800 mg/kg of extract respectively for 3 days. Results showed increase (P < 0.05) in mean blood glucose and decrease (P < 0.05) in total white and differential white cell counts of B1, B2 and B3. Three days administration of annona muricata seed extract caused a significant reduction (P < 0.05) in mean blood glucose and further caused a decline in total and differential white cell count. Data conclude that annona muricata seed extract exerted hypoglycemic effect on clozapine treated rats without improving decreased total and white cell count.
Keywords: Annona muricata, Clozapine, Bloodglucose, Total white cell count, Differential white cell count
Cite this paper: Agbai E. O., Mounmbegna P. P. E., Njoku C. J., Nwanegwo C. O., Awemu G. A., Iwuji S. C., Effect of annona muricata Seed Extract on Blood Glucose, Total and Differential White Cell Count after Repeated Exposure to Clozapine, Research in Neuroscience , Vol. 4 No. 1, 2015, pp. 10-15. doi: 10.5923/j.neuroscience.20150401.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
1.1. Background of the Study
- Clozapine (dibenzodaizepine) is an effective atypical antipsychotic for the treatment of schizophrenia is associated with a relatively high incidence of drug induced agranulocytosis (Ip and Uetrecht, 2008) and impaired glucose tolerance (Chae and Kang, 2001). Besides agranulocytosis, other hematological and metabolic side effects and a variety of cardiovascular problems have been reported (Meltzer, 2012), although the most serious adverse effect of clozapine remains drug-induced agranulocytosis. Data have showed that thrombocytopenia (1-3% of patients), anemia, leukocytosis and thrombocytosis (1% of patients) are associated with the use of clozapine (Lubran, 1989, Hampson, 2000). There are also reports of increased mean levels of blood glucose, insulin and C-peptide (Yazici et al., 1998), weight gain, hyperglycemia, seizures, tachycardia, myocarditis and neuromalignant syndrome (Van-Kammen and Marder, 2000), impaired glucose tolerance (Chae and Kang, 2001) and insulin growth factor binding protein I (Howes et al., 2004). Reports in rat model showed that clozapine impaired glucose metabolism by increasing blood glucose independent of insulin (Murashita et al., 2007).However, there is a paucity of scientific data on repeated administration of clozapine. Data on repeated use of clozapine was studied on frontal cortex showed reduced number of dopamine cells per track in ventral tegmental area dopamine-containing neurons in rat (Chiodo and Bunney, 1985) and selective attenuation of serotonin-mediated excitation in neuronal circuitry (Zahorodna et al., 2004). Another report showed attenuated phencyclidine-induced hyperlocomotion and blocked phencyclidine-induced increases in glutamate levels in medial prefrontal cortex (Abekawa et al., 2007).This article studied post-treatment with annona muricata seed extract on some clozapine side effects because of its relevance in treatment of anemia (Agbai et al., 2014) and hyperglycemia (Adeyemi et al., 2009, Alhaya et al., 2014). Annona muricata commonly called sour sop is a small erect evergreen tropical plant belonging to the family of Annonaceae growing 5-6 m in height (Arthur et al., 2011). The leaf extract is used against hematoma cell lines in vitro (Chen et al., 2000), as prophylactic against breast tissue cell proliferation (Minari and Okeke, 2014). Our recent study showed that single dose administration of clozapine at 5mg/kg, 10mg/kg and 20mg/kg caused a decrease in serum cortisol and white cell count in a dose-dependent manner after 7 days while blood glucose increased "in press".This article investigated the ameliorative effect of annona muricata seed extract on blood glucose, total white cells and differential counts after repeated exposure of rats to 20mg/kg of clozapine.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
- Twenty male albino wistar rats weighing 186-236 g were used for this study. They were randomly divided into two groups of A and B. the rats were kept in standard wooden cages in a room with a temperature between 27 to 32°C where they could observe the dark/light cycle throughout the duration of the experiment and had access to tap water and rat food. They were acclimatized for two weeks before the commencement of the experiment. Experimental procedures involving the animals and care were conducted in conformity the University guidelines that are in compliance with National and International laws and guidelines for care and use of laboratory animals.
2.2. Drug and Extract Preparation
- Clozapine (Norvatis) was purchased in tablet form (100 mg/tablet). Two tablets were dissolved in 50 ml of distilled water to obtain a concentration of 200 mg/50 ml which equals to 4 mg/ml. If 1 kg of rat receives 20 mg of clozapine, therefore 1 g will receive 0.02 mg/g. For example, if a rat weighed 200 g will receive 0.02 x 200 = 4 mg of clozapine. In order to administer clozapine in ml will be 4 mg = 1 ml, therefore; 4 mg (200 g body weight) will receive 1 ml of clozapine. All animals had free access to food and water. Animal handling and treatment were conducted in conformity with Animal Ethical Committee of the department.Fresh fruits of annona muricata were bought from a local market (Rivers State, Nigeria). The fruits were cut in pieces in order to remove the seeds from the creamy pulp. The seeds were rinsed and sundried in an electric oven (Gallenkamp) at 45°C. The dried seeds were ground into a coarse powder form with electric grinder. 50 grams of the ground seed was macerated in 250 ml of methanol and sieved after 48 hours. The filtrate was concentrated using rotator evaporator (Buchi) and dried in the electric oven (45°C). The extract was preserved in a refrigerator (4°C) until ready for use.
2.3. Extract and Drug Administration
- Group A (Control) which received tap water. Experimental group B received oral administrations of 20 mg/kg body weight of clozapine at different intervals of 1 week, exposed after 3 hours, and re-exposed after another 3 hours. Group B rats were represented as B1, B2 and B3 according to intervals of repeated administration. Following the last three hours of clozapine administration, group B3 rats were randomlysubdivided into group C and D, and treated with 600 and 800 mg/kg of annona muricata seed extract respectively. Arthur et al., (2011) have showed safety of animals after extract administration up to 2500 mg/kg. Blood was collected from tail vein to assess basal glucose level in all groups (A and B) before administration of clozapine, and the animals exhibited blood glucose level < 100 mg/dl. The glucose levels were estimated after one week of first clozapine administration, 3 hours after second clozapine administration and another 3 hours after third clozapine administration before extract administration for three days. At the end of the experiment, glucose levels, differential white blood cell and total white blood cell count were estimated by glucose oxidase principle (Beach and Turner, 1958), manual counting and manual differential.
2.4. Principles of Total White Blood Cell Count
- Total white blood cell count and differential white blood cell count were done by manual white blood cell counting. Whole blood is diluted 1 in 20 in an acid reagent which hemolyzes red cell, leaving the white blood cells to be counted. White cells are counted microscopically using an Improved Neubauer ruled counting chamber (haemocytometer) and the number of white blood cells per liter of blood calculated.
2.5. Principles of Differential White Blood Cell Count
- A thin blood film is prepared by spreading a small drop of blood evenly on a slide so that there is only one layer of cells. The slides were dip in Giemsa stain for 10 seconds and afterwards in distilled water for 20 seconds for darker staining. The white blood cells were estimated by noting number of white cells per field x 1000.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
- Statistical significance of differences between control and experimental groups, between experimental control group and experimental groups were expressed as means ± SEM. ANOVA was used to analyze results. Any significant ANOVA was further analyzed by Tukey post hoc test. P values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
3. Results
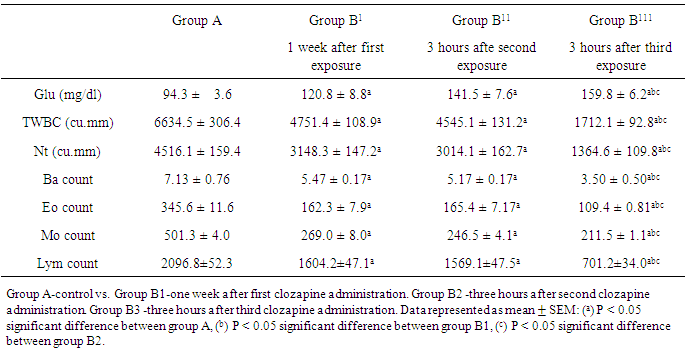
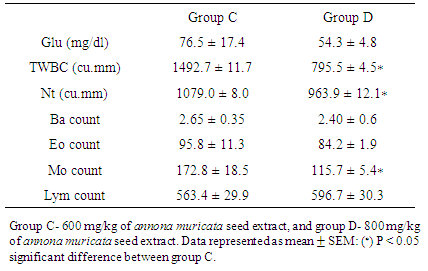
- Results showed statistically significant increase (P < 0.05) in mean blood glucose at different times of clozapine administration in B1 (120.8 ± 8.8), B2 (141.5 ± 7.6) and B3 (159.8 ± 6.2) compared to group A (94.3 ± 3.6). Total white cell count showed statistically significant decrease (P < 0.05) in B1 (4751.4 ± 108.9), B2 (4545.1 ± 131.2) and B3 (1712.1 ± 92.8) compared to group A (6634.5 ± 306.4). Differential white cell count also showed statistically significant decrease (P < 0.05) in B1 (neutrophils: 3148.3 ± 147.2, basophils: 5.47 ± 0.17, eosinophils: 162.3 ± 7.9, monocytes: 269.0 ± 8.0, lymphocytes: 1604.2 ± 47.1), B2 (neutrophils: 3014.1 ± 162.7, basophils: 5.17 ± 0.17, eosinophils: 165.4 ± 7.17, monocytes: 246.5 ± 4.1, lymphocytes: 1569.1±47.5), B3 (neutrophils:1364.6 ± 109.8, basophils:3.50 ± 0.50, eosinophils: 109.4 ± 0.81, monocytes: 211.5 ± 1.1, lymphocytes: 701.2 ± 34.0) compared to control (neutrophils: 4516.1 ± 159.4, basophils: 7.13 ± 0.76, eosinophils: 345.6 ± 11.6, monocytes: 501.3 ± 4.0, lymphocytes: 2096.8 ± 52.3). However, there was no statistically significant difference in total white cell and differential count (P > 0.05) between group B1 (one week after first clozapine administration) and group B2 (3 hours after second clozapine administration), but there was statistically significant difference in total white cell and differential count (P < 0.05) between group B2 and group B3. Post treatment results with the extract showed statistically significant decrease (P < 0.05) in mean blood glucose level of group C (76.5 ± 17.4) and group D (54.3 ± 4.8) rats. The total white cell count showed statistically significant decrease in group C (1492.7 ± 11.7) and group D (795.5 ± 4), although there was statistically significant difference (P < 0.05) between group C and D. Results also showed further decrease in differential count, but there was statistically significant difference in differential white cell count after three days treatment with extract between group C and D in neutrophil and monocyte counts (1079.0 ± 8.0 and 172.8 ± 18.5) and (963.9 ± 12.1 and 115.7 ± 5.4) respectively except in basophils, eosinophil and lymphocyte counts between group C (2.65 ± 0.35, 95.8 ± 11.3 and 563.4 ± 29.9) and group D rats (2.40 ± 0.6, 84.2 ± 1.9 and596.7 ± 30.3) at P > 0.05.
4. Discussion
- It is generally known that agranulocytosis is the most common adverse effect of clozapine, thus these results in table 1 were expected. This article demonstrated that repeated administration of clozapine resulted in a progressive decline in total white blood cell count and differential count. Recent study showed that single dose administration of clozapine at doses of 5mg/kg, 10mg/kg and 20mg/kg resulted in a significant decrease in total and differential white cell count in a dose dependent manner ("in press"). Studies have demonstrated the action of clozapine in agranulocytosis involved formation of reactive nitrenium ion metabolite upon oxidation by peripheral neutrophils and their precursors in the bone marrow (Ip and Uetrecht, 2008), and generation of reactive products of clozapine by either hepatic metabolism or oxidation by horseradish peroxidase-peroxide system of activated neutrophils (Tschen et al., 1999). Several studies have also reported that clozapine inhibited cell survival signaling genes in the bone marrow (Kim et al., 2004), inhibited stromal viability (Pereira and Dean 2006) and caused mesenchymal stromal cell death (Lahdelma et al., 2010).
|
5. Conclusions
- This study concludes that annona muricata seed extract caused a decrease in mean blood glucose in dose-dependent manner except that total and white cell counts were not improved after three days.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- The author is grateful to the laboratory technologists in Department of Physiology at Madonna University for technical support.
References
| [1] | Abekawa, T., Ito, K. Koyama, T. (2007). Different effects of single and repeated administration of clozapine on phencyclidine-induced hyperlocomotion and glutamate releases in rat medial prefrontal cortex at short- and long-term withdrawal from this antipsychotic. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch pharmacol., 375(4): 261-271. |
| [2] | Adewole, S. O., Caxton-Martins, E. A. (2006). Morphological changes and hypoglycemic effects of annona muricata Linn (annonaceae) leaf aqueous extract on pancreatic B-cells of streptozotocin-treated diabetic rats. Afr. J. Biomed. Res., 9: 173-187. |
| [3] | Adeyemi, D. O., Komolafe, O. A., Stephen, A. O., Obuotor, E. M., Adenowo, T. K. (2009). Antihyperglycemic activities of annona muricata Linn. Afr. J. Trad. CAM., 6(1): 62-69. |
| [4] | Agbai, E. O., Nwanegwo, C. O., Iwuji, S. C., Mounmbegna, P. P. E., Awemu, G., Nwafor, A. (2015). Single dose administration of clozapine impairs cortisol concentration and body's defense in a dose-dependent manner ("in press"). |
| [5] | Agbai, E. O., Moumbegna, P. E., Nwafor, A. (2014). The beneficial effects of methanol extract of annona muricata seed on acute hemolytic anemia in albino wistar rats. J. Med. Sci. Clin. Res., 2(5): 958-967. |
| [6] | Alhaya, B., Ravishankar, K., Kiranmayi, G.V. N. (2014). Exploration of anti-hyperglycemic and hypolipidemic activities of ethanolic extract of annona muricata bark in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res., 5:21-27. |
| [7] | Arnolds, S., Kuglin, B., Kapitza, C., Heise, T. (2010) . How pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic principles pave the way for optimal basal insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Clin. Pract., 64(10):1415-1424. |
| [8] | Arthur, F. K. N., Woode, E., Terlabi, E. O., Larbie, C. (2011). Evaluation of acute and subchronic toxicity of annona muricata (Linn) aqueous extract in animals. Eur. J. Exp. Biol., 1(4): 115-124. |
| [9] | Beach, E. F., Turner, J. J. (1958). An enzymatic method for glucose determination uptake in body fluids. Clin. Chem., 4: 462-468. |
| [10] | Best, L., Yates, A, P., Reynolds, G. P. (2005). Action of antipsychotic drugs n pancreatic beta-cell function: contrasting effects of clozapine and haloperidol. J. Psychopharmacol., 19(6):597-601. |
| [11] | Chae, B. J., Kang, B. J. (2001). The effect of clozapine on blood glucose metabolism. Hum. Psychopharmacol., 16:265-271. |
| [12] | Chen, J. C., Tsai C. C., Chen, N. N., Wang, W. C. (2000). Therapeutic effect of gypenoside on chronic liver injury and fibrosis induced by CCl4 in rat. Am. J. Clin. Med., 28: 175-185. |
| [13] | Chiodo, L. A., Bunney. B. S. (1985). Possible mechanism by which repeated clozapine administration differentially affects the activity of two subpopulations of midbrain dopamine neurons. J. Neurosci., 5(9):2539-2544. |
| [14] | Lee, H. J., Jin, S. Y., Hong, M. S., Park, H. J., Kim, M. K., Yim, S. V., Kim, J. W., Park, H. K., Kim, S. S., Chung, J. H. (2004). Clozapine inhibits cell survival related genes in bone marrow cells. Mol. Psychiatry, 9(6): 545-546. |
| [15] | Guitton, C., Abbar, M., Kinowski, J. M., Chabrand, P., Bressolle, F. (1998). Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of clozapine in patients with chronic schizophrenia. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol., 18(6): 470-476. |
| [16] | Hampson, M. E. (2000). Clozapine-induced thrombocytosis. Br. J. Psychiatr., 176(4): 400. |
| [17] | Howes, O. D., Gaughran, F. P., Amiel, S. A., Murray, R. M., Pilowsky, L. S. (2004). The effect of clozapine on factors controlling glucose homeostasis. J. Clin. Psychiatr., 65(10): 352-355. |
| [18] | Ip, J., Uetrecht, J. P. (2008). Testing the hypothesis that selenium deficiency is a risk factor for clozapine-induced agranulocytosis in rats. Chem. Res. Toxicol., 21(4):874-878. |
| [19] | Lahdelma, L., Oja, S., Korhonen, M., Andersson, L. C. (2010). Clozapine is cytotoxic to primary cultures of human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol., 30(4): 461-463. |
| [20] | Lubran, M. M. (1989). Hematological side effects of drugs. Ann. Clin Lab. Sci., 19:114-121 |
| [21] | Minari, J. B., Okeke, U. (2014). Chemopreventive effect of annona muricata on DMBA-induced cell proliferation in the breast tissues of female albino mice. Egyptian J. Med. Hum. Genet., 15(4): 327-334. |
| [22] | Murashita, M., Kusumi, I., Hosoda, H., Kangawa, K., Koyama, T. (2007). Acute administration of clozapine concurrently increases blood glucose and circulating plasma ghrelin levels in rats. Psychoneuroendocrinol., 32(7): 777-784. |
| [23] | Pereira, A., Dean, B. (2006). Clozapine bioactivation induces dose-dependent drug specific toxicity of human bone marrow stromal cells: a potential in vitro system for the study of agranulocytosis. Biochem. Pharmacol., 76(2): 783-793. |
| [24] | Smith, G. C., Zhang, Z. Y., Mulvey, T., Petersen, N., Lach, S., Xiu, P., Phillips. A., Han, W., Wang, M. W., Shepherd, P. R. (2014) Clozapine directly increases insulin and glucagon secretion from islets: implication for impairment of glucose tolerance. Schizophrenia Res., 157(1-3): 128-133. |
| [25] | Testa, N. G., Dexter, T. M. (2001). The regulation of hemopoietic cell production. In Postgraduate Hematology, 4th edition. Edited by Hoffbrand, A. V., Lewis, S. M., Tuddenham, E. G. Co published by Arnold London and Oxford University Press 9-11. |
| [26] | Tschen, A. C., Rieder, M. J., Oyewumi, L. K., Freeman, D. J. (1999). The cytotoxicity of clozapine metabolites: implications for predicting clozapine-induced agranulocytosis. Clin. Phamacol. Ther., 65(5):526-532. |
| [27] | Van Kammen, D. P., Marder, S. R. (2000). Serotonin/dopamine antagonists. In Comprehensive Textbook of Psychiatry. 7th edition. Edited by Kaplan, H. I., Sodock, B. J. Baltimore MD: Lippincot Williams and Wilkins 2455-2473. |
| [28] | Yazici, K. M., Erbas, T., Yazici, A. H. (1998). The effect of clozapine on glucose metabolism. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes, 106(6): 475-477. |
| [29] | Zahorodna, A., Bobula, B., Grzegorzewska, M., Tokarski, K., Hess, G. (2004). The influence of repeated administration of clozapine and haloperidol on the effects of the activation of 5-HT1A, 5-HT2 and 5-HT4 receptors in rat frontal cortex. J. Physiol. Pharmacol., 55(2): 371-379. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML