-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Research in Neuroscience
p-ISSN: 2326-1226 e-ISSN: 2326-1234
2014; 3(1): 22-28
doi:10.5923/j.neuroscience.20140301.03
Protective Role of Either Ginger or Lipoic Acid in Senile Female Rats
Nadia M. S. Arafa1, Elham H. A. Ali2
1Faculty of Science, Biology Department, Jazan University, KSA & National Organization for Drug Control and Research, Department of Physiology
2Zoology Department, Faculty of women for Arts, Science and Education, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt
Correspondence to: Nadia M. S. Arafa, Faculty of Science, Biology Department, Jazan University, KSA & National Organization for Drug Control and Research, Department of Physiology.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Aging associated with neurodegenerative disorders. The dysregulation of brain lipid metabolism might contribute to the mechanisms of aging and Alzheimer's disease. The study aimed to evaluate the change in free fatty acids and free calcium ion contents, as well as the total antioxidant activity in senile female rat's brain. Moreover, the possible protective effect of either ginger or alpha lipoic acid. The experimental groups (n=6/group) administered orally for four weeks and classified into: 1- Control adult female rats group and 2- Senile female group (both groups) received one ml/100 g b.wt. 0.5 g/100 ml CMC. 3- Senile ginger group received 250 mg/kg ginger. 4- Senile lipoic treated group administered 65 mg/kg lipoic acid. The results suggested protective effect of ginger and alpha lipoic acid in senile female rats through modulation of, saturated, unsaturated fatty acids and the total antioxidant capacity in cortex and hippocampus. In addition, the cortical free calcium ions content that could protect the senile rats from ageing diseases.
Keywords: Ginger, Alpha Lipoic Acid, Cortex, Hippocampus, Free Fatty Acids, Total Antioxidant Capacity
Cite this paper: Nadia M. S. Arafa, Elham H. A. Ali, Protective Role of Either Ginger or Lipoic Acid in Senile Female Rats, Research in Neuroscience , Vol. 3 No. 1, 2014, pp. 22-28. doi: 10.5923/j.neuroscience.20140301.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The central nervous system is particularly vulnerable to oxidative injury. It contains high concentrations of readily oxidizable poly-unsaturated fatty acids and has a high rate of oxygen consumption per unit volume. Also possesses relatively low levels of antioxidant defense system (Koenig and Meyerhoff, 2003; Freitas, 2009).In the central nervous system, lipids are one of the main targets of reactive oxygen species, because their cell membranes are rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids (Cini and Moretti, 1995). Studies suggesting that dysregulation of brain lipid metabolism might contribute to the mechanisms of aging and Alzheimer's disease (AD); lipid metabolism has not evaluated extensively in aging brain (Snigdha et al. 2012). Epidemiological studies implicate that the high-fat diet confers a significant risk for development of AD and the degree of saturation of fatty acids is critical in determining the risk for AD (Mattson et al., 2002). The saturated free fatty acids (FFAs), palmitic and stearic acids, caused increased amyloidogenesis and tau hyperphosphorylation in primary rat cortical neurons. These FFA-induced effects observed in neurons mediated by astroglial FFA metabolism (Patil et al., 2007). Fatty acid is required for both the structure and function of every cell in the body and forms an important component of cell membranes. It undergoes changes during the process of injury, repair and cell growth (Cameron and Cotter 1997; Murugan and Pari, 2007). These FFA-induced effects observed in neurons mediated by astroglial FFA metabolism (Patil et al., 2007). Fatty acid is required for both the structure and function of every cell in the body and forms an important component of cell membranes. It undergoes changes during the process of injury, repair and cell growth (Cameron and Cotter 1997; Murugan and Pari, 2007).Deficiencies in polyunsaturated essential fatty acids (PUFA) implicated in mood disorders (Sublette et al., 2009). Linoleic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA, 20:5) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA, 22:6) are especially important during human brain development. Maternal deficiency of omega-3-fatty acids related to deficits in neurogenesis, neurotransmitter metabolism, and altered learning and visual function in animals (Shahidi et al., 2005; Innis, 2008). Dietary omega-3-fatty acids are certainly involved in the prevention of some neuropsychiatric disorders, particularly depression, as well as in dementia, notably Alzheimer’s disease (Calon and Cole, 2007). Alpha linoleic acid and DHA is essential for nervous tissue growth and function (Bourre, 2004). Ginger (Zingiber officinale) used in the Indian traditional system of medicine for digestive disorders, common cold, and rheumatism (Sharma and Singh, 2012). The nonvolatile pungent compounds namely gingerols, shogaols, paradols, and zingerone) are some of the extensively studied phytochemicals. They account for the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antiemetic, and gastroprotective activities (Kubra and Jaganmohanrao, 2012).The nonvolatile pungent compounds (namely gingerols, shogaols, paradols, and zingerone) are some of the extensively studied phytochemicals and account for the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antiemetic, and gastro protective activities (Kubra and Jaganmohanrao, 2012).Alpha lipoic acid (ALA, DL-6, 8-dithiooctanoic acid) is a naturally occurring compound synthesized in small quantities by most plants and animals (Perera et al., 2011). Considered as endogenous thiol antioxidant that quench ROS, regenerate glutathione (GSH). It chelate metals such as iron, copper, mercury, and cadmium, which known to mediate free-radical damage in biological systems (Akpinar et al., 2007; Applegate et al., 2008). The study aimed to declare the possible protective effect of ginger or alpha lipoic acid on senile female rats as antioxidants through studying the change in metabolic brain free fatty acids in cortex and hippocampus.
2. Material and Methods
- Twenty-four female rats, 18 senile (30 months old) and 6 adults (6 months) obtained from the National Organization for Drug Control and Research (NODCAR). Animals housed plastic cages each cage contained six rats. Animals were maintained under controlled temperature of 25±2℃ and 12 hours light/12 hours dark cycle throughout the experiment. The animals allowed to food, as commercial pelleted diet and water were available ad libitum. Chemicals: Ginger purchased from Arab Co. For Pharmaceuticals & Medicinal Plants MEPACO- EGYPT as tablet contains treated ginger (Zingiber officinale) 400mg. Lipoicacid supplied as tablets containing 300 mg manufactured by EVA Company, Egypt.Saturated fatty acids (SFAs), lauric (C12:0), myristic (C14:0), palmitic (C16:0), stearic (C18:0) and arachidic (C20:0). Unsaturated fatty acids (USFAs), oleic (C18:1ω–9), linoleic (C18: 2ω–6),), cis-5.8.11.14.17-eicosapentaenoic (C20:5ω–3) (EPA) and cis-4.7.10.13.16.19-docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) (22:6ω-3). All FAs purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Co.(St. Louis, USA). All other chemicals and solvents used were of the High Performance Liquid Chromatography and analytical grade. Animal Grouping: The animals divided into four main groups; each one contained six rats as follows: 1- control normal adult female rats (C) received 1 ml/100 g.b.wt. Carboxymethylcellulose sodium salt (CMC) orally. 2-Control senile female rats (S) received CMC as group 1. 3-Senile ginger group (S+G) received 250 mg/kg in CMC. 4-Senile lipoic acid group (S+L) received 65 mg/kg lipoic acid in CMC. Treatments extended for four weeks with daily oral administration. Doses calculated as equivalent to the human recommended dose according to Reagan-Shaw et al. (2008).Biochemical Assay: Following the completion of the experiments, the rats sacrificed after 12 hours from the last dose by rapid decapitation. Brain cortex and hippocampus excised for the determination of free fatty acids as methyl estersby GC according to the method previously described in Firląg et al., (2013). Using column HP-5 (Methyl siloxane). Cortex also used for the determination of Ca+ contents according to the method in Arafa (2010) and the total antioxidant capacity according to the method of Koracevic et al. (2001).Statistical Analysis: Reported values represent means ± SE. Statistical analysis evaluated by one-way ANOVA. Once a significant F test obtained, LSD comparisons performed to assess the significance of differences among various treatment groups. Statistical Processor System Support "SPSS" for Windows software, Release 21.0 (SPSS, Chicago, IL) was used.
3. Results and Discussion
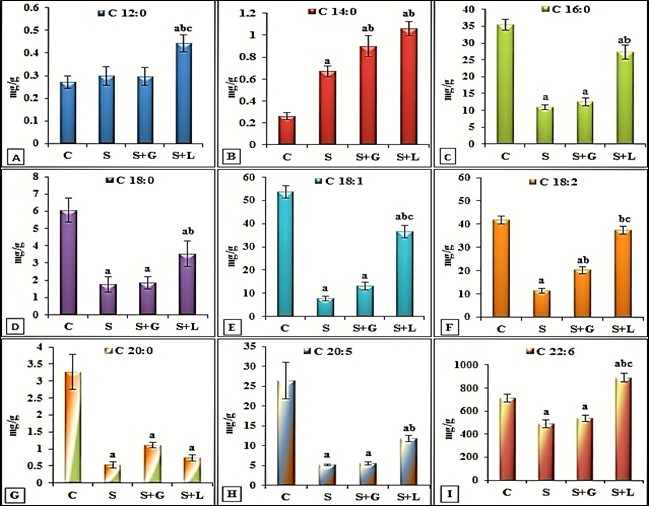
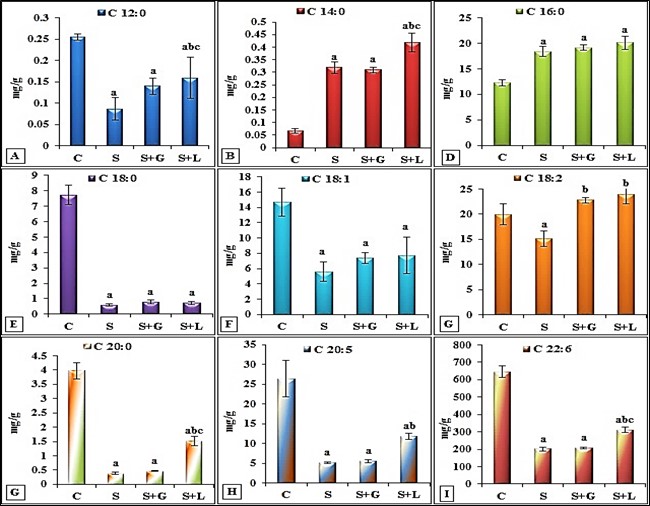
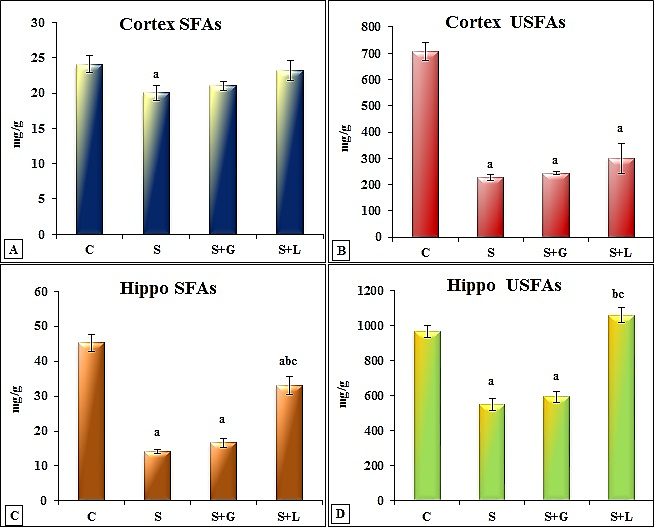
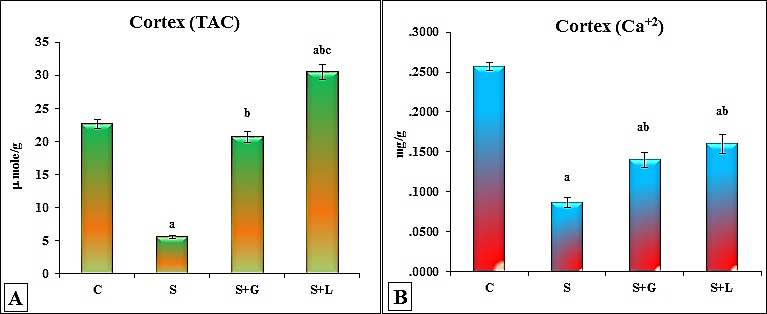
- The data depicted for senile female group showed in cortex (Figure 1 (A-I)) significant decrease in SFAs (palmitic, stearic and arachidic) and USFAs (oleic, linoleic, EPA and DHA) and a significant increase in myristic acid. While showed, significant decrease in SFAs (lauric, stearic and arachidic) and USFAs (oleic, linoleic, EPA and DHA), but significant increase in SFAs, myristic and palmitic in hippocampus (Figure 2 (A-I)) as compared to the adult control values. The data in Figure 3 (A-D) demonstrated the significant decrease in cortex and hippocampus total saturated (SFAs) and unsaturated (UFAs) fatty acids in senile female rats as compared to the control values. In cortex, TAC and Ca+2 contents decreased significantly in senile group as compared to the control values (Figure 4(A and B)).
4. Conclusions
- The results suggested protective effect of ginger and alpha lipoic acid in senile female rats. That through modulation of fatty acids in cortex and hippocampus, as well as the cortical free calcium ions content. Such could protect the senile rats from aging diseases and their supplementation as complimentary could improve brain antioxidant functions in the senile rats.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors gratefully acknowledge the help of the National Organization for Drug Control and Research (NODCAR).
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML