-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Marine Science
p-ISSN: 2163-2421 e-ISSN: 2163-243X
2014; 4(1): 1-9
doi:10.5923/j.ms.20140401.01
Characterization of Water Reflectance Spectra Variability: Implications for Hyperspectral Remote Sensing in Estuarine Waters
Chunlei Fan 1, Robert A. Warner 2
1Biology Department/PEARL, Morgan State University, Baltimore, MD 21251, USA
2NOAA/Center for Coastal Monitoring & Assessment, Silver Spring, MD 20910, USA
Correspondence to: Chunlei Fan , Biology Department/PEARL, Morgan State University, Baltimore, MD 21251, USA.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
As a part of a large scale hyperspectral remote sensing campaign, water bio-optical properties were measured at 151 field stations from 2002 to 2008 at five U.S. estuaries: Apalachicola Bay, FL; ACE basin, SC; Grand Bay, MS; Delaware Bay, DE; and Chesapeake Bay, MD. At each station, water irradiance reflectance R(λ) spectra were acquired by ocean optic 2000 spectroradiometers. Simultaneously, concentrations of chlorophyll a and total suspended solids, as well as absorption of colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM) were measured. This paper focused on the relationships between reflectance R(λ) spectra and the in situ bio-optical constituents. A principal component analysis was conducted to characterize the general variability of reflectance R(λ) spectra, and a Canonical Correspondence Analysis was further performed to explore the relationships between spectral reflectance and water optically active constituents in coastal environments. The results suggested that water reflectance spectra in estuarine waters are the results of complex interactions among phytoplankton pigments, total suspended solids, and CDOM. The first principal component, which represents 72% of total variance of R(λ), is affected by backscattering of total suspended solids, and the absorption of CDOM at blue-green region of spectra; while the second principal component that representing 20% of variation of R(λ), is mainly driven by the absorption of Chlorophyll a in red and near infrared spectral regions. Furthermore, the results of this study could provide insights for using hyperspectral remote sensing as a cost effective approach for monitoring water quality in coastal waters.
Keywords: Remote sensing, Water quality, Case 2 water, Bio-optical constituents
Cite this paper: Chunlei Fan , Robert A. Warner , Characterization of Water Reflectance Spectra Variability: Implications for Hyperspectral Remote Sensing in Estuarine Waters, Marine Science, Vol. 4 No. 1, 2014, pp. 1-9. doi: 10.5923/j.ms.20140401.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Coastal waters are under increasing pressures from developmental disturbances and subsequent impacts such as land erosion, urban runoff, habitat alternation, and increases of nutrient loading[1,2]. These anthropogenic activities could affect various biological and chemical processes that occur over multiple spatial and temporal scales. Consequently, there is a need for effective tools to monitor such biogeochemical processes at appropriate spatial and temporal scales for better management decisions. Remote sensing offers the most effective means for frequent, synoptic water quality measurements over large areas[3,4]. Over the last several decades, various empirical, semi-analytical, and analytical ocean color models have been developed to derive the water quality parameters of interest (e.g. concentrations of Chla, total suspended solids (TSS), and the absorption of colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM))[5-8]. Majority of these models have focused on the case 1 waters where water optical properties are determined primarily by phytoplankton and its related CDOM and detritus degradation products[9]. However, coastal and estuarine waters are optically deep and complex and the signal that a remote detector collects is a mixed signal influenced by various water optically active constituents from different sources[10]. For these case 2 waters, attempts to apply case 1 models resulted in poor predictive ability in retrieval of various optical proprieties [7,8]. Thus, the optical complexity of estuarine waters has limited the success of ocean color models in case 2 environments, creating a need for new algorithms applicable to coastal waters. The first step toward the development of such models is the better understanding of the coastal bio-optical properties. Water irradiance reflectance R(λ) is proportional to the backscattering coefficient bb(λ) and inversely proportional to the absorption coefficient a(λ) [11,12]. In turn, these water inherent optical properties (IOPs) are determined by optically active constituents such as Chla, CDOM, and TSS. Hence, a detailed understanding on how different bio-optical constituents regulate water reflectance R(λ) in case 2 waters is crucial for accurate estimates of water quality parameters from ocean color remote sensing. The mechanisms which control the ocean color variability (i.e. the spectral shape of R(λ)) and general applicable algorithms for the retrieval of such water constituents from case 2 waters still remain poorly known[13]. Over the past several decades, considerable effects have been devoted to this subject[10,14], and suggested that backscattering by suspended particles is the dominant driver of ocean color variability in coastal waters. However, most of these studies only covered a single study area with a relative short temporal scale, further study with larger geographic coverage over a longer temporal scale is needed to generalize the mechanisms which regulate R(λ) in estuarine waters.A series of hyperspectral remote sensing missions were conducted by NOAA supported Environmental Science Cooperative Science Center (ECSC) at 5 estuaries on the east and south coasts of US from 2002 to 2008. As an integrated part of this research activity, water irradiance reflectance R(λ) spectra, as well as the discrete water samples for optically active constituents measurements, were collected at 151 field stations. In this study, we examined the relationship between the water optically active constituents and the variability of water reflectance R(λ). The objectives for this study are first to characterize the general variability of the in situ water reflectance spectra R(λ) which represented a wide range of bio-optical properties due to the various biogeochemical and physical processes at different geographic regions. We then explored the mechanisms of how optically active constituents in coastal waters could influence the variability of reflectance spectra, and further provide some insights for hyperspectral remote sensing of water quality in optically complex coastal environments.
2. Methods
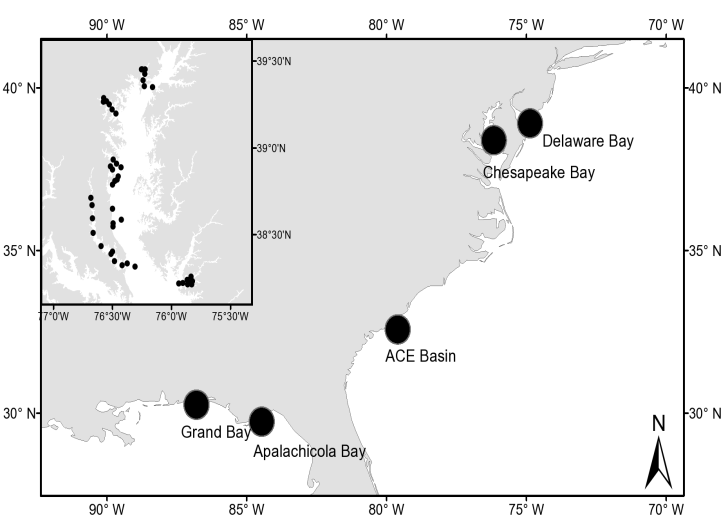
2.1. Description of the Study Area
- From October 2002 to July 2008, the NOAA supported ECSC has conducted a series of hyperspectral remote sensing missions at 5 estuaries on the east and south coasts of US (Fig. 1): Apalachicola Bay, Florida on October 2002; ACE Basin, South Carolina on June 2003; Grand Bay, Mississippi on October 2003; Delaware Bay on June 2004; and Maryland portion of Chesapeake Bay on the summer of 2005 to 2008. These five estuaries are different in size, geographic location, freshwater input, tidal range, as well as the land use within the watershed. These five sites provide a diverse set of optical variables (namely ranges in Chla, TSS, and CDOM) to adequately comprehend the variability of bio-optical properties in coastal waters. Fig. 1 shows the location of these 5 estuaries, as well as the field stations occupied during the Chesapeake Bay remote sensing mission from July 2005-2008. These stations were generally selected along longitudinal river and estuary transects to capture a salinity gradient from river to bay to offshore. The stations reflected the diversity of estuarine habitats, from the low salinity, high clay and CDOM concentration waters in the upriver to the mesohaline, low clay concentration waters at the open ocean area.
2.2. In Situ Optical Measurements
- The in situ optical measurements were made on board a research vessel within 3.5 h of solar noon. Hyperspectral (approximately 2000 bands with sampling interval of ~0.3 nm and a spectral resolution of ~1.5nm) water irradiance reflectance R(λ) was measured with a dual Ocean Optics USB2000 radiometer system from 350 to 1000 nm range. Light was brought to the radiometers by 200-micron diameter, shielded fiber optic cables. The first radiometer equipped with a cosine collector (yielding a hemispherical 180° field of view), and was pointed upward to measure downwelling incident irradiance (Ed). The second radiometer equipped with a 25° field-of-view simultaneously measured the upwelling radiance of water (Lw) from just below the water’s surface. The upwelling fiber was pointed 15-20° from nadir in the direction of 90° away from the sun to minimize sun glint and sky radiance. Each reflectance spectra was an average of 8-15 scans, and six separate spectra were collected. Therefore, a single, average spectrum may be an average of 50-80 scans. The water irradiance reflectance R(λ) was computed as: R(λ) = π*(Lw/ Ed). Furthermore, the reflectance R(λ) was calibrated by measuring the upwelling radiance of a white Spectralon reflectance panel (99% reflectance, Labsphere, Inc., North Sutton, NH), and a custom software package called “CALMIT Data Acquisition Program” or CDAP (University of Nebraska, Lincoln, NE) compared the signals from the two fibers and generated a normalized percentage of reflectance as R(λ)*100. A smoothing and integrating macro were used to resample the percentage of reflectance R(λ) at 1 nm intervals in the range of 400 to 800 nm for further analysis. The smoothing process did not affect the shape or magnitude of the spectral features of interest, but rather reduced the number of spectral bands.
2.3. Discrete Water Sampling
- At each field station, the following physical, chemical and biological parameters were measured: GPS Coordinates, secchi disk depth (m), salinity (psu), temperature C°, Chla and TSS concentration, and CDOM absorbance at 440 nm. The bulk water samples were collected near surface by bucket and transferred to 20L polyethylene container and placed in the shade. At the laboratory, samples were refrigerated and usually processed within 6 h of collection. All laboratory procedures are consistent with Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater[15]. Chla was extracted using 90% acetone and measured with a SpectronicGenesys II spectrophotometer (Spectronics, Inc.). Total suspended solids analysis was performed by filtering water samples on pre-weighed filters, which were then placed in a drying oven at 70°C for 24 hours and reweighed. Any weight gain was considered to be the TSS dry weight. The CDOM absorbance was measured using filtrate from the glass fiber filtration procedure for Chla and TSS analysis. The absorbance was measured in quartz cuvettes (10 cm path length) at 40 nm intervals between 320 nm and 580 nm using the Genysis II Spectrophotometer. CDOM absorbance at 440 nm is reported here.
2.4. Statistical Methods
- Principal component analysis (PCA) analysis is a common statistical method that can be used to determine the inherent dimensionality of the dataset and reduce the data redundancy. The principal components determined by PCA can be further related to the concurrently measured discrete water properties to explore how optically active water constituents affect the shape and variability of the observed water reflectance R(λ). In the analysis, reflectance values from 400-800 nm derived from Ocean Optics USB2000 were included. In order to simulate the airborne hyperspectral bandwidths, in situ water reflectance spectra R(λ) were further normalized to 10 nm interval by smoothing and integrating using a macro in Microsoft excel. So each spectrum in the PCA represented a vector, with 40 elements, which can be treated as an observation of a 40 dimensional stochastic variable at different wavelengths. The reflectance R(λ) dataset thus can be treated as n observations, where n (n = 151) is the number of the reflectance spectrum obtained from field stations. This data matrix was further normalized by subtracting the spectrum mean from each spectrum, which means the PCA was run on a covariance matrix.PCA gives uncorrelated variables as its result, e.g. the principal components are strictly orthogonal to one another, which can greatly complicate the interpretation of each component or mode. However, in the natural environments, measurements of variables are seldom uncorrelated, so the correlation analysis was also applied to the various optically active water constituents (Chla, CDOM, and TSS) to explore the relationships among each optical constituent.Furthermore, a Canonical Correspondence Analysis (CCA) was performed to explore the relationships between spectral reflectance information and water optical active constituents e.g. Chla, TSS and CDOM. CCA further combines the ordination and regression, and allows the two multivariate dataset (OACs and reflectance) to be directly related where ordination axes are constrained to be linear combinations of the original variables. In this study, the CCA was performed by a software package of XLSTAT (Addinsoft Inc.).
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Parameters
- The biogeochemical parameters exhibited a great spatial variability among the five estuarine systems in this study (Table 1). Since all measurements were carried out during summer and fall seasons, the water temperatures were relatively high, average water temperature ranged from 9.7ºC at Chesapeake Bay to 31.3ºC at Grand Bay. The salinity also has a large variability, with values ranging from 0 psu to more than 35 psu because of the diverse geographic setting of the study areas. The secchi depth also exhibited a similar large variability, ranged from the 10m at some oceanic stations in Grand Bay, MS to only 0.2 m at some upriver stations in ACE basin in South Carolina where were strongly influenced by the terrestrial input of sediments and CDOM.
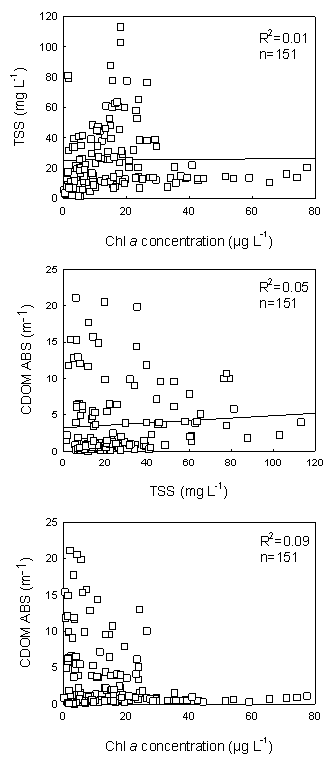 | Figure 2. The relationships of bio-optical properties (e. g. Chla concentration, TSS concentration, and CDOM absorbance) of 151 field stations |
3.2. Variability of in Situ Reflectance
- The measured spectral reflectance R(λ) was in the visible and near infrared (NIR) range from 350 to 1000 nm, however, the signal to noise ratio at the low and high ends of this spectral region was high, so only the spectral range of 400 to 800 nm was presented here. Corresponding to the wide ranges of optically active water constituents, the water reflectance R(λ) measured at the five estuaries on the east and south coasts of US also displayed a high degree of variation both in magnitude and shape over the visible and NIR spectral regions (Fig. 3A). This significant variability is the direct result of largely uncorrelated optically active water constituents with various concentrations. Even in the presence of large variability, there is a common spectral pattern as shown in Fig. 3B: Most of the spectra show a reflectance peak around 570 nm, suggesting a minimal absorption by phytoplankton pigments and an important role of backscattering by particulates. Another reflectance peak was observed at red/NIR spectral range around 695 nm, this peak could be the result of Chla absorption at 675 nm and the strong water absorption at wavelength longer than 700 nm. Also, as showed in Fig. 3B, the standard deviation of reflectance had similar pattern as the mean of reflectance, and it is wavelength dependent with a larger variance at the green spectral region. In contrast to most case 1 waters, the reflectance R(λ) at blue spectral region was lower in this study, and with a small variability compared to the green, red, and NIR spectral regions (Fig. 3B)[14] suggesting a strong absorption by CDOM, as well as phytoplankton pigment at this spectral region.
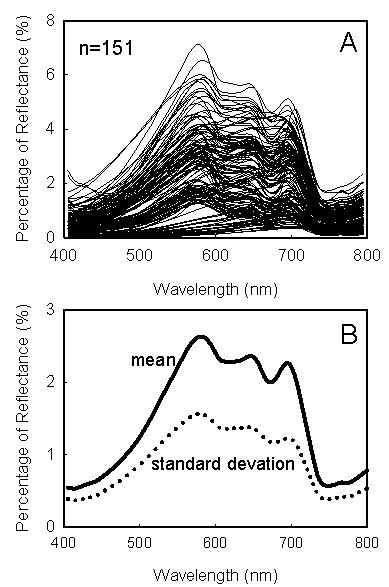 | Figure 3. (A) Water reflectance R(λ) spectra measured at 151 field stations from 5 estuarine systems on the east and south coasts of US. (B) The mean and standard deviation of the spectra |
3.3. Statistical Analysis
- A PCA analysis of the reflectance dataset yield three dominant principal components which represented more than 97% of the total variance of the in situ water irradiance reflectance R(λ) observed at five estuaries (Fig. 4). However, the first two principal components accounted for more than 93% of the total variance in the dataset, so only these two components are considered in the following discussion.
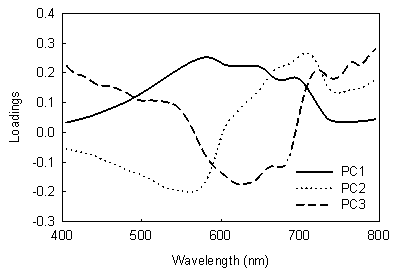 | Figure 4. The loading weights of the first three principal components resulting from Principal Component Analysis on the reflectance R(λ) dataset |
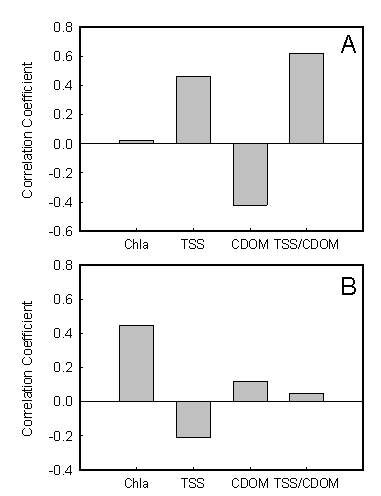 | Figure 5. Correlation coefficient calculated between the principal component loadings and the water bio-optical parameters for (A) PC1 and (B) PC2 |
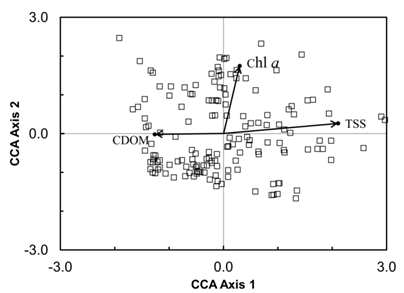 | Figure 6. Biplotresulting fromCanonical Correspondence Analysis on the reflectance R(λ) dataset. The influence of Chla, TSS and CDOM are indicated by the vectors on this biplot |
4. Discussion
- Development of ocean color models for retrieval of water constituents based on optical signatures measured by sensors aboard on satellite or aerial platforms is essential for remote sensing of the water quality over large spatial areas. Due to the widely variable and poorly correlated Chla, suspended solids and CDOM, such attempts in case 2 waters are often site-specific with poor predictive ability[16]. With the availability of hyperspectral data, which can provide higher spectral resolution for the specific features of water quality parameters, recent hyperspectral remote sensing holds the promise to accurately estimate water quality parameters[17]. However, a detailed analysis of the variability of such data in various case 2 waters is the first step toward the band selection and universally applicable algorithms development.R(λ) variability: The results of this study clearly demonstrate that estuaries of US have complex mixtures of biogeochemical materials and have high spatial and temporal variability in optically active constituents (Chla, TSS, and CDOM). Compared to few previous studies that have attempted to explore the ocean color variability[10, 14, 18], the dataset acquired in this study covered a much wider range of bio-optical properties. Such as, in a three-year study conducted by Toole and Siegel[14] within the Santa Barbara Channel, California, the range of Chla concentration were from 0.06 to 11.04 mg m-3 with a mean of 1.67 mg m-3, and the range of CDOM absorption was 0.08 to 0.169 m-1, respectively. However, the range of Chla concentration in this study was from 0.2 to 77.4 µg L-1, and the CDOM absorbance at 440 nm was from 0.1 to 21.1 m-1, all exhibited a much higher variability. This represents an excellent dataset to explore the optical variability in case 2 water.The variations in bio-optical constituents had a substantial influence on irradiance reflectance observed in this study. Reflectance R(λ) varied dramatically about a mean state across the all spectral regions, with the highest value at green spectral range (550-600 nm). There is also a similarity in shape between the mean and standard deviation of the reflectance (Figure. 3), indicating the variability in the dataset was closely related to the optical constituents that impact R(λ) at different spectral regions, and majority of the variance in R(λ) could be identified by portion of the visible/NIR spectrum that best describe the different optical constituents in the water column. The mean observed R(λ) is consistent with previous study performed by Lubac and Loisel[10], who found the reflectance maximal peak at 570 nm, and then decreased to 750 nm, suggesting an universal backscattering by suspended solids at this spectral region. However, mean R(λ) in our study also has a peak at NIR region, which can be contributed to stronger absorption by higher Chla concentrations (15.6 µg L-1 in this study vs. 8.3 µg L-1 in Lubac and Loisel[10]) at 675 nm. This NIR peak is also consistent with Flink et al.[19] who collected spectral data from two lakes in Sweden. In the short wavelength region (400 - 500 nm), the R(λ) were generally characterized by low values and relative smaller variability both in the current study and in the study of Lubac and Loisel[10]. However, this was controversial to Toole and Siegel[14] who observed a higher mean value and variability of reflectance R(λ) in the blue spectral region. This difference should be attributed to the overall much lower concentrations of bio-optical constituents, especially the low CDOM absorption in their studies (average of 0.05 m-1 at 443 nm). The optical properties in their study still exhibited some characteristics of case 1 water, which have high reflectance values in the blue region because of the lack of strong suppression of CDOM, as well as the absorption by Chla in blue spectral region. Principal components of R(λ) variability: Principal component analysis has been used to explain the variability in the complex dataset, such as the reflectance spectra collected in this study[10, 14, 18, 20]. The results of the PCA analysis in this study showed that more than 97% of the total variance of R(λ) can be explained by the first three principal components. This is also consistent with the few previous analysis conducted by Toole and Siegel[14] and Lubac and Loisel[10] who found that the first three PCs account for 94% and 93% of the total variance, respectively. In the study by Hunter et al.[20], total of 98.7% of the total spectral variance of the original dataset was also explained by the first two principal components.Furthermore, the general spectral shape of first principal component was similar to those previous studies. The loadings of PC1 across all wavelength were positive, with a peak at 550–600 nm green spectral range, suggested a universal backscattering associated with this component. This interpretation is further refined by a positive relationship between component scores and TSS concentrations at various field stations (Figure. 5). However, the difference between the current study and previous studies is that a negative correlation was also observed between PC1 and CDOM absorbance, which suggested that CDOM absorption also plays an important role in regulating this component and the overall variance of R(λ). The role of CDOM in the regulation of ocean color variability is largely neglected in the studies of Toole and Siegel[14] and Lubac and Loisel[10]. This might be contributed to the much lower CDOM absorbance in their studies, which were on the average 0.05 m-1 and 0.15 m-1, respectively. In our study, the average CDOM absorption was 3.7 m-1 at 440 nm, which was an order of magnitude higher than those observed in previous studies. This further resulted in the low reflectance and variance at the blue spectral range of this study, indicating the strong effects of CDOM in this spectral range. As the result, most of the CDOM retrieval band algorithms has selected the bands in this spectral region, However, the predictive ability was highly affected by the concentration of CDOM, as well the interference from Chla absorption[9,22]. The spectral shape of the second principal component was inversely related to PC1 below 600 nm, suggesting this principal component was governed by a different process. In contrast to the previous researches[10,14], where a reflectance peak was observed near 570 nm for PC2, a trough (minimal value) was observed in this study. The trough at 570 nm in the spectral shape of PC2 observed in this study can be explained by the minimal Chla absorption at the green region, suggesting that PC2 could be associated to phytoplankton pigment absorption. The correlation analysis of component score and Chla concentration further confirms this association.A scatter biplot (Figure. 6) of the first two axes of CCA further demonstrates the influences of optical active constituents on water reflectance R(λ). In this biplot, the field stations with different bio-optical properties are clearly separated based on their weighted mean spectral response scores, and the distribution of the sample points within the biplot reveals patterns of the association between reflectance R(λ) and their bio-optical properties[22,23]. The first spectral axis, which accounts for 72% of the total variance of R(λ), were regulated by both the backscattering of TSS and absorption of CDOM. The field station with high reflectance features, such as high TSS concentration, has a more positive position on this axis, while stations with high CDOM absorption will have a more negative value on this axis. Therefore, this spectral axis could be described as the brightness (reflectance) axis. On the other hand, Chla has significant correlation with second spectral axis. The stations with high concentration of Chla tend to have a positive value on this axis, and low Chla station tends to have a negative value. A study[21] on a mesocosm experiment also showed the similar pattern: as the Chla concentration increased in their experiments, the spectral response score on second axis also increased. Moreover, the influence of Chla is nearly perpendicular to the TSS-CDOM gradient on the biplot. This indicates that Chla and TSS/CDOM to be spectrally independent variables and a simple way to describe the variability of water reflectance is through the scattering gradient of TSS/CDOM and absorption gradients of Chla. Implication for hyperspectral remote sensing: Results observed here could be further applied to the data acquired by hyperspectral remote sensing sensors, such as the Airborne Imaging Spectrometer Applications (ASIA). Hyperspectral remote sensing inevitably has a large amount of redundant data[24]. This study suggests that hyperspectral imagery could be reduced from a large amount of wavelength channels to two or three axes on the spectral space by ordination techniques. These limited numbers of spectral axes can further be associated to the optically active constituents that regulate the variability residing in the hyperspectral data. As indicated by Figure. 6, the first spectral axis is can be an indicator of the relative amount of TSS and CDOM based on their scores on this axis. Similarly, the second spectral axis was closely related to the absorption by phytoplankton Chla, and the score on this axis could serve as an indicator of phytoplankton biomass.This study also provides the insight for bands selection in the algorithms development for case 2 waters. The loadings for each principal component are different across the spectral range, so the wavelength regions most sensitive to explain the reflectance variance can be identified. This component can further be related to certain or a combination of water bio-optical constituents. Thus, the band selection or model development should focus on these wavelength regions for retrieval of such optical constituents. For example, in this study, the second spectral component is most sensitive at red and NIR (670-750 nm), and is associated with Chla absorption process. Thus, the algorithm for Chla retrieval should focus on this spectral range. A simple forward stepwise multiple linear regression model (SPSS, IBM Inc.) was performed on the all wavelength channels in this spectral region for Chla estimation. This stepwise regression model reached to best prediction by using only three spectral channels at 675 nm, 695 nm and 735 nm, and explained about 77% of the total variance of Chla concentrations in our dataset (Figure. 7). The results of current study is consistent with the previous studies[7,16], and suggest that Chla retrieval in case 2 water should be focused more on the red and NIR region. Such as in a study[12] who used a 3 component model that confirmed the importance of red/NIR spectral region in Chla prediction in estuarine waters. However, since the TSS and CDOM both associate with the first spectral axis, and their influences are in the opposed direction, the simple band arithmetic algorithm is not applicable to retrieve such bio-optical constituents in our dataset. Nevertheless, considering dataset presented here covers a large geographic area with large variability, it is not surprising for having the poor predictive ability for TSS and CDOM by using simple bands arithmetic algorithm.
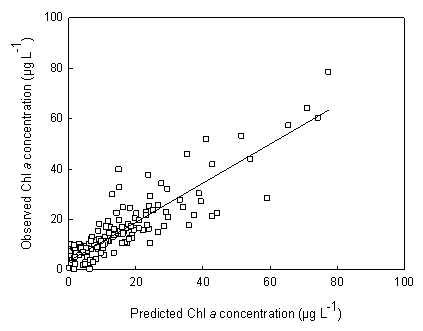 | Figure 7. The correlation between measured Chla concentration and predicted Chla concentration based on stepwise multiple linear regression by using three spectral bands (675 nm, 695 nm, and 735 nm) at the red/NIR spectral region |
5. Conclusions
- Overall, this study presents an extensive and unique dataset of water reflectance R(λ) spectra with the large spatial and temporal scales that was not found in the previous studies. It further explored the ocean color variability and the mechanisms that regulate such variability by water bio-optical constituents. Our results suggest that TSS and CDOM will mainly influence the backscattering of water, especially at the blue and green spectral regions. The variability of water reflectance R(λ) at the red/NIR regions are mainly influenced by the phytoplankton biomass (e.g. Chla concentration). These general features of water reflectance observed from in situ measurements could further provide insights regarding wavelength bands selection likely to be used for retrieval models to predict the water quality parameters. However, Future study of the direct measurements of in situ inherent optical properties (IOPs), such as backscattering and absorption coefficients over different estuarine systems are needed for further development of algorithms for water quality retrievals, especially for TSS and CDOM by remote sensing in estuarine waters.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- We appreciate the field help from Morgan State University Estuarine Research Center, and the early comments and discussions on this work. This work was partly supported by NOAA ECSC program, the NSF GEO0914546 to Morgan State University, and the NSF award 1036586 to university of Maryland Eastern Shore.
References
| [1] | Glibert, P.M.; Magnien, R.; Lomas, M.W.; Alexander, J.; Fan, C.L.; Haramoto, E.; Trice, M.; Kana, T.M. Harmful algal blooms in the Chesapeake and coastal Bays of Maryland, USA: Comparison of 1997, 1998, and 1999 events. Estuaries 2001 24, 875-883. |
| [2] | Anderson, D.M.; Glibert, P.M.; Burkholder, J.M. (2002) Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: Nutrient sources, composition, and consequences. Estuaries 2002 25, 562-584. |
| [3] | Platt, T.S.; Sathyendranath, S.; Caverhill, C.M.; Lewis, M.R. Ocean primary production and available light: further algorithms for remote sensing. Deep Sea Res 1988 35, 855-879 . |
| [4] | Muller-Karger, F.E.; Walsh, J.; Evans, R.H.; Meyers, M.B. On the seasonal phytoplankton concentration and sea surface temperature cycles of the gulf of Mexico as determined by satellites. J Geophys Res 1991 96, 12645-12665. |
| [5] | Ritchie, J.C.; Cooper, C.M. An algorithm for estimation surface suspended sediment concentration with Landsat MSS digital data. Water Resour Bull 1991 27, 373–379. |
| [6] | Sathyendranath, S.; Platt, T.; Trwin, B.; Horne, E. A multispectral remote sensing study of coastal waters off Vancouver Island. Int J Remote Sens 2004 25, 893-919. |
| [7] | Schalles, J.F. (2006) Optical remote sensing techniques to estimate phytoplankton chlorophyll a concentrations in coastal water with varying suspended matter and CDOM concentrations. In Remote sensing of aquatic coastal ecosystem processes: Science and management applications, Richardson, L.; Ledrew, E. eds; Springer, 2006; pp. 27-79. |
| [8] | Odermatt, D.; Gitelson, A.; Brando, V.; Schaepman, M. Review of constituent retrieval in optically deep and complex waters from satellite imagery. Remote Sens of Environ 2012 118,111-126. |
| [9] | Matthews, M.W. A current review of empirical procedures of remote sensing in inland and near-coastal transitional waters. Int J Remote Sens 2011 32, 6855-6899. |
| [10] | Lubac, B.; Loisel, H. Variability and Classification of remote sensing reflectance spectra in the eastern English Channel and southern North Sea. Remote Sens Environ 2007 110, 45-58. |
| [11] | Morel, A.; Prieur, L. Analysis of variations in ocean color. Limnol and Oceanogr 1977 22, 709-722. |
| [12] | Gitelson, A.A.; Schalles, J.F.; Hladik, C.M. Remote chlorophyll-a retrieval in turbid, productive estuaries: Chesapeake Bay case study. Remote Sens of Enviro 2007 109, 464-472. |
| [13] | IOCCG. Partition of the ocean into ecological province: Role of Ocean-Color Radiometry. In Reports of the international Ocean Color Coordinating Group, Lee, Z.P. eds; IOCCG 2009, 122 p. |
| [14] | Toole, D.A.; Siegel, D.A. Modes and mechanisms of ocean color variability in the Santa Barbara Channel. J of Geophys Res 2001 106, 26985-27000. |
| [15] | Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 17th edition, American Public Health Association, Washington D.C., 1989; 1527 p. |
| [16] | Dall’Olmo, G.; Gitelson, A.A.; Rundquist, D.C.; Leavitt, B.; Barrow, T.; Holz, J.C. Assessing the potential of SeaWiFS and MODIS for estimating chlorophyll concentration in turbid productive waters using red and near-infrared bands. Remote Sens of Environ 2005 96,176-187. |
| [17] | Chang, G.C.; Dickey, T.; Lewis, M. Toward a global ocean system for measurements of optical properties using remote sensing and in situ observations. In Remote Sensing of the Marine Environment: Manual of Remote Sensing, Gower, J. eds; Springer, 2006; pp. 285-326. |
| [18] | Sathyendranath, S.; Prieur, L.; Morel, A. A three-component model of ocean color and its application to remote sensing of phytoplankton pigments in coastal waters. Int J Remote Sens 1989 10, 1373-1394. |
| [19] | Flink, P.;Lindell, T.; Ostlund, C. Statistical analysis of hyperspectral data from two Swedish lakes. Sci of the total Environ 2001 268,155-169. |
| [20] | Mueller, J.L. Ocean color spectra measured off the Oregon coast: Characteristic vectors. Applied Optics 1976 15, 394-402. |
| [21] | Hunter, P.D.; Tyler, A.N.; Présing, M.; Kovács, A.W.; Preston, T. Spectral discrimination of phytoplankton color groups: The effect of suspended particulate matter and sensor spectral resolution. Remote Sens Environ 2008 112, 1527-1544. |
| [22] | Ma, R., Ma,X., Dai, J. Hyperspectral feature analysis of chlorophyll a and suspended solids using field measurements from Taihu Lake, eastern China. Hydro Sci. 2007 52, 808-824. |
| [23] | Yue,Y.M.; Wang, K.L.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Z.C.; Jiao, Q.J.; Liu, B.; Chen, H.S. Exploring the relationship between vegetation spectra and eco-geo-environmental conditions in karst region, Southwest China. Environ Monit Assess 2010 160,157-168. |
| [24] | Lee, Z.P.; Carder, K. Hyperspectral Remote Sensing. In Remote Sensing of Coastal Aquatic Environments, Miller et al. eds, Springer, 2005; pp. 181-204. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML