-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Marine Science
p-ISSN: 2163-2421 e-ISSN: 2163-243X
2012; 2(5): 39-47
doi: 10.5923/j.ms.20120205.01
Biodiversity of Sessile Fauna on Rocky Shores of Coastal Islands in Santa Catarina, Southern Brazil
Janayna L. Bouzon 1, Frederico P. Brandini 2, Rosana M. Rocha 1
1Department of Zoology, Federal University of Paraná, Curitiba, 81531-980, Brazil
2Oceanographic Institute, University of São Paulo, Butantã, 05508-120, Brazil
Correspondence to: Janayna L. Bouzon , Department of Zoology, Federal University of Paraná, Curitiba, 81531-980, Brazil.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The epilithic sessile fauna of coastal islands off Santa Catarina, southern Brazil, was analyzed along two 30 m long sublitoral transects. A total of 111 taxa were identified of which 55 are new records for the South Atlantic epilithic assemblages. Exotic sponges, bryozoans and ascidians (Paraleucilla magna, Schizoporella errata, Bugula dentata, Styela plicata respectively) were found at Marine Protected Areas. This paper gives further knowledge on the marine sessile fauna of the coastal islands of southern Brazil for environmental monitoring programs. A more complete list of epilithic species will certainly provide a baseline to detect future environmental changes and local anthropogenic impacts on the biodiversity of southern Brazilian ecosystems.
Keywords: Epilithic Fauna, New Records, Brazilian Islands
1. Introduction
- The rocky shores off Santa Catarina, southern Brazil, extends for 562 Km bordering the coastline of the mainland and 130 islands scattered from the Babitonga Bay until the southernmost limits of the main Santa Catarina Island[1]. The epilithic community of the sublitoral zones is rich and diverse, mostly dominated by sessile groups[2]. The Marine Biological Reserve of Arvoredo (REBIOMAR), the only Brazilian full marine protected area (MPA) in southern Brazil, occupies a polygon of 17,600 ha to protect sublitoral rocky environments of some islands and few submerged reefs, all fringed with a broad band of subtidal hard bottom communities. This MPA was set up in 1990 to ensure recruitment and recolonization ofadjacent areas which are permanently threaten by all kinds of anthropogenic impacts associated with the economic development along Santa Catarina coastal zone[3]. However, the proximity of the islands with the mainland threatens the biodiversity of their rocky habitats subject to the contamination of urban and industrial development in the last decades.Due to the co-occurrence of a wide variety of organisms and their trophic interactions, including symbiosis, the sessile benthic communities formed a specific rocky ecosystem with great heterogeneity of micro-habitats and, therefore, high biological richness[4,5].The knowledge of the benthic invertebrate fauna in Brazil remains weak and the number of recorded species is muchlower than the world records, reflecting insufficient studies[3]. Studies on the biodiversity of sessile benthic invertebrates in Santa Catarina reports 32 species of Porifera[6-16], 14 Anthoathecata and Leptothecata hydrozoans[17-19], four octocorals[20,21], 34 ascidians[22]. In addition, 14 scleractinians anthozoans recorded at the outer continental shelf[23,24]. From a total of 346 species of bryozoans reported in Brazil, 40 from the Paraná coast, nearby our study site that were, however, never identified for in the epilithic assemblage of Santa Catarina[25].An important factor to consider is presence and abundance of species considered invasive due to the fact that these organisms interfere in the survivability of other community species[26], plus the ability to generate economic and environmental damage, and in some cases to human health. Invasive organisms can cause marked changes in communities by altering the evolutionary pathway of native species by competitive exclusion site, niche displacement, hybridization, introgression, predation, and possibly extinction[27,28]. Together the introduction of exotic species, degradation and / or transformation of habitat, overexploitation of organisms for consumption or ornaments, are the biggest threats to marine and coastal biodiversity.Worldwide, the rate of degradation of natural coastal habitats has been faster than conservation initiatives. In Brazil the actual legal framework that supports conservation policies along the coast is poorly supported by ecological data[3]. This study aims to contribute for a better knowledge of the marine biodiversity in the State of Santa Catarina, with emphasis on cnidarians and bryozoans, in order to provide technical support for marine conservation in southern Brazil.
2. Study Area
- The region is in a transitional belt of latitudes between tropical and temperate regions, on the western boundary of the South Atlantic basin. Oceanographic conditions off southern Brazilian coast are strongly affected by the seasonal north-south displacement of the Subtropical Convergence. Onshore bottom intrusions of the oceanic South Atlantic Central Water (ACAS) along the Santa Catarina continental shelf in summer are due to north winds-induced Ekman transport of surface waters offshore, decreasing water temperatures at the bottom. In winter, winds are predominantly from south. They transport subantarctic waters of lower salinities, strongly affected by the outflow of the La Plata River. The hydrographic environment is therefore very dynamic during the annual cycle[29,30]. This affects the composition and the seasonal dynamics of regional epilithic assemblages[31,3]. The hard bottom of the islands is relatively shallow but physically heterogeneous, consisting of rounded rocks arranged in a delicate slope toward the sandy bottom. Large rocks form caves and walls up to about 15 m deep. The sublitoral cliffs at REBIOMAR, may extend beyond 30 m depth.
3. Fieldwork
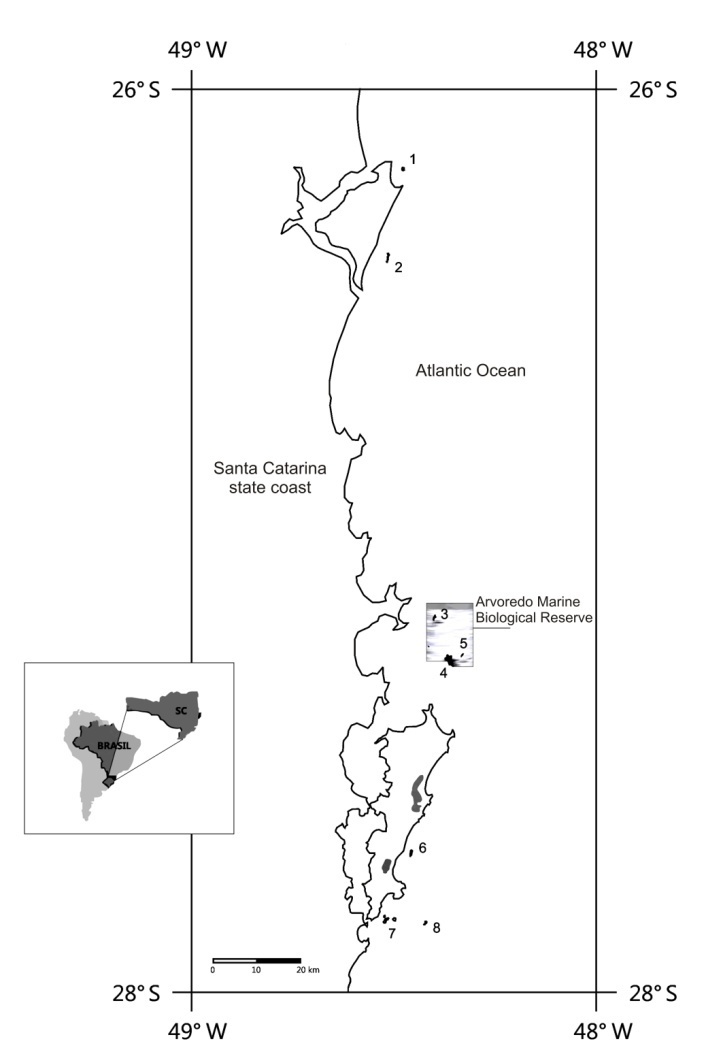 | Figure 1. Map of the study area showing the coastal islands where benthic community was sampled. 1. Graças Archipelago; 2.Tamboretes Archipelago; 3.Galés Island; 4.Arvoredo Island; 5.Deserta Island; 6.Campeche Island; 7.Três Irmãs Islands; 8. Moleques do Sul Archipelago |
4. Results
- We have recorded 111 taxa belonging to the phyla Porifera, Cnidaria, Bryozoa, Entoprocta and Chordata (subphylum Tunicata, class Ascidiacea), distributed in 54 families, of which 27 taxa could not be identified at the specific level. The most representative groups were the Cnidaria with 38 hydrozoans and 11 anthozoans, followed by ascidians with 32 taxa, 18 sponges, 11 Bryozoa species and Entoprocta with only one not identified species (Table 2). Representatives of dominant sessile groups indentified during the sampling surveys can be seen in the photographic panels of Figures 2a (sponges), 2b (cnidarians) and 2c (ascidians and bryozoans).
 | Figure 2a. Taxa of sponges of the Santa Catarina coastal islands.Porifera: (A) Guitarra sepia, (B) Dragmacidon reticulatum, (C) Suberites aurantiacus, (D) Polymastia janeirensis, (E) Tedania ignis, (F) Clionacelata |
 | Figure 2b. Taxa of cnidariansof the Santa Catarina coastal islands.(A) Eudendrium carneum, (B) Parazoanthus sp., (C) Palythoa caribeorum (D) Carijoa riisei, , (E) Corynactis sp., (F) Astrangia rathbuni |
 | Figure 2c. Taxa of ascidians and bryozoans of the Santa Catarina coastal islands.Ascidiacea: (A) Didemnum granulatum, (B) Lissoclinum perforatum, (C) Diplosoma listerianum, (D) Distaplia bermudensis, (E) Euherdmania vitrea; Bryozoa: (F) Schyzoporella errata |
|
|
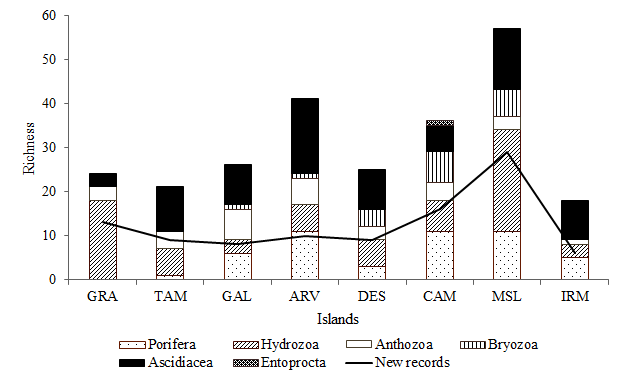 | Figure 3. Species richness and new records of sessile benthic organisms to Santa Catarina state (GRA, Graças; TAM, Tamboretes; GAL, Galés; ARV, Arvoredo; DES, Deserta; CAM, Campeche ; MSL, Moleques do Sul; IRM, Irmãs). Note. There wasn’t collection effort of the Phyllum Porifera in the GRA and TAM islands |
5. Discussion
- Biodiversity inventory is the first step for understanding ecological processes at coastal or even at broader oceanic scales. The remarkable number of new records of benthic fauna in Santa Catarina islands reveals the lack of taxonomic studies to better access the state of the marine conservation in the southern Brazilian coast. So far we have been unable to identify endangered species, due to the scarcity of data that might indicate even natural fluctuations of sessile invertebrate populations threatened by many anthropogenic impacts such as sedimentation associated with habitat losses at the coast, pollution and overfishing[38,39]. In general, a reef environment exposed to excessive loads of pollutants, responds to changes and often simplify the structure of biological communities[40]. Unfortunately, little is known on the effect of overfishing on the biodiversity in Brazilian subtidal reefs and rocky shores[41,42].Among the new records for the South Atlantic the sea squirt Didemnum cf. calliginosum, originally described by[43] on the Caribbean island of Guadeloupe, had its distributional range extended to the State of Santa Catarina, more exactly on the Campeche I. The ascidian community in Brazil is typically tropical with little overlap with the Argentina and Patagonia fauna[44]. The presence of these species in Santa Catarina state subtropical waters is probably due to the multiple introductions of the species in the southern coasts[45,46] where major harbor facilities are located. The lack of historical records prevents us from defining the status of many species that remain cryptogenic, but we believe the development of molecular studies of global scope will reveal invasion of exotic species in the western Atlantic, some of them already recorded in Brazilian waters. According to[47] there are forty species of exotic zoobenthos along the Brazilian coast, twelve of which are sessile animals. In the coastal islands off Santa Catarina four species of his list of exotic zoobenthos were identified. For instance, the invasive sea squirt Styela plicatawas first recorded to Brazil at Rio de Janeiro[47]. The type specimen was from Philadephia and some authors consider S. plicata as widely distributed species along the warmer coast of Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Ocean and also Mediterranean Sea[48]. Here it was found within the MPA of Arvoredo and Galés Is. Dense aggregates of this species are formed at the sublitoral of Santa Catarina Is. where each individual takes an elongated shape with a stalk of attachment. In southern Brazil, it is rarely found in the natural environment, preferring strings of mariculture grounds and floating artificial substrates of harbour facilities[49]. Yet, it was first recorded in a natural rocky shore of Santa Catarina.The calcareous sponge Paraleucilla magna[50]has an undefined status about native or exotic specie status. P. magna has been found along the Brazilian coast and it was found in the Moleques do Sul and Aranhas archipelagos, in the northern coast of the Santa Catarina island (Bouzon, personal observation). She is a cryptogenic specie (Cavalcanti, personal communication), i.e., cause we cannot say whether it is native or exotic specie. It has a full life cycle in nature and evidence of population increase over time, but without apparent environmental or socioeconomic impact. The exotic bryozoan Schizoporella errata(Figure 2c) while Bugula dentata were commonly found in the islands. The first is an established species and B. dentata is present in the natural environment but without further increase in abundance and distribution[46]. However, since we found it in reasonable abundance in the islands of Santa Catarina as well as in the coast off Cabo Frio, Rio de Janeiro the status of this exotic species in Brazil should be reviewed because we considered it considered already established.Distributional limits of the northern Brazilian tropical sessile fauna were extended southwards in our records. Subtropical provinces of the southeastern and southern Brazil have been regarded as a transitional zone for the temperate fauna of the western Atlantic[51]. However, the study area belongs to the Paulista Province[52] where ca 40% of the records which are also found along other sections of the Brazilian coast were endemic to it. This province extends from the Espírito Santo to Rio Grande do Sul (~ from 22° to 32° S) and is characterized by high incidence of endemic species, and can expect a small difference in species composition across the province, with the predominance of tropical species to the north and temperate species to the south. Nevertheless, besides low temperatures in southern Brazil during winter time, the lacking of rocky shores further south from Santa Catarina represents an additional barrier for the dispersal of epilithic organisms.The taxonomic analyses of the sessile fauna here described for the southernmost islands off Florianópolis have demonstrated they are equally or even more diverse than the assemblages of the islands of the Arvoredo MPA in the northern coast of Santa Catarina. Hence it should also be protected. This study has improved substantially the knowledge on the marine biodiversity in the coastal zone of Santa Catarina state. We hope it will contribute for the development of a more technically oriented conservation policy for the coastal ecosystems of southern Brazil.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- We would like to thank the contributors MSc. João Luís Carraro and Dra. Beatriz Mothes of the Porifera Marine Laboratory of the Natural Sciences Museum of the Zoobotanic Foundation of Rio Grande do Sul to identification of the sponges, Dra. Maria Angélica Haddad and students Ana Caroline Cabral, Halina L. Heyse and Júlia Beneti of the Biology Laboratoryof the Hydrozoans and Bryozoans of the Universidade Federal do Paraná (UFPR) to identification of the cnidarians and bryozoans, and the MSc. Thais Miranda and Dr. Antônio Carlos Marques of Medusozoa Laboratoryof the Universidade do Estado de São Paulo to the identification and confirmation of hydrozoans species. We also thank Laura P. Kremer and Rafael Metri for their help in field work. Field trips were funded by CNPq (grant number 475367/2006-5 to S.R. Floeter; 474566/2007-2 to R. M. Rocha). CNPq also awarded PhD scholarship to J.L. Bouzon (141398/2007-8).
References
| [1] | Gaplan,1986, Atlas de Santa Catarina. Rio de Janeiro. Aerofoto Cruzeiro. |
| [2] | Mazzer, A. M., 2002, Aspectos da geografia física das ilhas costeiras catarinenses. Florianópolis. Anais do Simpósio: Ilhas Costeiras e Ilhas Oceânicas. |
| [3] | Amaral, A. C. Z., and Jablonski, S., 2005,Conservação da biodiversidade marinha e costeira no Brasil. Megadiversidade 1, 43–51. |
| [4] | Ribeiro, S. M, Omena, E. P., and Muricy, G., 2003, Macrofauna associated to Mycale microsigmatosa (Porifera, Demospongiae) in Rio de Janeiro State, SE Brazil. EstCoastShelfSci. 57, 951–959. |
| [5] | Henkel, T.P., and Pawlick, J.R., 2005, Habitat use by sponge-dwelling brittlestars. Mar Biol 146, 301–313. |
| [6] | Volkmer-Ribeiro, C.,andMothes-de-Moraes, B., 1975,Esponjas tetraxonidas do litoral sul-brasileiro. I - Redescrição de Cydoniumglariosus Sollas, 1886 e Erylusformosus Sollas, 1886. Iheringia 47, 3–22. |
| [7] | Mothes-de-Moraes, B., 1985,Primeiro registro de Myriastra purpurea (Ridley, 1884) para a costa brasileira (Porifera, Demospongiae).Rev. Bras. Zool. 2, 321–326. |
| [8] | Mothes, B., and Lerner, C.B., 1994, Esponjas marinhas do infralitoral de Bombinhas (Santa Catarina, Brasil) com descrição de três espécies novas (Porifera: Calcarea e Demospongiae). Biociências 2, 47–62. |
| [9] | Lerner, C. B., 1996, Esponjas da Ilha da Galé, Reserva Marinha Biológica da Ilha do Arvoredo, Santa Catarina, Brasil (Porifera; Desmospongiae). Biociências 4, 101–129. |
| [10] | Lerner, C. B. and Hajdu, E., 2002,Two new Mycale (Naviculina)(Mycalidae, Poecilosclerida, Demospongiae) from the Paulista Biogeographic Province (SW Atlantic). Rev. Bras. Zool. 19, 109–122. |
| [11] | Carvalho, M.A., Carraro, J.L., Lerner, C.B. and Hajdu, E., 2003,First Record of Ciocalypta (Demospongiae: Halichondrida) from Brazil, Southwestern Atlantic,with description of a new valid species. Zootaxa 302, 1–8. |
| [12] | Lerner, C. B., Hajdu, E., Custódio, M. and Soest, R. Van., 2004,Guitarra sepia n.sp. from the southwestern Atlantic (Demospongiae, Poecilosclerida, Guitarridae). First record of a Guitarra without placochelae. Bollettino dei Musei e degli Istituti biologici dell’ Universitá di Genova. Genova 68, 405–411. |
| [13] | Lerner, C. B., Mothes, B., and Carraro, J.L., 2005, Novos registros e ampliação de limites meridionais de distribuição de poríferos (Porifera, Demospongiae) no Atlântico sudoeste. Ver. Bras. Zool. 22, 596–612. |
| [14] | Lerner, C.B., Carraro, J. L., and Soest, R. V., 2006,Raspailia (Raspaxilla) bouryesnaultae, a new name for Brazilian Raspaxilla elegans Boury-Esnault, 1973 (Demospongiae, Poecilosclerida, Raspailiidae) with a redescription and a new record. Zootaxa 1129, 37–45. |
| [15] | Mothes, B., Kasper, G. L., Lerner, C. B., Campos, M., and Carraro, J.L., 2006,Spongia (Heterofibria) catarinensis sp. nov. (Porifera, Spongiidae) no litoral de Santa Catarina, Brasil. Iheringia 96, 335–338. |
| [16] | Mothes, B., Campos, M. A., Eckert, R. A. and Lerner, C. B., 2008, Latrunculia (Latrunculia) verticillata sp. nov. (Porifera, Poecilosclerida, Latruncullidae) fron the bathyal region off the coast of Santa Catarina State, Brazil, Southwestern Atlantic. Zootaxa 1744, 59–65. |
| [17] | Migotto, A.E., 1996, Benthic Shallow - water hydroids (Cnidaria, Hydrozoa) of coast São Sebastião, Brazil, including a checklist of Brazilian hydroids. Zool. Verhandelingen 306, 1-125. |
| [18] | Migotto A.E., Marques A.C., Morandini, A.C. and da Silveira, F.L., 2002, Checklist of the Cnidaria Medusozoa of Brazil, Biota Neotrop. 2, 1–31. |
| [19] | Marques, A.C., Morandini, A.C., and Migotto, A.E.,2003,Synopsis of knowledge on Cnidaria Medusozoa from Brazil. Biota Neotrop. 3, 1–18. |
| [20] | Castro, C.B., Echeverría, C.A., Pires, D.O., and Fonseca, C.G., 1999, Distribuição do bentos (Cnidaria e Echinodermata) em costões rochosos da Baía de Ilha Grande, Rio de Janeiro, Brasil. In Silva SHG & Lavrado HP (Eds). Ecologia dos Ambientes Costeiros do Estado do Rio de Janeiro. Série Oecol. Bras. VII, Rio de Janeiro, Brasil. |
| [21] | Castro, C.B., Medeiros, M.S. and Loiola, L.L., 2010,Octocorallia (Cnidaria: Anthozoa) from Brazilian reefs. Jour. Nat. Hist. 44, 763–827. |
| [22] | Rocha, R. M., Moreno, T. R.,and Metri, R., 2005, Ascídias da Reserva Biológica Marinha do Arvoredo, SC. Rev. Bras. Zool.22, 461–476. |
| [23] | Laborel, J., 1969, Madreporaires et hydrocoralliaires récifaux des côtes Brasiliennes. Systématic, écologie, répartition verticale et geographique. Annales de l'Institut Oceanographique Paris 47, 171–229 |
| [24] | Kitahara, M.V., 2006,Novas ocorrências de corais azooxantelados (Anthozoa, Scleractinia) na plataforma e talude continental do sul do Brasil (25-34ºS).Biotemas 19, 55–63. |
| [25] | Vieira, L.M., Migotto, A.E., and Winston, J.E., 2008, Synopsis and annotated checklist of recent marine Bryozoa from Brazil. Zootaxa1810, 1–39. |
| [26] | Elliott, M., 2003, Biological pollutants and biological pollution an increasing cause of concern. Mar. Poll. Bull. 46, 275–280. |
| [27] | Mooney, H.A., and Cleland, E.E., 2001,The evolutionary impact of invasive species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 98, 5446–5451. |
| [28] | Lotze, H.K., Lenihan, H.S., Bourque, B.J., Bradbury, R.H., Cooke, R.G., Kay, M.C.,Susan, M. Kidwell, S.M., Kirby, M.X., Peterson, C.H. and Jackson, J.B.C., 2006,Depletion, degradation, andrecovery potential of estuariesand coastal seas. Science 312, 1806–1809. |
| [29] | Castro, B.M., and Miranda, L.B., 1998, Physical oceanography of the western Atlantic continental shelf located between 48N and 348S. In Robinson A.R. and Brink K.H. (eds) The sea. New York: John Wiley and Sons, pp. 209–251. |
| [30] | Seeliger, U., Odebrecht, C. and Castello, J.P.,1997, Subtropical convergence environments: the coast and sea in the southwestern Atlantic. Berlin: Springer. |
| [31] | Borzone, C. A., Pezzuto, P. R., and Marone, E., 1999, Oceanographic Characteristics of a Multi-Specific Fishing Ground of the Central South Brazil Bight. Mar. Ecol. 20, 131–146. |
| [32] | Sars, G.O., 1874, Bidrag til Kundskaben om Norges Hydroider. Forhandlinger i Videnskabsselskabet i Kristianina. 91-150, pls 2–6. |
| [33] | Gmelin, J.F., 1791, C. Linnaeus, Systemae naturae. Thirteenth edition, edited by J.F. Gmelin. Vol. 1, part 6 (Vermes): 30213910. Lipsiae, G. E. Beer. |
| [34] | Linnaeus, C., 1758, Systema naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. Editio decima, reformata: 1–823. Holmiae (Stockholm), L. Salvii. |
| [35] | Bale, W.M., 1888. On some new and rare Hydroida in the Australian Museum collections. Proc. Linn. Soc. N.S.W. (2)3(2): 745-799, pis 12–21. |
| [36] | Monniot, C., and Monniot, F., 1984, Ascidies littorals de Guadeloupe. 7. Espèces nouvelles et complementaries a l’inventaire. Bull. Mus. Nat. Hist. Nat.Ser. 4, A, 6(3):567-582. |
| [37] | Vervoort, W., 1967,Report on a collection of hydroida from the caribbean region, including an annotated checklist of caribbean hydroids. Zool. Verhandelingen 92, 1–122. |
| [38] | Maughan, B. C.,2001,The effects of sedimentation and light on recruitment and development of a temperate, subtidal, epifaunal community. Jour. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 256, 59–71. |
| [39] | Maldonado, M., Giraud K., and Carmona, C.,2008,Efects of sediment on the survival of asexually produced sponge recruits. Mar. Biol.154, 631–641. |
| [40] | Lobban, C.H., and Harrison, P.J.,1994, Seaweed ecology and physiology. Cambridge University press. United Kingdom. |
| [41] | Floeter, S. R., Halpern, B. S. and Ferreira, C. E. L.,2006,Effects of fishing and protection on Brazilian reef fishes. Biol. Cons. 128: 391–402. |
| [42] | Ferreira, B. P., and Maida, M. ,2006, Monitoramento dos Recifes de Corais do Brasil, situação atual e perspectivas. Ministério do Meio Ambiente 120 pp. |
| [43] | Rodrigues, S.A., Lotufo, T. and Rocha, R.M., 1999, Classe Ascidiacea. In: Migotto, A.E. and Tiago, C.G. (Eds.), Biodiversidade do Estado de São Paulo, Brasil. Síntese do conhecimento ao final do século XX: 3 - Invertebrados marinhos.FAPESP, São Paulo. |
| [44] | Rocha, R.M., Kremer, L.P., Baptista, M.S. and Metri, R., 2009, Bivalve cultures provide habitat for exotic tunicates in southern Brazil. Aquat. Inv. 4: 195-205. |
| [45] | Rocha, R. M., Muniz, G. M. and Lotufo, T.M.C., 2011, Checklist das ascídias do Estado de São Paulo. Biota Neotrop. 11(1a). |
| [46] | Lopes, R.M., 2009, Informe sobre as Espécies Exóticas Invasoras Marinhas no Brasil. Brasília, Ministério do Meio Ambiente, Série Biodiversidade 33, 439 p. |
| [47] | Barros, R. C., Rocha, R. M. and Pie M. R., 2009, Human- mediated global dispersion of Styela plicata (Tunicata, Ascidiacea). Aquat. Inv. 4, 45-57. |
| [48] | Van Name, W.G., 1945,The North and South American Ascidians. Bull. Am. Mus.Nat. Hist. 84. New York. 520p. |
| [49] | Floeter, S. R., Soares-Gomes, A., and Hajdu, E., 2009, Biogeografia Marinha. In: Pereira, R. C. and Soares-Gomes, A. (Orgs.). Biologia Marinha. Editora Interciência, Rio de Janeiro, 2ª edição, pp. 421–441. |
| [50] | Klautau, M., Monteiro, L. and Borojevic R. 2004. First occurrence of the genus Paraleucilla (Calcarea, Porifera) in the Atlantic Ocean: P. magna sp. nov. Zootaxa, 710, 1-8. |
| [51] | Laborel, J., 1969, Madreporaires et hydrocoralliaires récifaux des côtes Brasiliennes. Systématic, écologie, répartition verticale et geographique. Ann. Inst. Oceanogr.(Paris)47, 171–229. |
| [52] | Palácio, F. J., 1982,Revisión Zoogeográfica Marina Del SurDel Brasil. Bol. Inst. Oceanog. 31, 69–92. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML
