-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Marine Science
p-ISSN: 2163-2421 e-ISSN: 2163-243X
2012; 2(4): 27-33
doi: 10.5923/j.ms.20120204.01
Polychlorinated Dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs), Polychlorinated Dibenzofurans (PCDFs), and Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in Olivaceous Cormorant (Phalacrocorax brasilianus) from Sepetiba Bay, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Aldo Pacheco Ferreira
Center for the Study of Workers Health and Human Ecology, Sérgio Arouca National School of Public Health, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Correspondence to: Aldo Pacheco Ferreira , Center for the Study of Workers Health and Human Ecology, Sérgio Arouca National School of Public Health, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
An expressive number of man-made chemicals have been introduced in the aquatic environment represent the major problems arising in the development worldwide. Many of these chemical contaminants are persistent polyhalogenated aromatic hydrocarbons known to bioaccumulate and biomagnify as they move through the aquatic food web, effecting species associated with aquatic systems. Concentrations of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs), polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDFs), and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) were measured in Olivaceous Cormorant Phalacrocorax brasilianus collected from 2007 to 2011 on Sepetiba Bay, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Detectable hepatic concentrations of PCDD/Fs and PCBs were found in all samples analyzed. These data represent some of the first measurements of PCDD/Fs and PCBs in seabirds from this area. While levels of these contaminants in the tested specie currently appear to fall below critical values, continued monitoring is warranted for these compounds, especially in this bay.
Keywords: Marine Pollution, Risk To Environment and Health, Persistent Organic Pollutant, Seabird, Polychlorinated Biphenyl Ethers
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Oceans cover about 70% of the earth's surface. Effects of pollution on marine ecosystems have become a matter of great concern, especially to coastal states[1]. The oceans cannot supply an infinite sink for anthropogenic wastes but inadequate attention has been given to evaluating the limits of capacity of coastal areas for waste assimilation[2]. Thus, instances of fisheries shortage, spoiled beaches, destroyed coral reefs and wildlife habitat, toxic blooms and lost coastal ecological communities are extensive, with a corresponding determination of cost benefit[3]. Current concerns about connectivity of ocean health issues and the relationship to human disease highlight an essential area for research[1,3]. Awareness of the ocean and the impact of human performance on it can expose the complexity and interdependence of all aspects of the system[4]. Enhanced acquaintance and predictive capabilities are required for more effective and sustained development of the marine environment to obtain associated economic benefits and to preserve marine resources.Worldwide contamination by dioxin-related compounds, such as polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs), polychlorinated dibezofurans (PCDFs), and coplanar polychlorinated biphenyls (coplanar PCBs), is of great concern due to the persistence, bioaccumulative nature, and toxicity of these compounds[5]. For several decades, these compounds have been produced and extensively used for various purposes. Numerous of these chemical contaminants are persistent polyhalogenated aromatic hydrocarbons known to bioaccumulate and biomagnify as they move through the aquatic food web, effecting species associated with aquatic systems, including humans[6,7].Due to its position in the marine food chain and their long life length, seabirds congregate significant levels of trace elements. Are good sentinel species because they are observable, sensitive to toxicants, and live in different trophic positions[8,9]. Consequently, studies assessing avian population status, reproductive success, and toxicological importance of metal exposures can be extrapolated to other wildlife and probably humans[10,11]. Pollution in the marine environment has become a subject of enormous apprehension, especially to coastal states. The oceans cannot provide an infinite sink for anthropogenic wastes but little attention has been given to evaluating the limits of the capacity of coastal areas for waste assimilation[12]. Knowledge of the ocean and of the impact of human activities on it can reveal the complexity and interdependence of all aspects of the system[13]. Improved acquaintance with these and better forecasting ability are required for more effective and sustained development of the marine environment to obtain associated economic benefits and to preserve marine resources[14]. Recent concerns about the connectivity of ocean health issues and their relationship to human disease highlight an important area for study.
1.1. PCDDs/Fs and PCBs Contamination
- The study of PCDDs/Fs and PCBs contamination in aquatic environments has allowed to predict or identify sources of pollution and extensiveness of these pollutants, since they potentially pose a threat to ecosystem balance, being an important instrument to predict the affection to human health and animal[15,16].There are 75 different PCDDs and 135 PCDFs, which differ from each other in the number and positions for the chlorine atoms[16,17]. From the human/biota point of view, 17 PCDD/Fs chlorine substitution in the (2,3,7,8) positions are considered to be toxicologically important[10,18,19]. PCDDs have a planar aromatic tricyclic structure with 1-8 chlorine atoms as substituents. Some PCBs are called dioxin-like (co-planar/non-ortho-) PCBs. Those congeners do not have any or have only one chlorine atom (mono-ortho- PCBs) in the ortho-position to the carbon-carbon bond between the two benzene rings. Approximately 120 of PCBs are present in commercial products such as Aroclor 1254, Aroclor 1260 and Chlopen A60[17]. The PCDD and PCDF, commonly called "dioxins", are two classes of "quasi-planar" tricycles aromatic ethers with 210 different compounds (congeners) in total. The PCDD/F have similar physical-chemical properties but different biological potencies[20]. Figure 1 shows the general structure of these classes of compounds.Most industrial countries have restricted or stopped their use since 1970s, leading to decreasing concentrations in long-term environmental surveillance programmes[21,22]. However, compounds remained in ecosystems either due to their persistency or transport from developing countries where use in agricultural and industrial purposes is still current. Due to their chemical stability and hydrophobic nature, these compounds are adsorbed onto particles, accumulated in aquatic organisms, and highly biomagnified through the aquatic food webs[23]. Many organochlorines have been implicated in a broad range of adverse biological effects, including impaired reproduction and immuno suppression[24].The Olivaceous Cormorant (Phalacrocorax brasilianus) is widespread on both the Atlantic and Pacific coasts of America and inland waters, from Panama to Tierra del Fuego in southern Argentina. It feeds in shallow to deep water along lake shores, rivers, estuaries, and beaches[25]. Due to abundance of this specie at study site, it was then chosen for this research.
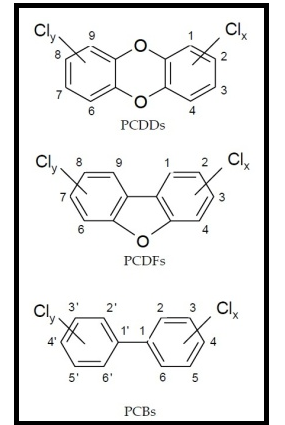 | Figure 1. Generalised structures of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs), polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDFs), and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) |
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Analysis: Identification and Quantification
- A total of thirty four specimens (adults) found stranded or dead in areas related to the study site, between March 2007 and December 2011. All fresh carcasses were necropsied following a standardised protocol[27], while putrescent specimens were discarded. Livers were collected, weighed, and maintained at - 20℃ for later analysis.Chemical analysis of PCDDs, PCDFs (PCDD/Fs) and coplanar PCBs followed the method described in a previous report, USEPA Method 1668[28], and USEPA Method 8290 A[29]. Five grams of liver samples were weighed and lyophilised. Dry tissues were inserted in a steel extraction cell and placed in the Accelerated Solvent Extractor (ASE 200, Dionex). This machine using organic solvents operates under high pressure and temperature conditions (10 minutes at 125℃ and 1500psi) and allows the extraction of the different organic compounds present from the biological matrix. After being extracted, the samples were concentrated using Kuderna-Danish, the extract evaporated down to 1 ml, and the solvent was transferred to 10 ml of n-hexane. Fat content was determined gravimetrically from an aliquot of the extract[30,31].Seventeen 2,3,7,8-substituted 13C-labeled tetra- through octa-CDD and CDF congeners and 12 dioxin-like PCBs (IUPAC Nos. 81, 77, 126, 169, 105, 114, 118, 123, 156, 157, 167, and 189) were spiked. Furthermore, aliquots were treated with sulfuric acid (approximately 7-10 times) in a separation funnel. Then the hexane layer with PCDDs/DFs and PCBs was rinsed with hexane-washed water and dried by passing through anhydrous sodium sulphate in a glass funnel.The solution was concentrated to 2 ml and sequentially subjected to silica gel, alumina, and silica gel- impregnated activated carbon column chromatography. Extracts were passed through a silica gel-packed glass column (Wakogel, silica gel 60; 2g) and eluted with 130 ml of hexane. The hexane extract was Kuderna-Danish concentrated and passed through alumina column (Merck- Alumina oxide, activity grade 1; 5g) and eluted with 30 ml of 2% dichloromethane in hexane as a first fraction, which containedmulti-ortho-substituted PCBs. The second fraction eluted with 30 ml of 50% dichloromethane in hexane, containing non- and mono-ortho-PCBs and PCDDs/DFs, was Kuderna- Danish concentrated and passed through silica gel- impregnated activated carbon column (0.5g). The first fraction eluted with 25% dichloromethane in hexane contained mono- and di-ortho-PCBs. The second fraction eluted with 250 ml of toluene containing PCDDs/DFs was concentrated and analyzed using a high-resolution gas chromatograph interfaced with a high-resolution mass spectrometer (HRGC/ HRMS). Identification and quantification of 2,3,7,8-substituted congeners of PCDDs/DFs and dioxin-like PCBs (non- and mono-ortho-substituted congeners) was performed by use of a (i) Shimadzu GC-14B gas chromatograph with AOC-1400 auto-sampler. Columns: CBP-1 (SE-30) and CBP-5 (SE-52/54 confirmatory column). Injection: Splitless (30seg.) 300℃. Temperature program of the oven: 110℃ (1 min.); 15℃/min up 170℃; 7.5℃/min up to 290℃, hold for 10 minutes. Total run time: 25 minutes. Electron Capture Detector (63Ni) temperature: 310℃; (ii) HPLC: Shimadzu LC-10AS; Mobile phase: acetonitrile: water 80%, isocratic run. Column: Shimadzu STR-ODS-II (C-18 reverse phase) 25cm, L: 4mm ID. UV/VIS detector model: Shimadzu SPD-10A. A procedural blank including extraction of blank Kimwipe and whole purification procedure was run with every batch (normally seven samples). The limit of quantification (LOQ) was set at 2 times the detected amount in the procedural blank. Reproducibility and recovery were confirmed through four replicate analyses of an abdominal adipose tissue sample with and without standard spiking. The relative standard deviations of concentrations of individual PCDD/F and PCB-congeners were less than 5.8%, and the recoveries were more than 96%. The lipid contents were determined gravimetrically after aliquots of the sample extracts were evaporated to complete dryness.
 | Figure 2. Study area: Coroa Grande mangrove, Sepetiba Bay, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil |
- TEQ is the product of the concentration of an individual dioxin-like compound (DLC) in an environmental mixture and the corresponding TCDD TEF for that compound. Equation 1 is the formula for calculating exposure concentration for n DLCs in a mixture in TCDD toxic equivalence (TEQ). Exposure to the ith individual PCDD, PCDF, or PCB compound is expressed in terms of an equivalent exposure of TCDD by computing the product of the concentration of the individual compound (Ci) and its assigned TEFi. TEQ is then calculated by summing these products across the n DLCs compounds present in the mixture. The TEQ may be compared to the dose-response slope for TCDD and used to assess the risk posed by exposures to mixtures of DLCs.
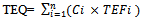 | (1) |
3. Results
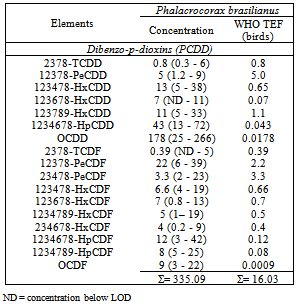
- No significant species-related differences in PCB and PCDD/Fs concentrations were found. Concentrations of PCB-congeners with fat percentages are presented (Table 1), and Concentrations of PCDD/Fs-congeners with fat percentages are presented (Table 2).
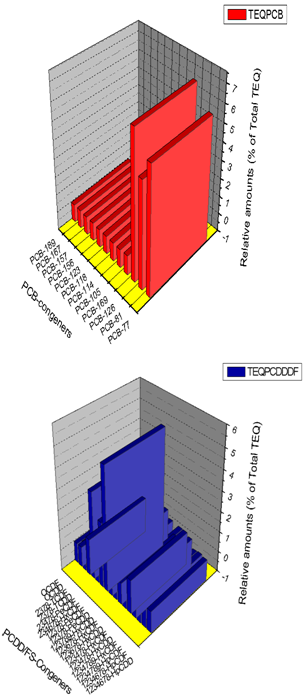 | Figure 3. Contributions of PCDDs, PCDFs and dioxin-like PCBs to Total TEQ (pg/g lipid) |
|
4. Discussion
- The choice of seabirds for analysis of pollutants, rather than the analysis of pollutants in the abiotic environment, it becomes more attractive and promising because these indicators can provide precise information on the bioavailability of pollutants, their bio-magnification and transfer. Thus, indicating that the magnitude of the observed data, reinforces that there are startling signs regarding the potential risks to public health and these indicators are important to environmental monitoring by being at top the food chain, are sensitive to toxic products, respond to subtle changes in the environment, and also because of its high metabolic rate[21, 36-38]. The fundamental question to answer is whether the trophic level is harmfully disturbed when polluted by toxicants. To answer this important question, quantitative understanding of the pollutants behaviour within ecosystems is essential, and therefore researchers develop methods to manage this. The presence of anthropogenic pollutants, such as PCDD/F and PCB-congeners, throughout all compartments of the marine environment has been of international concern for a number of decades[39-41]. While a great number of datasets documenting absolute concentrations of persistent organic pollutants in a variety of marine biota are available, the bioaccumulative nature, toxicity, biomagnification, and the fate of these compounds in the marine ecosystem is still poorly understood. Data on contaminant levels in Brazilian seabirds are limited, and no information exists regarding levels of new or emerging contaminants.Reported adverse effects of POPs in wildlife include population declines, increases in cancers, reduced reproductive function, disrupted development of immune and nervous systems, and also elicit toxic responses which could result in the disruption of the endocrine system[7].In previous studies, the monitoring of POPs in seabirds has been limited by the availability in organs[42-45]. This approach can easily be combined with ecological investigations of seabirds, and so this could dramatically increase the availability of seabird samples, including repeated sampling on identical birds. Recently, electronic tracking tags have revolutionized our understanding of the large-scale movements and habitat use of mobile marine animals[46].Increased human activities such as industrialization, coupled with over-population and increased ambient temperature amongst other factors, have become major environmental issues in recent years. As a result of such actions, additional studies which include the environment and their indicators are important because they can show potential impacts that are being reflected, and extending to public health.It was presented a scientific approach for assessing the ecological condition of the Sepetiba Bay and the impacts caused by PCBs and PCDD/FS in a particular species of bird used as indicator, which has weights throughout Latin America. The key assumptions underlying the approach are: (a) the importance of putting analysis on ecosystems attributes of public importance, (b) the consistent with scientific understanding of what is important to sustain ecosystems structure and function, (c) measurements in environmental indicators must be scientifically defensible, and (d) are there implications on health risk to man and along marine trophic chains public health?
5. Conclusions
- The presence of tissue levels of POPs has been associated with biological and physiological effects in marine organisms, in specially seabirds. The animals sampled in the current study had PCDD/F and PCB congeners that exceeded the values found in these studies. Wide ranges of POP concentrations were measured in these animals, and our findings indicate that these animals are exposed to POPs levels that may affect their health, and in some classes of toxic POPs that may increase their risk to adverse effects.The present study confirms the ubiquity of POPs in Phalacrocorax brasilianus, belonging the marine environment of Sepetiba Bay, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Biomagnification may be the cause of the levels in the species collected and analysed. Further assessments are recommended on organisms at higher trophic levels for ecotoxicological impacts. The ubiquity of these pollutants in Sepetiba Bay’s marine environment supports the need for a greater awareness of bioaccumulation processes, particularly for organisms cultivated (shellfish) or fished locally and destined for human consumption.This research gives reasonable alerts in pollution marine with relevant information that can support the decision-making process and provides a baseline to evaluate future clean up and restoration activities at Sepetiba bay. There are clear management decisions that must be made concerning what to clean up, and to what levels.
Acknowledgements
- The author is grateful for financial support received from the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico – CNPq (302946/2011-0).
References
| [1] | L.E. Fleming, K. Broad, A. Clement, E. Dewailly, S. Elmir, A. Knap, S.A. Pomponi, S. Smith, H. Solo Gabriele, P. Walsh, Smith S., Gabriele H., P. Walsh, “Oceans and human health: emerging public health risks in the marine environment’, Elsevier, Marine Pollution Bulletin, vol. 53, pp. 545-560, 2006. |
| [2] | H. L. Kite-Powell, L. E. Fleming, L. C. Backer, E. M. Faustman, P. Hoagland, A. Tsuchiya, L. R. Younglove, B. A. Wilcox, R. J. Gast, “Linking the oceans to public health: current efforts and future directions”, BioMed Central, Environmental Health, vol. 7, supl. 2, pp. 1-15, 2008. |
| [3] | A. Knap, É. Dewailly, C. Furgal, J. Galvin, D. Baden, R. E. Bowen, M. Depledge, L. Duguay, L. E. Fleming, T. Ford, F. Moser, R. Owen, W. A. Suk, U. Unluata, “Indicators of ocean health and human health: developing a research and monitoring framework”, U.S. National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, Environmental Health Perspectives, vol. 110, pp. 839–845, 2002. |
| [4] | J. R. Stewart, R. J. Gast, R. S. Fujioka, H. M Solo-Gabriele, J. S. Meschke, L. A. Amaral-Zettler, E. del Castillo, M. F. Polz, T. K. Collier, M. S. Strom, C. D. Sinigalliano, P. D. R. Moeller, A. F. Holland, “The coastal environment and human health: microbial indicators, pathogens, sentinels and reservoirs”, Biomed Central, Environmental Health, vol. 7, supl. 2, pp. S3, 2008. |
| [5] | T. Savinova, S. Batterman, S. Konoplev, V. Savinov, G. W. Gabrielsen, L. Alekseeva, A. Kochetkov, E. Pasynkova, D. Samsonov, A. Koryakin, S. Chernyak, “New environmental contaminants in seabirds from the seven islands archipelago (Barents sea, Russia)”, Organohalogen Compounds, vol. 69, pp. 1681-1684, 2007. |
| [6] | J.P. Giesy, J.P. Ludwig, D.E. Tillitt, “Dioxins, Dibenzofurans, PCBs and colonial, fish-eating water birds”, In: Dioxins and Health. A. Schecter. Plenum Publishers, New York, USA, 1994. |
| [7] | Ruth E. Alcock, Peter A. Behnisch, Kevin C. Jones, Hanspaul Hagenmaier, “Dioxin-Like PCBS in the environment. Human exposure and the significance of sources”, Elsevier, Chemosphere, vol. 37, no. 8, pp. 1457-1472, 1998. |
| [8] | M.L. Tasker, J.B. Reid JB. “Seabirds in the marine environment: Introduction”, Oxford Journals, Ices Journal of Marine Science, vol. 54, pp. 505-506, 1997. |
| [9] | M.L. Mallory, S.A. Robinson, C.E. Hebert, M.R. Forbes, “Seabirds as indicators of aquatic ecosystem conditions: A case for gathering multiple proxies of seabird health”, Elsevier, Marine Pollution Bulletin, vol. 60, no. 1, pp. 7-12, 2010. |
| [10] | B.J. Alloway, D.C. Ayres, Chemical Principles of Environmental Pollution, 2° ed., Ed. Chapman & Hall, New York, USA, 1997. |
| [11] | D.O. Carpenter, “Polychlorinated Biphenyls and Human Health”, Springer Verlag, International Journal of Occupational Medicine and Environmental Health, vol.11, n.4, pp. 291-303, 1998. |
| [12] | M. Schmitt-Jansen, U. Veit, G. Dudel, R. Altenburger R., “An ecological perspective in aquatic ecotoxicology: Approaches and challenges”, Basic and Applied Ecology, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 337-345, 2008. |
| [13] | Márcia S. Pereira, “Polychlorinated Dibenzo-p-Dioxins (PCDD), Dibenzofurans (PCDF) and Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCB): Main sources, environmental behaviour and risk to man and biota”, Química Nova, vol. 27, no. 6, pp. 934-943, 2004. |
| [14] | R. Costanza, J. Farley, “Ecological economics of coastal disasters: Introduction to the special issue”, Ecology Economics, vol. 63, no. 2-3, pp. 249-253, 2007. |
| [15] | K.S. Kumar, K. Kannan, O.N. Paramasivan, V.P.S. Sundaram, J. Nakanishi, S. Masunaga, “Polychlorinated Dibenzo-p-Dioxins, Dibenzofurans, and Polychlorinated Biphenyls in human tissues, meat, fish, and wildlife samples from India”, ACS Publications, Environmental Science & Technology, vol. 35, no. 17, pp. 3448-3455, 2001. |
| [16] | K. Breivik, A. Sweetman, J.M. Pacyna, K.C. Jones, “Towards a global historical emission inventory for selected PCB congeners - a mass balance approach 2. Global production and consumption”, Elsevier, Science of Total Environment, vol. 290, pp. 181-198, 2002. |
| [17] | C.H. Walker, S.P. Hopkin, R.M. Sibly, D.B. Peakall, “Principles of Ecotoxicology”, 3rd ed.,CRC Press, USA, 2006. |
| [18] | A.P. Ferreira, “Environmental fate of bioaccumulative and persistent substances. A synopsis of existing and future actions”, Gerencia y Politicas de Salud, vol. 7, no. 15, pp. 14-23, 2008. |
| [19] | G.C. Pereira, N.F.F. Ebecken, “Knowledge discovering for coastal waters classification”, Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 36, no. 4, pp. 8604 – 8609, 2009. |
| [20] | H. Hagenmaier, “Abschlussbericht zum Forschungs- und Untersuchungsvorhaben - Belastung der Umwelt mit Dioxinen”, Umweltministerium Baden-Württemberg ed., Tübingen, Germany, 1987. |
| [21] | J. W. Choi, M. Matsuda, M. Kawano, B. Y. Min, T. Wakimoto, “Accumulation profiles of persistent organochlorines in waterbirds from an estuary in Korea”, SpringerLink, Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, vol. 41, no.3, pp. 353–363, 2001. |
| [22] | B. Thompson, T. Adelsbach, C. Brown, J. Hunt, J. Kuwabara, J. Neale, H. Ohlendorf, S. Schwarzbach, R. Spies, K. Taberski, “Biological effects of anthropogenic contaminants in the San Francisco Estuary”, Environmental Research, vol. 105, no. 1, pp. 156 – 174, 2007. |
| [23] | R. Lauwerys, P. Hoet “Industrial Chemical Exposure. Guidelines for biological monitoring”, Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, 1993. |
| [24] | M. Rittler, E.E. Castilla, “Desreguladores endócrinos e anomalias congênitas”, Cadernos de Saúde Pública, vol. 18, no. 2, pp. 421-428, 2002. |
| [25] | O.S. Dias, “Poluentes orgânicos persistentes na biota marinha do arquipélago de São Pedro e São Paulo”, Dissertação de Mestrado. Instituto Oceanográfico. Universidade de São Paulo, Brasil, 2010. |
| [26] | Graham Copeland, Teófilo Monteiro, Scott Couch, Alistair Borthwick, “Water quality in Sepetiba Bay, Brazil”, Elsevier, Marine Environmental Research, vol. 55, no. 5, pp. 385 – 408, 2003. |
| [27] | T. Jauniaux, L. Brosens, P. Meire, H. Offringa, F. Coignoul, “Pathological investigations on guillemots (Uria aalge) stranded at the Belgian coast during the winter 1993-1994”, British Veterinary Association, Veterinary Record, vol. 143, no. 14, pp. 387 – 390, 1998. |
| [28] | United States Environmental Protection Agency (Usepa), “Method 1668: Revision A. Chlorinated Biphenyl congeners in water, soil, sediment, biosolids, and tissue by HRGC/HRMS”, 2003. |
| [29] | United States Environmental Protection Agency (Usepa), “Method 8290 A: Revision 1. Polychlorinated Dibenzodioxins (PCDDS) and Polychlorinated Dibenzofurans (PCDFS) by high-resolution gas chromatography/high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRGC/HRMS)”, 2007. |
| [30] | G. Becher, J.U. Skaare, A. Polder, B. Sletten, O.J. Rossland, H.K. Hansen, “PCDDS, PCDFS, and PCBS in human milk from different parts of Norway and Lithuania”, Taylor & Francis, Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, vol. 46, pp. 133-148, 1995. |
| [31] | H. Kiviranta, R. Purkunen, T. Vartiainen, “Levels and trends of PCDD/FS and PCBS in human milk in Finland”, Elsevier, Chemosphere, vol. 38, no. 2, pp. 311-323, 1999. |
| [32] | K.S. Guruge, S. Tanabe, M. Fukuda, “Toxic assessment of PCBs by the 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin equivalent in common cormorant (Phalacrocorax carbo) from Japan”, SpringerLink, Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, vol.38, no. 4, pp. 509–521, 2000. |
| [33] | I. Windal, “Développement de méthodes rapides d’analyse des dioxines dans lês poussières d’incinérateurs et destruction des dioxines par eaux subcritique”, Thesis, University of Liège, Belgium, 2001. |
| [34] | Katrin E. Holmström, Urs Berger, “Tissue distribution of perfluorinated surfactants in common Guillemot (Uria Aalge) from the Baltic sea”, ACS Publications, Environmental Science & Technology, vol. 42, no. 16, pp. 5879–5884, 2008. |
| [35] | M. Van Den Berg, L.S. Birnbaum, M. Denison, “The 2005 World Health Organization re-evaluation of human and mammalian toxic equivalency factors for dioxins and dioxin-like compounds”, The Journal of Toxicology Science, vol. 93, no. 2, pp. 223-241, 2006. |
| [36] | Kurunthachalam Kannan, Simonetta Corsolini, Takashi Imagawa, Silvano Focardi, John P. Giesy, “Polychlorinated -naphthalenes, -biphenyls, -dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans and p,p_-DDE in bluefin tuna, swordfish, cormorants and barn swallows from Italy”, Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, Ambio, vol. 31, no. 3, pp. 207–211, 2002. |
| [37] | H. Kruuk, J.W.H. Conroy, “Concentrations of some organochlorines in otters (Lutra lutra L.) in Scotland: implications for populations”, Elsevier, Environmental Pollution, vol. 92, no. 2, pp. 165–171, 1996. |
| [38] | Kurunthachalam S. Kumar, Kurunthachalam Kannan, Simonetta Corsolini, Thomas Evans, John P. Giesy, Junko Nakanishi, Shigeki Masunaga, “Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzo- furans and polychlorinated biphenyls in polar bear, penguin and south polar skua”, Elsevier, Environmental Pollution, vol. 119, no. 2, pp. 151–161, 2002. |
| [39] | F. Moriarty, “Ecotoxicology. The study of polluants in ecosistems”, 3rd ed., Academic Press, California, USA, 1999. |
| [40] | Anders Olsson, Karlis Valters, Sven Burreau, “Concentrations of organochlorine substances in relation to fish size and trophic position: a study on perch (Perca fluvialis)”, ACS Publications, Environmental Science & Technology, vol. 34, no. 23, 4878-4886, 2000. |
| [41] | J. Lailson-Brito, P.R.B. Dornelesa, C.E. Azevedo-Silva Ce, A.F. Azevedo, L.G. Vidal, R.E. Zanelatto, C.P.C. Lozinski, A. Azeredo, A.B.L. Fragoso, H.A. Cunha, J.P.M. Torres. O. Malm, “High organochlorine accumulation in blubber of guiana dolphin, Sotalia Guianensis, from Brazilian coast and its use to establish geographical differences among populations”, Elsevier, Environmental Pollution, vol. 158, no. 5, pp. 1800-1808, 2010. |
| [42] | D.B. Peakall, D.G. Noble, J.E. Elliott, J.D. Somers, G. Erickson, “Environmental Contaminants in Canadian peregrine falcons, Falco Peregrinus: A toxicological assessment”, Mendeley, Canadian FieldNaturalist, vol. 104, no. 2, pp. 244–254, 1990. |
| [43] | D. Mackay, W.Y. Shiu, K.C. Ma, “Illustrated handbook of physical-chemical properties and environmental fate for organic chemicals”. Volume I. Monoaromatic Hydrocarbons, Chlorobenzenes and PCBS. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, 1991. |
| [44] | W.A. Montevecchi, “Birds as indicators of change in marine prey stocks”, In: R.W. Furness, J.J.D. Greenwood (Eds). Birds as monitors of environmental change. Chapman & Hall, London, 1993. |
| [45] | N.J. Morley, “Interactive effects of infectious diseases and pollution in aquatic molluscs”, Elsevier, Aquatic Toxicology, vol. 96, no. 1, pp. 27-36, 2010. |
| [46] | S.A. Shaffer, Y. Tremblay, H. Weimerskirch, D. Scott, D.R. Thompson, P.M. Sagar, H. Moller, G.A. Taylor, D.G. Foley, B.A. Block, D.P. Costa DP., “Migratory shearwaters integrate oceanic resources across the Pacific ocean in an endless summer”, PNAS, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, vol. 103, pp. 12799−12802, 2006. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML