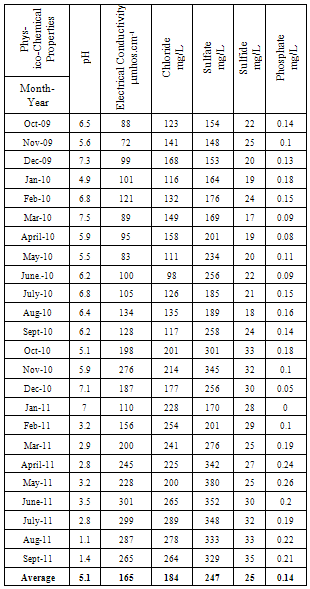
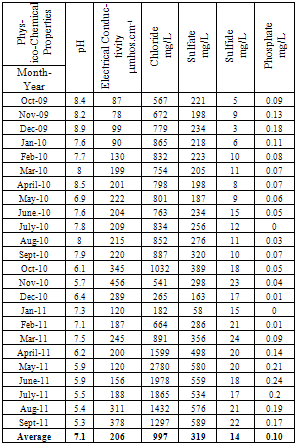
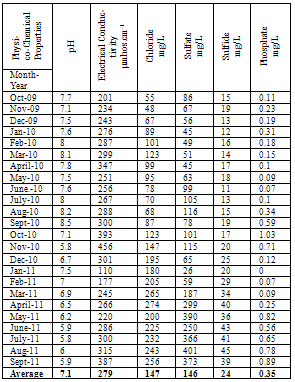
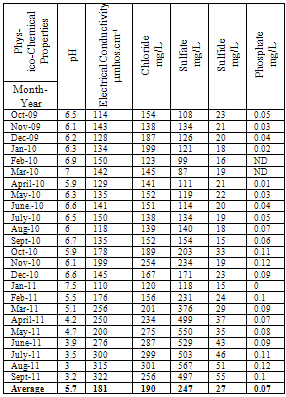
| [1] | Sala O.E., Chapin III F.S., Armesto J.J., Berlow E., Bloomfield J., Dirzo R., Huber-Sanwald E., Huenneke L.F., Jackson R.B., Kinzig A., Leemans R., Lodge D.M., Mooney H.A., Oesterheld M., Poff N.L., Sykes M.T., Walker B.H., Walker M. and Wall D.H. (2000), Global biodiversity scenarios for the year 2100, Science, 287(5459), 1770–1774. |
| [2] | Abowei, J.F.N. and Sikoki, F.D. 2005, Water Pollution Management and Control, Double Trust Publications Company, Port Harcourt; ISBN: 978-30380-20-16, pp: 236. |
| [3] | Stronkhorst J., Brils J., Batty J., Coquery M., Gardner M., Mannio J., O'Donnell C., Steenwijk J. and Frintrop P., 2004, Discussion document on Sediment Monitoring Guidance for the EU Water Framework Directive., Version 2. EU Water Framework Directive expert group on Analysis and Monitoring of Priority Substances. May 25th, 2004 |
| [4] | Mucha, A.P., Vasconcelos, M.T.S.D., and Bordalo, A.A., 2003, Macrobenthic community in the Douuro Estuary: relation with trace metals and natural sediment characteristics., Environmental Pollution, 121(2), pp.169 –180. |
| [5] | Praveena, S. M., Ahmed, A., Radojevic, M., Abdullah, M. H., Aris, A. Z., 2007, Factor-cluster analysis and enrichment study of mangrove sediments-an example from Mengkabong, Sabah., Malaysian J. Anal. Sci., 11(2), pp. 421-430 |
| [6] | Lokhande, R.S., Singare, P.U., and Pimple, D.S., 2011, Pollution in Water of Kasardi River Flowing Along Taloja Industrial Area of Mumbai, India,. World Environment (In Press). |
| [7] | Lokhande, R.S., Singare, P.U., and Pimple, D.S., 2011, Toxicity Study of Heavy Metals Pollutants in Waste Water Effluent Samples Collected From Taloja Industrial Estate of Mumbai, India., Resources and Environment (In Press). |
| [8] | Lokhande, R.S., Singare, P.U., and Pimple, D.S., 2011, Study on Physico-Chemical Parameters of Waste Water Effluents from Taloja Industrial Area of Mumbai, India. International Journal of Ecology (In Press) |
| [9] | Singare, P.U, Lokhande, R.S., and Bhanage, S.V. 2011, Study of water pollution due to Heavy metals in Kukshet lakes of Nerul, Navi Mumbai, India. International Journal of Global Environmental Issues, 11(1), pp.79–90. |
| [10] | P.U. Singare, Lokhande, R.S., and Jagtap, A.G., 2011, Water pollution by discharge effluents from Gove Industrial Area of Maharashtra, India: Dispersion of heavy metals and their Toxic effects., International Journal of Global Environmental Issues, 11(1), pp.28–36. |
| [11] | Singare, P.U., Lokhande, R.S. and Naik, K.U., 2011, Impact Assessment of Pollution in some Lake water Located at and around Thane City of Maharashtra, India: Physico chemical properties and Toxic effects of Heavy metal content., Interdisciplinary Environmental Review, 12 (3), pp.215-230. |
| [12] | Singare, P.U., Lokhande, R.S., and Bhanage, S.V., 2011, Water pollution study of the Shirvane and Nerul lakes situated at Nerul, Navi Mumbai, India., Interdisciplinary Environmental Review, 12(1),pp.1-11. |
| [13] | Singare, P.U., Lokhande, R.S., and Jagtap, A.G., 2010, Study of Physico-chemical quality of the Industrial Waste Water Effluent from Gove Industrial Area of Bhiwandi City of Maharashtra, India., Interdisciplinary Environmental Review, 11(4), pp.263-273. |
| [14] | Singare, P.U., Lokhande, R.S., and Naik, K.U., 2010, A Case Study of Some Lakes Located at and Around Thane City of Maharashtra, India, with Special Reference to Physico-Chemical Properties and Heavy Metal content of Lake Water., Interdisciplinary Environmental Review, 11(1), pp.90-107. |
| [15] | Hodson P.V., 1986, Water quality criteria and the need for biochemical monitoring of contaminant effects on aquatic ecosystem. In: Water Quality Management: Freshwater Eco-toxicity in Australia, Hart, B.T. (ed.), Melbourne Water Studies Center, pp. 7-21. |
| [16] | Haslam S.M., 1990, River pollution: An ecological perspective, Belhaven Press. London, pp.253. |
| [17] | Biney C., Amazu A.T., Calamari D., Kaba N., Mbome I.L., Naeve H., Ochumba P.B.O., Osibanjo O., Radegonde V., and Saad M.A.H., 1994, Review of heavy metals in the African aquatic environment., Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 31, pp. 134-159. |
| [18] | Barbour M.T., Gerritsen J., Snyder B.D., and Stribling J.B., 1998, USEPA Rapid Bioassessment Protocols for Use in Streams and Wadeable Rivers. Periphyton, Benthic Macroinvertebrates, and Fish., Second Edition. EPA/841-B-98-010. U.S. Environmental ProtectionAgency; Office of Water; Washington, D.C. |
| [19] | Barbour M.T., Gerritsen J., Snyder B.D., and Stribling J.B.,1999, Rapid bioassessment protocols for use in and wadeable rivers—Periphyton, benthic macroinvertebrates, and fish (2d ed.): U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water, EPA 841–B—99–002. |
| [20] | Lokhande, R.S., Singare, P.U., and Pimple, D.S., 2011, Quantification Study of Toxic Heavy Metals Pollutants in Sediment Samples Collected from Kasardi River Flowing along the Taloja Industrial Area of Mumbai, India., The New York Science Journal 4(9), pp.66-71. |
| [21] | Singare, P.U., 2011, Distribution Behaviour of Trace and Toxic Metals in Soil and Sediment along the Thane Creek Near Mumbai, India., Interdisciplinary Environmental Review, 12(4), pp. 298–312. |
| [22] | Singare, P.U., Lokhande, R.S., and Bhattacharjee, S.S., 2011, Physico-Chemical Analysis of the Sediment Samples collected from Thane Creek of Maharashtra, India., Interdisciplinary Environmental Review, 12(2), 95-107. |
| [23] | Menounou, N., Presley, B.J., 2003, Mercury and Other Trace Elements in Sediment Cores from Central Texas Lakes., Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 45(1), 11–29. |
| [24] | Spooner, D.R., Maher, W., and Otway, N., 2003, Trace Metal Concentrations in Sediments and Oysters of Botany Bay, NSW,Australia., Arch. Environ.Contam. Toxicol. 45(1), 92–101. |
| [25] | Sahu, S.K., Ajmal, P.Y., Pandit, G.G., and Puranik, V.D., 2009, Vertical distribution of polychlorinated biphenyl congeners in sediment core from Thane Creek area of Mumbai, India., Journal of hazardous materials, 164(2-3), 1573-1579. |
| [26] | Radojevic, M., and Bashkin, V. N., 1999, Practical Environmental Analysis. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, New York. |
| [27] | Al-Shiwafi, N., Rushdi, A. I., and Ba-Issa, A., 2005, Trace Metals in Surface Seawaters and Sediments from Various Habitats of the Red Sea Coast of Yemen., Environmental Geology. 48(4-5), pp.590-598. |
| [28] | Jung, H., Yun, S., Mayer, B., Kim, S., Park S., and Lee, P., 2005, Transport and Sediment-Water Partitioning Of Trace Metals in Acid Mine Drainage: An Example from the Abandoned Kwangyang Au-Ag Mine Area, South Korea., Environmental Geology. 48(4-5), pp.437-449. |
| [29] | APHA, AWWA and WEF, 1998, Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater., 20th edition, Clesceri, L.S. Greenberg, A.E. and Eaton, A.D. (Eds.), American Public Health Association, American Water Work Association, Water Environment Federation, Washington DC |
| [30] | Jackson, M.L., 1973, Soil Chemical Analysis., Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited, New Delhi. |
| [31] | Langmuir, D., 1997, Aqueous Environmental Chemistry., Prentice-Hall, Inc., New Jersey. |
| [32] | Hattersley, J.G., 2000, The Negative Health Effects of Chlorine., The Journal of Orthomolecular Medicine.15(2), pp.89-95. |
| [33] | akashima, T., Fukunishi, N., Nishiki, T., and Konishi, Y., 2002, Anaerobic oxidation of dissolved hydrogen sulfide in continuous culture of the chemoautotrophic bacterium Thiobacillus denitrificans., Kagaku Kogaku Ronbunshu, 28(1), pp.25–30. |
| [34] | Lucassen, E.C.H.E.T., Smolders, A.J.P., Van der Salm, A.L., and Roelofs, J.G.M., 2004, High groundwater nitrate concentrations inhibit eutrophication of sulfate-rich freshwater wetlands., Biogeochemistry, 67(2), pp.249–267. |
| [35] | Faust, S.D., and Osman, A., 1983, Chemistry of water treatment., Butterworth Publishers, Woburn, MA. |
| [36] | Singh, G., and Bhatnagar, M., 1989, Inhibition of bacterial activity in acid mine drainage., International Journal of Mine Water, 7(4), pp.13-26. |
| [37] | Hammarstrom, J.M., Seal, R.R., Meier, A.L., and Kornfeld, J.M., 2005, Secondary sulfate minerals associated with acid drainage in the eastern US: recycling of metals and acidity in surficial environments., Chemical Geology, 215(1-4), pp.407-431. |
| [38] | Boomer, K.M.B., and Bedford, B.L., 2008, Influence of nested groundwater systems on reduction-oxidation and alkalinity gradients with implications for plant nutrient availability in four New York fens., Journal of Hydrology, 351(1-2), pp.107–125. |
| [39] | Armstrong, J., Afreen-Zobayed, F., and Armstrong, W., 1996, Phragmites die-back: sulfide- and acetic acid induced bud and root death, lignifications, andblockages within aeration and vascular systems., New Phytologist, 134(4), pp.601–614. |
| [40] | Van der Welle, M.E.W., Smolders, A.J.P., Den Camp, H.J.M.O., Roelofs, J.G.M., and Lamers, L.P.M., 2007, Biogeochemical interactions between iron and sulfate in freshwater wetlands and their implications for interspecific competition between aquatic macrophytes., Freshwater Biology. 52(3), pp.434–447. |
| [41] | The Environment (Protection) Rules 1986 Available on Internet: cpcb.nic.in/GeneralStandards.pdf |

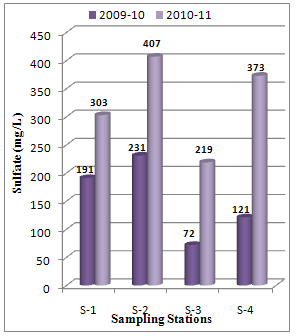
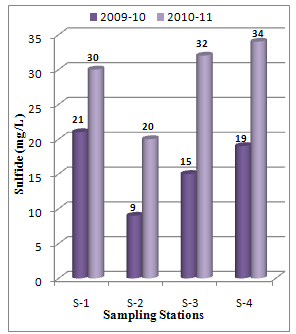
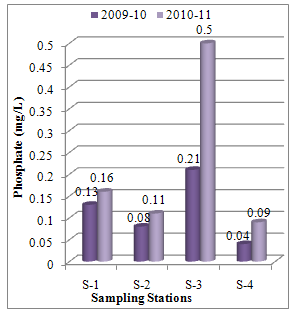
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML