-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Management
p-ISSN: 2162-9374 e-ISSN: 2162-8416
2021; 11(1): 1-19
doi:10.5923/j.mm.20211101.01
Received: Jan. 13, 2021; Accepted: Jan. 30, 2021; Published: Feb. 6, 2021

The Impact of Total Quality Management on Achieving Competitive Advantage in the Vocational Education Sector in Lebanon- The Case of Bir Hassan Technical Institute
Fadel Fadel, Mohammad Yassine
Faculty of Business Administration, Jinan University, Lebanon
Correspondence to: Fadel Fadel, Faculty of Business Administration, Jinan University, Lebanon.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

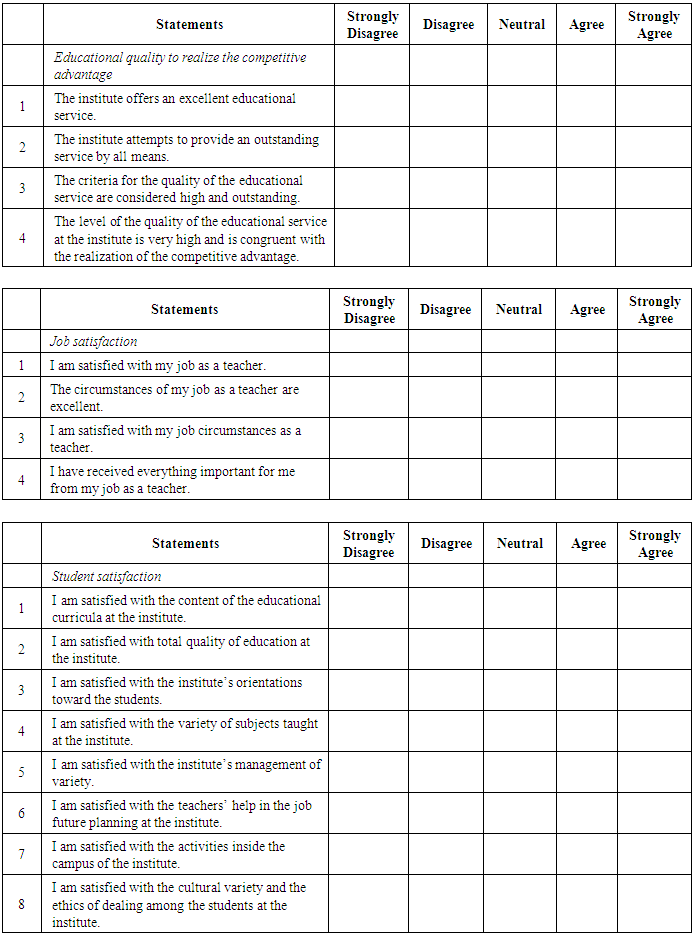
The application of total quality management in organizations is a critical step towards ensuring organizations achieve and maintain their competitive advantage in the long run. However, not all organizations are aware of the key criteria and elements of a successful total quality management application, which negatively impacts their employee satisfaction and overall quality of their processes. This research project explores the application of total quality management, taking the case of the Bir Hassan Technical Institute in Lebanon. It set a number of key objectives: first, to determine the degree to which the total quality criteria are applied in the vocational and technical sectors at Bir Hassan Technical Institute. Second, to identify the impediments which stand in the way of applying total quality criteria and whether the senior administration has a clear strategic plan for the application of total quality management at that institute. Using a qualitative and quantitative methodology to gather and analyse the data, the project finds that vocational and technical education in Lebanon, for the most part, still lacks planning and coordination, with the main problem lying in the educational curricula and the way they are applied, in addition to the means and their variety in applying the subjects and teaching them. In the case of the Bir Hassan Technical Institute, the organization suffers from the dissatisfaction of the teachers and administrators with their job circumstances, which was a reason for dysfunction and a barrier to the provision of quality education, all of which are symptoms of the lack of total quality management application.
Keywords: Total quality management, Employee satisfaction, Job conditions, Quality assurance, Academia
Cite this paper: Fadel Fadel, Mohammad Yassine, The Impact of Total Quality Management on Achieving Competitive Advantage in the Vocational Education Sector in Lebanon- The Case of Bir Hassan Technical Institute, Management, Vol. 11 No. 1, 2021, pp. 1-19. doi: 10.5923/j.mm.20211101.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The progress of countries is measured by the extent to which they keep up with the rapid technological developments and by their ability to grow economically and improve the living standards of their citizens. It was, therefore, inevitable to attend to the human factor and work on educating, training and preparing young people. In this context, human resources are considered to be the most important factor in the processes of economic development. Therefore, vocational education is one of the most significant factors which contribute to preparing man to enter the job market and to the development of the nation. This approach to education directly affects the building of societies and their development with the human resource development it offers in line with the demands and needs of society and the high qualifications that lead the different development processes. In this respect, the developed industrial countries have realized the role of vocational education and have given it great attention. In fact, the increased international competition among the institutions of vocational training to attract students to join them has contributed to attributing great importance to these institutions (Elliot & Healy, 2001).Applying the approach of total quality management in vocational and technical education has played a significant role in the rise of the sector and in realizing its goals. It has also played a role in raising the level of the students, in fulfilling their desires, developing and improving the level of teaching and in providing educational curricula that would fit the learning processes. With the development of the needs of the Lebanese job market and the pursuit to open it to the external world through finding jobs for the graduates of the technical education in the local and international job markets, it has become necessary to improve the quality of these centers. As they started to realize the value of vocational education, the concerned parties had to study the reality of this type of education for the purpose of enabling it to realize the competitive advantage.
2. Research Problem
- The centers of vocational training in Lebanon are not enough to satisfy the needs of the local job market and have not kept pace with the technological advancements. There is also a shortage in the number of specialists in both quantity and quality as well as in some of the other variables related to the learning environment, the curricula and their cognitive content. This is why the researcher had the idea of analyzing the reasons behind the weak total quality management on the level of individuals as well as centers. He also sensed the need to suggest a proposition for the criteria of total quality in order to be used as an index for evaluation in the vocational education centers in the pursuit of the promotion of the performance of those centers according to the criteria of total management in order to realize the competitive advantage. Consequently, the problem of the study can be summarized by responding to the following principal question:Does the application of the criteria of total quality management in the vocational and technical sector in Lebanon contribute to the realization of the competitive advantage? The following are sub-questions:1. What are the impediments which stand in the way of applying total quality criteria in order to realize the competitive advantage in the vocational and technical sectors at Bir Hassan Technical Institute?2. Does the senior administration have a clear strategic plan for the application of total quality management at Bir Hassan Technical Institute?3. What are the levels of employee satisfaction with the vocational and technical sectors at Bir Hassan Technical Institute?4. What are the levels of student satisfaction with the vocational and technical sectors at Bir Hassan Technical Institute?
3. Variables of the Study
- The independent variable is the total quality management in the vocational education centers, whereas the dependent variable is realizing the competitive advantage.
4. Hypotheses of the Study
- Hypothesis 1: There is a statistically significant positive relationship between the application of total quality criteria and the realization of the competitive advantage.Hypothesis 2: There is a statistically significant positive relationship between the vision of the administration and the application of total quality management.Hypothesis 3: There is a statistically significant positive relationship between the application of total quality criteria and the satisfaction of the workers.Hypothesis 4: There is a statistically significant positive relationship between the application of total quality criteria and the satisfaction of the students.In order to analyze the data, the simple linear regression test, which tests the effect of each independent variable on the dependent variable, will be used. The ANOVA test will be also employed in order to test the statistically significant differences of variables of the demographic study. If the value of alpha is smaller than 0.05 (α > 0.05), we can conclude that there is a relationship between these variables, while if the value of alpha is bigger than 0.05 (α > 0.05), we can conclude that there is no relationship between these variables.
5. Objectives of the Study
- The present study seeks to realize the following objectives:1. Determine the degree to which the total quality criteria are applied in the vocational and technical sectors at Bir Hassan Technical Institute.2. Identify the impediments which stand in the way of applying total quality criteria in order to realize the competitive advantage in the vocational and technical sectors at Bir Hassan Technical Institute.3. Determine whether the senior administration has a clear strategic plan for the application of total quality management at Bir Hassan Technical Institute.4. Ascertain employee satisfaction with the vocational and technical sectors at Bir Hassan Technical Institute.5. Ascertain student satisfaction with the vocational and technical sectors at Bir Hassan Technical Institute.
6. Research Significance
- The significance of the present study lies in the attempt of the supervising authority on the technical education to change the negative directions toward this type of education and associate it with the needs of the working forces and the developmental plans as well as to contribute to the development and enhancement of the alignment of the educational system and its adaptation to the requirements of the national economy.
7. Key Terms
- Development: refers to a strategy which includes the specific use of the internal and external forces in order to realize change. It allows for the high possibility for the development of individuals and for the establishment of collective work and its coherence (Al Feirouzy, 2000, p. 322).Technical education: is the process of the individual acquiring majors and skills, information or directions (values) or the process of providing him with them or developing them for these individuals in a way that leads to the adaptation of his behavior so that he becomes capable of performing a complete work or a group of actions in an adequate way (Atwan, 2011, p. 19).Centers of technical education: are the institutions in which the teaching processes practice majors inside special centers supplied with the necessary tools and equipment for teaching and training and are developed according to the technological development (Odwan, 2006, p. 9).Total quality management: is an administrative system which is based on customer satisfaction and includes an organized approach in order to assure the compliance of the products and services with the specific criteria on a regular basis and is subject to continuous improvement. The competitive advantage: this advantage evolves as soon as the institution discovers new and more efficient ways used by the competitors. It becomes able to embody this discovery in the field once a process of innovation in its wider sense takes place (Porter, 1993, p. 48).
8. Literature Review
- Nasser’s (2018) study entitled “The extent of the availability of the requirements of total quality management in public vocational and technical institutes in Lebanon and their employability by the administration and faculty.”The study aimed at determining the extent of the availability of the requirements for the application of total quality management in the public vocational and technical institutes in Lebanon, their employability by the administration and faculty, as well as the impediments and problems posed. The research, which employed the analytic-descriptive approach, concluded that there is a statistically significant relationship between the educational level and the number of years of experience of the administrative members on one hand, and the extent of availability of the requirements of applying total quality management on the other. The study also concluded that there is a statistically significant relationship between the employment conditions and the education level of the teachers on one hand, and the extent of the availability of the requirements of applying total quality management on the other. It was evident that there is no statistically significant relationship between the number of years of experience of the teachers and the extent to which the requirements of applying total quality management are available.Nasser’s study recommended the necessity of adopting a system for total quality management in the public vocational and technical institutes in Lebanon by the concerned parties and working on formulating each of the mission and vision statements in the light of the requirements of the application of total quality assurance for this education. It also recommended the need for benefiting from the successful international experiences in applying the criteria of total quality management in this domain and working on the periodic and continuous evaluation by conducting on-going field studies and research and launching the program of quality assurance from the sector of the administrative and public services and working on preparing the teaching and administrative staff in order to fit the desired goals.Issa’s (2011) study entitled “The degree of alignment of the outcomes of the vocational training centers of the Ministry of Labor in Gaza Strip with the requirements of the local job market”The study aimed to determine the degree of alignment between the outcomes of the vocational training centers of the Ministry of Labor with the requirements of the local labor market through examining the centers of the study (preparing graduates, graduate competencies, training programs, the proposed majors, field training, and the requirements of the local job market). The researcher mainly employed the descriptive-analytic approach and the study reached the conclusion that there is a statistically significant relationship between each of the number of graduates, the competencies of the graduates, the training programs, the proposed majors, field training, and the requirements of the local job market.The study recommended raising awareness on the importance of vocational training and assigning periodic programs for the trainers in alignment with production technological advancements in production techniques and the needs of the job market, raising the level of curricula by developing them and signing partnership agreements on vocational training between the Ministry and the developed countries in order to benefit from their experiences.Mosdonat’s (2012) study entitled “Education and vocational training, evasion and moving to work”The study aimed to identify the difficulties of moving from academic to vocational education and the causes that underlie the evasion of vocational training. The researchers employed the analytic-descriptive approach, and semi-structured interviews were used as a data collection tool. The study concluded that there are difficulties in adaptation as a result of moving from academic to vocational education, in addition to the existence of problems in learning or the work environment. The study recommended the necessity of raising awareness among the students on the nature of vocational training through the school sessions, moving the students to vocational education when there is no doubt about their psychological state of mind and preparing them by involving them in a transitional period.Hakan and Willkund’s (2013) study entitled “Innovation and total quality management in Swedish higher education institutions: potentials and risks”The current study aimed to provide an overview of the available potentials of the Swedish universities in order to apply total quality management. It also presented the impediments that stand in the way of applying it. The study employed the descriptive approach by employing the educational literature using the desktop research approach. The study concluded that assuring and improving total quality management have become one of the basic future traits of higher education policy in the Scandinavian and other European countries, and it recommended the necessity of working by the system of quality control developed by the National Agency for Higher Education in Sweden and focusing on innovation and continuous improvement of all educational services.
9. Discussion of the Literature Review
- The researcher found that Nasser’s study most resembled the current study in the sense that it discussed the concept of total quality management and the possibility of its application in the technical and vocational education institutions. This study emphasized the necessity of applying total quality management in technical education and vocational and technical training due to its positive impact on the outcomes of vocational and technical training. The current study differs from a number of other studies which discussed technical education since it hasn’t addressed the application of total quality management in the institutes of technical education, for it focused on the significance on the outcome quality and its alignment with the local job market.
10. Comparison with Other Studies
- The current study is different from the previous studies since it proposes criteria for total quality in vocational education in a way that the current study associates the development of these centers with the criteria of total quality management in order to realize the competitive advantage in them.
11. Research Methodology
- In order to realize the objectives of the study, the researcher employed the descriptive-analytic approach that describes the phenomenon which is the subject of the study, presents the analysis of its data and studies the relationship among its constituents and the opinions which are posed around them in addition to the processes they involve and the effects they cause (Al Hamdany, 2006, p.100).Participants in the studyParticipants in the current study include all the students and workers at Bir Hassan Technical Institute, including the professional trainers, instructors and administrators.Tools of scientific researchAs to the method of data collection and analysis employed in order to prove the hypotheses or annul them, the researcher will used the questionnaire since it is one of the most important tools of scientific research. The questionnaire compromises various questions which are related to each other in a way that realizes the objective that the researcher seeks to realize through the problem posed by the research.LimitationsTime limitations: The academic year 2018-2019Place limitations: Bir Hassan Technical InstituteThe purpose of selecting the sampleThe objective of selecting the sample lies in the fact that the research deals with the effect of total quality management on realizing the competitive advantage in the vocational education sector in Lebanon. (Community of the study: Bir Hassan Technical Institute). Therefore, the sample is supposed to include different employees, students and administrative faculty in a purposeful manner so that the results of the research are inferred from those concerned with vocational education and those benefiting from it, given the number representing the cooperating individuals who have responded to the questionnaire since the research has taken this center as a goal for a research which examines the effect of total quality on realizing the competitive advantage. This study has attempted to represent all the traits and characteristics of the original society so that it reaches information that is enough to verify the hypotheses or annul them by focusing on the rich source to collect data.Justification for selecting the topicThe selection of the topic of the effect of total quality management on the realization of the competitive advantage in the vocational education sector in Lebanon is attributed to many scientific and objective considerations.Scientific considerations: Working on changing the false conceptions concerning vocational and technical education and showing its importance to the Lebanese society and its role in development, being the cornerstone which has contributed to the construction of many countries that experienced setbacks in the world wars such as Japan, Britain and Germany.Objective considerations: Lately, the job market has been in desperate need of finding technicians from the various technical specializations in order to be able to rise with the country. The Lebanese public and private institutions have become overloaded with unqualified employees and workers; therefore, this kind of support may support these institutions with specialized powers which would promote the competitive advantage of the national economy and income.
12. Concepts, Goals and Dimensions of the Total Quality Management and the Competitive Advantage
12.1. Part One: Practices of Total Quality Management
- Total quality management practices are represented by the following (Al Shaar & Al Najjar, 2015):1. Focus on the client: Focusing on the client is considered to be the goal sought by any organization through satisfying him, providing the goods and services which fulfill his needs and increase his desire to use the goods or the services. It is defined as one of the dimensions of total quality management which is based on improving the services and goods offered to clients for the purpose of satisfying them.2. Support of the senior administration: Is the solid ground and the main center from which the administrative employees and workers take orders and directions which would improve performance as well as goods and services, for they are considered to be one of the most important requirements of total quality management. The senior administration is responsible for assuming the role of leadership and supervision on the general performance, in addition to building an organizational culture which realizes the goals that the organization aspires to.The support of the senior administration forms a set of decisions and processes that it follows that aim to improve the performance of the employees and develop their abilities, which is reflected on the organizational performance (Ahmed et al., 2014).3. Working in teams: The role of activating team work in problem solving and reaching common solutions through cooperation and activating the role of each individual and listening to their suggestions and making use of their skills. This would guarantee the improvement of the offered services and goods and coming up with new innovative methods which would realize the objectives of the organization (Mathews & Mclees, 2015).4. Research and development: which are considered to be the basis and winning paper that enable the organization to face the surprises and problems that might occur in the future, study the deep dimensions, and plan for problem management and resolutions before any problems even occur. It is defined as a creative act which takes place on scientific bases for the purpose of increasing the scientific and technical knowledge credit which might be used to new applications in the administrative and productive activity (Salim, 2010).5. Training: The organization has to seriously seek to train its employees, improve their administrative and productive processes and develop their tools, methods and human resource abilities so that they would be able to offer the best results for the organization. It is also defined as the reinforcement of the abilities of the employees and the improvement of their performance through training sessions and programs which help develop the team spirit in them (Chang & Chen, 2016).Therefore, the significance of total quality management spring from the fact that it is a comprehensive approach for change, and it is furthest from a system which follows written methods in the form of rules or measures. Furthermore, the commitment of any organization implies, in essence, its ability to change the behavior of quality direction. Thus its application implies that the organization has started considering its activities as a whole as complementary so that quality constitutes the end result of the association between the effort of the employees and the employees in order to realize the desired goals (Al Azzawi, 2005).Quality is the primary basis which distinguishes the service-providing organizations from other organizations due to the significance total management practices and the novelty of their practice by the different organizations. The practices of total quality management help in providing quality for them from the beginning through continuous improvement, that is, through the contribution of the activities and processes as a series of loops associated with each other and relying on quality in completing their tasks (Al Mihawi, 2006).It becomes obvious from the above that the significance of total quality management lies in its aim to realize continuous improvement and development through developing and training the employees in order to increase their ability to solve problems, raise their spirits, and consolidate their sense of belonging to and pride in the organization for the purpose of promoting the reputation of the organization.
12.2. Part Two: The Competitive Advantage
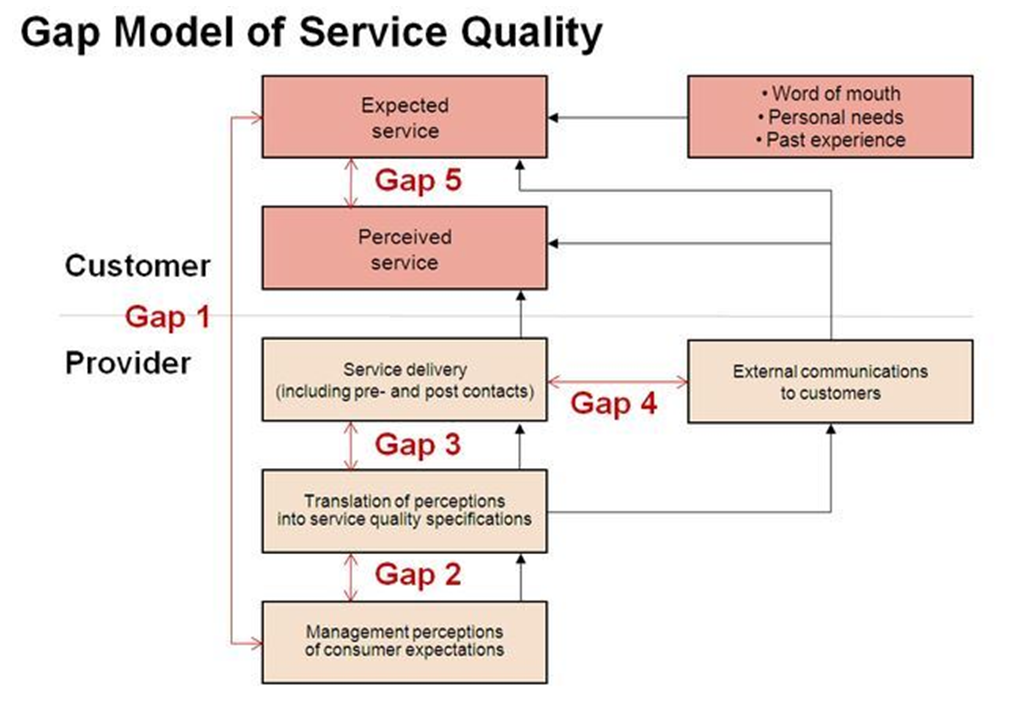
- Anik et al. (2010) defined the competitive advantage as the ability of the sectors to satisfy the needs of the clients in relation to offering high quality services and products for the purpose of satisfying them, in addition to fulfilling the needs of the employees in the organization and providing return on investment in order to realize and improve the quality of services to realize development and growth and reach the desired goals and objectives. In their turn, Baroto et al. (2012) defined the competitive advantage as a set of factors which are directly or indirectly associated with the stability of the organization in the market and as those that comprise active involvement in the economic, administrative and service domains.The competitive advantage is also defined as the superior policy which is followed by the organization in order to compete in the market and realize the best results it aspires to achieve by following specific instructions that would realize the competitive advantage. In this context, Namusonge and Naliaka (2015) defined the competitive advantage as the best tool which aims to discover new and innovative ways to produce and offer goods and services more efficiently than the other competitors in the market so that they can embody these ways and methods on the ground and bring about a process of creation which surpasses its counterparts.As a conclusion, it is agreed that the competitive advantage is the ability of the organization to satisfy the requirements and needs of the customers which affect the stability of the organization of the market and provides it with competitive supremacy in a way that increases its market share and its profit.Second: Dimensions of the competitive advantageThe competitive advantage indicates the central characteristics and competencies as well as the supremacy sides that organizations enjoy and which distinguish it from the competitors. Usually a competitive advantage is believed to exist when the performance rises above average (Salim, 2010). The most important dimensions of the competitive advantage are clarified as follows:Market share: The market share is considered to be an index to identify the type of offered services as well as the size of the sales of the organization in the market. Increasing the market share helps provide a solid ground so that the organization can continue its work normally and efficiently. The smart administration in the organizations seeks to draw and design comprehensive plans in order to collect data about the needs and requirements of the customers, analyze the abilities and capabilities of its competitors as well as the situation of the market and the changes that occur to it, and identify the amount of profit and loss so that it can predict the future and realize the objective and goals that it aspires it to (Alghamdi, 2016).Quality: Quality is also considered to be one of the most important indexes which show the organization the degree to which it has realized the competitive advantage in the market. Quality is defined as a set of complementary activities and processes that the organization adopts as a strategy to improve its performance, reduce the cost and obtain customer satisfaction, and realize the competitive goals of the organization (Yang, Huang, Hsu, & Chen, 2013). It is also defined as a policy adopted by the organization in order to evaluate the quality of the services and the products which agree with and satisfy the customers’ expectations.From the above, it can be observed that improving the quality of the offered services and goods is always reflected on the reputation of the organization and realizes high competitive advantage for it in the market, enabling it to target national and international markets.Third: Characteristics of the competitive advantageThe desired benefits of applying the competitive advantage require focusing on the outcomes, the existence of harmony and concentration in every organization, in addition to the presence of the domain of leadership and goal stability and the domain of developing and involving individuals (Almilijy, 2012). The characteristics of the competitive advantage are represented in the following:1. It should be constant, in the sense that it should be pioneering in the long run.2. It is characterized by being proportional in comparison with the competitive organizations and the time period within which this competitive advantage is realized.3. Keeping pace with the developed modern and technological updates in the abilities and resources of the organization.4. The competitive advantage should be in line with the set objectives of the organization in order to realize the desired outcomes.5. Adopting the policy of continuous change which seeks to develop the organization and improve performance.6. The competitive advantage is characterized by its ability to attract the skilled employees and those who enjoy exceptional skills and abilities as well as the creative employees who are able to create new plans and policies for the organization.7. Flexibility in designing and applying plans commensurate with the changes that take place.From the above, it would be safe to say that the competitive advantage is characterized by being flexible with a long term vision and that tt designs innovative plans and designs an accurate approach for the organization. It is also characterized by keeping pace with the modern technologies and techniques so that the organization can realize the goals and the objectives it desires.Fourth: Sources of the competitive advantageThe sources of the competitive advantage of the organization are many. The following are some (Mounir & Nehme, 2008):Creativity: Creativity is considered to be a main source for the realization of a high competitive advantage in the dynamic environment as well as a central point in the strategy of organizations. With the massive development in the field of technology and communications, innovation has become a basic pillar and is considered an important dimension in the strategic performance. Therefore, it has become vital that the organizations seek to adapt with the external environment and respond to the organizational changes imposed on them by powerful competition for the purpose of realizing a sustainable competitive advantage (Al Wahab, 2012).Time: Time is considered to be one of the most important sources which realize a big competitive advantage for the organization, for time is equivalent to money. Furthermore, good management of time contributes to the reduction of the planning cycle, raising the performance level, and developing and improving its competence. The significance of time is highlighted in the ability to design and draw strategic plans and in managing the hierarchy of the organization, thus affecting the reputation of the organization (Sachitra et al., 2016).Knowledge: Knowledge is one of the most important strategies of any organization which desires to invest in the competition in the competitive market, to reach success, and discover new more efficient methods than those used by the competitors. It also helps transform the important data and skills that the organization owns and which it considers necessary for the different administrative functions as problem resolution, decision making and strategic planning (Hamshari, 2013).The organization can build a competitive advantage through its strategic choices and relationship with others.Conclusion: This chapter has presented an overview of total quality management and the competitive advantage in the institutions, in addition to the significance of the practices of total quality management. The aim is to realize continuous improvement and development through developing and training the employees for the purpose of increasing their ability to solve problems and improve moral spirits in order to realize the competitive advantage, eventually promoting the reputation of the organization. Institutions and organizations should adopt international criteria of quality, recognize the actual reality of those institutions and centers, and collect data and analyze it in order to identify the existing gaps for the purpose of removing the impediments to achieving the competitive advantage.Fifth: Measuring customer satisfaction by using the model of Servqual’s criteria (Zeithaml)The public organizations face a lot of difficulties in achieving customer satisfaction, which is affected negatively or positively with previous experiences and the impression created by the individual. The biggest reason why people do not satisfy the customer in a distinguished way is that they do not have enough information about those they need to satisfy, when they are unable to do it. SERVQUAL is a tool and a method to measure the difference between the expectations of the customers with the service and the service provided to them (Zeithaml et al., 1990). SERVQUAL has attracted a lot of attention and has been widely used since it was first designed by Zeithaml in 1985. Some developments were made to it until 1998 and were based on five dimensions in which light the customer evaluates the quality of the service: the tangible equipment, facilities, individuals and objects; reliability and validity in dealing; speed in response; trust in dealings and caring for customers.Figure 1 below shows the SERVQUAL model to measure the gap between the expected and offered service
 | Figure 1 |
13. Concepts, Characteristics and Criteria of Total Quality Management in Education and the Evolution of Vocational and Technical Education in Lebanon
13.1. Part One: Concepts, Characteristics and Goals of Vocational and Professional Education
- Vocational and technical education has become a tool for realizing sustainable development, growth and rising with the economy and facing challenges in many countries of the world for the last centuries. Vocational and technical education has included various concepts, characteristics, goals and criteria in order to provide skills and knowledge sought by the employers to satisfy their needs.First: The concept of vocational and technical educationThe vocational and technical education agreement adopted by the general conference of the UNESCO in its 25th session in 1998 stated that all forms of levels of the teaching process which includes, in addition to the general knowledge, the study of technology and the related sciences, acquiring the scientific skills, know-hows, attitudes and cognitive skills related to the vocational practices in the economic and social life sectors (Nasser, 2018, p. 164).Second: Characteristics of vocational and technical educationOne of the most significant policies and characteristics of technical and vocational education is the availability of the multiple skills instead of just mastering one skill or specialization so that the individual would be able to deal with the small electronics, the computer, the automatic machines and the different types of management. He should also be able to read data and process them fast, use specific languages in reading them, take the right decisions and discover mistakes and correct them (Nasser, 2018, p. 167).Third: Goals of vocational and technical educationVocational and technical education forms one of the basic pillars for the economic and social growth of any country. A lot of countries have taken particular interest in this type of education and set strategies and educational and training policies in order to realize a number goals, some of which are: helping the learners acquire skills and knowledge; supporting economic growth in the country; ensuring the integration of the marginalized groups in the social and economic life; increasing productivity and self-confidence; boosting the moral spirit of the workers; and improving the job satisfaction and the beneficiaries. Some of the goals are preserving the equipment and maintaining them as well and developing the sense of belonging and self-realization in order to keep up with the technological development and be ready for the era of globalization which is nominated for expansion unequivocally (Alshoubasy, 2019, p. 23).Fourth: Total quality management for developing the teaching methods in the educational institutionsThe institution works on providing a specialized center concerned with developing the abilities of the faculty. It should have a clear vision of the data, knowledge and required skills for the faculty and technicians in order to be able to offer them to the students in the form that achieves the efficiency of the teaching-learning process. The following conditions should be taken into consideration:1. The educational organization has a clear vision of the level of data and knowledge required to fit its future vision.2. Providing the suitable learning halls, laboratories and workshops and equipping them with all the educational means.3. Providing appropriate training in order to develop the skills and abilities of the faculty members and technicians.4. Providing the specialized and modern libraries which would satisfy the needs of the students as well as the faculty members.5. Providing the training programs to use the learning sources for the students and instructors.6. Providing the ethical rules/controls to use the learning resource centers (computers, the Internet, email, chat) (Mohamad, 2015, p. 14).Fifth: Quality criteria in the educational organizationThe next eleven key points are considered to be a guide for the educational organization in order to identify the necessary conditions for each key point, in addition to the specific practices of each key point in order to conduct the self-evaluation process1. The vision, mission and goals of the educational organization2. Leadership and administrative organization3. Resources4. Faculty members5. Students6. Student services7. The academic programs and teaching methods8. Scientific research9. Social service10. Evaluation11. Educational ethics (Mohamad, 2015, p. 12).Sixth: Models of total quality criteria in vocational educationLately, pioneering international organizations have emerged and assumed the responsibility of the process of stimulating the institutions and pushing them towards institutional excellence by designing models which serve as a guide for institutions. Some of these are (Al Daradika, 2002, p. 49):Krosby’s criteria: These include four givens for total quality management: First, defining quality, which means matching the criteria; second, a system for achieving quality and means a rational system to prevent flaws; third, the performance criterion which is the zero defect; and fourth, the quality cost index which confirms the cost of non-conformity, repeated work, reserve, tests and examination (Al Tani et al., 2009, p. 226).Baldridge’s criteria: This system is adopted in order to control the quality of 11 basic values related to education. It includes 28 secondary criteria for quality education which are integrated in 7 sets, including leadership, data and analysis, procedural and strategic planning, managing and developing human forces, educational management, performance of the educational institution and students’ results, and student satisfaction as well as the satisfaction of funders of the educational system. Some of these are criteria of total evaluation, the model of the European institution for quality management for excellence in higher education, and the model of the Accrediting Council for Continuing Education and Training (ACCET) (Baldridge’s prize for excellence, 2014).Seventh: Measuring customer satisfaction by using the model of Servqual’s criteria (Zeithaml)The public organizations face a lot of difficulties in achieving customer satisfaction, which is affected negatively or positively with previous experiences and the impression created by the individual. The biggest reason why people do not satisfy the customer in a distinguished way is that they do not have enough information about those they need to satisfy, when they are unable to do it. SERVQUAL is a tool and a method to measure the difference between the expectations of the customers with the service and the service provided to them (Zeithaml et al., 1990). SERVQUAL has attracted a lot of attention and has been widely used since it was first designed by Zeithaml in 1985. Some developments were made to it until 1998 and were based on five dimensions in which light the customer evaluates the quality of the service: the tangible equipment, facilities, individuals and objects; reliability and validity in dealing; speed in response; trust in dealings and caring for customers.Eighth: The significance of the self-evaluation processThe self-evaluation process should be a central part of the annual planning, for this helps in studying performance and identifying the weaknesses and strengths, in addition to the requirements of achieving continuous progress and development, and developing the database. Consequently, it includes the following sides: the financial measures, measures of worker satisfaction, and measures of customer satisfaction (Laskel, 1998, p. 258).Ninth: Customer careSatisfying customer needs is the best method to survive and be able to compete, and the public administration has to repel the traditional bureaucratic intellect which the customer considers the person in need. This need can only be satisfied through the public administration, and consequently there would be no need for creation where there is no competition, and the service would be acceptable by the client whatever form it takes (Osborne & Garbler, 1992, pp. 164-166).Tenth: Measuring customer satisfaction as an introduction to measuring performanceThe suggestion that has become almost acceptable for most researchers the suggestion in total quality management is that satisfying the customers’ needs ensures their satisfaction. It is also doubtless that the continuous attempt at recognizing the extent of the quality of the offered service based on the extent of the satisfaction of the service receiver makes us more capable of being constantly knowledgeable of the level of the offered service and the extent of the customer’s satisfaction with it, and this continuous measurement can be considered a system for measuring the quality of the service (Capezio & Morehouse, 199, p. 38).Eleventh: Impediments to total quality management in the educational institutionsWhen applied in the educational institutions, the total quality management system faces many impediments, some of which are: the non-conformity of some parts of the total quality management system with the reality of the educational institution, centralization in policy and decision making, the insufficiency of the trained and qualified cadres in the domain of total quality management, the poor equipment and financial system, in addition to the lack of conviction in obtaining feedback from the students and graduates (Mansour, 1995, p. 161).
13.2. Part Two: The Evolution of Vocational and technical Education in Lebanon
- Vocational and technical education in Lebanon has passed through many historical periods before it finally settled on its current situation, for since the nineteenth century, this type of education has been known in Lebanon when one of the foreign missionaries established a center for teaching upholstery in 1863, the lead of which many missionaries followed later. In Beirut, the first vocational school was the Sanaea’ and Arts Institute, which was established by the Ottoman Empire in 1905 (Abu Ghazaleh, 2019). In 1943, it was still believed that vocational education was just for the groups who are unable to pursue their academic learning; however, after this year, the government started to give attention to this education, so it established 7 schools at the end of the 40’s, when the total number of students reached 954, and the number of graduates reached 638 at the end of the 50’s. The period stretching from the beginning of the 60’s till 1975 was known as the period of organization of vocational and technical education since most of the acts were issued during this period, the most significant of which was the organizational act no. 9193 dated 28/12/1962. Nine schools were also established in the different Lebanese regions, so the number of schools and institutes reached 18 schools before 1975 and included 5354 students in the different Lebanese regions (Al Shoubasy, 2019).At the beginning of the 80’s, and despite the raging civil war, the vocational and technical education sector entered the battlefield of the process of curricula modernization in cooperation then with the Educational Center for Research and Development, the UNESCO and the UNDP. At the end of the 80’s, the private administrations of vocational education were not able to apply the system of training cycles which were covered by the modernization process for two reasons: the first was related to the security circumstances which prevailed the country, and the second had to do with the inability of the educational institutions to bring about a big change in their educational systems without being preceded by training processes for their administrative and teaching faculties on the new system. In 1995, the Educational Center for Research and Development adopted a new system for education in Lebanon, yet this system remained deficient in comparison with the developed countries.First: The reality of the vocational and technical education in LebanonThis type of education in Lebanon should be considered as a tributary for the national economy and the engine for the wheel of development. This is why we need to establish the culture of vocational education that we lack and to spread it in the society as a whole (Kazzi, 2019).Second: The structure of the current system of vocational and technical educationVocational and technical education is officially divided into specialization domains and levels and is branched into two specific systems: the domain of vocational education, and he domain of technical education with 146 majors at all levels, including the industrial majors, medical and health majors, scientific and engineering majors, educational and social majors, financial and business majors, touristic majors, and management and information system majors.Third: The problems of vocational and technical education in LebanonVocational and technical education in Lebanon is facing a lot of impediments which stand in the way of realizing total quality management in this education. These are: the multiplicity of the parties which care for and sponsor vocational and technical education, the existence of different interpretations, the absence of effective coordination among the concerned parties, negligence and indifference of those in charge and the whole Lebanese society, old curricula, successive financial crises, deficiency in vocational orientation, the lack of a unified book, etc,… (Nasser, 2018, p. 200). Finally, there is the fact that the students who have earned the (BT), (TS) and (BP) face the problem of pursuing their higher education later on.ConclusionGiven that the current age is that of revolution in all domains of science, information and telecommunication, innovation and inventions in all fields, it is time for the vocational education institutions to adopt the philosophy of quality education or total quality management, which imposes on those concerned the adoption of international criteria for quality in vocational education in order to realize the competitive advantage and remove the impediments which stand in the way of realizing the desired goals.
14. A Field Study on the Effect of Total Quality Management on Realizing the Competitive Advantage in Vocational and Technical Education
14.1. Part One: Research Tool and Participants
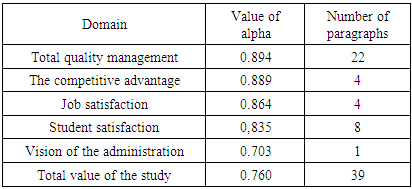
- This research aims to identify the reality of the application of the dimensions of total quality management in Bir Hassan Technical Institute and its relationship with the degree of realizing the competitive advantage in vocational education. First: Participants A total of 80 questionnaires were distributed on the participants who represented the administrative and teaching faculty as well as the students at Bir Hassan Technical Institute. 19 questionnaire were lost and the responses for the remaining 61 ones (76%) were entered into SPSS for analysis.Second: Likert scale and relationshipsIn order to show the results of data collection and analysis, we employed the Likert scale, which is considered to be a tool for measuring behaviors and preferences. In order to test the hypotheses, the Spearman test was used.Third: Reliability and validityIn order to ensure the ability to use the results of the research, we employed Alfa Cronbach’s test. This index is considered weak if its results are less than 60%, acceptable between 60% and 70% , good between 70% and 80%, and excellent if it is beyond 80%. After using Cronbach’s Alpha on the dependent and independent variables (total quality management, the competitive advantage, student satisfaction, teacher satisfaction), we found out the following:
|
14.2. Part Two: Description of the Basic Variables of the Research and Analysis of Relationships among Variables
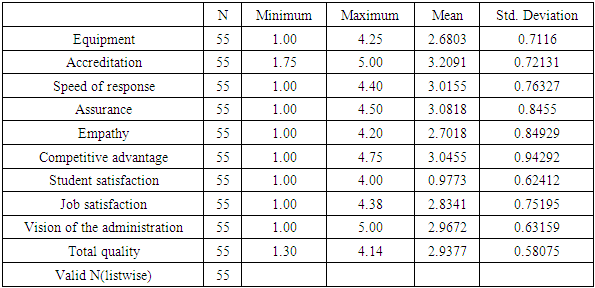
- This part focuses on describing the main variables of the study: 61 students, administrators and teachers participated as follows: 44 students; 3 administrative employees; 2 supervisors; and one directorDescription of the principles of total quality management: This part includes a description of the dimensions of total quality management represented by accreditation, tools and equipment, speed of response, assurance, and empathy as follows:
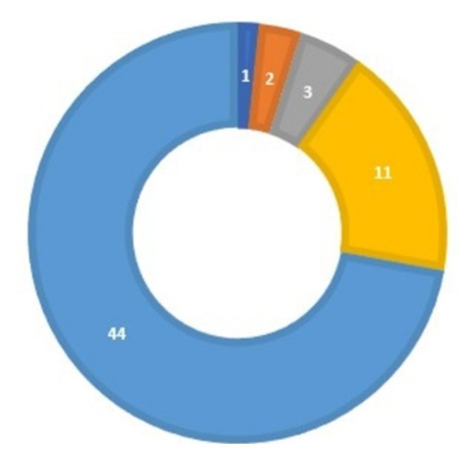 | Figure 2. Capacity of the research sample members |
|
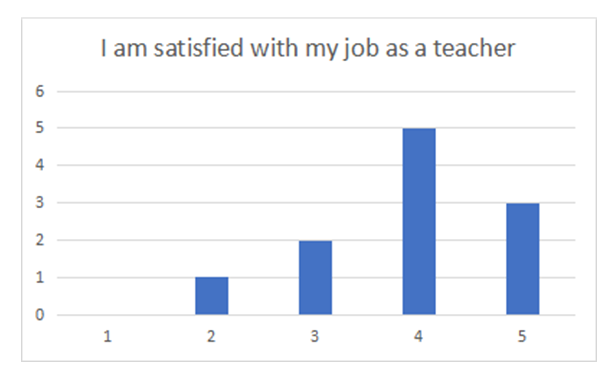 | Figure 3. Teacher job satisfaction |
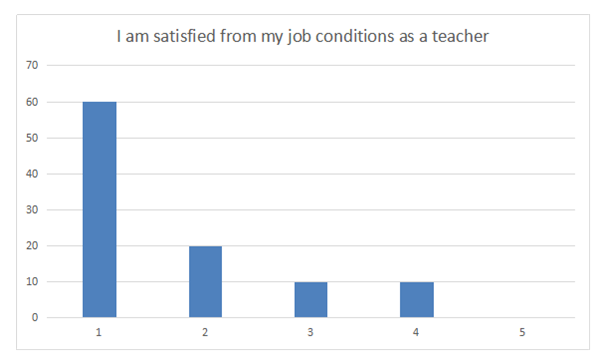 | Figure 4. Teachers’ job conditions satisfaction |
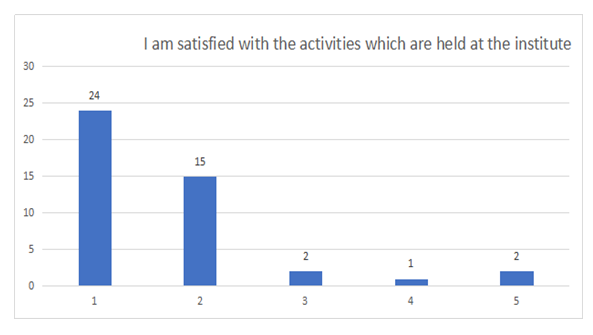 | Figure 5. Satisfaction towards activities held at the institute |
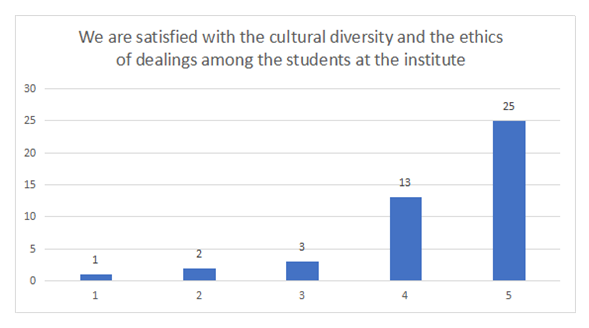 | Figure 6. Cultural Diversity and Ethics Satisfaction |
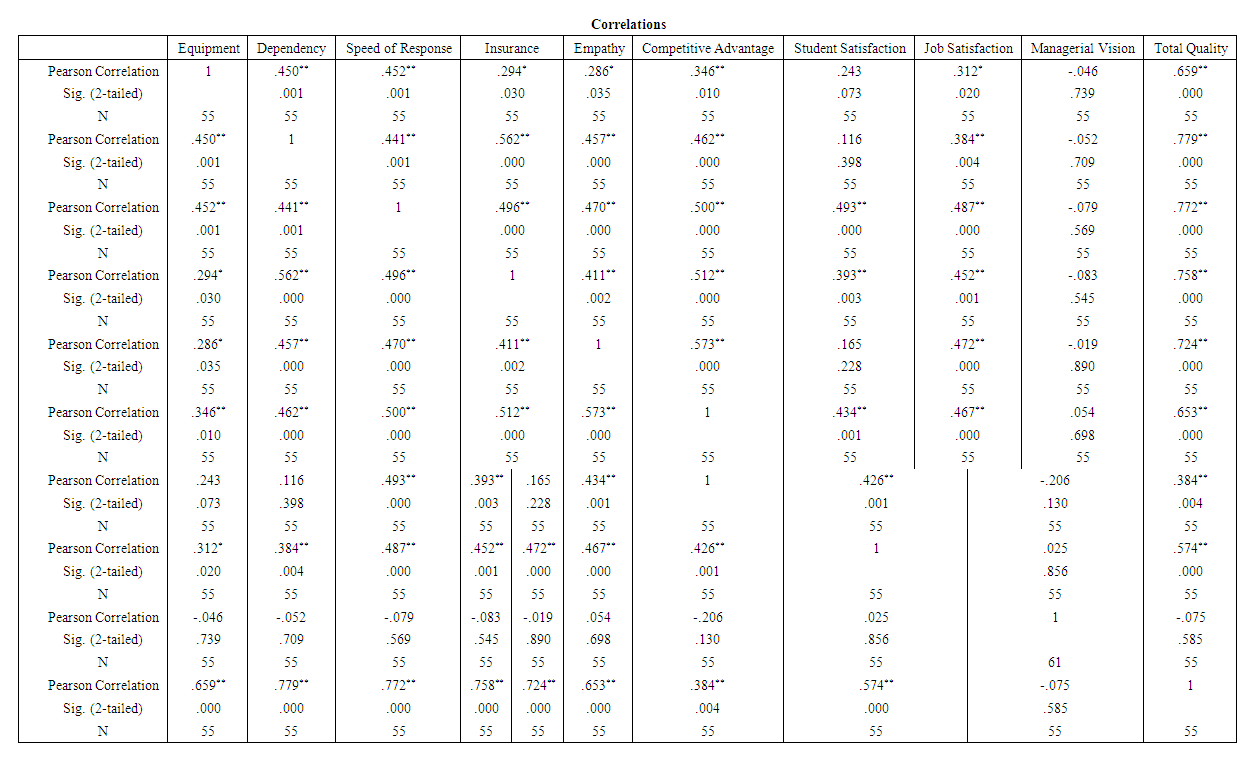 | Table 3. Correlations among the variables of the study |
14.3. Part Three: Analyzing the Correlations and Testing the Hypotheses
- For this purpose and in order to test the set of hypotheses, we used the Simple Linear Regression Analysis which tests the effect of each independent variable on the dependent variable. We also used the ANOVA test in order to test the significant differences of the variables of the demographic study. The results of the analysis of the questionnaire data at alpha level 0% and freedom levels 54 revealed the following:Hypothesis 1: There is a statistically significant positive correlation between the application of total quality and realizing the competitive advantage**The effect is statistically significant at α ≤ (0.05)
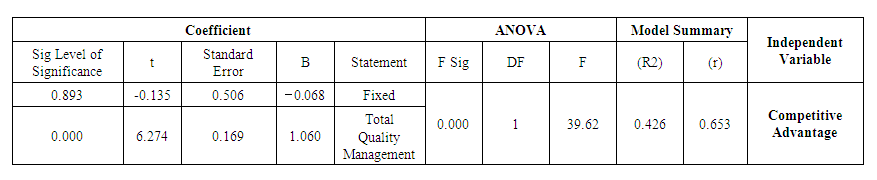 | Table 4. ANOVA Test – Hypothesis 1 |
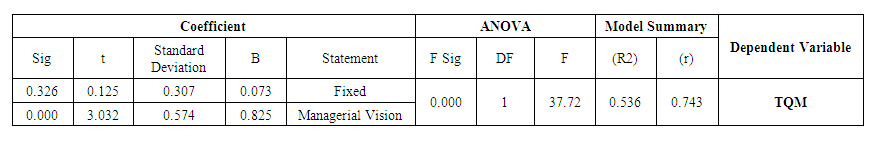 | Table 5. ANOVA Test – Hypothesis 2 |
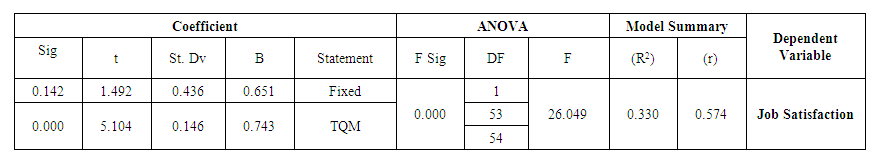 | Table 6. ANOVA Test – Hypothesis 3 |
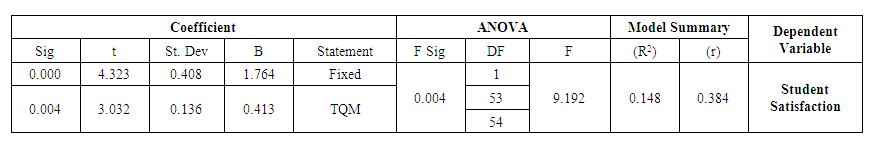 | Table 7. ANOVA Test – Hypothesis 4 |
15. Conclusions
- After conducting a survey in the institute, many problems became evident for us. In addition to the absence of any guide, there institute suffers from organization and the lack of any significant activities. After conducting many statistical tests, and in the light of the description of the research variables and analysis of the relationships, we came to the following conclusions:• The administration suffers from the existence of many impediments which stand in the way of applying total quality management.• Most students believe that the institute suffers from a poor ability to realize the competitive advantage.• The existence of impediments which prevent the application of total quality management leads to a weakness in realizing the competitive ability.This confirms the validity of the first hypothesis.• The institute lacks the existence of this vision according to the opinion of the participants in the survey, despite that having a clear vision might help the institute realize its goals, improve performance of the employees, and develop the work.• The lack of a clear vision at the institute is reflected negatively on the ability to apply the criteria of total quality.This confirms the validity of the second hypothesis.• The teacher, in general, is satisfied with his job as a teacher, but he is dissatisfied with the circumstances of his job and does not get all of the important things for him from his job as a teacher.• The inability to apply the criteria of total quality leads to poor teacher satisfaction, especially in relation to the provisions offered to them.This confirms the third hypothesis.• We notice that a high percentage of the students who are satisfied with the cultural variance and the ethics of dealings among the students at the institute. This might be due to the presence of students from different nationalities at the institute and to the good ethics among them.• The inability to apply the criteria of total quality affects student satisfaction, for, in general, the students are dissatisfied with the content of the educational curricula and with the quality and variety of the subjects which are taught at the institute.This confirms the validity of the fourth hypothesis.Results and recommendations• The institute should seek to check the application of the principles of total quality management. And in order to do that, the institute should be equipped with modern and up to date equipment. It should also be credible in its dealings and assure empathy among the workers in the institute and the students. The provision of competencies and incentives for the teachers might help in encouraging them to apply these principles.• The administration of the institute should work on implementing the decisions which it takes concerning the improvement of the performance in order to realize total quality management and achieve the competitive advantage.• The administration of the institute should work on developing a clear vision of the future, which would enable it to realize its goals, and it might seek the help of some competent teachers to help realize this goal.• The institute should work on providing efficient communication channels with the students in order to ensure their satisfaction with the content of the educational curricula and with the quality and variety of the subjects taught at the institute.• The senior administration should work on teacher selection and training with extra care by conducting specialized training sessions in order to ensure the provision of an excellent educational service; however, this has to be coupled with good provisions for the teachers to ensure their satisfaction.Conclusion of the studyVocational and technical education plays a positive role in human development, and it is completely distinct from theoretical academic education. Its significance lies in the fact that it prepares the human resources so that they are capable of facing the international technological developments. It also has an efficient and a special role in increasing productivity and realizing the competitive advantage. However, keeping pace with the modern technology has moved vocational education from the era of traditional education into that of modern education through applying total quality in education. Vocational and technical education has made important and special steps in most of the developed countries since it has contributed to the rise of those countries and to their rapid and efficient progress, whereas most Arab vocational and technical institutes, one of which is Lebanon, rely on extremely centralized and bureaucratic systems which have led to losing the opportunities of growth and to the non-compliance of the educational curricula and vocational and technical training with the needs of the job market and the realization of the competitive advantage. These countries are affected by the inferior outlook at the vocational and technical education and contribute to the refraining of the students from enrolling in this type of education, which has been observed by the existence of a small number of students at the institute, which is the subject of the current study.Through this study, we have found that vocational and technical education in Lebanon, for the most part, still lacks planning and coordination, with the main problem lying in the educational curricula and the way they are applied, in addition to the means and their variety in applying the subjects and teaching them. Vocational and technical education in Lebanon also suffers from the dissatisfaction of the teachers and administrators with their job circumstances, which can form a dysfunction and a barrier to the provision of quality education. We have sought to identify most of the significant and critical bases which realize the ability to prepare the students and teachers to accept every novel addition to the educational process in order to realize the competitive advantage through activating total quality management.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- I wish to acknowledge the value of the contributions from the secondary research sources in this article, in addition to the support received from Our Professors in the University.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML