-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Management
p-ISSN: 2162-9374 e-ISSN: 2162-8416
2020; 10(2): 55-69
doi:10.5923/j.mm.20201002.03
Received: Aug. 28, 2020; Accepted: Sep. 22, 2020; Published: Oct. 15, 2020

Challenges of Entrepreneurs Live with Disabilities to Establish and Expand Their Own Business in Case of Guraghe Zone, Ethiopia
Dereje Kefale, Fuad Hussein
Lecturer at Wolkite University, Wolkite, Ethiopia
Correspondence to: Dereje Kefale, Lecturer at Wolkite University, Wolkite, Ethiopia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Disability is the major impediments of most disabled peoples to participate in entrepreneurial activities and being self-employed. This may also linked with major challenges like start-up capital, lack of entrepreneurial skill, socio-cultural problems and personal attitude are the barriers which will affect them to participate in entrepreneurial activities. Therefore, this study was aimed to identify and examine the major challenges of persons live with disabilities to start and expand their own business. In undertaking the investigation four independent variables was used (Start-up capital, personal attitude, socio-cultural issues and entrepreneurial skill) and one dependent variable (Entrepreneurial success). To conduct the study both qualitative and quantitative research design was employed. By using simple random sampling method 372 samples was drawn from seven selected clusters and questionnaires were distributed and from these only 326 questionnaires were returned. And the analysis was made by using descriptive statistics like mean and standard deviation and inferential statistics like correlation and regression. From the result of the analysis the major challenges of disabled peoples are identified: lack of start-up capital, personal attitude, and lack of entrepreneurial skill as the major problems which significantly affect the disabled peoples to be successful in business. Finally, it is suggested that the government, financial institutions, disabled peoples and other concerned bodies should eager to help and simplify those challenges.
Keywords: Disability, Disabled entrepreneurs, Entrepreneurial success
Cite this paper: Dereje Kefale, Fuad Hussein, Challenges of Entrepreneurs Live with Disabilities to Establish and Expand Their Own Business in Case of Guraghe Zone, Ethiopia, Management, Vol. 10 No. 2, 2020, pp. 55-69. doi: 10.5923/j.mm.20201002.03.
Article Outline
1. Background of the Study
- Disability is a challenging, multifaceted and argumentative problem in the world. As a result many researchers and writers find out and acknowledged different challenges of disabilities. The impression of disability is mostly raised from society regarding the disabled peoples beside to their mental attitude. The society by itself convinces them as they are disabled. Disability results from the interaction between persons with impairments and attitudinal and environmental barriers that hinder their full and effective participation in society on an equal basis with others”. Defining disability as an interaction means that “disability” is not the desire of an individual. The interaction of disabled peoples with the society can be improved through minimizing or avoiding the challenges which impede them in their life (World report, 2011). According to Yeo (2001), disability can be defined as a complex system of social restrictions imposed on people with impairments resulting in a denial of rights and equal opportunities.Due to their disability most disabled peoples are not employed. For that matter their matter is depend on family or other peoples. According to (Thurik and Wennekers, 2005), self-employment is very important for physically challenged peoples from different rules and regulation perspectives of a country, acknowledging the way running own business among economically disadvantaged groups, providing equal employment opportunity with the non-disabled peoples and avoiding stigma and discrimination. According to Jones and Latreille (2005), it is known that disability affect disabled peoples negatively to be employed and earn an income to survive. It has been suggested by Harper and Momm (1989) that people with disabilities make natural entrepreneurs since having a disability can also be a stimulus for independent problem-solving and innovation.According to Ethiopian Center for Disability and Development (ECDD), 2019, study conducted on the title 'Quality of life of persons with disabilities in Southern Nations Nationalities and peoples region, Ethiopia, more than half of disabled peoples are unemployed. Even the employed peoples are some employed in government office, some wage employed and only a few are self and group employed. As a result most disabled peoples are in great challenges: lack of money to meet their needs, to participate in social life, to educate, to get health care and lack of awareness from where the finance or loan is sourced to start their own business. As a result, most disabled peoples are not participated in entrepreneurial activities. Therefore, this study aims to identify the major challenges which may affect disabilities to participate in different entrepreneurial activities in Ethiopia by taking Guraghe Zone as a case area. Statement of problemStarting a new venture is full of difficulties whether an entrepreneur is non-disabled or disabled. Several challenges to be entrepreneur are confronted by both non-disabled and disabled person may be too difficult to overcome, including: access to start-up capital, interaction with the benefit system, and finding out about and accessing appropriate training and advice. In addition, disabled people report a lack of understanding and even active discrimination on the part of financial institutions, business consultants, and the employment service. Personal power and financial resource are key input factors for the start-up success and growth of firms. Especially in the case of micro and small enterprises, an individual, usually the owner-manager, must have both technical and managerial skills (Neuberger and Rathke, 2009), but also needs the financial capital to finance start-up costs, necessary investments in equipment, and so on. Harper and Momm (1989) emphasized access to capital and lack of customers as the two major barriers to self-employment by people with disabilities.In Ethiopia, which is the main target of this study, the source of disability is wrongly perceived as a curse; and a consequence of a sin or wrong doing or evil deeds by parents, ancestors, and the persons with disabilities themselves or supernatural presence. Such thinking can predominantly be ascribed to the traditional (moral) model which associates disability with sin, shame and feeling of guilt (Tirusew, 2006, cited by Yared, 2008). This is historically the oldest model resulting in general social rejection and ostracism, generating a feeling of self-hatred, dependency and hopelessness (Yared, 2008). Similarly, a study on ‘The Development of Special Needs Education in Ethiopia’ by Chernet and Endrerud (2004) showed that despite the large number of people with disabilities, the provision of special education and other services is extremely limited. The inaccurate understanding of disability and its relationship with moral wrong doing forces parents to hide their children with disability at home, to be ashamed of them and to undermine the child’s potential to learn and lead an independent life (Tirusew, 2006). So those studies show the low access of education for disabled peoples can be taken as a factor to be dependent. So these all social and cultural problems may challenge the peoples live with disabilities to run their own businesses. Even if such different studies conducted on the challenges of entrepreneurs and small business enterprises in Ethiopia and also many studies conducted on the nature of disability and social acceptance but there is no any study conducted related to entrepreneurs live with disabilities. Therefore this research aimed to identify the major factor which may challenge the disabled peoples to establish and expand their businesses in Ethiopia, by taking Guraghe Zone as a case area. Research QuestionsThis study was conducted to answer the following basic research questions:1. What is the current state of peoples with disabilities in self-employment?2. What barriers do people with disabilities face to start and expand a business? 3. What is the impact of entrepreneurial challenges has on the success of entrepreneurs live with disabilities? Objectives of the studyGeneral ObjectiveThe general objectives of the study were to identify the major challenges which affect the physically disabled entrepreneurs to establish and expand their own businesses.Specific objectivesØ To evaluate the current state of the disabilities on self-employment. Ø To identify the major barriers disabilities face while starting and expand businesses.Ø To examine the impact of entrepreneurial challenges has on the success of disabilities.Scope of the studyEntrepreneurship incorporates wide areas of business and managerial practices. Though, it is challenging and uncontrollable to conduct the study in all areas that reviews entrepreneurship in terms of time, finance, and research manageability. Therefore, the scope of this study is delimited to specific context that is the challenge of peoples live with disabilities to start and expand their own business. Specifically the independent variables inculcated in the study are start-up capital, socio-cultural issues, personal attitude and entrepreneurial skills and the dependent variable, entrepreneurial success. Beside to this the study delimited to the case areas in Wolkite, Butajira, Enemur and Ener, Abeshge, Ezya, Cheha and Meskan Woreda's only due to the efficiency of cost, time and difficulty to cover wide area. Significance of the studyInvestigating challenges of disabled entrepreneurs to start and expand business in this complex and dynamic world is believed to have the following importance’s to the academicians, policy makers; and specifically, for the disabled peoples.Specifically this study is intended to address the following important point as:Ø It insight the disabled entrepreneurs the factors which may challenge them in business world.Ø It helps as an input to provide the governments strategic policy in the future.Ø It helps to make further research and It can be a source of data for other researchers on related topic.
2. Literature Review
- Entrepreneurship and DisabilityDefinition of entrepreneurship and EntrepreneurEntrepreneurship is defined in different ways by different scholars. Entrepreneurship is the process of finding and recognizing opportunities in business and marketing environment, organizing and planning resources to use this opportunity and using the resources to get profit and maximize wealth. It comprises producing capital through using business resources to establish and run business (Peter Drucker, 1984). On the other hand, entrepreneurship is defined as the processes through which individuals become aware of business ownership then develop ideas for, and initiate a business. Entrepreneurship can also be defined as the process of creating something different and better with value by devoting the necessary time and effort by assuming the accompanying financial, psychic and social risks and receiving the resulting monetary reward and personal satisfaction. In this case an individual should come up with something different and better in order to the named as entrepreneur. And also entrepreneurship is the art of identifying viable business opportunities and mobilizing resources to convert those opportunities into a successful enterprise through creativity, innovation, risk taking and progressive imagination.Entrepreneurship is a practice and a process that results in creativity, innovation and enterprise development and growth. It refers to an individual’s ability to turn ideas into action involving and engaging in socially-useful wealth creation through application of innovative thinking and execution to meet consumer needs, using one’s own labor, time and ideas. Engaging in entrepreneurship shifts people from being “job seekers” to “job creators”, which is critical in countries that have high levels of unemployment. It requires a lot of creativity which is the driving force behind innovation (Bidyadhar Behera, 2014). In general, the process of entrepreneurship includes five critical elements. These are: The ability to perceive an opportunity, the ability to commercialize the perceived opportunity i.e. innovation, the ability to pursue it on a sustainable basis, the ability to pursue it through systematic means and the acceptance of risk or failure. The term entrepreneur is mostly used interchangeably with entrepreneurship, but they have defined differently by many authors and researchers. An entrepreneur is any person who creates and develops a business idea and takes the risk of setting up an enterprise to produce a product or service which satisfies customer needs. An entrepreneur can also be defined as a professional who discovers a business opportunity to produce improved or new goods and services and identifies a way in which resources required can be mobilized. An entrepreneur is an individual who: has the ability to identify and pursue a business opportunity; undertakes a business venture; raises the capital to finance it; gathers the necessary physical, financial and human resources needed to operate the business venture; sets goals for him/herself and others; initiates appropriate action to ensure success; and assumes all or a major portion of the risk (Bidyadhar Behera, 2014).The role of entrepreneur in EconomyEntrepreneurship in recent times has become an important area of study. It is considered to be a solution for creating wealth, generating employment and providing new and better goods and services (Bidyadhar Behera, 2014). Developing the spirit of entrepreneurship among the young has become vital because the government cannot provide jobs for all kinds of unemployed youth and the corporate sector will provide limited jobs only to the best and that too without any job security. Entrepreneurship is simply finding new opportunities to do things better and then seizing the opportunity. With changes like globalization, deregulation, open competition and technological change taking place, our society is becoming an entrepreneurial society. In an entrepreneurial society, individuals face a tremendous challenge. An entrepreneur is one who innovates and initiates something new. But this may not always be true, practically in less developed or developing countries, where an entrepreneur is often an imitator. Jeremy Boissevain (1997) in his article “Small European Entrepreneurs” mentioned that Entrepreneurs are those who manage enterprise for the pursuit of profit, in the course of which they innovate. And successful entrepreneurs are usually regarded as having self-confidence, achievement orientation, perseverance and resourcefulness. They must be willing to accept risk, to work hard and to save. They must also possess the ability to network – that is, to maintain and cultivate a range of useful contacts. Sometimes, entrepreneurship has been considered as a quality which can be acquired by an individual and is a function of various factors like psychological, socio-cultural, economic etc.Persons with disabilities include those who have long-term physical, mental, intellectual or sensory impairments which, in interaction with various barriers, may hinder their full and effective participation in society on an equal basis with others. Disability has been predominantly defined as having any enduring physical, mental, intellectual or sensory impairments which affects individuals’ interactions and activities and hampers their effective and equal participation in society as other people (Renko et al. 2015). Persons with disabilities are often discriminated peoples with respect to social and economic integration, and this is mostly practiced in developing countries (ILO 2002). Many studies suggest that persons with disabilities frequently are discriminated against which often means that these persons are among the poorest and most vulnerable members of society (Beisland and Mersland 2014). People with disabilities have long been struggling with getting employment and on the job various challenges, barriers and constraints all over the world (Hwang and Roulstone, 2015). Particularly, disabled people in developing countries encounter more serious employment and workplace challenges and difficulties (Namatovu and Dawa 2012). Scholars attributed these challenges mainly to the lack of a well-established legal and regulation system for disabled people compared to the strong laws that protect disable's rights including their employment in other countries such as the U.S (Moore and Kornblet 2011). Entrepreneurship is a feasible employment option for people with disabilities (Shaheen, 2016). Maija Renko (2016), verified in its entrepreneurship study considering context specificity and societal dimensions, entrepreneurship among people with disabilities needs to be analyzed and understood in its social context. It also state the role that people with disabilities play in contributing to economic development by fostering social inclusion and employment, often for others with disabilities. Also, indicate to what extent those with disabilities become self-employed out of necessity rather than choice. Existing theoretical concepts and theories in entrepreneurship should be expanded to incorporate explanations for the distinctiveness of entrepreneurship among people with disabilities. However, people with disabilities have no awareness of utilizing the resources, accommodations, benefits, and programs available to them when thinking about entrepreneurship as an employment option. Not only this disabled peoples also face challenges to start and expand their own businesses like financial problems, personal attitude, social challenges, access to education and problems related to rules and regulations (Tihic, Mirza, 2019). In Ethiopia also entrepreneurship plays a great role for the economic development of the country (Andualem, 2003, Singh & Belwal, 2008, WB, 2013). Mostly small business enterprises are the agents of change for the life standards of the unemployed peoples through providing job opportunity. Not only creating job opportunity also different advantages like job experience, skill and knowledge is organized while employed in Ethiopia (Zuzana, etal, 2013). Market environment also balanced to some extent through the production of different products and delivering to the consumers. So, the needs and the requirements of peoples or consumers are fulfilled through the business enterprises which are established by entrepreneurs (Ethiopian Economic Association, 2019). And also government income through taxation and import export business practices is increased through time in expansion of entrepreneurial activities (Wolday, 2015). So, an entrepreneur can be a change agent in the economic development of the country. But most disabled peoples are not participating in entrepreneurial activities. To understand the reason why most disabled peoples do not participate in entrepreneurial activities some challenges are discussed below.Challenges of entrepreneurs live with disabilitiesThere are many challenges that will hinder peoples with disabilities to run their own business and be self-employed. In this context some challenges like lack of start-up capital, limited access to education, infrastructural problems, socio-cultural factors, personal attitude, lack of entrepreneurial and managerial skill and Rules, regulation and governance will be discussed. 1. Lack of start-up capitalFinancial capital is vital for establishing enterprises and run businesses. Every entrepreneur needs money to be successful in entrepreneurial practices. Not only disabled peoples most people's lack financial capital to start their own business and to expand it. This may be due to lack of awareness of source of capital, limited access of financial institutions and lack of credit facilities (Maija Renko, 2015). It verifies that disabled peoples do not get start-up capital easily because the financers want to evaluate the competence and level of disability to release fund for them. Maziriri & Madinga (2016), also revealed that most disabled peoples challenged to get start-up capital and as a result their only choice is to use own minimum capital if they will have it. The sources of funds should be informed to disabled peoples. There is no structured way of working in financial institutions to serve and help disabled peoples. Even disabled peoples are discriminated (Ahmar Uddin Mohammed, 2015). Persons with disabilities like other poor people have entrepreneurial skills necessary to carry out their business but would be constrained by lack of funds due mistreatment of financial institutions and credit unions. Boylan and Burchardt (2003) also reveal some challenges of organizing start-up capital (e.g. lack of own financial resources, poor credit rating, disinterest / discrimination on the part of the banks) as a major problems facing people live with disabilities to establish own business. In Ethiopian cases Muleta and Mohammed (2019) conduct a study on socio-economic challenges of peoples live with disabilities and reveal as most disabled peoples in the country are economically disadvantaged due to lack in economic service like start-up capital and different economic resources. 2. Socio-cultural challengesDisability in different society interpreted wrongly as it is given from god because of their sin. As a result they are stigmatized and discriminated in the society. Again most peoples have a bad attitude on their ability to work and equal participation in social life. Even some believe that if they meet the disabled peoples, they will get disabled (Yared, 2008). Therefore they do not want to contact them and do not use their products. Even, their families also fear of societies claim and stigma and want to hide their disabled child at home. World Health organization (2011), also stated the disabled peoples are mostly discriminated and isolated by the society from different social participation. This may demoralize them to be an entrepreneur because they will fear of risk and losses since the society may not use their goods and services. Disabled peoples are not supported to be employed in different government institutions and private organizations. Even they are not motivated to be self-employed because of their disability (Balcazar, etal, 2014). Socio-cultural (norms and views toward disability and underestimating disabled capabilities) was also stated as a challenge of disabled entrepreneurs by Bagheri and Abbariki. In most developing countries there is a limited and weak social service from the disabled peoples association and their households. In Ethiopia where this study is conducted there is a challenge disabled peoples faced from the society like discrimination, stigma, underestimation and the like (Birhanu, 2015). Even in family a disabled person is considered as not capable and weak to work and contribute for the family income and remain dependent on other (Muleta and Mohammed, 2019). They are also marginalized from different social services like education, health service, transportation access, giving priority in public services and the like. This means most services are not inclusive (Yohannis, 2013, WHO, 2011).3. Personal AttitudeMostly people has a belief disability is given from God due to the sin their family did and the disabled nothing to perform. As a result disabled peoples are left without consideration from society and concerned bodies. Even these peoples are having no good relation with different classes of the society (National Organization on Disability, 2010). This weak social relationship with disabled may create a bad attitude in the mind of disabled peoples to participate in business activities because they assume as the society will not use their goods and services and even they may not believe their ability to work. Personal attitude is a major problem that will hinder disabled peoples to get an opportunity and lessen their social relationship since it result discrimination and stigma (Wapling & Downie, 2012). Because of the impact raised from the society and culture disabled peoples perceive as they do not have a skill and ability to work. Rather than running their own business or searching job they want to beg to overcome their life and to have money. Less in support and motivation due to the feeling of inferiority also create a bad attitude among the self-employment of disabled people. Physically disabled persons may lack confidence and capability to work own business. And also lack in courage and support from other may lead to fail in their business performance (Foster, 2010). A study conducted in Ethiopian cases by Yohannes (2012) reveal as attitude is a barrier which excludes people with disability from employment and different social services. Birhanu (2015) also indicate most peoples with disabilities thought themselves as hopeless, weak and incapable to participate in business. As a result they remain dependent on other to survive rather than creating own business. 4. Entrepreneurial skillsIn order to be an entrepreneur entrepreneurial skill should be required. So, peoples live with disabilities need to be developed their entrepreneurial skill and knowledge through entrepreneurship training and education (Maziriri & Madinga, 2016). Entrepreneurial skills may include the way the business opportunities will be identified, selection of business idea, preparation of business plan, organizing start-up capital, establishing venture and formulating expansion strategies and policies. Therefore, the disabled should develop those entrepreneurial skills to have their own business and enterprises'. Providing training for disabled peoples regarding developing business idea, preparation of business proposal (plan), design of production, directing financial resources and hiring skilled man power may lead them to business success (Mohammed & Jamil, 2015). To develop the entrepreneurial skill of disabled peoples the education system should be inclusive. According to Yohannis (2012) in Ethiopia there is not inclusive education system to educate disabled peoples and enable them to be skilled and capable for self-employment. As a result they are demotivated to learn by adapting those unsuitable education environments. There is no good environment created to learn specifically building without rap, transportation, health service and the like (Birhanu, 2015, Muleta, 2019).Empirical reviewTo rationalize the study and further understanding previous researches and variables related to the challenges of entrepreneurs living with disabilities was reviewed in this section: In 2012, study titled with 'Entrepreneurs with disability in Uganda' was conducted by Namatovu and others, in Makerere University, Kampala, Uganda. The purpose of the study was to evaluate entrepreneurs with disabilities challenges and successes. To conduct the study three stage research designs was employed: 1) Secondary research (collect data from existing documents), 2). Purposive method and 3). Documentary film, by asking about business life of disabled entrepreneurs. Accordingly, the data was collected through semi-structured questionnaires by selecting 97 entrepreneurs with disabilities, semi-structured interviews with 8 entrepreneurs, semi-structured key informant interviews 5 experts, case studies with one individual and video filming by using participants. The collected data was analyzed by using SPSS for the quantitative data tools like frequencies, percentiles, tables and charts used. The qualitative data described and interpreted using social and psychological context. The result of the analysis indicates that most disabilities are dependent and begging due to lack of employable skills. They also lack start-up capital, since the financial institutions do not deal with disabled peoples. Disabled which start business operate in unregistered enterprises, in poor open roadside makeshift structure due to lack of infrastructural facilities for disabled peoples. The governments little effort to give training on business skill for disabled peoples and lack of support from government and non-government organizations also some other challenges of the entrepreneurs with disabilities to be successful in their business. Even if, the study identified these all challenges, the impact those variables have on the success of entrepreneurs and the correlation between the variables with success not analyzed. Beside to these, the study is limited with few variables environmental aspect, education and training and source of capital only. Some other challenges that will affect entrepreneurs like entrepreneurial skill, managerial skill, socio-cultural issues and they are not included. A study by Margaret Wanjiku Mwangi (2013), on a title 'Factors that affect the success of physically challenged entrepreneurs in their business activities: A survey of Thika Municipality-Kiambu County, Kenya' was conducted to identify the factors that will affect the success by the physically disabled entrepreneurs. The design of the research was survey and snowball technique were employed to select 27 samples from physically disabled peoples. The data was collected using interviews, questionnaire and observation. The finding of the research showed that the prominent barriers to start own business with physically disabled peoples are obtaining start-up capital, lack of suitable premises, and mobility barriers in the environment. In this study not all factors are identified and even the impact of the identified challenges not examined by using convenience statistical tools. On the one hand a study was conducted in Tanzania on 2014, with title 'challenges facing people with disabilities and possible solutions in Tanzania' by Uromi and Mazagwa. The objective of the study was to identify the nature and challenges facing people with disabilities. The study used secondary data and review different previous studies related to the topic and identified different challenges of disabled peoples to fulfill their social needs. Challenges like lack of health center infrastructure, discrimination from society to be employed, lack of physical power, poverty (lack money), limited access to information and bad attitude from society are identified in this study. But the study does not focus on the challenges of disabled entrepreneurs to be self-employed or run their own businesses. A study was also conducted by Viriri and Makurumidze (2014), entitled 'Engagement of disabled people in entrepreneurship programs in zimbabwe'. The study aimed to identify the factors which affect the business growth and performance of businesses run by entrepreneurs with disabilities in Zimbabwe. The research design is exploratory in nature since it intends to identify major factors related entrepreneurs with disabilities. A snowball sampling method was used and 30 sample individuals (16 female and 14 male disabilities) were selected. A qualitative and quantitative approach was employed to gather and analyzed data. The study focused on the relationship between lack of capital, entrepreneurial training and development and networking in entrepreneurship with engagement in business. Accordingly the regression and correlation analysis used to state the relationship. So, it indicate that the performance of the business run by disabilities not explained by government funding. In addition the result of the analysis show most business do not registered (due to beaurocracy), most people's do not participate in training (the chi-square also indicate that the disabled peoples do not supported by training) and peoples with disabilities are not partially networked with key stakeholders like customers, suppliers, global markets, internet services and government agencies. Again these study also do not include other major factors like managerial skill, entrepreneurial skill, personal attitudes, infrastructural issues and the like. A research entitled 'Entrepreneurial barriers faced by disabled in India', by Mohammed and Jamil (2015) was conducted to highlight the barriers of disabled entrepreneurs and to find out if these barriers are different than those faced by other entrepreneurs. A sample of 150 disabled and 150 non-disabled entrepreneurs are selected and data were collected through using questionnaire and interview. The collected data was analyzed by multinomial logit regression. In this study variables like market prejudices, business contacts, access to finance, experience, role models, self-belief and government support. Beside to this, the study lack in including some challenges like socio-cultural issues, managerial skills, education, infrastructural issues and the like. In 2017, Maziriri and Madinga conducted a research on the title 'A qualitative study on the challenges faced by entrepreneurs living with physical disabilities within the Sebokeng Township of South Africa'. The study aimed to investigate the challenges that will hinder the success of entrepreneurs living with disabilities in the selected case area. The data was collected through interview (30 entrepreneurs), focus group discussion (23 participants in three groups) and observation (15 entrepreneurs observed). The challenges identified were education and training, lack of access to finance, inadequate government support and lack of equipment. Even if the study identified these all factors not the only challenges that will impede the success of entrepreneurs living with physical disabilities. Personal attitude of entrepreneurs, entrepreneurial skill, managerial skills and challenges faced from the society and culture should be considered. Finally, a study was conducted on the title 'challenges faced by people with disability for getting jobs: Entrepreneurship solution for unemployment' by Rozali and others (2017). The study analyzed the challenges that disabled people faced in obtaining employment. Accordingly, the challenges it observed are perception and discrimination, environments work place, motivation, family support, education, and vocational training are the barriers that will limit disabled peoples to be employed in government and non-government organizations. So, the study indicates entrepreneurship as a best solution to get a job for the disabled peoples. But the study did not identify the barriers that will hinder the disabled peoples to be successful entrepreneurs. In general these all studies are conducted related to the barriers that the disabled peoples faced to engaged in their own businesses in different countries. But there is no any research conducted in Ethiopian cases and the selected case area on the topic. But, some studies and reports indicate some challenges of disabled peoples to be employed. Muleta & Mohammed (2019) conducted a research on the socio-economic impact of disabled peoples in Ethiopia and reveal most disabled peoples are challenged by society’s attitude and cultural belief. In 2012, Yohannis also conduct a study on the challenges of disabled peoples it indicate transportation, education and other services is not inclusive. Birhanu (2015) also indicate attitude of the society has an impact on the confidence and ability of the disabled person (Birhanu D., 2015). There is also lack in entrepreneurial and work skill due to lack in inclusive education system in the country (Abdulfetah M., 2018). Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the major factors that will affect the entrepreneurs live with disabilities beyond the challenges identified by the above discussed researches and evaluate the impact of the identified factor has on the success of the entrepreneurs. Conceptual Frame workAs discussed so far in the literature under the title of challenges of entrepreneurs live with disabilities so far many author and researcher explains different challenges which may face the disabled entrepreneurs. Therefore the challenges are taken as independent variables and the success of disabled entrepreneurs to establish and expand own business is taken as dependent variable. In general those factors are clearly stated by using diagram as follows:
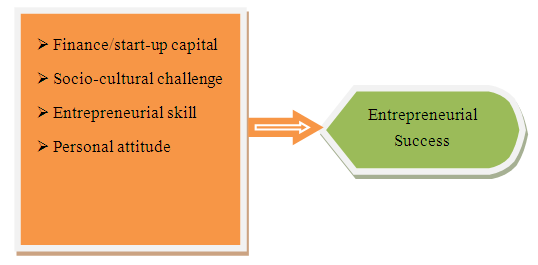 | Figure 1. Developed by the researcher |
3. Research Methodology
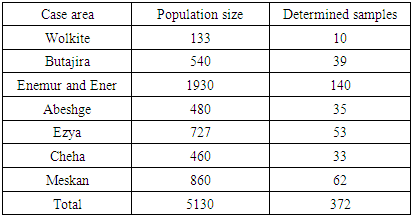
- Research designThe study employed both quantitative and qualitative research design. The qualitative approach enabled the researcher to highlight the perspectives held by the disabled entrepreneurs in regard to the activities they do and the challenges faced. Through this research design, the researcher was able to gain insight into the experiences of the disabled in business from their own perspectives. In addition, this research design was flexible, Bogdan & Biklan (1982), and provided an opportunity to obtain information that was rich with details to better understand the phenomenon of disability and entrepreneurship. The qualitative approach was triangulated by the quantitative approach which enabled the researcher to fulfill the objectives of the research. Wright (1995) argues forcefully that by combining qualitative methods to quantitative methods, the resulting results would be much more meaningful and would have greater probability of being valid, of actually measuring what it purports to measure. Data source and instrumentationTo undertake this study both primary and secondary data was collected. The primary data has been collected by distributing structured questionnaires for the employees and by observing the case area while secondary data will be collected from internets and different books related to entrepreneurship. The questionnaire contains two types of questions. The first part contains respondent’s demographic information. And the second one contains objective questions on the challenges of disable entrepreneurs. The questionnaire developed by using Likert five scales and Dichotomous questions (yes or No).Population and Sampling techniqueThis research intends to assess the challenges of disabled entrepreneurs to start and expand businesses in case of Guraghe Zone. There are 13 Woredas and two cities in Guraghe Zone. Therefore multi-step sampling technique is used to select the case area and to determine a representative sampling technique. Firstly the scope of the case area is delimited to 5 Woreda's and two city administration, which are selected by the researcher using purposive method. Those are Wolkite, Butajira, Enemur and Ener, Abeshge, Ezya, Cheha and Meskan Woreda's. Those case areas are selected purposively by considering the number of disabled peoples in each woreda's. Thus, to determine the sample size the researcher preferred to use a method developed by Yemaneh (1967). Accordingly from the total disabled 5,130 in the selected area 372 will be selected which is determined as follow with in a confidence level of 5%. Let error (e) = 0.05Population size (N) = 5130Sample size (n) = N/ 1+N (e) 2
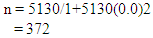 Again those 372 samples will be selected from each case area using proportional techniques as follows:sample from each area = sample size ÷ total population × population size in the case area
Again those 372 samples will be selected from each case area using proportional techniques as follows:sample from each area = sample size ÷ total population × population size in the case area
|
|
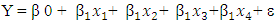 Where, Y= Entrepreneurial successβ 0= Constant
Where, Y= Entrepreneurial successβ 0= Constant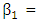 Change of y due to the impact of those variables
Change of y due to the impact of those variables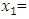 Finance/start-up capital
Finance/start-up capital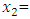 Socio-cultural challenge
Socio-cultural challenge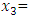 Personal attitude
Personal attitude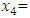 Entrepreneurial skill
Entrepreneurial skill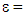 Possible error
Possible error4. Result and Discussion
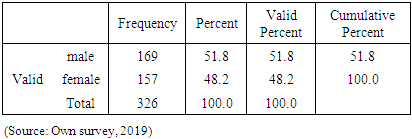
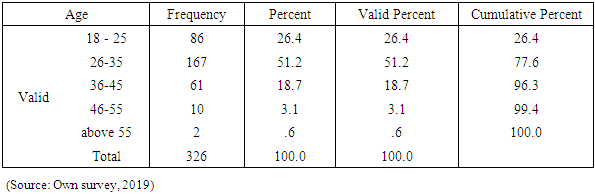
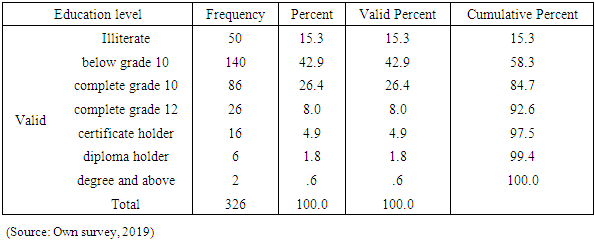
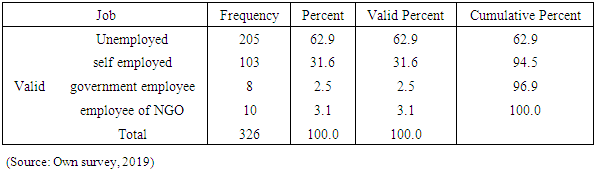
- This chapter deals with presentations, discussion and interpretation of the data collected through questionnaire and interview. The discussion particularly focuses on respondents profile, challenges of entrepreneurship and challenges of disabled entrepreneurs.Out of 372 questionnaires distributed to respondents 326 were returned (accepted). This accounts for 87.6% of response rate. Thus, based on the responses obtained from the respondents data analysis and presentation were made as follows.Analysis and presentation of respondent’s demography The demographic profile of the sample respondents is presented and analyzed below. The purpose of assessing respondents’ age, sex, is that, to determine whether the researcher considered heterogeneity of sample units. On the other hand assessing the work experience and education level of the respondents’ is that, when the respondents are more experienced and educated they have better opportunity to understand the case and give better response than else.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
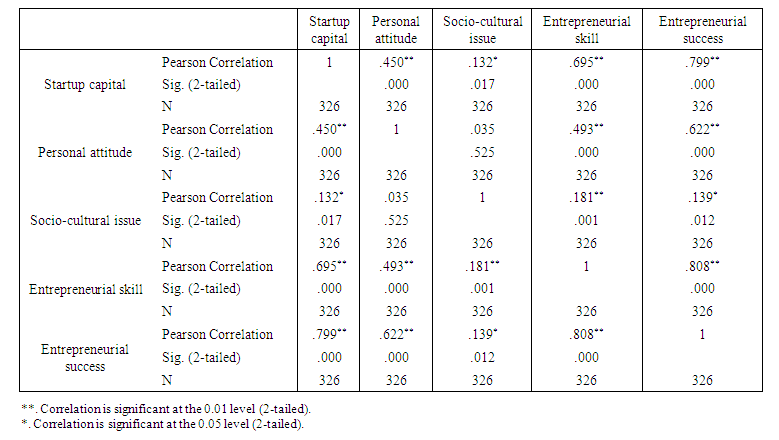 | Table 11. Correlations |
|
|
|
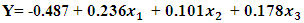 Definition key terms, y= Entrepreneurial Success
Definition key terms, y= Entrepreneurial Success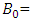 constant
constant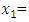 Start-up capital
Start-up capital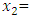 Personal attitude
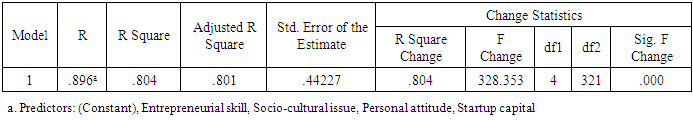
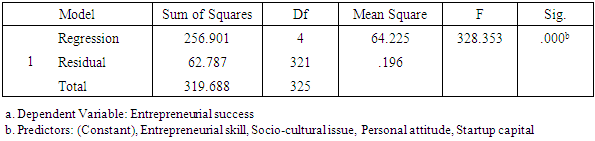
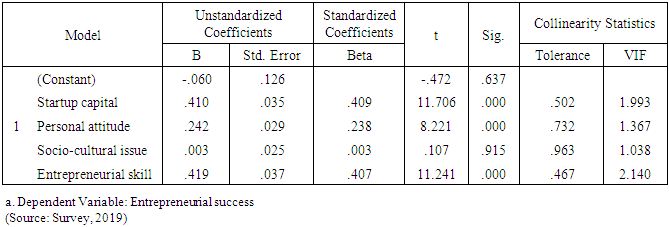
Personal attitude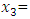 Entrepreneurial skillBy looking at the Sig.-value in Table above it is possible to interpret whether the particular independent variable has a significant relationship with the dependent variable. The relationship is significant if the Sig.-value is not larger than 0.05 (Pallant, 2010). The results show that there is a significant relationship for start-up capital (0.236), personal attitude (0.101) and entrepreneurial skill (0.178). This means that these variables are good predictors of the dependent variable entrepreneur’s success. The independent socio-cultural issues is not significantly related to the variable entrepreneurial success and thus is not good predictor since its sig. value is greater than 0.05. As a result it is not used in the formulation of the regression equation. Furthermore, the study aims to identify which of the variables contributed the most to prediction of the dependent variable. This information can be investigated via Standardized coefficient (Beta in Table). The standardized coefficients mean that “values for each of the different variables have been converted to the same scale so they can be compared” (Pallant, 2010, p.161). In this study the highest Beta value is 0.246 for start-up capital, the second is 0.178 for entrepreneurial skill and the last is 0.101 for personal attitude. Except socio-cultural issues all independent variables are statistically significant since the Sig. value is less than 0.05 (Pallant, 2010).
Entrepreneurial skillBy looking at the Sig.-value in Table above it is possible to interpret whether the particular independent variable has a significant relationship with the dependent variable. The relationship is significant if the Sig.-value is not larger than 0.05 (Pallant, 2010). The results show that there is a significant relationship for start-up capital (0.236), personal attitude (0.101) and entrepreneurial skill (0.178). This means that these variables are good predictors of the dependent variable entrepreneur’s success. The independent socio-cultural issues is not significantly related to the variable entrepreneurial success and thus is not good predictor since its sig. value is greater than 0.05. As a result it is not used in the formulation of the regression equation. Furthermore, the study aims to identify which of the variables contributed the most to prediction of the dependent variable. This information can be investigated via Standardized coefficient (Beta in Table). The standardized coefficients mean that “values for each of the different variables have been converted to the same scale so they can be compared” (Pallant, 2010, p.161). In this study the highest Beta value is 0.246 for start-up capital, the second is 0.178 for entrepreneurial skill and the last is 0.101 for personal attitude. Except socio-cultural issues all independent variables are statistically significant since the Sig. value is less than 0.05 (Pallant, 2010). 5. Conclusions and Recommendations
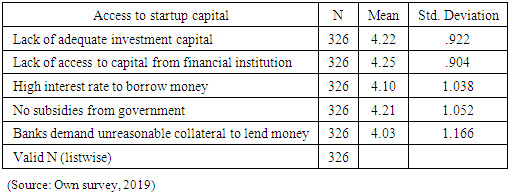
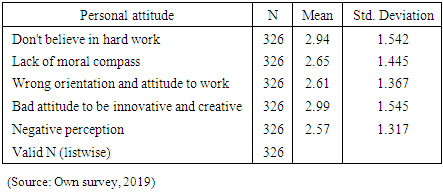
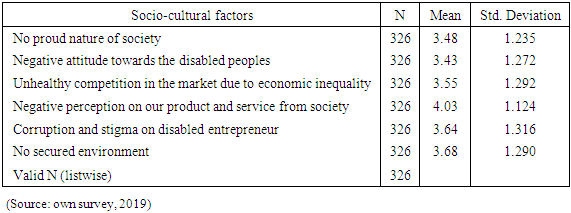
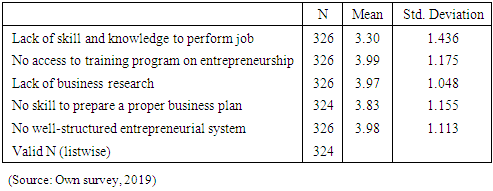
- ConclusionBased on the analysis made the following major problems are concluded regarding the challenges of disabled entrepreneurs that will hinder to establish and expand their own businesses:Ø There are some problems regarding the startup capital like lack of adequate investment capital, lack of access to capital from financial institution, high interest rate to borrow money, banks demand unreasonable collateral to lend money and no subsidies from the government which are a great challenges for an entrepreneurs to run businesses.Ø Most disabled peoples have no good attitude on their entrepreneurial ability, which means they don't believe in hard working, they lack moral compass to participate in business nearby non-disabled peoples, they adopt wrong orientation and attitude to work, they have a bad attitude on their innovativeness and creativity and have a negative perception on their successfulness if they engaged in business. Ø The disabled peoples also face challenges from the society and cultures; they believed that disability is given from god to punish them because of the sin they done. As a result mostly they are corrupted and stigmatized, the products and services of disabled peoples not demanded, not secured and they faced unhealthy competition in the market due to economic inequality and unacceptability among society. Ø Most disabled peoples lack entrepreneurial skills like lack of skill and knowledge to perform job, no access to training program on entrepreneurship, lack of business research, no skill to prepare a proper business plan and no well-structured entrepreneurial system. This may resulted due to inaccessibility of education for the disabled peoples in the country. Ø The correlation analysis was done to see the relationship between the independent variables and dependent variable entrepreneurial success. Accordingly, variables like start-up capital (0.799), personal attitude (0.622), socio-cultural issues (0.139) and entrepreneurial skill (0.808) have a strong positive correlation with the entrepreneurial success except socio-cultural issues which has a weak positive relation. Ø Regression analysis was also done to see the impact of those independent variables have on entrepreneurial success. Accordingly, the result indicates that variables like start-up capital (0.236), personal attitude (0.101) and entrepreneurial skill (0.178) has a significant impact on entrepreneurial success. But, a socio-cultural issue has no significant impact. Ø In general these all challenges are the major problems of disabled peoples of Ethiopian and some developing countries to start own business since different studies and reports verified. In Ethiopian cases research conducted at country level shows personal attitude, lack of capital resources and lack of entrepreneurial education (inclusive education) to developed their skills are the major barriers of disabled peoples (Mitiku, Yitayal & Semahegn, 2014, Muleta and Mohammed, 2019, Birhanu, 2015). WHO (2011) also indicate as disabled peoples in Ethiopia and different developing countries are economically disadvantaged due the challenges they may face to be employed. In the report lack in inclusive in education system, lack skill to start a business, lack in business resources and social discrimination and stigma are mentioned as the challenges of disabled peoples. RecommendationFor the problems identified in the conclusion on the success of entrepreneurs with disabilities to start their business and expand it, the following suggestions are given by the researcher for the concerned bodies. Ø The government should provide subsidies or facilitate credit facilities by integrating with different organizations to help the entrepreneurs with disabilities to get start-up capital. And the financial institutions should also give a special attention to help and lend loan with a minimum possible interest rate without asking unreasonable collateral. Ø Special need education should be expanded to educate the disabled peoples to change their mind, to develop their skill of working, to aware entrepreneurial and managerial skill and improve their way of life. Different training on life skill, entrepreneurship, management and financing skill should be given. Ø The entrepreneurs with disabilities should also change their attitude; they have to believe as they can do everything like the non-disabled entrepreneurs. Disability doesn't mean inability. So, if they work hardly and become successful in business, the attitude of the society also changed regarding disabilities and starts to support and want to create a smooth relation with disabled peoples. In general most entrepreneurs with disabilities are significantly challenged by factors like lack of start-up capital, personal attitude and entrepreneurial skills. Therefore, the government, financial institutions, the Ethiopian disabled peoples union, World health organization, labor unions, worlds disabled peoples unions, the entrepreneurs themselves and other concerned institutions and peoples should eager to help and simplify these challenges for the success of entrepreneurs.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML