-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Management
p-ISSN: 2162-9374 e-ISSN: 2162-8416
2017; 7(5): 180-184
doi:10.5923/j.mm.20170705.04

Competitiveness Strategy Model for Effective Organizational Structure of Higher Education in East Kalimantan
Fajar Apriani1, 2, Sangkala3, Muhammad Yunus3, Baharuddin3
1Graduate of Public Administration Doctoral Program, Hasanuddin University, Makassar, Indonesia
2Administration Department of Social and Political Sciences Faculty, Mulawarman University, Samarinda, Indonesia
3Public Administration Department of Social and Political Sciences Faculty, Hasanuddin University, Makassar, Indonesia
Correspondence to: Fajar Apriani, Graduate of Public Administration Doctoral Program, Hasanuddin University, Makassar, Indonesia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This research aims to analyze higher education organization competitiveness strategy model in East Kalimantan. This is a deductive-qualitative research by data collecting through observation and semi-structure interview to the organizational strategy apex and its middle line in organizational plan. This research was conducted in three universities at East Kalimantan. The research focuses are included the strategy formulation stages and the organizational transformation process. The research result showed that East Kalimantan Higher Education were not competitive in competition. Thus, the strategic management process of East Kalimantan Higher Education has to be addressed by focusing on the alignment between components in the organizational design, includes a structural component and a human component. In addition, there has to be an addition of strategy in the formulation of competitiveness strategy that has been used to erasing the restricting factors of competitive advantage that has possess by the organization. East Kalimantan Higher Education need to prepare their human resources including leaders, lecturers, academic and administration elements, and another supporting elements, especially from the quality aspect in order to reach it vision to be an international institution of higher education.
Keywords: Competitiveness strategy, Higher education, Strategic management process, Organizational design
Cite this paper: Fajar Apriani, Sangkala, Muhammad Yunus, Baharuddin, Competitiveness Strategy Model for Effective Organizational Structure of Higher Education in East Kalimantan, Management, Vol. 7 No. 5, 2017, pp. 180-184. doi: 10.5923/j.mm.20170705.04.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Strategic management is a management process in an organization that over and over again creating value and the ability to deliver and expand its distribution to stakeholders as in [1]. Strategy is a part of the strategic planning which is a tool in the strategic management of the organization. Thus, in the study of public administration, strategy is one of the aspects of the study of the strategic management of the organization.The adoption of business aspects including strategies for competing in the business organization by public sector organization in the perspective of public administration is inseparable from the inability of public administration during this time in responding to the environment demands, both internal and external, resulting the emergence of a second paradigm of public administration: public management.The number of universities in Indonesia which is currently only about six percent of the total number of colleges in Indonesia, encourages competition between colleges in national settings. The college faced competition as well as intense competition experienced by non-profit companies, related to competition in the field of quality, price and service. Nevertheless, the scope includes differences in terms of orientation, market share and its strategy.College today and in the future faces the problem of low levels of strategic feasibility deriving from the existence of a gap between environmental demands and competition with its internal resources. The competitiveness of a number of community colleges in higher education tends to decrease competition and threaten the position of excellence and sustainable college, including universities in East Kalimantan. Therefore required an application of the proper competitiveness strategy in order to maintain the existence of the college organization in an environment of intense competition going on.There is the whole flow of the suggested formation of a strategy from as in [2] which is a different way of looking at each other, mostly reflected in management practice. Ten of these schools are grouped in three large groups: perspective in nature, descriptive the strategies and configuration. The strategy formation schools delivers the author to examine the competitiveness strategy used by some colleges in order to maintain its existence as a provider of higher education and trying to analyze the competitiveness strategy model that capable to providing a greater benefit for the college using the strategy formation schools as its mainstream.This research tried to intend some proposition for East Kalimantan condition, that the development of universities competitiveness not only needed a customer focused strategy formulation, but also need appropriate structural components of organization design. Another improvement of this research is the other research object are in industry and manufacture sector as in [3-5], or in the higher education sector but using resource-based model as in [6-9], while the author research is in higher education sector by integrated-based model.
2. Methods
2.1. Location, Objects and Research Design
- This research was conducted in some universities at East Kalimantan, such as Mulawarman University, Samarinda Government Polytechnic and Sultan Sulaiman’s Government Islamic High School. This is a deductive-qualitative research that attempts to analyze the characteristics of a model strategy for the competitiveness of the organization as a target implementation of strategic operational planning universities in East Kalimantan, using qualitative techniques. Strategic planning of the organization as the internal aspects of the organization that become the research focus into micro phenomena, while the implementation of the organization competitiveness strategy as an external aspect, considered to be macro phenomena.
2.2. Data Collection Techniques
- Data collected through field study and library research. As a consequence of qualitative research, the data collection technique used observation, interview that used a tape recorder and documents searching. Data analysis technique is interactive model.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. SWOT Analysis of East Kalimantan Higher Education Organization
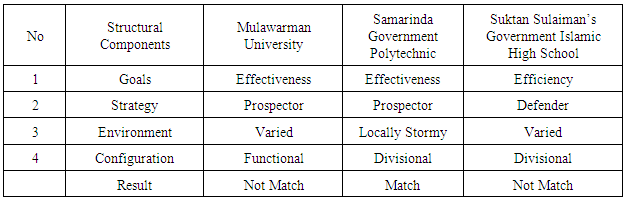
- Based on SWOT analysis of East Kalimantan Higher Education Organizations, the author found empirical things that there is not appropriate strategy formulation with the ability and resources condition that they have. Based in ten formulation strategic schools as in [10], East Kalimantan Higher Education Organizations use configuration school in their organization competitiveness strategy formulation. It appears from the combination of improvement objective in organizational culture aspects, organizational human resources and organizational change process. Besides that, there are some activities of organizational management development that focus on customer and product or services in special specs. In this case, Sultan Sulaiman’s Government Islamic High School try to develop their organization to be Government Islamic Institute, while Mulawarman University have a great spirit to develop their commercial business units that potential to increasing university’s income since becoming a General Services Organization (called BLU in Indonesia) at 2009.In the case of East Kalimantan higher education organization, the SWOT analysis is used as a tool to facilitate the analysis and strategy formulation. With variant internal and external condition that each higher education organization faced, make the strategy that its used has a different types depend on its SWOT analysis.
3.2. Empirical Model of East Kalimantan Higher Education Organization Competitiveness Strategy
- Strategic management process stages in the East Kalimantan higher education organization, among others, environmental scanning stage, vision and mission, which can be generalize want to become an international institution of higher education, albeit with different emphasis. Then proceed with the formulation of a strategy whereby the organization design activities carried out on two types of focus. First, formulate structural components, and second, formulated human resource components (see Figure 1).
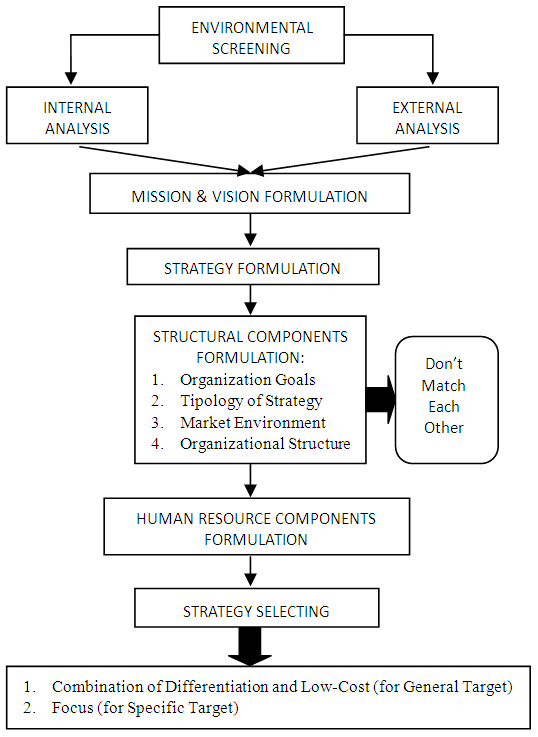 | Figure 1. Empirical Model of East Kalimantan Higher Education Organization Competitiveness Strategy |
|
3.3. The Relevance of Burton’s Structural Components of the Organization Design Outline
- An organization design should be selected based on some specific context, and the description of its context has to be multidimensional, include the structural and human resource components as in [10]. Structural components are goals, strategy, and structure. While the human resource components are job process, peoples, coordination and control, incentive mechanism. As the research focus, the analysis space in this research has been selected only to analyze the structural components of East Kalimantan higher education organization design. This research used theoretical formula about the suitability between the four structural components in the organizational as in [10].
3.4. The Relevance of Gilley and Maycunich’s Organization Transformation Process Model
- The author linked structural components of organizational design that has made by East Kalimantan higher education organization with its transformation in the process of organizational position. Thus, it will be analyzed for compliance between the structural components of the organization with the stages of progression toward organizational changes that have been traversed. The stage of development of the organization in the transformation process is divided into three phases, namely the traditional organization phase, the learning organization phase and the development organization phase as in [11].East Kalimantan higher education organization is on the learners and development organization phase. Learning organization phase characterized by the presence of learning within the organization to adapt to the environment. In its lesson, East Kalimantan higher education organizations require more knowledge creation process, expressed that learning and development organization will successfully achieve when it occurs the process of knowledge creation as the core of knowledge management as in [12].
3.5. The Relevance of Porter’s Generic Strategy Model
- Five types of competitive strategy in the form of generic strategies theoretic model as in [13], use in this research to improve an effective competitiveness strategy model for East Kalimantan higher education organizations. Competitive strategy is a way to attract the attention of consumers and in the implementation of organizations faced with the situation and the specific market environments require different variations. Therefore, it will certainly be a lot of competition strategy according to the number of competitors that faced by the organization.
3.6. Alternative Model of East Kalimantan Higher Education Organization Competitiveness Strategy
- Understand the conditions that East Kalimantan higher education organization faced that had the vision to an international institution, but it still may be a number of weakness in the strategy formulation, the author offers an alternative model of strategic management which contains the organization competitiveness strategy formulation (look at figure 2).
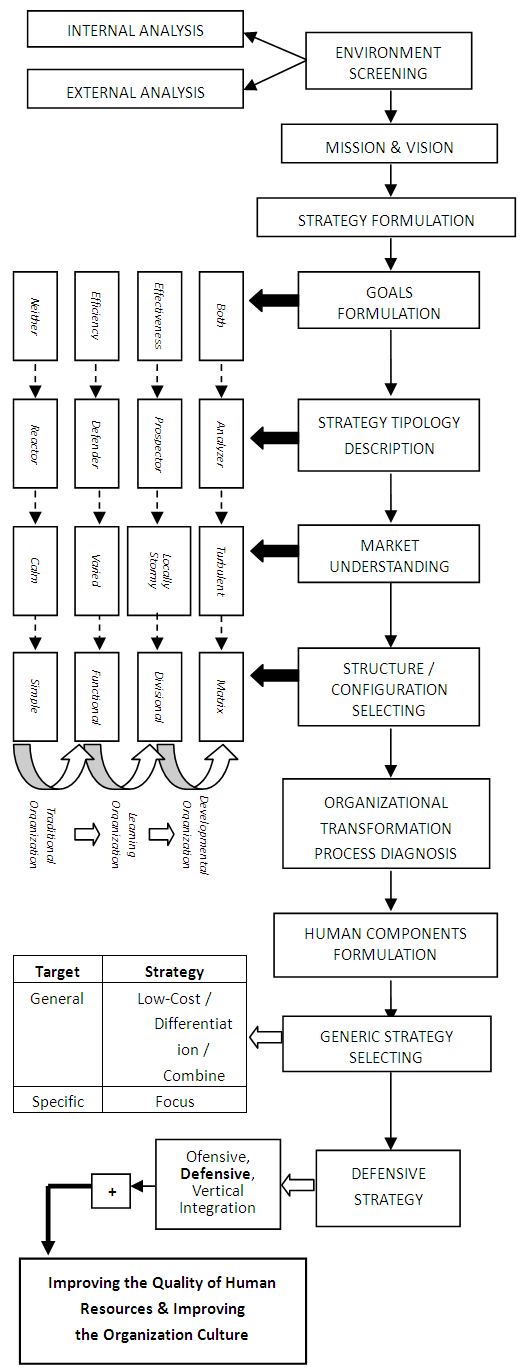 | Figure 2. Alternative Model of East Kalimantan Higher Education Organization Competitiveness Strategy |
3.7. Empirical Propositions
- This research resulted in several propositions from the analysis of the empirical findings with theoretic formula:1. Major Proposition: When an organization of higher education wants to be competitive in a competition area, then the strategy management process should be refers to the appropriately competitiveness strategy formulation model.2. Minor Propositions:a. When the formulation of structural components of the organization design already match each other, then the strategic planning organization will be just right.b. When a number of generic strategies are combined in their implementation, the different strategic target will be achieved.c. When organizations want to secure their competitive advantage, then the defensive strategy needs to set out after the election of generic strategy.d. When the public sector organization wants to obtain better effectiveness organization criteria, then the organization will need to undergo continuous transformation process.
4. Conclusions
- The research result showed that East Kalimantan Higher Education has competitiveness strategy that according to their organizational internal and external condition, but in the formulation of the structural components from the organizational design, there are some components that are not appropriate each other as Burton’s theoretical formula. It makes East Kalimantan Higher Education are not competitive in competition. Thus, the strategic management process of East Kalimantan Higher Education has to be addressed by focusing on the alignment between components in the organizational design, includes a structural component and a human component. In addition, there has to be an addition of strategy in the formulation of competitiveness strategy that has been used to erasing the restricting factors of competitive advantage that has possess by the organization. East Kalimantan Higher Education need to prepare it human resources including leaders, lecturers, academic and administration elements, and another supporting elements, especially from the quality aspect in order to reach it vision to be an international institution of higher education.The research implications for the development of organization theory, the author submitted a contribution in the form of alternative models of thought organization competitiveness strategy of the universities of East Kalimantan called Fitted and Strengthening Competitiveness Strategy Model, which is expected to be applied as a competitiveness strategy for public sector organization of higher education who wish to maintain the superiority of competition and become more competitive. Besides it also adds scientific insight that focused on the field of strategy study as part of the strategic planning organizational theory through discussion of deepening about organizational competitiveness strategy model.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- We are very grateful to Rector of Mulawarman University, Director of Samarinda Government Polytechnic and the Head of Sultan Sulaiman’s Government Islamic High School for permissions to visit and to research in their higher education organizations. This research received funding from the General Directorate of Higher Education in Indonesian through Doctoral Dissertation Research Term with Agreement No.334/H17.16/PG/2013 dated May 20, 2013. We also gratefully acknowledge two excellent men of helpful suggestions, Deddy Tikson and Haedar Akib.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML