-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Management
p-ISSN: 2162-9374 e-ISSN: 2162-8416
2017; 7(3): 126-130
doi:10.5923/j.mm.20170703.04

Bundling Pricing Strategy on Purchasing Decision: A Case of Indihome Product
Muhammad Ichwan Musa
Department of Management, Universitas Negeri Makassar, Indonesia
Correspondence to: Muhammad Ichwan Musa , Department of Management, Universitas Negeri Makassar, Indonesia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This paper aims to measure the influence of bundling pricing strategy on costumer’s purchasing decision in IndiHome product in Makassar (Indonesia). This study employed quantitative research by distributing questionnaires to 369 respondents, with random sampling method. By employing regression analysis, it was found that the bundling pricing strategy has significant influence toward purchasing decision in IndiHome product in Makassar.
Keywords: Bundling Pricing Strategy, Purchasing Decision, Marketing Management, Quantitative research
Cite this paper: Muhammad Ichwan Musa , Bundling Pricing Strategy on Purchasing Decision: A Case of Indihome Product, Management, Vol. 7 No. 3, 2017, pp. 126-130. doi: 10.5923/j.mm.20170703.04.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Global competition has force organizations to deploy their marketing strategies in order to attract costumers’ attention which eventually lead to market share extension. A great product is not enough. Organization must be able to formulate their marketing strategies in order to win the competition. Also, by able to understand customer’s behaviors, will enable organizations to formulate marketing strategies in the future. In the middle of the high-speed competitive environment, companies are forced to strive for their existence (Haeruddin, 2016a). Bundling pricing strategy as one of the advanced marketing strategies is best known for its effectiveness (Stremersch & Tellis, 2002; Prasad, Venkatesh, & Mahajan, 2015; Shaddy & Fishbach, 2017). However, it its applications bundling pricing strategy is also has its own drawbacks, for example: how a particular product is dominating the other product in a bundling price scheme, which would lead to the unbundling decision (Paun, 1993; Stremersch & Tellis, 2002; Haeruddin, 2016b).In order to face with the global competition challenges, coupled with increasing needs of mobility and connectivity, telecommunications industry must be able to create their own characteristics and valued added in their product and marketing strategies. PT. TELKOM as a state owned organization has expanded its portfolio which covers telecommunications, information, media and edutainments (TIME) areas. Telkom product that we know that is a home phone, speedy wifi, and now Telkom released its latest product IndiHomeTv, is a service of television interactive and online media; IndiHome internet that can be enjoyed by customers through a triple screen (television, PC/laptops, and smartphones) with live TV streaming features, international channel subscription package, a collection of video on demand in the form of movies box-office, drama and video clips as well as online games. It can be argued that TELKOM’ latest product have good specifications and more advanced than previous products. The quality of this IndiHome product itself must continue to be developed and improved as well as more attention to the value added to the consumers, because it will affect the purchase decision of the potential consumers. According from the abovementioned problematization, author proposes a research titled Bundling Pricing Strategy on Purchasing Decision: A case of IndiHome product.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Marketing Mix
- The success of a marketing plan relies heavily on some important elements that constitute one entity or value chains that must be integral and cannot to be separated from one another, these elements came to be known by the term "Marketing Mix". The definition of the marketing mix according to Swastha (2002: 33) is "a combination of four variables or activities that constitute the core of the company's marketing system: product, price structure, promotional activities and distribution systems". Meanwhile, according to Lamb, Hair, and McDaniel (2013: 40), the marketing mix refers to a blend of product strategy, promotional distribution, and unique pricing designed to produce mutually satisfactory exchange with the intended market.Activities included in the four variables, namely:Ÿ Product (product)Products are goods or services offered into the market to be noticed, owned, used or consumed so as to include physical objects, services, people, organizations, and ideas.Ÿ Price (Price)Lamb, Hair, and McDaniel (2013: 44) argue that price is "what buyers should get in order to get a product."Ÿ Promotion (Promotion)Promotion is a flow of information or one-way persuasion made to direct a person or organization that is with the aim to introduce the results of production and facilitate the exchange in marketing.Ÿ Distribution Channels (Place)Distribution channels are groups of companies or individuals who take rights/help in the transfer of rights to certain products, as long as they move from producer to consumer.
2.2. Price
2.2.1. Understanding Price
- In the theory of price economy, values and benefits are interrelated terms. It is a thing that can satisfy needs. While value is acknowledge as a representation of the goods that can attract other goods in an exchange. In exchange or to measure the value of a good we must use money (the term used is price). So the price is the value of a good, which is stated in money (financial standard).In any product or service offered, the marketing department is entitled to determine the cost of goods. Factors to consider in pricing include cost, profit, rival practices, and changes in market demand. The definition according to Lamb, Hair, and McDaniel (2013: 60) price is "what should be given by buyer to get a product." Meanwhile, according to Swastha and Irawan (2005: 9) the price is "the amount of money needed to get some combination of products and services." In the context of service marketing, simply the term price according to Tjiptono (2014: 11) can be interpreted "as the amount of money and or other aspects that contain specific utility or usability required to obtain a service". While it is viewed from a marketing standpoint, the price is the amount of money charged for a product or service.This understanding is in line with the concept of exchange in marketing. From the consumer's point of view, prices are often used as an indicator of the value of how the price is linked to perceived benefits of a good and a service. Generally, in determining the values of a consumer goods or services is by comparing the ability of goods or services in meeting particular needs. Based on this understanding can be concluded that the price is a sum of money and or other aspects used to get the goods or services that consumers want.
2.2.2. Pricing Strategy
- Pricing strategies can be grouped into 8 groups, namely:a) New product pricing strategy.The price set for a new product should have a good effect on the market growth, also to prevent the emergence of the fierce competition within the globalization era. According to Tjiptono (2002: 102) there are two things to note in the pricing of new products:Ÿ Skimming PricingSkimming pricing is a strategy that sets a high price on a new product, equipped with a vigorous promotional activities, its purpose is:× Serving customers who are not too price sensitive, while the competition is not there yet.× To cover the costs of promotion and research through a large margin.× As a precaution the occurrence of errors in pricing, because it would be easier to lower the price of the initial price increase.Ÿ Penetration PricingPenetration pricing is a strategy by setting a low price at the start of production, with the aim to achieve a large market share and at the same time blocking the entry of competitors. With low prices companies can also seek to achieve economies of scale and decreased per-unit costs. This strategy has a long-term perspective, where short-term profits are sacrificed in order to achieve sustainable competitive advantage. There are four forms of prices using a "Penetration Pricing", among others:× Prices were controlled (restrained price), the price sets in order to maintain a certain price level during a period of inflation.× Elimination price, i.e. the price fixing at a certain level which may cause competitors - a specific competitor (especially small ones) out of the competition.× Promotion price is set low prices with the same quality, with the aim to promote specific products.× Keep -out price, a certain pricing so as to prevent competitors entering the market.b) An established new product pricing strategy.According Tjiptono (2002: 133) there are several factors that cause a company should always review the pricing strategy of products that already exist in the market, including:Ÿ There is a change in the market environment, for example a big competitor lowers the price.Ÿ The existence of a shift in demand, for example the change in consumer tastes.In reviewing the pricing that has been established, the company has three alternative strategies, namely:× Maintaining Price, this strategy is implemented with the aim of maintaining a position in the market and to improve a good image in the community.× Lowering the price, this strategy is difficult to implement because the company must have a large financial capability, while the consequences, the company received a profit margin to a small extent. There are three reasons or causes of the company should reduce the price of established products, among others:- Defensive strategy, where the company cut prices in the face of increasingly tough competition.- Offensive strategy, where the company has a goal to win the competition with their competitors.- Response to customer needs caused by environmental companies. For example, sustained inflation and rising prices are increasingly causing consumers to be more selective in shopping and in pricing.Ÿ Increased Price, a company conducts a price-raising policy with the aim of maintaining profitability in the inflation period and for segmenting certain markets. In order for this strategy to produce satisfactory results, there are two requirements that must be done by the company, among others:× Price elasticity is relatively low, but elasticity remains high when it comes to quality and distribution.× Reinforcement of the elements of the marketing mix remains favourable.c) Price Flexibility StrategyPrice flexibility strategy is a different price setting for different markets. The advantages of implementing a price, among others: a stable market growth, a good image, a constant margin and cost of sales decreased. The use of flexible pricing contains several disadvantages:Ÿ There are customers who are not satisfied because there are other customers enjoy lower prices.Ÿ When consumers know then bargaining can benefit them.Ÿ Some salespeople become accustomed to price reductions.d) Product line pricing strategyProduct Lining is a marketing strategy to sell some types of products. Unlike product bundling, product lining sold separately several interrelated products. One product line consists of several products with various size variations, colour type, quality or price. While price lining is an activity where you use price limits for all products in the line.This technique is commonly used by stores that use one price for all its products such as a five-thousand-dollar store where all goods sold in the store are in the price range of five thousand. The pricing is based on the relation and impact of a product on its line, whether competitive or complementary.e) Leasing strategyUnderstanding leasing is crucial in every activity of corporate finance in the form of supply of capital goods to be used by a company for a certain period, based payments regularly accompanied by a voting rights for the company to purchase capital goods concerned or extend the term of the lease based on the value of the remaining money that has been mutually agreed upon.f) Bundling pricing strategyBundling pricing strategy, the company sold two or more products in one package, wherein the package price is cheaper than the total price of each item if sold separately. Bundling pricing is a strategy to enter the extra margin on the price to cover the various functions and services required to sell and maintain the product over its useful life.g) Price leadership strategyPrice savings occur when a firm becomes a price leader when a price leader changes prices, and other companies will follow that change. Price leaders are typically more efficient companies where the cost structure of increments and average costs are lower than inefficient firms. This strategy is usually implemented by the industry "leader" to make price control which will be followed by other companies.f) Pricing strategy to establish market shareStrategy by setting a low price for a new product in order to capture a large market share so that the company gets a cost advantage and its market cannot be controlled by a competitor.
2.2.3. Buying Decision
- According to Kotler, Keller, Ancarani, and Costabile (2014:240) the factors that affect consumer behavior and decisions consist of:a) Cultural Factors. It has the widest and deepest influence on consumer behavior.b) Social FactorsConsumer behavior will also be influenced by social factors namely:Ÿ GroupGroups that directly affect and in which a person is a member are called membership groups. There is a so-called primary group, where members interact informally like family, friends.Ÿ FamilyMembers of buyer groups can exert powerful influence on behavior. Family orientation is a family of parents giving direction in terms of religious, political, economic, and self-esteem guidance.Ÿ Roles and SocialA person in each group can be determined in terms of roles and status. Each role carries a status that reflects public appreciation.c) Personal FactorsA buyer's decision is also influenced by personal characteristics such as:Ÿ Age and Stage of Life CyclePeople will change the goods and services they buy throughout their lives. The needs and tastes of a person will change with age.Ÿ WorkA person's work affects the goods and services he or she buys. Thus marketers can identify groups related to positions that have an above average interest in their products.Ÿ Economic SituationStrongly influence product selection. Its income-sensitive products are careful to pay attention to trends in personal income, savings and interest rates.Ÿ LifestylePeople from Sub-culture, social class and work can have different lifestyles. One's lifestyle shows the pattern of life in question reflected in its activities, interests and opinions.Ÿ Personality and Self ConceptEach person has a distinctive personality and this will affect his buyer's behavior. Personality refers to its unique psychological characteristics and generates a relatively constant response to its own environment.d) Psychological FactorsThe choice of one's purchase is also influenced by the main psychological factors:Ÿ MotivationMost of the needs are not strong enough to motivate someone to act at a certain moment. A need will turn into a motive when this need has reached a certain level.Ÿ PerceptionSomeone will be motivated to be ready to react. How that person acts is influenced by perceptions of the situation.Ÿ Shopping ProcessThe shopping process explains the company in a person's arising behavior and experience and most human behavior is the result of the learning process.Ÿ Trust and AttitudeThrough action and learning process, people will gain trust and attitude which then influence buyer behavior.From the eighth pricing strategy that has been discussed above, in this research will be focused on bundling pricing strategy. Definition of bundling pricing as argued by Tjiptono (2014: 140) is "pricing strategy by offering two or more products in one bundle package, with low price / special price". Bundling is also defined as a company that sells two or more products in one package, where the package price is cheaper than the total price of each item if sold separately. Another sense bundling the sales strategies of two or more different products in one package price is at a discount, or an offer of some products that are not integrated at the level of the lower price if offered separately, without the integration of any of the products (not integrated is translated that customers can still use one of these products without compromising the function of the others). Theoretical framework for this research can be seen from the following figure 1.
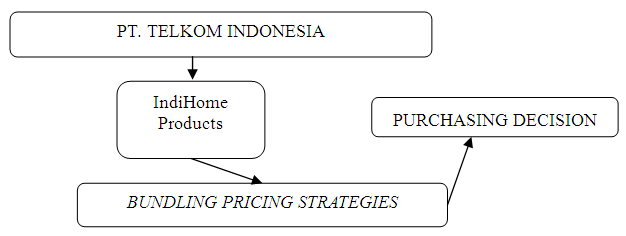 | Figure 1. Theoretical Framework |
3. Research Methods
- Population in this research is significantly massive that is 30.221 costumers. Therefore, according to Slovin’ sample formula, it can be found the sample of this research as follows.
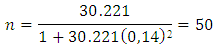 Questionnaires distributed to the sample with random sampling method. In analyzing data, simple linear regression formula is employed, which can be seen as follows.
Questionnaires distributed to the sample with random sampling method. In analyzing data, simple linear regression formula is employed, which can be seen as follows. 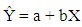 Ŷ= Purchasing decisiona= interception Constantab= regression coefficientsX= bundling pricing
Ŷ= Purchasing decisiona= interception Constantab= regression coefficientsX= bundling pricing4. Results & Discussion
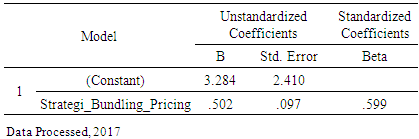
- As has been stated in the hypothesis that there is a significant influence bundling pricing strategy to IndiHome products purchasing decisions on PT TELKOM in Makassar City, formulation on SPSS software found the result as follows:
 Furthermore, according to the formulation, it can be found the equation as follows:
Furthermore, according to the formulation, it can be found the equation as follows: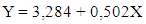 In the equation it is translated, that if the bundling pricing strategy factor is considered constant or negligible then the purchasing decision is 3.284%. If the bundling pricing strategy variable (X) increases, the purchase decision is 0.502% or if added with the coefficient value α (3.284), the contribution of bundling pricing strategy to the purchase decision reaches 3.786%. It can be seen from the amount of Beta that the extent of bundling pricing strategy influence on purchasing is around 0.599 or 59.9%.According to the finding, it can be argued that this research is in line with previous research which confirming the significant positive influence of bundling pricing strategy on consumers’ purchasing decision (Stremersch & Tellis, 2002; Ahmetoglu, Furnham, & Fagan, 2014; Prasad, Venkatesh, & Mahajan, 2015; Haeruddin, 2016a; Shaddy & Fishbach, 2017). Yet, this research contributes to the existing literatures. As IndiHome is acknowledged as a high-end product, which brings prestige to its users, it is also confirming that costumer’s preference in purchasing is strongly influenced by socio-cultural pressures, which depicted on the questionnaires’ data tabulation. Indonesian costumers, particularly the younger generation, are strongly argued as highly influenced by the current trend, coupled with the highly intensive used of social media which added the reason of purchasing decision on particular products. As explored on the data (questionnaires), younger generations’ purchasing decisions are mostly influenced by peer group. Therefore, further explorations on this issue need to be conducted.
In the equation it is translated, that if the bundling pricing strategy factor is considered constant or negligible then the purchasing decision is 3.284%. If the bundling pricing strategy variable (X) increases, the purchase decision is 0.502% or if added with the coefficient value α (3.284), the contribution of bundling pricing strategy to the purchase decision reaches 3.786%. It can be seen from the amount of Beta that the extent of bundling pricing strategy influence on purchasing is around 0.599 or 59.9%.According to the finding, it can be argued that this research is in line with previous research which confirming the significant positive influence of bundling pricing strategy on consumers’ purchasing decision (Stremersch & Tellis, 2002; Ahmetoglu, Furnham, & Fagan, 2014; Prasad, Venkatesh, & Mahajan, 2015; Haeruddin, 2016a; Shaddy & Fishbach, 2017). Yet, this research contributes to the existing literatures. As IndiHome is acknowledged as a high-end product, which brings prestige to its users, it is also confirming that costumer’s preference in purchasing is strongly influenced by socio-cultural pressures, which depicted on the questionnaires’ data tabulation. Indonesian costumers, particularly the younger generation, are strongly argued as highly influenced by the current trend, coupled with the highly intensive used of social media which added the reason of purchasing decision on particular products. As explored on the data (questionnaires), younger generations’ purchasing decisions are mostly influenced by peer group. Therefore, further explorations on this issue need to be conducted.5. Conclusions and Further Research
- The purpose of this study was to investigate the influence of Bundling Pricing Strategy toward costumers’ purchasing decision on IndiHome products of PT. TELKOM. As a result, practical implications extend to PT. TELKOM and similar organization within Information, Communication and Technology industry which might pursue market expansion and profit in promoting their products in Makassar. Moreover, understanding the why and how costumers decide on purchasing a product can lead organizations to improve and develop their level of awareness, knowledge, and innovation on Telecommunications, Information, Media and Edutainments (TIME). As PT. TELKOM is a state owned organization, they should be able to compete with their competitors (private organizations) such as TELKOMSEL and INDOSAT in offering ICT products to the costumers. The present findings have demonstrated that the bundling pricing strategy which influence costumers’ purchasing decision are mainly based on the word of mouth way, particularly by the socio-cultural pressures (peer pressures) as IndiHome is acknowledged as a high-end product which brings prestige to its users. Future works should also add more variables that can explain deeper understanding of purchasing decision on similar products.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML