-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Management
p-ISSN: 2162-9374 e-ISSN: 2162-8416
2017; 7(1): 29-34
doi:10.5923/j.mm.20170701.03

C2B Increase Students Enrolment
Selvarajah Krishnan, Norizzati Bahsri, Amaliya Shteyneker, Jaya Priah Kasinathan, Ahnoosh Selvarajah
International University of Malaya-Wales, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Correspondence to: Selvarajah Krishnan, International University of Malaya-Wales, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The purpose of this research paper presents how C2B approach can be optimize in both traditional recruitment (TR) and (MR) modern recruitment to increase students’ enrolment in private universities (PU’s) in Malaysia and globally. Furthermore, explore the effectiveness of traditional and modern students’ recruitment process using C2B approach. Simple random sampling technique and self-administered questionnaires were distributed by mail and online to students in Malaysia. Found that the correlation between TR, MR and students’ intention (INT) to make decision in selecting private university in Malaysia, was positive relationship and significant. Additionally, the results identified as full moderators are attitude (ATT) and subjective norm (SN) and have positives significant effect between independent variables (TR and MR) and dependent variables (INT). The study conducted that the use of word of mouth, friends’ advice, suggestion from family, were the most effective in traditional recruitment (TR), whereas the usage of social media C2B has the most effective from modern recruitment (MR). Therefore it is recommended that the private universities should adopt these C2B approach to enhance their recruiting on advertising, promoting and creating attractive messages to attract students. Thus enable the PU’s to reduce marketing budgets, and obtain larger market share and also sustain in business for coming years. Furthermore finding helps PU’s to plan effective marketing strategy accordingly to overcome their competitors and gain additional new students.
Keywords: C2B, Traditional Recruitment, Modern Recruitment
Cite this paper: Selvarajah Krishnan, Norizzati Bahsri, Amaliya Shteyneker, Jaya Priah Kasinathan, Ahnoosh Selvarajah, C2B Increase Students Enrolment, Management, Vol. 7 No. 1, 2017, pp. 29-34. doi: 10.5923/j.mm.20170701.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Education is a global service, which most of the countries strive to provide for their citizen to enhance the socio and economic development of the country. The accelerated growth of population has caused high demand in the educational industries to accommodate growing numbers of students (Selvarajah and Sulaiman, 2014). This has brought about a significant growth of the private educational institutions to serve the rise of student population. The intense competition amongst the private education institutions to maximize profit has encouraged institutions to implement creative ways of recruiting students as well as satisfying their preferences and needs (Onyemae, 2013). The higher education in Malaysia has been expanding and contributing tremendously to the Malaysian economic growth (Hassan & Sheriff, 2006). Malaysian private higher educational strives to have both international and local students. In order to gain perspective market, institutions are forced to search for competitive marketing strategy. Therefore, to explore the factors influencing students’ choice of educational institution, should become a important part of marketing strategy for planning on students recruitment of higher institution (Joseph, 2010). The revolution of information technology and communication has changed the way people conduct the business today. Nowadays, most of the communication and businesses are related to electronic devices and internet. According to Krishnamurthy (2006), E – Marketing is a term which refers to the use of internet, web and other related information technology to conduct marketing. Social media marketing is used more frequently today, and this fast spread of marketing makes the company to adapt new methods of communication with their consumers. The most frequent social media being used for marketing purpose are Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Google+, YouTube, Pinterest and Instagram (A. Stelzner, 2015). There are still practices of traditional marketing, such as face to face, phone calls, flyers, billboards, newspaper print ads, radio and television used for students recruitment by higher institutions. Marine and Foskett (2002) state that in competitive marketing analysis, the educational institutions will be interested to know the use of effective communication tools to attract the students effectively to choose their institution over their competitors. Based on various types of trading partners, there are many categories of business, for example C2B (Consumer to Business) Dai (2013) pointed out that the concept of C2B e-commerce, business model and evolution path, and put forward the real C2B model was consumer demand first and enterprise production second. Chen (2013) discussed the C2B model running mechanism and characteristics from the angle of consumer demand, and provided the reference for e-commerce model innovation. Gao (2014) pointed out that under the C2B model, the active participation of consumers to customize individualized product can meet their own needs.
2. Research Questions
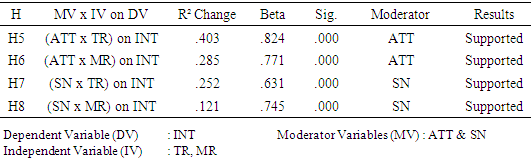
- This study embarks on the following research questions; What is the most effective media on students’ enrolment intention to university? What is the relationship between MR, TR, ATT, and SN on students’ intention enrol (INT) to university? Is there any moderator and/or mediator effect on students’ enrolment intention to university?
3. Significant of Study
- The purpose of this study is to enhance the recruitment strategies in IUMW growth. The finding helps to determine the most effective method on students’ recruitment strategies for IUMW to increase the profit and sustain in future. Furthermore finding will help IUMW to plan effective marketing strategy accordingly to overcome their competitors and gain additional new students. Finally this research will tested Modern students’ recruitment and Traditional Students recruitment in Malaysia and United Kingdom and will clarify how it’s should make changes in students recruitment, to improve the number of students in International University of Malaya Wales.
4. Literature Review
- Higher education has become increasingly diverse and competitive in the 21st century (Han, 2014). It will be more challenging for the education institutions as the students are tending increasingly to be extremely critical and analytical when choosing their educational institutions (Binsardi & Ekwulugo, 2003). It has proven in a research done by Basheer in 2008 showing that marketing actions and marketing activities conducted by higher education service providers do create added value for students, leading to not only student satisfaction and trust but also to relationship continuity, and positive word of mouth. A good marketing actions in recruiting students will determine the sustainability of higher education institution (HEI) especially for private HEI. There are two marketing or recruitment methods than can be apply to recruit students which are traditional recruitment and modern recruitment. As stated by Salehi et al. (2012), traditional marketing used to speak more and more attracting customers to purchase their goods or services while modern marketing is the new method of attracting customers by using modern facilities and technologies. Traditional recruitment methods includes all methods that did not involve content posted on the Internet such as flyers, E-mails to students, and all printed advertisements (Raviotta et. al, 2014). It is proven that traditional media such as TV and print campaigns are best suited to increase brand awareness, while corporate weblogs or brand profiles on social media are best suited to improve brand image (Bruhn et. al, 2012). Modern recruitment includes social media marketing channels such as Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, and Whatsapp. This modern method of recruiting students is relatively new area of study. However, the number of studies on social media marketing and their effectiveness is still limited, and very little is known about the suitability of the social media as tools for higher education marketing (Constantinides & Stagno, 2011). Chris et al. (2011) undertake a study that shows the evident that UK universities can be segmented in terms of brand communication through their websites. From this finding, it shows the importance of using websites as one of modern marketing tool. While, a study by Uchendu et al. in 2015 had found that modern recruitment method is favorable in reaching prospects and portray of the education institution especially through media and networks. It is align with the research findings by Kara in 2007 that shows most respondents in Hong Kong preferred to use the internet, instead of magazines, newspapers, radio and television to search for information such as to further their education.
5. Methodology
- The purpose of this study is to determine C2B approach as one of the recruitment strategies to increase students’ enrolment in PU’s. A cross sectional of over 645 students from Malaysian private universities with ranking in SETARA of Tier 4 and 5 as a sample frame. Simple random sampling technique was adopted and self-administered questionnaires was distributed by mail and online to the students. Further, qualitative survey was conducted on students and university staff at private universities. The primary data will be process using the SPSS for quantitative and qualitative for NVivo. Found that the previous researchers distributed self-administered questionnaires more than their sample size such as add 6 to 8 times of sample size because to obtain reasonable response rate for statistical analysis purposes. Sampling errors for this study is + 5% and represent the total error in research because the level of confidence 95%. Furthermore, research instruments were redesigned, modified and constructed based on content validity from previous researchers. Pilot studies were carried out for the reliability of the instrument and determined by pre-testing questionnaire. Therefore, the population is normally distributed with mean µ and standard deviation α, and then the interval µ ±1.96α includes 95% of the population.
6. Findings
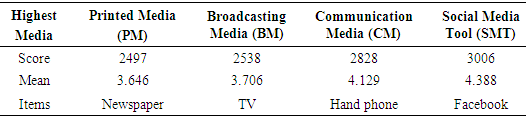
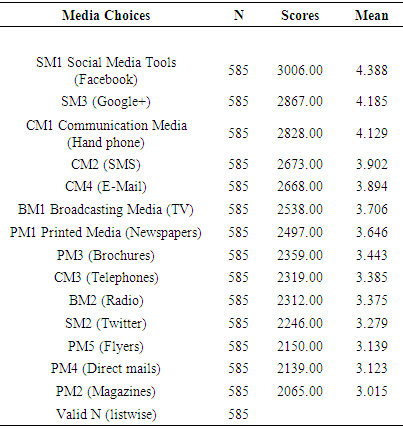
- According to Coakes and Ong (2011) the researcher process the primary raw data to a usable data file for statistical analysis. The process involves data editing, coding, entering, labelling, valuing, detecting outliers, screening, transforming and determining level of significance. Transforming raw data from the data source to data file is the crucial conversion. These preparatory steps minimise the errors during the analysis process. Outliers on univariate and multivariate found nominal data were used to identify the dichotomous variables and satisfactory. The interval data for univariate and multivariate outliers also found satisfactory. The researcher proceed to test the data input and confirmed the significance level supported by Hair et al. (2006). For this study the significance level is set at p < 0.05 level and found most of the previous study adopted. The p value of 5% error is acceptable for this study and supported by previous researchers supported by (Bryman, 2012). Finally, the questionnaire reliability is measured based on Cronbach’s alpha method was .853 for pre-Test and .884 actual survey. Overall the variables are distributed at acceptable level of normal distribution and curve, and are based on the rule of thumb and recommendation by previous researchers.A total of 585 respondents were used for statistical analysis. The respondents are consisting of 40.7% male and 59.3% female, age ranges from 18 to 28 year olds belonging to bachelor or master degree holders. Most of the respondents are Malay 64% followed by Chinese 21.8%, Indian 11.4%, Sabah/Sarawak bumiputra 1% and others 1.8%. Mustafa et al. (2012) pointed out that the average age answering the questionnaire is 17 years old. The number of respondents in their study is 999 with 583 females or 58.4 percent and 416 males or 41.6 percent. Furthermore, 986 respondents or 99.2 percent are Malay, 2 or 0.2 percent Chinese and 4 or 0.4 percent are among other races. Mustafa et al. (2012) and this study shown the Malay is monopoly because they are majority in population and followed by Chinese, Indian and others. The findings also highlighted differences between male and female preferences. Samples indicate that females placed more importance on information provided by people around them and on facilities provided by the HEIs than their male counter-parts. This finding is supported by Joseph and Joseph (2000) where they also found that females place more importance in the information provided by the institutions. These elements must be kept in mind by those that address potential female students in the markets.The finding shown that newspapers scored the highest mean in printed media, TV scored the highest mean in broadcasting media, hand phone scored the highest mean in communication media and Facebook scored the highest mean in social media tools. Overall the results indicated that among the group of media the Social Media Tools scored the highest mean as shown in Table 1.
|
|
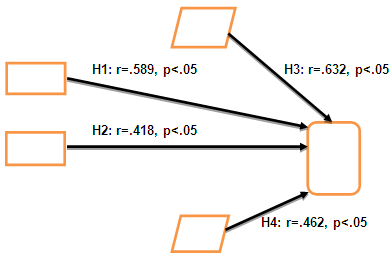 | Figure 1. Correlation - Hypotheses from H1 to H4 |
 | Figure 2. P-P Plot of Regression |
 | Figure 3. Homoscedasticity of DV |
|
7. Conclusions
- The findings of this research suggest that effective recruitment strategies consist of both traditional and modern marketing method. Although the use of modern marketing method such as social media is becoming popular amongst the millenials, but usage of traditional marketing method such as word of mouth is still effective and relevant. Found that the correlation between Traditional, Modern recruitment and students intention to make decision in selecting PU in Malaysia was positive relationships and significant. Additionally, the results identified the full moderators are attitude and subjective norm and have positives significant effect between independent variables (TR and MR) and dependent variable (INT). This study concluded that the PU’s are lacking in maximising the usage of the effective methods and process to attract students. Therefore, it is recommended that the PU’s should adopt best practices from foreign universities to enhance their recruiting on advertising, promoting and creating attractive messages to attract students. Thus, enable the PU’s to recruit more students, reduce marketing and promotion budgets, obtain larger market share and sustain in business for future. This research contributed that C2B approach can be optimize in both traditional recruitment (TR) and (MR) modern recruitment to increase students’ enrolment in private universities for local and globally.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML