-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Management
p-ISSN: 2162-9374 e-ISSN: 2162-8416
2015; 5(5): 148-159
doi:10.5923/j.mm.20150505.02

Exploring the Delays at Empty Container Off-Dock Depots: Useful Perceptions by Stakeholders
Rosmaizura Mohd Zain1, Mohd Nizam Ab. Rahman2, Nizaroyani Saibani2, Zulkifli Mohd Nopiah3, Ainon Ramli1, Norzaliha Jusoh1
1Faculty of Entrepreneurship and Business, Universiti Malaysia Kelantan, Pengkalan Chepa, Malaysia
2Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Faculty of Engineering and Built Environment, Bangi, Malaysia
3Unit of Fundamental Engineering Studies, Faculty of Engineering and Built Environment, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Bangi, Malaysia
Correspondence to: Rosmaizura Mohd Zain, Faculty of Entrepreneurship and Business, Universiti Malaysia Kelantan, Pengkalan Chepa, Malaysia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

To date, however, there has been little investigation into how and why bottlenecks occur at the empty container off-dock depots around the world. Therefore, we accomplished the case study at the off-dock depot which located outside the terminal of Port Klang, Malaysia. The purpose of this paper is to investigate the delays that hinder the rapid movement of empty containers in the context of bottlenecks and congestion. In particular, the paper aims to reveal the stakeholders’ perceptions and identify the main causes of the bottlenecks that exist at off-dock container depots. Based on direct observations and in-depth interviews with a panel of thirty experts in the physical movement of empty containers, the results indicated that the most frequent causes of bottlenecks that stakeholders perceived included work attitudes, operations handling, monitoring, information and facilities/others. Of these, the ‘operations handling’ related to container depots was considered the most significant identifiable barrier to container movements. The research outcomes should assist the container chain players to understand the practice requirements for empty containers in Malaysia.
Keywords: Delays, Empty containers, Off-Dock depots, Bottlenecks, Stakeholders, Perceptions, Practice, Container chain players
Cite this paper: Rosmaizura Mohd Zain, Mohd Nizam Ab. Rahman, Nizaroyani Saibani, Zulkifli Mohd Nopiah, Ainon Ramli, Norzaliha Jusoh, Exploring the Delays at Empty Container Off-Dock Depots: Useful Perceptions by Stakeholders, Management, Vol. 5 No. 5, 2015, pp. 148-159. doi: 10.5923/j.mm.20150505.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- This study is crucial at this juncture due to ‘containers’ appearing to be a key element in the domestic and international cargo flow. The containerization trade is also likely to be influenced by the demand for the raw materials required for industrial production to manufacture goods. Therefore, the seaport/maritime sector has become a channel through which a country can accomplish business with other countries. The growth in container trade and the seaport sector has also led to a rapid expansion in the hinterland transportation industry. The growth of containerization has also induced ports in Malaysia to manoeuver almost 80 per cent of the international commerce when linking to the sea as a transport network in this country. In the containership industry, the key participants consist of containership owners or leasers, liner companies and other logistics service providers to support the shippers’ business.At present, there is an empty container depot belonging to the so-called ‘off-dock depot’ located outside Port Klang’s premises to provide empty container storage and services. The purpose of establishing an off-dock depot is to give significant benefits to the port authority by improving its efficiency in terms of serious traffic congestion, space limitations and gate delays within the Port Klang terminal. At the off-dock depot, more stakeholders can be involved, since the empty box will be taken and returned by the trucking companies during importing or exporting. Accordingly, under the Tenth Malaysia Plan (2011–2015), the total container throughput of Malaysia increased from 12 million twenty-foot equivalent units (TEUs) in 2006 to 20 million TEUs in 2009. Hence, it is evident that the strong demand has led to the requirement for Malaysia to take appropriate measures in container handling management. As reported by the Ministry of International Trade (Malaysia), Malaysia’s international trade growth is achieved by sea, with the port providing the important interface between shipping and several modes of landside transportation companies. Therefore, transport operation (such as empty trucks) connected to the empty container practice is a very important medium to increase the efficiency of the physical flow through modern logistics and supply chain management. Indeed, hinterland transportation is also included in the container logistics to deal with the storing, stripping, stuffing and handling process activities in the terminals (Islam et al., 2010; Levinson, 2006). The integration of seaborne and hinterland transportation has greatly affected the rapidity in the container transport chain. To be competitive with other leading ports in the world, it is very important to emphasize the need to improve the efficiency level of the off-dock depot areas, as many truck operators are involved in collecting and dispatching the boxes. At this point of time, the empty container movements need to be managed effectively to achieve greater service excellence, which leads to increased customer satisfaction (Kannan, 2010). Complexity or fragmentation of the chain in this situation is unavoidable, yet this issue has not been sufficiently thoroughly addressed in the previous research. It can be seen that the business environment has become more and more complex due to the uncertainties, particularly when dealing with the specific perspectives of the container supply chain and logistics. The paper is organized as follows: first is a brief introduction of the movement of empty containers linked to the hinterland transportation, as well as the port throughput worldwide and in the Asia region, including the specific focus on Port Klang, Malaysia. The following sections pertain to the research motivation together with the existing literature; the research objectives and method; the findings and the recommendations. The conclusion is presented at the end of the study.
2. The Physical Movement of Containers and the Port Throughput
- Empty containers induce the rapid movement of goods when globalization increases positively (Yur & Esmer, 2011). Therefore, to achieve just-in-time movement for every type of goods or products, containers and transportation have to be considered as a very visible element to support the supply chain and logistics and the most important means of the global supply chain. In reality, a supply chain is a process responsible for the development and management of the total supply system’s links to internal and external stakeholders (Kia et al., 2000). Mol (2007) stated that empty containers have become very important for the purpose of shipping cargo, together with the information flow. Figure 1 shows the practice of empty container movement linked to hinterland transportation adapted from Hanh (2003), Jula et al., (2006), Mittal et al., (2013) and Roso (2008). That is, the container movement links to many nodes, which may consist of empty container depots (on/off-dock depots), the customers’ or shippers’ premises, container terminals, vessels, hinterland transport and so forth to make sure that the containers can be delivered in good time to the customers. The nodes in container transportation are also accomplished by several key participants, for example truck operators, ship companies or railway companies. Therefore, a container port requires good coordination and collaboration with the hinterland container transport system, which enables it to produce the vital effect on the port’s performance as well as bringing the maximum value to all the parties (Tseng et al., 2005). Generally, an empty container is located at a specific depot, and the truck driver (hinterland transportation) picks up the container for stuffing at the shipper’s premises. The laden container is then transported to the seaport terminal. Subsequently, the container is shipped to the port of destination. After arrival at the port, the container is moved by hinterland transportation to the customer’s premises for stripping. Finally, this empty box will be repositioned in other empty depot belonging to the container owners. Overall, maritime container shipping is part of the supply chain function to support the global trade as a whole (Lun & Browne, 2009).
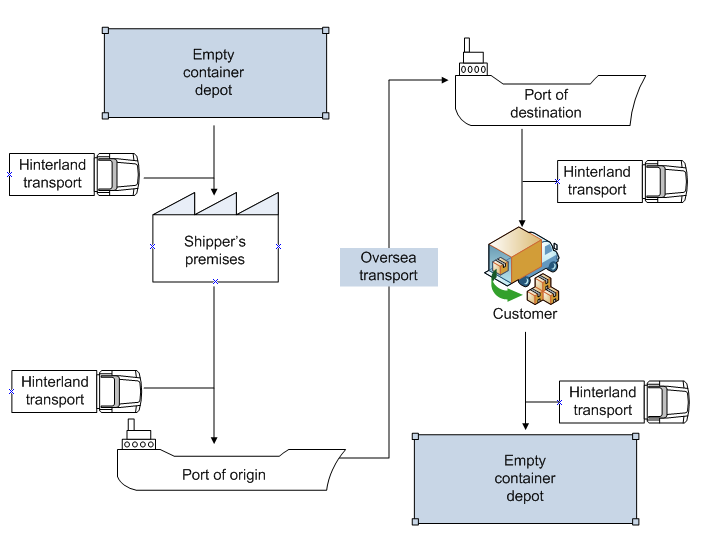 | Figure 1. Empty containers’ movement to hinterland transportation. Source: Adapted from Hanh (2003), Jula et al., (2006), Mittal et al., (2013) and Roso (2008) |
3. Research Motivation
- Terminal container yards (CYs) and off-dock container depots have become two principal locations to manage and interchange containers (Tioga Group, 2002). Hanh (2003) and Jula et al., (2006) stressed two possible practices for distributing or relocating empty containers, namely the street turn and depot direct practices. In the depot direct practice, the empty containers are stored, maintained and interchanged by dropping them off and picking them up at the yards at the off-dock container depots. In contrast, in the street turn practice, the empty containers are moved directly from local consignees to local shippers. At the depot, the containers must be cleaned or repaired before being reused by other customers (Kroon & Vrijens, 1995). Through this practice, the shipping lines can take advantage of lower-cost services, including storage, cleaning, maintenance and inspection services. In the current scenario, off-dock empty depots accept empty containers for one or more marine terminals and ocean carrier clients. The concept of an off-dock empty depot may be more attractive and promising in the long term than in the short term. However, in the short term, if an empty depot accepts too many container owners, the backlog of containers would introduce a significant delay for the container truck drivers. In practice, the off-dock depots are developed to prevent bottlenecks and mitigate the shortage of space at the marine terminals (Haralambides & Gujar, 2011; Tioga Group, 2002). However, in some cases, the whole of the container chain system will operate inefficiently if the flows of empty containers are not managed in an orderly fashion (Choong et al., 2002). The problems or disruptions in this flow may affect one other; these problems may influence different types of activities in transportation, shipping and depots, thus leading to uncertainty in the delivery to customer/shippers. According to Roso et al., (2009), the rapidly growing container flows have introduced some problems, such as terminals crowded with containers, bottlenecks that reduce the efficiency of port activities and prolonged dwelling time for container operations. As supported by Park and Dragovic (2009), in the development of the container transport chain, container terminals have encountered disruptions, such as bottlenecks. Jula et al., (2006) concluded that the growth in container traffic may contribute to regional congestion. As noted by Longo (2010), the performance of a container terminal can be measured by the fastest time for the containers leaving the port. Therefore, better coordination among the key players in the supply chain must be developed. Bottlenecks in a container supply chain can limit the picking up and dropping off of containers, loading or unloading, information flows and administrative activities (Veenstra et al., 2010). Fan et al., (2012) find that the congestion and flows of containers imported to US ports could negatively affect the logistic functions. Accordingly, containerization can increase container traffic, causing congestion in and around the Malaysian ports. Surprisingly, the research on empty container movement at the off-dock depot in Malaysia is limited, particularly in the context of congestion or bottlenecks. For example, Xui (2005), in his master thesis, analysed the Malaysian port performance with respect to port productivity, capacity and efficiency measurement. The aim was to compare the port operations among Malaysian container terminals and Singaporean ports by using a non-parametric approach to ensure sufficient capacity of ports toward continuous improvement. Tahar and Hussain (2000) proposed a simulation model to increase the port performance at the Kelang container terminal in Malaysia. Moreover, numerous studies deal with empty container management. Mhonyai et al., (2011) reviewed the problem of empty container management among the key players in the supply chain. Braekers et al., (2011); Yur and Esmer (2011); Dong et al., (2013) discussed the problems of empty container repositioning. Bin and Zhongchen (2007) reported on intermodal empty container repositioning of land carriage, while Diaz et al., (2011) studied the forecasting of volumes of empty containers at ports to minimize the costs of repositioning them. Chen et al., (2003) and Choong et al., (2002) analysed the problem related to the tactical management of empty containers. The recent study by Tarudin (2013) underlined the importance of the street turn strategy of container movements by haulage operators to encourage a healthy environment and reduce traffic congestion. Zaid and Shah (2007) discussed the important role that container haulage operators play in moving containers to customers’ or ports’ locations; this study proposed several performance measures to identify the efficiency of the container haulage system in Malaysia. Shariff et al., (2011) investigated the service quality provided by the Malaysian container haulage and attempted to identify the critical determinants of customer satisfaction with service quality. However, many of the previous studies focused mainly on the container haulage perspective. To obtain an efficient logistics system, container chain parties must develop a new practice. The present article is a continuation study from Zain et al., (2014). However the focus of the present study is to provide the further insight on issue of off-dock depots, which are one of the essential components of container chain activities and part of the supply chain that influences the distribution of goods in the country. Therefore, research questions have been defined to obtain a satisfactory range of answers regarding the following areas: the main issue/problem at the off-dock depot; the root causes/factors of the problems highlighted by stakeholders; the key players who are most involved in dealing with the problems at the off-dock depot; and, finally, the implications of these interruptions for the container key players from the viewpoint of stakeholders.
4. Methodology
- According to the research question, the study firstly aims to examine the stakeholders’ perceptions of the issues arising at the off-dock depot pertaining to bottlenecks. Additionally, the study intends to gain an understanding of the practices of container movement at the depot yard. Therefore, the perceptual differences between shippers, liners, hauliers and depot firms will be discussed concerning the main factors of the bottleneck involved. To deepen our understanding, this study seeks to interpret the themes/factors of related issues from the insider’s perspective of the interviewees. Therefore, it is based on qualitative, semi-structured and in-depths interviews. Coleman and O’Connor (2007), Nian et al., (2014), Peek et al., (2010), Smith and Holm (2010) and Trichon and Tetnowski (2011) used such guidelines to solicit information in the data collection process. Coleman and O’Connor (2007) believed that qualitative research is linked to how and why questions with the aim of achieving in-depth explanations. In reality, qualitative research also allows the researcher to explore the richness of knowledge without drawing hypotheses (Chrisman et al., 2013). The qualitative method also enables the researcher to understand more about the topic discussed and gather more information through personal data collection methods (Nian et al., 2014). The current study consisted of three phases. In phase 1, a literature review was conducted through various sources and methods, such as market reports, previous journals, news, manufacturing companies, shipping companies and relevant websites, to develop the research framework. A pilot study was carried out in phase 2 with panel experts including the port authority, shipping companies, shippers and forwarder members with the aim of understanding the perceptions of the current problems at the depot located outside the Port Klang terminal. In phase 3, in-depth interviews were conducted to explore the important knowledge of empty container practices of 30 respondents, including internal or local carriers, manufacturing firms, trucking companies, intermodal transport operators, freight forwarders and marine container logistics specialists involved in the issue. Creswell (2007) suggested that the number of respondents or interviewees should range from 5 to 25 in each case. In this study, semi-structured questionnaires were the chosen method of data collection and face-to-face interviews were conducted in 2012. The interview lengths averaged 40-80 minutes with each participant. In addition, on-site observations were performed to understand the practices of empty container movement by truck. All the interviews were tape recorded and transcribed verbatim with coded themes and sub-themes. The transcriptions were carefully checked and read through several times. The transcripts were then index-coded using the Atlas.ti management software to organize the approximately 80 pages of transcripts. All the codes were defined thematically with reference to the semi-structured questions. The objective of selective coding is to identify a key category or theme that can be used as the core of the study results (Coleman & O’Conner, 2007). The combination of more than one qualitative method and multiple resources and the rigorous procedure were able to attain triangulation and greater research credibility (Patton, 1999). Finally, the themes and codes were compared with the different perceptions of the interviewees and the study ended with discussion of the main factors of bottlenecks.
5. Results
5.1. The Main Issue/Problem at the Off-Dock Depot
- In this paper, our attention is focused on the off-dock depot, which has become a hub to link shipping and land transportation. Using qualitative software, we extracted 21 codes from almost 200 quotations on the perceptions, knowledge and experience of the related participants. The coding scheme was used to answer the research question as mentioned above. The Atlas.ti approach uses selective coding to achieve the objective of the study. The transcripts were coded independently and the few inconsistencies were resolved by discussion with experts. After intensively analysing the data, it can be seen that 90 per cent of the respondents agreed that congestion or bottlenecks are a problem in the off-dock depot area, and the rest of the respondents highlighted that no critical problem was evident in this phenomenon because the movement of empty containers on trucks was efficient, with only minor problems. Figure 2 shows the ‘network view’ based on the selective coding represented by the respondents who viewed the issue. Respondent no. 3 reflected that the slow operation of depot operators in picking up and dropping off containers caused delays and congestion. Other interviewees (respondents no. 4, 5, 6 and 12) corroborated the claims that the bottleneck problems faced daily by haulage companies and their drivers resulted in them having to wait for many hours to collect a box and transport it to the shipper’s premises. The congestion problem occurs because there are many empty-truck movements in the container terminal, which causes difficulties in continuing operations (respondent no. 8). According to respondent no. 11, the operation at the depot starts in the early morning hours; however, at certain hours, the container depot is extremely busy (with more trucks arriving), and at other times, the depot could be less busy (with fewer trucks arriving). It can be seen that the results reflected the fact that unsolved problems remain within the container chain.
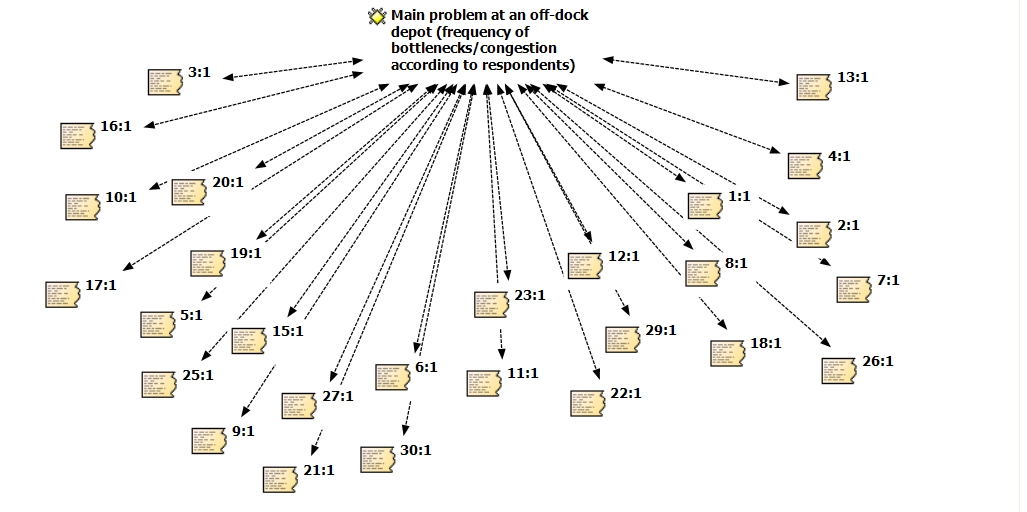 | Figure 2. Network view according to respondents of the bottlenecks issue at the off-dock depot |
5.2. The Root Causes/Factors of Bottlenecks According to the Stakeholders
- Furthermore, after analysing and interpreting the transcripts from the 30 respondents, the following major themes emerged: (1) work attitudes, (2) information, (3) operations handling, (4) monitoring and (5) facilities/others. For each major theme, all the text quotes were extracted from the transcripts and grouped according to the subthemes. After classifying the major themes, frequency tables of the codes were developed to identify the most salient responses from the participants. As De Langen (2004) noted, work attitudes influence the attractiveness of container terminal performance. Inefficiency due to training, skills, a low level of supervision and unavailability of manpower to perform operations can contribute to supply chain disruptions (Veenstra et al., 2010). Moreover, the information flow attribute is important to the efficiencies in a supply chain; thus, a lack of information will lead to circumstances of congestion at the terminal (Kia et al., 2000). A representative attribute for operations handling refers to the associated problem in a container supply chain, for example the movement and flow of empty containers, the scheduling problem, the distribution planning problem, loading and unloading operations and the allocation problem (Hartmann, 2004; Mhonyai et al., 2011). Carbone and Martino (2003) advocated that the factor of operations handling at the container terminal influences the efficient use of resources in executing the services. Monitoring at the depot has become a necessary element to evaluate the depot supply chain performance, for example monitoring information flows, services, manpower participation, inventory levels and physical operations. In modern logistics, real-time monitoring by container practitioners requires the use of information and electronic technology to facilitate the exchange of data among firms and customers. The component of facilities/others found in this study is partly a consequence of the bottleneck problem, for example the management level needed to conduct an effective meeting between the logistics parties and the customers, consistency in service standards and the provision of sufficient container terminal infrastructure (e.g. the containers with conditions that comply with the grade and all parties being electronically linked to the depot). The previous studies have shown strong evidence of the elements or causes of fragmentation in the chain (see, e.g., Esmer, 2008; Islam et al., 2010; Jula et al., 2006; Veenstra et al., 2010). Kannan (2010) used the following seven criteria to benchmark the service quality of container carriers: customer service, operations, reputation, infrastructure, scheduling, information technology orientation and communication, and rate. Yeo and Song (2003) evaluated the major factors influencing port competitiveness from the logistics providers’ perspective. For example, the facility, location, service level, cargo volume and cost were found to be the most important determinants. As suggested by Yeo and Song (2003) and Yeo et al., (2008), the congestion issue could also be included in the criteria that are relevant to the port performance. The stimulated growth of container flows world- wide would thereby contribute to the traffic congestion in and around the container terminals (Tavasszy et al., 2011). Therefore, the congestion issue would play a significant part in developing the parameters to enhance the port performance and competitiveness.
5.3. The Frequency Results of the Bottleneck Causes Linked to the Key Players
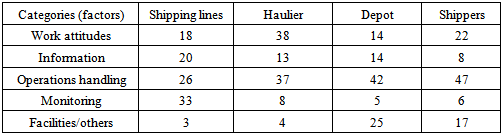
- Table 1 shows the frequency results in the interview transcripts of the 30 respondents. The results were categorized by different key players, for which the percentage values in the table denote the factors or attributes related to the bottleneck problem. Overall, it can be perceived that the information factor related to shipping lines reached the highest frequency of 20 per cent; thus, this rate exceeds that of the other key players. The monitoring factor under shipping lines contributes to the highest rate with 33 per cent, while the depot contributed to the lowest value, reaching only 5 per cent. The work attitude factor linked to the haulier/driver is estimated at 38 per cent, which reveals the highest value of the players; the operations handling factor under the depot accounted for 42 per cent. The operations handling linked to shippers, which has a close relationship with depot problems, reached at 47 per cent. The delays occurring at the depot would cause other problems in the factory. Finally, the facilities/others factor at the depot accounted for 25 per cent. In this study, the factor of operations handling at the container depot was deemed a significant element, meaning that the root cause of this problem lies with the container depot operators. To this end, the value of the factors would adversely contribute to bottlenecks, thus resulting in poor performance in the logistics chain.
|
5.4. Comparison of Stakeholders’ Perceptions of the Key Players in the Container Chain
- Accordingly, Figure 3 illustrates how the categories and subcategories are interrelated, based on the perceptions of key players in graphical form. The codes were refined and aggregated into categories by revisiting the transcripts to evaluate them against the perceptions and relationships of shipping lines, hauliers, depots and shippers with one another concerning this issue. As mentioned above, the quotations were coded into the following main categories/themes/family: attitude, information, operations handling, monitoring and facilities / others. Further enlightenment for each factor pertaining to the respondents’ perception will be provided in the following.
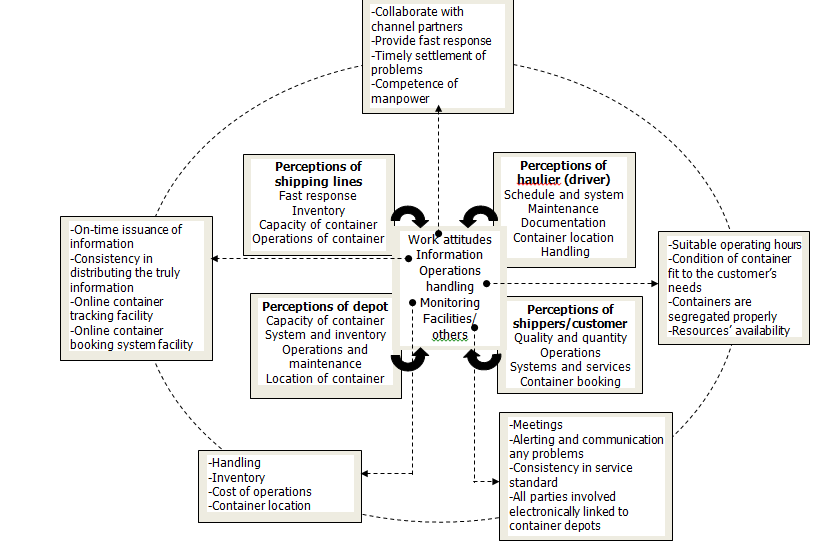 | Figure 3. Perceptions of bottlenecks based on key players in the container chain |
6. Managerial Implications and Recommendations
- In reality, serious bottlenecks frequently occur at the terminals and around the ports of China, the Republic of Korea, Long Beach and Los Angeles due to steeply increasing worldwide container traffic. Indonesian ports also suffer from congestion with long loading and unloading times. In the 1980s and 1990s, the container traffic expanded rapidly at Malaysian ports due to the tremendous demand from the manufacturing sectors. Thus, the need arose to use hinterland transportation (hauliers) to assist in container movement. Hence, there is strong evidence for the need for container chain players to provide the best services and overcome any foreseeable situations in response to the needs of the customers. The results proved that the opinions of the major respondents confirm the bottleneck issue as a barrier to the smooth flow of empty container movement. Previously, other researchers have paid more attention to the congestion inside the seaport terminals (Fan et al., 2012; Jiang et al., 2012; Murthy et al., 2005; Xui, 2005), but little space has been dedicated to the theme of off-dock empty container depots. The paper has presented some new findings on the container supply chain provided by practitioners from various logistics firms. The new cluster (as illustrated in Figure 3) posed several challenges to the key players to face competition for market survival. Moreover, the tabulated result (refer to Table 1) shows that operations handling is rated highly as the root cause of the bottleneck. It is advisable for depot firms to develop new strategies for the logistics services by taking into consideration the customers’ requirement. In this case, off-dock depots need to deal with multifaceted key players, including hauliers, shipping lines and shippers. Modern supply chains are very complex to manage. For that reason, it is necessary to increase collaboration in the information and physical flow and to develop an understanding link between depots and other relevant parties. According to the interviewees, a lack of comprehensive planning leads to inefficiency in container transport activities. For example, long operation hours result in problems of container delays and shortages and affect the efficiency of the process at the factories; haulage companies also suffer from huge losses due to the cash collections (depot gate charge) and maintenance costs of transport and reduce their daily trips (from one to two trips only, affecting their earnings). The respondents said that if the depots were more efficient, the hauliers would be able to make six or more trips. The implications of bottlenecks do not just apply to shippers and hauliers, but have an adverse impact on port operations (e.g. missed vessel schedules). Moreover, shipping lines have to bear the cost of overdue storage at the depot. According to other respondents, this problem may cause the factories and shipping lines to lose customers, and the companies’ reputation is at risk. To this end, the depots will ultimately suffer from these uncertainties, such as losing the gate surcharge and storage, cleaning, maintenance and other operation costs (e.g. lift on-lift off charges) that are devoted to key players. Hence, all the interruptions occurring will directly increase the operational costs. Accurate information is the most essential factor that the shippers expect from the shipping lines (for example, the location of the container, grade of the container and booking number). Any discrepancies occurring when disseminating information can result in a range of problems in the form of delays from the point of the depot to the point of the shipper; besides, the problems would spread to other relevant part of the logistics chain. It is important to note that all the key participants will be able reap the full benefits from the provision of good services. To develop positive relationships between customers in the container chain, several recommendations can be made based on the responses obtained with the help of thematic analysis. Another important expectation to develop a positive relationship between the shipping line and the depot is to work together to minimize costs, improve the ability to share information, issue documents promptly (e.g. damaged containers), respond promptly for container repair, conduct appropriate inspections of containers and facilities, and segregate the containers according to their type. Accordingly, to develop a positive relationship between the haulier and the depot, the respondents have suggested expectations, such as a high level of services by the depot (to pick up and drop off containers within operating hours, which takes no less than 45 minutes), depot accessibility (7 days per week and 24 hours per day), depot facilities, consistency in service standards, availability of equipment, consistency in distributing information, providing containers that fit the customers’ needs and real working time. Meanwhile, the shippers’ expectations regarding shipping lines, hauliers, depots and other affiliated key players consist of the efficiency of hauliers to deliver containers at the right time and fulfil the right orders, accuracy of information, zero containers found to be damaged or dirty and the ability to resolve customers’ complaint quickly. Therefore, the identification of expectations by stakeholders would perhaps interest the practitioners in the container chain in looking beyond the narrow differences in the requirements among container chain players.
7. Conclusions
- Business has no meaning without containerization and hinterland transportation. Therefore, managing the movement of empty containers is very important for improving the performance in the container chain and other relevant logistics service providers. This study achieved its main objectives. First, the stakeholders considered bottlenecks to be the main delay that hinders the rapid movement of empty containers to the shippers. Second, the study found that there are five significant factors or root causes of bottlenecks: work attitudes, information, operations handling, monitoring and facilities/others. The findings of this study indicate that the operations handling at the depot is the most significant factor in the barriers to container movement. At the end of this study, the related factors/categories from the verbatim analysis were used to develop a new cluster in graphical form to achieve a better understanding of the relationship in the chains of bottlenecks; in addition, the comparison of perceptions of key players produced some useful guidelines or recommendations based on the stakeholders’ points of view. Accordingly, under the different factors of bottlenecks, there are many sub-factors acting as barriers to successful collaboration among the key players. Therefore, the results generated several ideas for further studies in the area of container supply chains. The information will be very useful to all logistics companies, which will lead to improvements in the performance either at the strategic, the tactical or the operational level. Finally, in our future study, a simulation model will be developed to analyse the performance of off-dock depot operations. More detailed information is needed in the form of specific knowledge on container operations, data on the container truck waiting time, the quantity of empty container truck movements per day and any other parameters to model and simulate the event. Therefore, the further study seeks to make a possible decision on how to overcome the bottleneck problem in empty container off-dock depots, and a potential solution must be created to implement good collaboration and coordination in the container chain at the end of the research agenda. In other words, all stakeholders can obtain benefits, including positive relationships as well as efficient operations.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- This research was supported by Lean Logistics and Quality Improvement to Increase the Performance of Manufacturing Industry (GUP-2014-020) and Bridging and Greening the Lean Supply Chain Networks in SMEs (ERGS/1/2012/TK01/UKM/02/8).
References
| [1] | Adam, S. 2009, “Simulation and Analysis of Port Bottlenecks: The Case of Male,” Lincoln University, New Zealand. |
| [2] | Bichou, K., and Gray, R., 2004, A logistics and supply chain management approach to port performance measurement., Maritime Policy and Management, 31(1), 47-67. |
| [3] | Bin, W., and Zhongchen, W., 2007, Research on the optimization of intermodal empty container reposition of land-carriage., Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 7(3), 29-33. |
| [4] | Braekers, K., Janssens, G.K., and Caris, A., 2011, Challenges in managing empty container movements at multiple planning levels., Transport Reviews, 31(6), 681-708. |
| [5] | Carbone, V., and Martino, M.D., 2003, The changing role of ports in supply-chain management: An empirical analysis., Maritime Policy and Management, 30(4), 305-320. |
| [6] | Chen, C., Hsu, W. J., and Huang, S.Y., 2003, Simulation and optimization of container yard operations: A Survey., Proc. of the 2nd International Conference on Port and Maritime R&D and Technology, Singapore, 23-29. |
| [7] | Choong, S.T., Cole, M.H., and Kutanoglu, E., 2002, Empty container management for intermodal transportation networks., Transportation Research Part E, 38(6), 423–438. |
| [8] | Chrisman, S.P., Quitiquit, S., and Rivara, F.P., 2013, Qualitative study of barriers to concussive symptom reporting in high school athletics., Journal of Adolescent Health, 52, 330-335. |
| [9] | Coleman, G., and O' Connor., R.V., 2007, Using grounded theory to understand software process improvement: A study of Irish software product companies., Journal of Information and Software Technology, 49(6), 654-667. |
| [10] | Container Traffic Forecast. (2007). Regional Shipping and Port Development, United Nations, New York. [Online]. Available: http://81.47.175.201/transvisions/documents/CONTAINERS.pdf. |
| [11] | Creswell, J.W, Qualitative inquiry and research design: Choosing among five approaches, 2nd ed., Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2007. |
| [12] | De Langen, P.W. (2004). The performance of seaport clusters: a framework to analyze cluster performance and an application to the seaport clusters in Durban, Rotterdam and the lower Mississippi, Erasmus University, Rotterdam. [Online]. Available: file:///C:/Users/user/Downloads/EPS2004034ORG_9058920569_DELANGEN.pdf. |
| [13] | Diaz, R., Talley, W., and Tulpule, M., 2011, Forecasting empty container volumes., The Asian Journal of Shipping and Logistics, 27(2), 217-236. |
| [14] | Dong, J.X., Xu, J., and Song, D.P., 2013, Assessment of empty container repositioning policies in maritime transport., The International Journal of Logistics Management, 24(1), 49-72. |
| [15] | Esmer, S., 2008, Performance measurements of container terminal operations., Journal of Graduate School of Social Sciences, 10(1), 238-255. |
| [16] | Fan, L., Wilson, W.W., and Dahl, B., 2012, Congestion, port expansion and spatial competition for US container imports., Transportation Research Part E, 48(6), 1121-1136. |
| [17] | Hanh, L.D. (2003). The logistics of empty cargo containers in the Southern California region, final report, Metrans Transportation Centers, University of Southern California. [Online].Available: http://www.freightworks.org/. |
| [18] | Haralambides. H., and Gujar, G., 2011, The Indian dry ports sector, pricing policies and opportunities for public-private partnerships., Research in Transportation Economics, 33(1), 51-58. |
| [19] | Hartmann, S., 2004, Generating scenarios for simulation and optimization of container terminal logistics., OR Spectrum, 26(2), 171-192. |
| [20] | Islam, S., Arthanari, T., and Olsen, T., 2010, Empty container-truck movement problem: At Ports of Auckland., Proc., of the 45th annual conference of the ORSNZ, Auckland, New Zealand, 239-248. |
| [21] | Jiang, X., Lee, H.L., Chew, E.K., Han, Y. and Tan, K.C., 2012, A container yard storage strategy for improving land utilization and operation efficiency in a transshipment hub port., European Journal of Operational Research, 221, 64-73. |
| [22] | Jula, H., Chassiakos, A., and Ioannou, P., 2006, Port dynamic empty container reuse., Transportation Research Part E, 42(1), 43-60. |
| [23] | Kannan, V., 2010, Benchmarking the service quality of ocean container carriers using AHP. Benchmarking: An International Journal, 17(5), 637-656. |
| [24] | Karmelić. J., Dundović. Č., and Kolanović. I., 2012, Empty container logistics., Promet-Traffic & Transportation, 24(3), 223-230. |
| [25] | Kia, M., Shayan, E., and Ghotb, F., 2000, The importance of information technology in port terminal operations., International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics management, 30(3/4), 331-334. |
| [26] | Kroon, L., and Vrijens, G., 1995, Returnable containers: an example of reverse logistics., International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 25(2), 56-68. |
| [27] | Levinson, M. (2006). The box: how the shipping container made the world smaller and the world economy. [Online]. Available: http://empire-logistics.org. |
| [28] | Longo, F., 2010, Design and integration of the containers inspection activities in the container terminal operations., Int. J. Production Economics, 125(2), 272-283. |
| [29] | Lun, Y.H.V., and Browne, M., 2009, Fleet mix in container shipping operations., Int. J. Shipping and Transport Logistics, 1(2), 103-118. |
| [30] | Marchet, G., Perotti. S., and Mangiaracina, R., 2012, Modelling the impacts of ICT adoption for inter-modal transportation., International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 42(2), 110-127. |
| [31] | Mhonyai, C. Suthikarnnarunai, N., and Rattanawong, W., 2011, Container supply chain management: facts, problems, solution., in Proc., of the World Congress on Engineering and Computer Science, San Francisco, USA, 1-4. |
| [32] | Ministry of International Trade and Industry Malaysia. Performances and challenges of industrial development. Chapter 1, pp. 20. [Online]. Available: http://www.miti.gov.my. |
| [33] | Ministry of Transport Malaysia. [Online]. Available: http://www.mot.gov.my. |
| [34] | Mittal, N., Boile, M., Baveja. A., and Theofanis., S., 2013, Determining optimal inland-empty-container depot locations under stochastic demand., Research in Transportation Economics, 42(1), 50-60. |
| [35] | Mol, F., 2007, Logistics of empty marine containers: A research on strategies for port planning, concerning the storage and flow of empty marine containers in the port of Rotterdam. Delft University of Technology, Netherlands. |
| [36] | Murthy, K.G., Liu, J., Wan, Y.W., and Linn, R.,. 2005, A decision support system for operations in a container terminal., Decisions support systems, 39, 309-332. |
| [37] | Nian, T.Y., Bakar, R., and Islam, M.A., 2014, Students’ perception on entrepreneurship education: The case of Universiti Malaysia Perlis., International Education Studies, 7(10), 40-49. |
| [38] | Park, N.K., and Dragović, B., 2009, A study of container terminal planning., FME transactions, 37(4), 203-209. |
| [39] | Park, R., and De, P., 2004, An alternative approach to efficiency measurement of seaports., Maritime Economics & Logistics, 6(1), 53–69. |
| [40] | Patton, M.Q., 1999, Enhancing the quality and credibility of qualitative analysis., HSR: Health Services Research, 34(5), 1189-1208. |
| [41] | Peek, M.E., Young, A.O., Quinn, M.T., Bhat, R.G., Wilson, S.C., and Chin, M.H., 2010, Race and shared decision-making: Perspectives of African-Americans with diabetes., Social Science & Medicine, 71, 1-9. |
| [42] | Rensburg, J.J.V., He, Y., and Kleywegt, A.J., 2005, A computer simulation model of container movement by sea. Proc. of the 37th Conference on Winter Simulation, Orlando, 1559-1566. |
| [43] | Roso, V., Woxenius, J., and Lumsden, K., 2009, The dry port concept: connecting the container seaports with the hinterland., Journal of Transport Geography, 17(5), 338-345. |
| [44] | Roso, V., 2008, Factor influency implementation of a dry port., International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 38(10), 782-798. |
| [45] | Selva, T. (2008). Growth of freight transport volume at 7%’. [Online]. Available: http://www.thestar.com.my/story/?file=%2F2008%2F6%2F9%2Fmaritime%2F21455980&sec=maritime. |
| [46] | Shariff, D.N., Saharuddin, A.H., and Ahmad, S., 2011, Sustainable container haulage industry in Malaysian West Ports: Service quality perspective. In 2nd International Conference on Business and Economic Research proceedings, Kedah, Malaysia, 2745-2755. |
| [47] | Smith, L.H., and Holm, L., 2010, Research report: Social class and body management. A qualitative exploration of differences in perceptions and practices related to health and personal body weight., Appetite, 55, 311-318. |
| [48] | Song, D. W., and Panayides, P., 2008, Global supply chain and port/terminal: Integration and competitiveness., Maritime Policy and Management, 35(1), 73-88. |
| [49] | Tahar, R.M., & Hussain, K., 2000, Simulation and analysis for the Kelang Container Terminal operations., Logistics Information Management, 13(1), 14-20. |
| [50] | Tarudin, N.F., 2013, Street turn strategy: An analysis of its effectiveness as a ‘Green Logistics’ tool for the management of empty containers for road haulage in Malaysia., Management, 3(1), 16-19. |
| [51] | Tavasszy.L., Minderhoud, M., Perrin, J.F., and Notteboom, T., 2011, A strategic network choice model for global container flows: specification, estimation and application., Journal of Transport Geography, 19(6), 1163-1172. |
| [52] | Tenth Malaysia Plan (2011-2015). [Online]. Available: https://www.pmo.gov.my/dokumenattached/RMK/RMK10_Eds.pdf (accessed 5 October 2014). |
| [53] | The JOC Top 50 World Container Ports, 2012, Journal of Commerce. [Online]. Available:http://www.joc.com/special-topics/top-50-container-ports (accessed 10 January 2013). |
| [54] | The Tioga Group, 2002. Empty ocean container logistics study, pp. 1-105. [Online]. Available: http://www.log.cl/www/secondpages/container/Final_Empty_Containers_Report.pdf. |
| [55] | Trichon, M.. and Tetnowski,J., 2011, Self-help conferences for people who stutter: a qualitative investigation., Journal of Fluency Disorders, 36, 290-295. |
| [56] | Tseng, Y.Y., Yue, W.L., and Taylor, M.A.P., 2005, The role of transportation in logistics chain. Proc. of the Eastern Asia Society for Transportation Studies, Bangkok, Thailand, 1657-1672. |
| [57] | UNCTAD. (2013) Review of Maritime transport, United Nations, New York and Geneva. Retrieved from http://unctad.org/en/PublicationsLibrary/rmt2013_en.pdf |
| [58] | Veenstra, A., Hinsta, J., and Zomer, G., 2010, Global supply chain conpendium, Seventh framework programme, Theme 7. [Online]. Available: http://www.smartcm.eu/LinkClick.aspx?fileticket=x5bKRMvx2p4%3D&tabid=69&mid=433. |
| [59] | Vis, I.F.A., and Koster, R.D., 2003, Invited review transshipment of containers at a container terminal: An overview. European Journal of Operational Research, 147, 1-16. |
| [60] | Xui, L.C., 2005, Malaysian container port performance measurement, Malaysia University of Science and Technology, Malaysia. |
| [61] | Yeo, G.T., and Roe, M., and Dinwoodie, J., 2008, Evaluating the competitiveness of container ports in Korea and China., Transportation Research Part A, 42(6), 910-921. |
| [62] | Yeo, K.T., and Song, D.W., 2003, An evaluation of container ports in China and Korea with the Analytic Hierarchy Process., Journal of the Eastern Asia Society for Transportation Studies, 5(3), 726-741. |
| [63] | Yur, T., and Esmer, S., 2011, A review of the studies on empty container repositioning problem. Proc. of European Conference on Shipping, Intermodalism & Ports (ECONSHIP), Chios, Greece, 1-20. |
| [64] | Zaid, Z.M., and Shah, M.Z., 2007, Performance measurement in Malaysia container haulage industry: a critical evaluation. Postgraduate Seminar, Fakulti Alam Bina, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Skudai, Malaysia, 1-14. |
| [65] | Zain, R.M., Rahman, M.N.A., and Nopiah, Z.M., 2014. Quality Logistics Management: Managing empty container movement at the off-dock depot. Proc. of the 18th International Conference on ISO & TQM, Kuching Sarawak, Malaysia, 1-8. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML