-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Management
p-ISSN: 2162-9374 e-ISSN: 2162-8416
2013; 3(7): 480-483
doi:10.5923/j.mm.20130307.19
Modeling Green Purchase Intention in Nigeria: A Conceptual Proposition
Victoria Masi Haruna Karatu, Nik Kamariah Nik Mat
Othman Yeop Abdullah Graduate School of Business, Universiti Utara Malaysia, Sintok, 06010, Malaysia
Correspondence to: Nik Kamariah Nik Mat, Othman Yeop Abdullah Graduate School of Business, Universiti Utara Malaysia, Sintok, 06010, Malaysia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Even though the green agenda has been launched since 1990, Nigeria still lagged behind its counterparts on green growth as indicated by the low percentage (5%) of green product purchase. This shows that there is a low level of green awareness among Nigerian consumers. Furthermore, there seems to be an absence of environmental consciousness among her citizens such as lack of green awareness, lack of trust towards green product claims, expensive green product prices, poor waste management and worsening pollution scenario. The main objective of this study is to propose a research model for determining green purchase intention in Nigeria. The literature also identifies five probable factors (trust, corporate social responsibility (CSR), environmental concern, perceived value and governmental regulations) that could be the causal factors for poor green purchase intention. The proposed methodology is the quantitative approach by collecting primary data from consumers represented by government staff at five selected government ministries. The data collected will be analyzed using structural equation modeling. The expected findings will illustrate the real factors that could affect green purchase intention which could benefit the policy makers, consumers and the marketers of green products in Nigeria.
Keywords: Green Purchase Intention, Nigeria, Modeling, Environmental Consciousness, CSR, Trust
Cite this paper: Victoria Masi Haruna Karatu, Nik Kamariah Nik Mat, Modeling Green Purchase Intention in Nigeria: A Conceptual Proposition, Management, Vol. 3 No. 7, 2013, pp. 480-483. doi: 10.5923/j.mm.20130307.19.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Continuous human activities from time immemorial on the environment brought about negative impacts on it and its inhabitants (man, flora and faunas)[1,2, 3, 4]. In recent times, concern for the environment has increased steadily across the globe. This has translated into consumers’ awareness which is portrayed in their nutrition, health and the quality of food they go for in terms of purchase and consumption. Unprecedented growth in the demand for green or environmentally safe product was recorded. Confirming this [5] reported that environmentally friendly products’ market size was valued at 200 USD billion in 2006.Strengthening this further, a survey by Natural (Green) Marketing Institution reported that over 200 USD billion market of Lifestyle of Health and Sustainability (LOHAS) rose by 100% in 2010 and was expected to rise four times bigger by 2015[6]. A good example of this is the growth in Global Baby Food market which growths at the rate of 5% yearly[7]. Also, the following surveys declared that green product purchase and consumption has grown in some parts of the world exponentially[8, 9, 10]. However, in developing countries, some regions are still in the dark; there is low awareness about green products[11,12] In the Nigeria society, study showed that only 5% of Nigerians are engaged in green purchase behavior[13]
1.1. Research Problem
- Green Purchase behavior has been hampered by factors such as price sensitivity, quality of green products; availability is some regions[14]. Coupled with this; there is also low awareness of the green products[15, 16]. It has been noted with dismay that consumers no longer trust green product claims[17]. As regards to Nigeria, there is low level of purchase intention and the absence of environmental consciousness which have led to the parlous state of the Nigerian environment. To further emphasize this, it was quoted in[18] that Nigeria is confronted with several peculiar challenges which make green agenda unattainable.
1.2. Research Objectives
- The study seeks to achieve the following objectives:1. To examine the extent of direct relationship between the variables selected with green purchase intention.2. To explore the degree to which CSR mediate the relationship between government role and green purchase intention.3. To establish the mediating effect of green trust on the relationship between Perceived value, Environmental concern and CSR with green purchase intention.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Green Purchase Intention
- Green Purchase intention is explained as the possibility and willingness of an individual to give more preference to brands of products, services, etc which have environmentally safe characteristics in their purchase decision. It was posited by[19] that green purchase intention is significant factor and a proxy to actual purchase intention. Studies on green purchase intention showed that the variable is an influential predictor of actual purchase. The intention of the consumer is completely under his /her power and sterns from the fact that man is rational in his approach and may use information in a systematically organized way and make decision which is based on the expected outcomes[20]. Consumers who show concern for the environment will portray a positive attitude, norm and strong perceived behavioral control which will result in green intention. A consumer with strong and positive intention is more likely to buy green product than one who is not[21].Below are the antecedents of Green Purchase Intention which have been examined in previous studies. The findings revealed that green purchase intention was significantly influenced by these variables in the context they were investigated. They are Green Trust[22]; Corporate Social Responsibility[23]; Environmental concern[24; 25; 26]; Perceived value[27; 28] Government regulations[29;30]
2.2. Green Trust
- One of the basic factors employed in marketing of goods and services is trust; it enhances a long-term relationship between the consumers and the service providers or the manufacturer[31]. [32]posited that trust is the consumer ‘expectations about the product’ credibility and reliability for the purpose of which the consumer buys the product. It means the overall beliefs, desire and assumption directed towards specific brand of product[33]. Willingness of the consumer to have faith in the product based on the conviction that it is credible has benevolence and is eco-friendly[34, 35].
2.3. Environmental Concern
- The general attitude of the consumer which has direct impact on purchase intention is environmental concern[36]. It is the degree to which an individual or a group of individual are concerned about the environment and indicate this in their willingness to curb environmental problems[37]. The more concerned an individual is about the environment, the stronger his or her intention will be to buy green product. Environmental concern has causal effect on intention and has been used in various researches to denote the measure of importance people assign to the protection of the environment. Studies reveal that environmental concern positively influence purchase intention[38] and is one of the strongest attitude displayed in preserving the environment, [39].
2.4. Corporate Social Responsibility
- In a nutshell can be seen as establishing a commitment towards sustainability[40; 41]. Organizations use CSR to show that they are pro-environmental; CSR activities can influence a consumer and lead to high positive attitude towards the organization and its products[42]. Consumers are most often willing to pay high prices for products of an organization that is ethical and is socially responsible[43]. In addition, [44]pointed out that consumers are conscious of whether companies do practice CSR or not. Information on CSR activities is significant in influencing consumer purchase intention.
2.5. Perceived Value
- One of the variables which play an important role in impacting green purchase intention is Perceived value. The consumer’ overall appraisal of the usefulness of the product based on what he gave out for the product and what he expects in return is explained as perceived value[48]. Some studies have suggested that Perceived value is a strong predictor of purchase intention[49]. Consumer who positively evaluates a product based on his or her environmental and Sustainable expectations and green needs is most likely going to purchase the product in a future time because his purchase intention has been influenced by the assessment made.
2.6. Government Regulations
- These are Legislations and Laws which government formulate to intervene in environmental issues[50]. Environmental behavior could be influenced by government actions. Government awareness is a significant factor in influencing and predicting citizens’ environmental attitude and behavior. A study attested that there is positive relationship between political activities which is government orientated and the drivers of environmental attitude.[51] Also, [52]found a positive relationship between government regulations and green purchase intention. The role government plays in environmental preservation cannot be overemphasized. It is important that government initiates and promote sustainable activities to the community for awareness purposes which may later on translate into green purchase intention.
3. Hypotheses
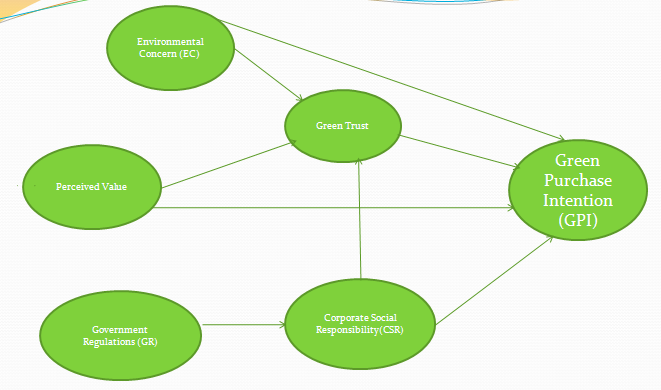
- H1: Green trust has a direct positive relationship with green purchase intention.H2: CSR has direct positive relationship with green purchase intention.H3: Environmental concern has direct positive relationship with green purchase intention.H4: Environmental concern has direct positive relationship with green trust.H5: Perceived Value has direct positive relationship with green trust.H6: Government Regulations has direct positive relationship with CSR.H7: Green trust mediates the relationship between CSR and green purchase intention.H8: Green trust mediates the relationship between Environmental Concern and green purchase intention.H9: Green trust mediates the relationship between CSR and green purchase intention.H10: Perceived value has a direct positive relationship with green purchase intention.H11: CSR mediates the relationship between government regulations and green purchase intention.
4. Research Model
5. Methodology
- For the purpose of this study, the proposed methodology is quantitative approach by collecting primary data from consumers represented by government staff at five selected government ministries. The five Ministries selected are Ministry of Education, Ministry of Finance, Trade and Industries, Defense ministry, Youth and sports and ministry of Women Affairs. The intended sample size is 750. (150 sample from each ministry The data collected will be analyzed using structural equation modeling.
6. Discussion
- The prevailing environmental problems and the issues surrounding green product have made this study significant Its important to ascertain consumer’ purchase intention in Nigeria as a developing nation. It is assumed that the proposed model in this study will give insight to why there is low purchase intention. The frame work will enlighten marketers especially, environmental marketing professionals informative insight for strategic decision marketing. The empirical findings on the antecedents of green purchase intention will serve as an impetus for studying drivers of green purchase intention. The paper is a conceptual proposition which aimed at Modeling Green Purchase intention in Nigeria by examining the direct relationship between green trust, corporate social responsibility, environmental concern, perceived value and the mediating effect of trust and CSR on the relationship with green purchase intention.
7. Conclusions
- Though these days consumers continue to be conscious of their health and are scrutinizing brands, they are also mindful of the environment and are willing to protect and conserve it through their actions and also consider the consequences of their inaction towards the environment. Though the variables in this study have not yet been tested, the complexity of the relationship between the variables are so glaring that it need to include them in this study becomes imperative.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML