-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Management
p-ISSN: 2162-9374 e-ISSN: 2162-8416
2013; 3(7): 475-479
doi:10.5923/j.mm.20130307.18
Antecedents of the Level of Risk Management Practices in Nigerian Local Government
Ishaya j. Dabari , Siti Zabedah Saidin
School of Accounting, College of Business (COB), Universiti Utara Malaysia
Correspondence to: Ishaya j. Dabari , School of Accounting, College of Business (COB), Universiti Utara Malaysia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Risk is one of human life certainties, and how the individual or organization deal with risk can have serious consequences on the achievement of their objectives. Risk management is a catalyst for promotion of good governance, enhancing effective internal control and organizational performance. The study focuses on antecedents of the level of risk management practices in Nigeria particularly the adoption and implementation of risk management practices in the Nigerian local government. A brief historical development of risk management and critical evaluation of the structure and problems of governance in Nigerian public sector will be discussed. The need for comprehensive risk management system to enhance good governance in the Nigeria public sector is paramount and requires a comprehensive system that will identify, assess, analyze, control and monitor all risks that will impede the achievement of the goals and objectives of local government. A framework for the implementation of risk management in the local government will be proposed.
Keywords: Risk Management, Nigeria, Local Government, Antecedents, Organizational Performance
Cite this paper: Ishaya j. Dabari , Siti Zabedah Saidin , Antecedents of the Level of Risk Management Practices in Nigerian Local Government, Management, Vol. 3 No. 7, 2013, pp. 475-479. doi: 10.5923/j.mm.20130307.18.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
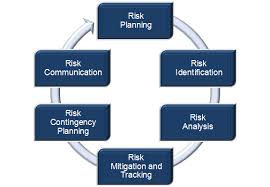
- Risk is one of human life certainties, and how the individual organization deal with risk can have serious consequences on the achievement of their objectives. There is always the possibility that we will not achieve the objectives we set for our self because uncertainty is always in involved in our plan. In every objective set, there is element of risk which needs to be effectively managed to mitigate the impact of risk on our goals. Despite this, there is little effort on the part of either the individual or organization to evaluate and manage risk. Traditionally, risk was seen as negative consequences associated with unfavorable events. Viewing risk in that negative perspective narrows the effects of risk and creates confusion in understanding the concept. The effect of uncertainty may result in either negative (threat) or positive (opportunity) and also the perception of risk influence the manner in which it is treated[12]. Moreover, risk taking sometimes provides some economic benefits, as organization may realize significant gains by taking risk.[3] Risk management is essentially enhancing effective control to mitigate risks and ensuring continuous improvement in corporate governance[4]. Risk management is a catalyst for promotion of good governance, enhancing effective internal control and organizational performance.There are various definitions of risk management. ISO 31000 defines risk as the “effect of uncertainty on objectives” which can have the effect of a positive or negative deviation against expected outcome. A popular and integrated risk management framework has been developed by Committee of sponsoring organizations of tread way commission[5]. Has given a burst to the approach of risk management in corporate governance.[5] Defines risk management as a….”process effected by an entity`s board of directors, management and other personnel, applied in strategy setting and across the enterprise, designed to identify potential events that may affect the entity, and manage risk to be within its risk appetite, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the achievement of entity objectives.” The integrated risk management framework encompasses internal control which has become a catalyst for providing a more robust technique and tool for management[6; 4]. The process of growth and development of any organization is full of challenges, ranging from financial, commercial and administrative risk from both within and external sources. Consequently, the need for a sound internal control system that will identify, assess, monitor and control risks to enhance good governance and organizational performance is imperative[3].Risk management has occupied an important position on the agenda of the international community both private and public sectors[7]. Risk management in the public sector plays a significant role in strengthening government capacities to recognize, understand, accommodate and capitalize on new challenges and opportunities. Risk management fosters flexibility and promote risk informed culture and capacity to fully realize performance improvement within the public sector organizations[8; 9]. However, there is contrary view by some researchers on the relevance of risk management application in the public sector as against the private sector[10; 11]. Various standards have been developed for the practices of risk management across the world examples are COSO 2004, ISO 31000. The argument for driving force of risk management rapid development across all sectors appears to have similarities across both the public and private sectors. Risk management has become an instrument to fight corruption and fraud in the world. However, there are limited studies on risk management in Nigeria despite the high level of corruption and fraud[12; 13]. Risk management is at rudimentary stage in Nigeria. This justifies the need for the study of antecedents of the level of risk management practices in Nigerian local government.Risk Management Process
1.1. Problem Statement
- The Federal government of Nigerian created local governments as the third tier government with the aim of bringing government closure to the people at the grass root level to enhance development and promote participatory democracy[14]. The functions of the local government are clearly split out in the constitution which includes, Promotion of freedom for decision making, local autonomy, participatory democracy, political integration, and above all, provision of effective service delivery at the grass root level. According[15] the success and the effectiveness of local government very much depend on the financial resources available to the individual local authorities, and the manner in which these resources are utilized. However, it is noted that in spite of the fact that the 1976 local government reforms granted greater autonomy, powers and functions to local governments, their performance is below expectation. The above statement is in consonant with the state of affairs in the local government system in Nigeria. • The main problem of the local government is lack of application of risk management principles to identify, evaluate, control and monitor risks that could impede the achievement of their goals and objectives. Risk management is still at rudimentary stage in Nigeria[12]• Closely related to above, is also the problem of overbearing influence of the States and State houses of assembly on LG administration in Nigeria particularly the Joint State local government account.Another critical problem inhibiting the performance of local government as in all levels and institutions of government in Nigeria which is predominately widespread, undiluted and unambiguous in the local governments[16].• There is contrary view by some researchers on the relevance of risk management application in the public sector as against the private sector[9; 17; 18]. This has created some inconsistencies in the importance and value creation of risk management. To support this point, Transparency International ranked Nigeria as the 139th out of 176 countries surveyed in 2012 under the corruption perceptions index. A respected audit and financial advisory firm, KPMG has rated Nigeria as the most fraudulent country in Africa under the 2012 survey. There is lack of legal framework for the implementation of risk management practices to enhance organizational performance in the Nigerian local government. Basel 11 Accord adopted for Banks only[12].
1.2. Research Questions
- What are the antecedents of risk management practices in Nigerian local government? To what extent do risk management influence organizational performance?
1.3. Research Objectives
- The main objective of the study is to identify the antecedents of risk management implementation in Nigerian local governmentTo determine the influence of risk management practices on organizational performance.
1.4. Scope of the Study
- The research focuses on determining the antecedents/ critical success factors for the implementation of risk management in the Nigerian local government. The study is limited to Nigerian local government only. This is because the local government is less studied and the practice of risk management is at its rudimentary stage in Nigeria[4; 12].
1.5. Justification of the Study
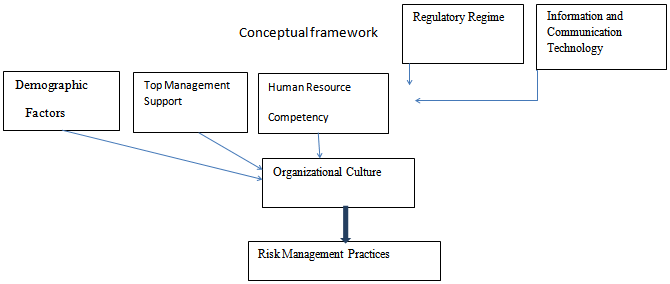
- There are inconsistencies on the role of risk management in enhancing organizational performance[7; 9; 17; 22; 24].There are limited studies conducted on risk management implementation in the public sector particularly the local government. The study will contribute to policy formulation and implementation, and change of legislation. It will also enhance organizational performance through proposal of risk management framework for adoption and implementation in Nigerian local government.It is based on this that I hang my study in order to fill the gap. The research will examine the relationship between dependent variable (Risk Management Practices) and independent variables which include top management support, demographic factors, regulatory regime, Human resource competency, information and communication technology while organizational risk culture is the mediating variable which will mediate the relationships between those IVs and DV and also determine their influences on organizational performance in Nigerian local government. The study is aimed at advocating the implementation of risk management practices in Nigerian local government to enhance organizational performance.
2. Literature Review
- Risk ManagementRisk is an integral to opportunities and threats that have serious consequences if not mitigated[3]. Risk management is essentially enhancing effective control to mitigate risks and ensuring continuous improvement in corporate governance[4]. Risk management is a catalyst for promotion of good governance, enhancing effective internal control and organizational performance.There are various definitions of risk management. Risk is defined as the “effect of uncertainty on objectives” which can have the effect of a positive or negative deviation against expected outcome. A popular and integrated risk management framework has been developed by[5]. [5] Defines risk management in corporate governance as a“….process effected by an entity`s board of directors, management and other personnel, applied in strategy setting and across the enterprise , designed to identify potential events that may affect the entity, and manage risk to be within its risk appetite, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the achievement of entity objectives”. The integrated risk management framework encompasses internal control which has become a catalyst for providing a more robust technique and tool for management[6]. The process of growth and development of any organization is full of challenges, ranging from financial, commercial and administrative risk from both within and external sources. Consequently, the need for a sound internal control system that will identify, assess, monitor and control risks to enhance good governance and organizational performance is imperative. Risk management is a powerful tool for local government management and local councils are required to evaluate their risk management on annual basis in order to determine their effectiveness in practice[19]. Most of the previous research that has been conducted is mainly in the private and public sector particularly central and State government[9; 20; 21]. [13]Opined that there is still need for a lot of research to be done on risk management. Therefore, this research extends the previous studies by examined the antecedents of the level of risk management practices in Nigerian local government.
2.1. Antecedents of Risk Management Practices
- [22] Identified four factors that can influence the implementation of risk management. They include, organizational culture, organizational structuring and design, communication and trustThese factors were found to be significantly associated with the implementation of risk management practices[23; 24] identify top management support and organizational size as critical success factors for the implementation of risk management While[25] Identify senior management support, effective communication and organizational issues for risk management implementation[26] considered effective communication, Training and information technology system significantly related to implementation of risk management.[11] Examined the following factors as CSFs for risk management implementation in the financial institutions. They are as follows; communication, culture, commitment and support from top management, organizational structure, trust, training and information technology and concludes that there is significant relationship between these variables and implementation of risk management even though the level of significance differ.[27] examined, Training, organizational culture, regularity and information technology as important factors in the implementation of risk management. In addition,[28] examined central government advice, organizational culture, experience, information and communication technology and organizational size as critical factors for the implementation of risk management. These factors were also examined by[29] However, others such as[9, 18] used other factors to re-examine the effectiveness of risk management in enhancing organizational performance.Having analyzed the antecedents or critical success factors and various models studied in the literature, the researcher proposes a more comprehensive model composed of seven factors or IVs including regulatory regime as new variable while organizational culture as the mediating variable. Based on the review of the literature, the seven listed CSFs are formed for risk management implementation. These antecedents were suggested by different studies. However, the seven factors including the mediating variable of organizational risk culture need to be tested empirically by this study. This conceptual paper is on ongoing PhD program.
3. Conclusions
- The need for effective system that enhances organizational performance cannot be over emphasized. The risk management approach is a system that will assist organizations to achieve their set targets and objectives and maximize available opportunity within their environment. This study is expected to contribute to policy formulation, implementation and monitoring by the governments at all levels especially with respect to risk management. It will also contribute to the body of knowledge theoretically and empirically. It will assist the local government officials to identify, assess and control risks that can impede them from achieving their objectives.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML