-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Management
p-ISSN: 2162-9374 e-ISSN: 2162-8416
2013; 3(7): 440-447
doi:10.5923/j.mm.20130307.15
A Theoretical Investigation on End-of-Life (EOL) Product Collection Methods in a Closed-loop Logistics Network
Hendrik Lamsali, Ahmad Shabudin Ariffin
School of Technology Management & Logistics, Universiti Utara Malaysia, 06010 Sintok, Malaysia
Correspondence to: Hendrik Lamsali, School of Technology Management & Logistics, Universiti Utara Malaysia, 06010 Sintok, Malaysia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The importance of reverse logistics is evident in various industries. The benefits of reverse logistics and product recoveryhave also been highlighted in previous theoretical investigations. The motivations of its implementation are generally divided into legal, economic and socio-environmental factors. One of the crucial components of a reverse logistics system is product return channels. The success of other components especially the recovery operations depends on the performance of the return channels. Although numerousinvestigations on product return channels have been carried out, research on some critical aspects remains wanting. This study presents a review that highlights this deficiency; depicts latest research development on product return channels, relevant decisions making issues and direction for future research. The review emphasizes on the collection methods of drop-off, pick-up and mail return as the main return avenues that have largely been neglected in the previous research. At the end of the study, we propose a new closed-loop logistics network and future research propositions.
Keywords: Closed-loop logistics, Reverse logistics, Product return channels
Cite this paper: Hendrik Lamsali, Ahmad Shabudin Ariffin, A Theoretical Investigation on End-of-Life (EOL) Product Collection Methods in a Closed-loop Logistics Network, Management, Vol. 3 No. 7, 2013, pp. 440-447. doi: 10.5923/j.mm.20130307.15.
Article Outline
1. Overview
- Minimizing environmental pollution and industrial waste has become one of the main concerns in many countries. Developed countries such as Japan, United States and the European Union (EU) have already enacted legislation on these issues. It is also acknowledgeable that other related problems such as scarcity of natural resources in certain industries, limited landfill capacities, and the negative effect of discarded products has undesirably amplified over the years. For some companies, engagement in environmental preservation and management of industrial waste is no longer an option. According to[1], many companies are now engaged in product recovery business due to increasing government pressure, environmental deterioration, economic pressure, resource reduction and social responsibilities. Hence, various governments have started pressuring companies to take responsibility over their products beyond its lifecycle. Reference[2] stated that legislation aimed at environment-benign production forces manufacturers to take back their products from end-users after they discard them. This is where reverse logistics and reverse supply chain management started.Logistics network design that encompasses decisions such as determining the numbers, locations, quantity of the flow and capacities of the facilities is one of the most important strategic decisions in the reverse supply chain management [3]. This network design becomes even more important with the legal implementation of the extended producer responsibility[4]. The extended producer responsibility states that manufacturers are responsible for free taking back and recovery of their end-of-life products and must bear all or a significant part of the collection and treatment costs[5]. At the same time, the amount of collected returned products should at least satisfy the required minimum collection rate. It is also noted that collection of used products potentially accounts for a significant part of the total costs of any closed-loop supply chain[6]. This study aims to review relevant studies on product return channels and highlights latest development as well as deficiencies that may lead to potential research propositions in the future. The motivations to embark on this study are twofold. First, there is still apparent lack of investigation on the collection methods particularly mail return. Secondly, research findings on this matter remaininconclusive. This paper is organized as follows: Section 1 discusses the introductory part of product return channels and how it is embedded in reverse logistics decision making sequences. Section 2 presents product return channels and the collection methods, Section 3 addresses the issue of collection effectiveness and then followed by Section 4 that discusses decisions making in product return channels. Section 5 illustrates latest research development and Section 6 emphasizes on related managerial implications. Section 7 depicts potential area for further investigations and finally Section 8 concludes the study.
2. Product Return Channels and the Collection Methods
- Product return channels can be defined as avenues or facilities for customers to return used or unwanted products back to the producers, collectors, remanufacturers or recyclers. It is part of the broader network design that may encompass both forward and reverse logistics decisions. Producers or remanufacturers are responsible for designing effective network design (collection channels) that may also include other non-logistical factors such as monetary incentives or marketing campaign. Most of the previous research highlighted that product return channels can be divided into either centralized or decentralized return channels[7]. These return channels are actually representing the type of decision making and degree of control practiced by the manufacturers. Details explanation on this matter can be found in Section 4. In the meantime, there are various ways of collecting used or unwanted products back from the consumers. Big companies such as Dell Computer and Hewlett-Packard offers return incentives to their customers in the form of free door-to-door pick up and mail return respectively. Other manufacturers use their retailers or distributors (intermediaries). There are also independent recyclers or remanufacturers that engage directly with customers to collect returned products either using their on-site drop-off facilities or door-to-door pick up services. Apart from that, there are government agencies or local authorities such as the city council offering similar services. In United Kingdom, large hypermarkets such as Tesco and Asda also provide on-site drop-off facilities (recycling centres) in return for loyalty points. It is one of the most important components in reverse logistics and is now viewed as another important avenue for profit making endeavour. Hence, designing the network design and measuring effectiveness of the return channels are also equally critical for the reverse logistics success.
3. Collection Effectiveness of Product Return Channels
- Collection effectiveness depends on the consumers’ willingness to return used products at the time of disposal[8]. It has been identified that two important factors which influence customers’ willingness to return their products are accessibility and incentives. Reference[9] point out that customers’ convenience when returning their products should be maximized as it will eventually encourage more future returns. There are three collection methods that are normally used by manufacturers namely mail delivery return, pick up collection and customer drop off. Installing a drop-off facility near residential or commercial areas encourages customers to return their products (easy access). This collection method requires the manufacturer to bear the cost of building or renting as well as operating the drop-off facilities in certain selected area. Nonetheless, the important decision is to decide how many drop-off facilities are needed and its locations. These type of return channels are actually depicting the decision making approach in reverse logistics network. Figure 1 illustrates the collection methods in product return channels. According to[10], convenience factors play important roles in the collection effort of solid waste. He identified five key convenience factors to increase collection rate: (1) knowledge requirement, (2) proximity to collection site, (3) opportunity to drop-off materials, (4) the draw of the collection site, and (5) ease of the process. The researcher also developed a performance matrix based on the abovementioned five convenience factors to help solid waste managers make decisions. The study highlighted that the convenience factors also refer to the availability and ease of the collection process for the customers. In other word, minimizing customer’s time, effort and travelling cost may positively influence product return rates.
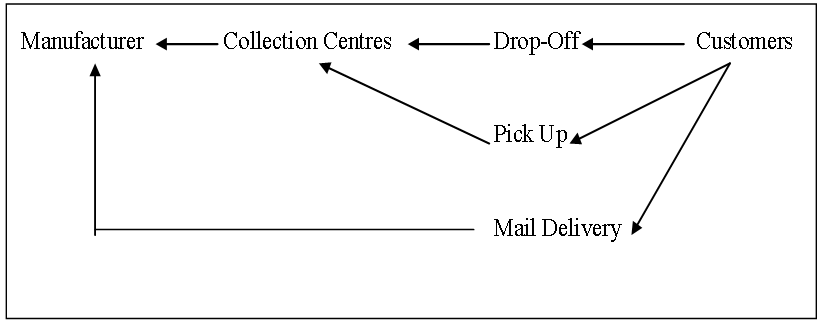 | Figure 1. Collection methods in product return channels |
4. The Collection Channels and Decision Making
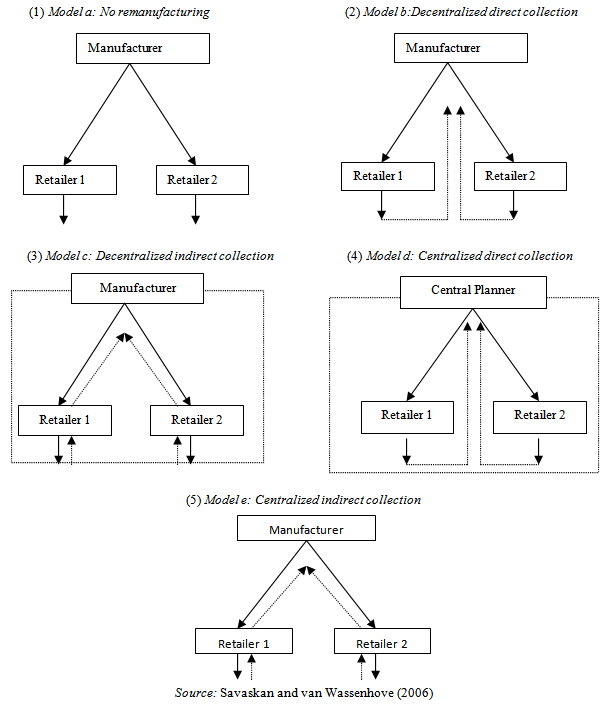 | Figure 2. Product Return Channel Structures |
5. Latest Research Development on Product Return Channels
- Most of the studies on product return channels remained focus on network design. In the broadest sense, this involves location and routing problems. Latest studies by[4],[17], [18],[19],[20],[21],[22] and[23] illustrates discussions on product return channels from the perspective of a network design problem. In the meantime, latest study by[15] addresses problem of collecting returned products using game theory and fuzzy theory. Their research represents some similarity with this study in the sense that the main decision is about selecting collection modes and its consequences. Reference[15] defines collection modes into three categories: (1) manufacturer’s direct collection, (2) retailers’ collection, and (3) third party collection. Under the (2) and (3) modes, collection rates and retail prices (buyback prices) are determined by retailers and the third party collectors. It resembles a decentralize collection channel. However, the model doesn’t specify the exact method of collecting the used products from customers. Reference[24] reviews vehicle routing and scheduling literatures in environmentally-conscious transportation problems. They highlighted that for pick-up delivery routing problem, most studies use insertion-based algorithm (multi-objective) or genetic algorithm (single objective). The research also mentioned about the growing concerns of environmental issues such as public health, global warming and economic safety. Reference [25] stated that pressing global challenges such as climate change and resources depletion demonstrates the need for structural change in our economic approach towards sustainable development. It appears that most of the location models rely on finite solutions and mixed- integer linear programming which allows for discrete mathematical optimization. Most location- allocation problems also rely on mixed-integer and linear programming model in which number of warehouses, capacities and locations were determined. Reference[26] stated that the number of customers supporting environmental protection by delivering their used products to collection points is increasing. In order to minimize the total reverse logistics cost and high utilization rates of collection points, selecting appropriate locations for collection points is critical issues in reverse logistics. In the meantime, study on collection and recycling policies of electronic scraps among countries around the world has been conducted by[27]. In their study, they compare policies and collection frameworks of selected European, US, Asian and South American countries. Some countries such as Switzerland and Germany have better comprehensive collection policies and regulations than other countries.
6. Managerial Implications
- Previous research on product return channels focused more on other ‘general’ return networks such as centralized and decentralized, and direct or indirect return networks[7], [13],[16],[28],[29],[30],[31],[32],[33],[34],[35],[36] and[37]. Only several researches studied the ‘groundwork’ collection methods albeit focusing on different scope and approach[1], [8],[9],[11],[12],[15]. Studies on the three collection methods namely drop-off, pick-up and mail return delivery remains insufficient. From the industry point of view, many firms prefer to outsource its reverse logistics function, let alone product collection activity. This scenario is understandable since not many firms able to facilitate three collection methods simultaneously. Costs to offer these facilities such as collection centre’s handling and setup costs (drop-off), and related transportation costs (pick-up) are relatively high. Hence, many firms prefer outsourcing some, if not all, of the collection jobs to the third party collectors [13],[27],[22]. In some cases, the firm prefers intermediaries such as retailers to collect returned products for them[7],[16]. These retailers offer drop-off facilities at their premises to the consumers to return their products. However, as more countries around the globe implement the extended producer responsibility legally[5],[38],[39] and[40], more firms realize that product recovery is no longer a burden, but an opportunity to make profit from a new avenue. Now, some firms prefer to have direct control over the collection of returned products to better manage and improve the collection rates. Subsequently, having the luxury to offer these three collection methods is a good option for as long as it is feasible. Nevertheless, from the practical point of view, the lack of empirical studies on the three collection methods may affect the abovementioned effort.
7. Potential Research Propositions
- In product return channel, most previous optimization models treated product return as location problem. Hence, it is more towards managing transportation of returns or finding the best routing strategy rather than looking for optimal assignment. So far, only a handful of study addressed collection problem comprehensively incorporating more than one method (pick-up or drop-off). Literature survey on mail return method is also very limited, if not non-existence[4],[8],[11],[12],[22],[23],[41],[42],[43],[44], [45],[46] and[47]. Based on the above analysis, follows are some potential research areas in product return channels that can be studied further:a. Feasibility study on the application of mail return method and its effectiveness.b. The optimizations of mail return as an alternatives to other collection methods in reverse logistics problem.c. Developing optimum incentives schemes for mail, drop-off and pick-up collection methods that can benefit firms in terms of collection rates, costs and profit.d. The applications of different incentives schemes for mail, drop-off and pick-up collection methods under centralized and decentralized decisions making policy.e. The effectiveness of mail, drop-off and pick-up under direct and indirect collection methods, as well as centralized versus decentralized decisions policy.f. The effect of quality categorization of returned products in each collection methods.In the meantime, we propose a new closed-loop logistic framework encompassing both forward and reverse movement of products (Figure 3). In conventional closed - loop logistics network, the reverse movement of products started with collection of returned products. So far, the collection activities have been depicted by a more general product collection avenue such as centralized and decentralized collection or direct and indirect methods. There is a loophole prior to products being send to the recovery facilities. Supposedly, it is not only about decision making policy (centralized vs decentralized) or the general return strategy (direct vs indirect). Hence, the new framework includes the initial collection methods in which the collection activities are actually happening involving the three methods. The product return channel that is highlighted at the end of the forward flow marks the beginning of the reverse network system. Again it is worth noting that the collection methods of drop-off, pick-up and the mail return has presented significant avenue for future research. Apart from it being the missing link in the previous conventional closed-loop logistics network, the importance of these three methods is also undeniably crucial in determining the success of the whole reverse logistics operations.
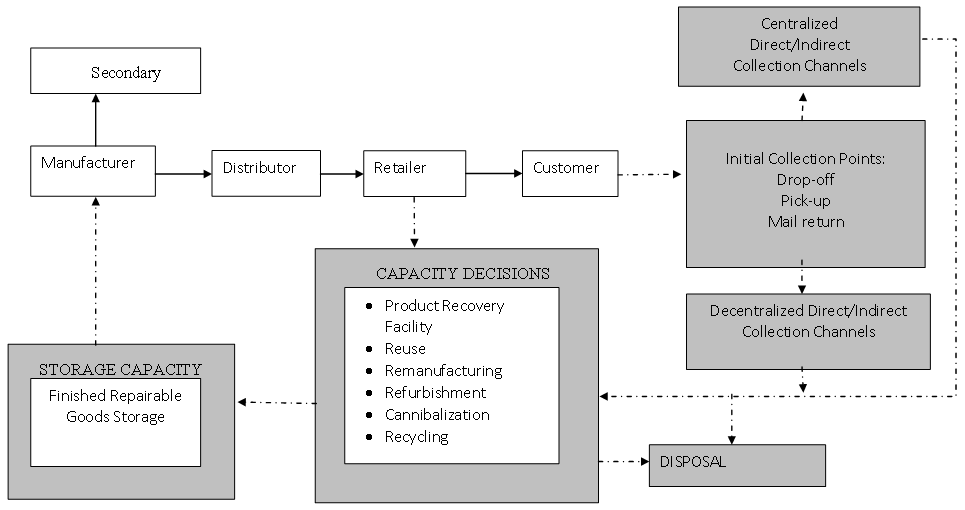 | Figure 3. The new closed-loop Logistics Network |
8. Conclusions
- Product recovery management in a closed-loop logistics network encompasses various activities such as collection channels, production (reprocessing, disassembly, separation and inventory management), capacity planning, procurement, warehouse distribution, and recovery networks (such as routings, and location-allocation decisions). This study reviews literature on reverse logistics network in which particular attention is given to the collection activities of returned products (product return channels). The criticality of product recovery management within the reverse logistics context is substantially significant with numerous studies being conducted to address various issues. In product return channels, most research addressed collection of returned products from a broader spectrum; whether collection should be (1) centralized or decentralized, and whether it should be handled (2) directly or indirectly[7],[13]. The role and impact of the initial collection points where the first contact between consumers and the return facilities occurs are hardly acknowledged. Relevant studies by[8],[11] and[12] acknowledging the optimization of product return’ initial collection strategy should be further analysed. At the end of this study, we propose several research areas for further investigation as well as a new framework for a closed-loop logistics network that includes the initial collection methods.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML