-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Management
p-ISSN: 2162-9374 e-ISSN: 2162-8416
2013; 3(1): 12-15
doi:10.5923/j.mm.20130301.03
Integration of the Internal Supply Chain Management (SCM) towards Long Run Competitiveness
Tengku Nurul Aishah 1, Jaafar Pyeman 2, Ramlah Mohd Tajuddin 3
1Malaysia Institute of Transport (MITRANS), Universiti Teknologi MARA (UiTM), Malaysia
2Arshad Ayub Graduate Business School (AAGBS), Faculty of Business Management, Universiti Teknologi MARA (UiTM), Malayisa
3Faculty of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi MARA (UiTM), Malaysia
Correspondence to: Tengku Nurul Aishah , Malaysia Institute of Transport (MITRANS), Universiti Teknologi MARA (UiTM), Malaysia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Economic growth of a country can be sustainable when it is able to be competitive in the long run. Hence, the Malaysian government has implemented Economic Transformation Program (ETP) to ensure the achievement of long-term and sustainable economic growth for the country. It is well accepted that there are many factors that influence the achievement of long-term and sustainable economic growth. These factors consist of internal and external supply chain management (SCM) components. Many studies had been conducted to evaluate the effects of external SCM components on the efficiency and performance for long-term and sustainable economic growth. However, very limited studies had been focused on the effects of internal SCM components in order to achieve long-term and sustainable economic growth of a country. Therefore this paper presents the findings from a research conducted to determine the factors and their integration towards the performance of internal SCM on the long term competitiveness and sustainable economic growth. 192 electrical and electronics (E&E) manufacturers were interviewed to determine their views on the importance of the integration of the internal SCM factors towards the achievement of long term and sustainable economic growth. The study focuses only on manufacturer perspective and concentrates on their views but not the whole channel members in the supply chain. The results provide insights on how the integration of internal SCM factors were applied in Malaysia E&E industry and how it could be improved in achieving towards long run competitiveness. This study helps to address the integration of internal SCM to identify their influence towards long run competitiveness.
Keywords: Internal Supply Chain Management (SCM), Competitiveness, Integration
Cite this paper: Tengku Nurul Aishah , Jaafar Pyeman , Ramlah Mohd Tajuddin , Integration of the Internal Supply Chain Management (SCM) towards Long Run Competitiveness, Management, Vol. 3 No. 1, 2013, pp. 12-15. doi: 10.5923/j.mm.20130301.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Nowadays, SCM has been a critical issue among industry players where it has been accepted to be one of the key factors contributes towards economic growth. Concerning towards transforming the nation, the government had come out with new implementation and strategic plan to be carried out. Economic Transformation Program (ETP) has been implemented to ensure long-term sustainable growth for the country’s economy for the well-being of all Malaysians[16]. Datuk Seri Idris Jala which is the minister in the Prime Minister’s Department said that as a trade-dependent country, Malaysia need to have “focus” and “competitiveness” as the key to achieve high-income nation by 2020[16]. Therefore, in order to increase the economic growth, it must have focus and competitive to become sustain for a longer period of time. Focusing on SCM, there are two major components identified which contributes towards competitiveness of the SCM which are the external and the internal components. However, many researches are not well focused on the internal components since these components seem to be under control by the organization. Through history, it also have been proven that many organizations collapsed due to the internal problems. Hence, it is important to focus on the internal SCM perspective which gives major impacts not only for the supply chain itself but also towards the country development. The objectives of this paper are to identify the integration of the internal SCM factors which contributes towards long run competitiveness and proposing a framework on selected internal SCM factors towards long run competitiveness.
2. The Importance of Integration
- Li and Lin (2006) explained that logistics must have integration, agility, measurement, and positioning in order to increase competence among industry members. Integration can be seen as a technique used for internal logistical operating excellence and development of external supply chain relationships. A firm’s can respond in a quick manner through integration of each element in the supply chain. Additionally, Bagchi et al. (2005) states that experts had agreed that integrated supply chain would enable firms to compete better. The basis of integration is well explained by Power (2005) where it can be characterized by collaboration, cooperation, trust, sharing of information and technology, and a shift from managing individual to integrate chains. Additionally, Lee, Kwon, and Severance (2007) had identified internal linkage as one of the major linkages which are critical and need to be focused on. This linkage needs integration where it helps in reducing costs[11] and enhance efficiency[9]. Thus, integration can help to facilitate supply chain process to enhance competitiveness.
3. Research Framework
- There are two major components in the supply chain which are the internal components which involves within an organization and the external components which involves between companies[5],[17],[21],[32]. In order to achieve long run competitiveness, the internal components in SCM can be seen as the most important factor compared to the external factor where prior studies had not well discovered. Stock et al. (2000) and Bahinipati et al. (2009) had agreed with the importance of the internal parameter which contributes to the effectiveness and efficiency of supply chain performance. Ample of studies had well mentioned about the fact that the success of the SCM comes from the behavior within the organization where it reflects the whole supply chain[24],[25],[27]. Thus, properly manage of the internal SCM helps in achieving towards long run competitiveness.Study by Grawe, Daugherty, and McElroy (2012) point out that competitiveness of an organization or a company comes from organizational itself. However, Aryee, Naim and Lalwani (2008) stated that companies are still grappling with internal process integration. Therefore, identifying the internal SCM components will help managing the company through a better performance. The direct relationship proposes to highlight the importance of these selected internal SCM factors which contribute in achieving long run competitiveness in the SCM process as illustrated in Figure 1 below.
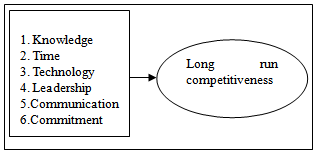 | Figure 1. Illustration of the internal SCM in a proposed framework towards long run competitiveness |
4. Methodology
- This part of research work deals with a different kind of stages where it involves in profiling issues through interviews, secondary data collection, and survey in order to have a better understanding. A structured questionnaire was designed by referring to the previous research by adopting and modified in order to maintain the reliability of the questions based on the structure of this research purpose. About 192 questionnaires were distributed to the manufacturer of E&E in Malaysia. After sampling had done, data from the questionnaire will go through a statistical analysis by using SPSS 19th version such as validity, reliability, normality, correlation, multiple regression, and ANOVA test.
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Knowledge
- Wu (2008) stated that knowledge has become the only resource that offers competitive advantage and continued growth and prosperity for supply chain partners. There are lots of research which agree on the importance of knowledge creation in the process of supply chain. It has been supported by Bapuji et al. (2011) and Van Vactor (2011) that knowledge does have a direct relationship with competitiveness. Additionally, for an organization to develop competitive advantage, identifying, capturing, sharing and accumulating knowledge are crucial[14] to sustain in the marketplace. Further, it has been supported by Hsu (2008), a company with a higher level of knowledge tend to have better performance which can bring enormous benefits to an organization. Therefore, knowledge can be seen as the important factor which create effective and efficient collaboration among members where it creates the performance of each member in the supply chain process not only internally but also externally. Hence, the importance of knowledge as the internal SCM factors has been well established towards generating business performance. In contrast with knowledge, the other factors which are leadership, time, technology, commitment and communication have a negative relationship with long run competitiveness. Although these factors have been found not to be significant, it does not totally embrace their less importance towards long run competitiveness. This is due to the other reasons which has been mentioned by Tompkins (1992) and Harland et al. (2008) that type of factor chosen as it have different in magnitude and size of the sample can be its cause.
6. Conclusions
- As a conclusion, the integration of the internal SCM factors (within the organization) which mainly focus on organizational performance is lacking in most of the research that were not being well stated in their framework. From the analysis results, only knowledge has been agreed to be important towards long run competitiveness which shows significant value. Unfortunately, the other factors do not have wide attention to their contributions. Thus, factors such as time, leadership, technology, communication, and commitment need to be well described regarding on how they need to perform in order to achieve long run competitiveness with the additional components needed. This paper introduces a new concept of a framework to highlight the important integration of internal SCM factors which contribute towards long run competitiveness. Therefore, we can conclude that not only knowledge is important but the other factors also play a major role towards achieving long run competitiveness. Hence, in order to achieve long run competitiveness in market performance, the integration of internal SCM play as the key factors in making the SCM become successful, well organized and competitive.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- I would like to express my gratitude to all those who gave me the possibility to complete this paper especially to the Malaysia Institute of Transport (MITRANS) for their support. I want to thank my supervisor whose help, stimulating suggestions and encouragement in all the time of writing this paper. Especially, I would like to give my special thanks to my mother whose patient love enabled me to complete this work.
References
| [1] | Aryee, G., Naim, M. M., & Lalwani, C. (2008 ), “Supply chain integration using a maturity scale”, Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management, Vol. 19 No. 5, pp. 559-575.. |
| [2] | Atilgan, C., and McCullen, P. (2011), “Improving supply chain performance through auditing: a change management perspective” Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, Vol. 16 No. 1, pp. 11-19. |
| [3] | Bagchi, P. K., Ha, B. C., Skjoett-Larsen, T., & Soerensen, L. B. (2005), “Supply chain integration: a European survey”, The International Journal of Logistics Management, Vol. 16 No. 2, pp. 275-294. |
| [4] | Bahinipati, B. K., Kanda, A., & Deshmukh, S. G. (2009), “Horizontal collaboration in semiconductor manufacturing industry supply chain: An evaluation of collaboration intensity index”, Computers & Industrial Engineering, Vol. 57 No. 3, pp. 880-895. |
| [5] | Banomyong, R., & Supatn, N. (2011), “Developing a supply chain performance tool for SMEs in Thailand”, Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, Vol. 16 No.1, pp. 20–31. |
| [6] | Bapuji, H., Loree, D., & Crossan, M. (2011). Connecting external knowledge usage and firm performance: An empirical analysis. Journal of Engineering and Technology Management, 28(4), 215-231. |
| [7] | Cadilhon, J. J., Fearne, A. P., Tam, P. T. G., Moustier, P., & Poole, N. D. (2005), “Collaborative commerce or just common sense? Insights from vegetable supply chains in Ho Chi Minh City”, Supply Chain Management, Vol. 10 No. 3, pp. 147-149. |
| [8] | Chow, G., Heaver, T.D., & Henriksson, L.E. (1995), “Strategy, structure and performance: a framework for logistics research”, The Logistics and Transportation Review Vol. 31 No. 4, pp. 285–308. |
| [9] | Danese, P., & Romano, P. (2011), “Supply chain integration and efficiency performance: a study on the interactions between customer and supplier integration, Supply Chain Management: An International Journal,Vol. 16 No.4, pp. 220–230. |
| [10] | Fisher, M. L. (1997), “What is the right supply chain for your product? Harvard Business Review”, Vol. 75 No. 2, pp. 16-105. |
| [11] | Flynn, B. B., Huo, B., & Zhao, X. (2010), “The impact of supply chain integration on performance: A contingency and configuration approach”, Journal of Operations Management, Vol. 28 No.1, pp. 58-71. |
| [12] | Grawe, S. J., Daugherty, P. J., & McElroy, J. C. (2012), “External organizational commitment among organizational implants: The case of logistics service providers”, Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, Vol. 48 No. 1, pp. 165-177. |
| [13] | Harland, C. M., Caldwell, N. D., Powell, P., & Zheng, J. (2007). Barriers to supply chain information integration: SMEs adrift of eLands. Journal of Operations Management, 25(6), 1234-1254. |
| [14] | Hsu, I.-C. (2008). Knowledge sharing practices as a facilitating factor for improving organizational performance through human capital: A preliminary test. Expert Systems with Applications, 35(1), 1316-1326. |
| [15] | Ko, M., Tiwari, A., & Mehnen, J. (2010), “A review of soft computing applications in supply chain management”, Applied soft computing, Vol. 10, pp. 661-674. |
| [16] | Kok (2012), “Transforming the nation”, StarBizWeek, 16 June, pp. 20. |
| [17] | Kotzab, H., Teller, C., Grant, D. B., & Sparks, L. (2011), “Antecedents for the adoption and execution of supply chain management. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, Vol. 16 No.4, pp. 231–245. |
| [18] | LaLonde, B. J., & Masters, J.M. (1994), “Emerging logistics strategies: blueprints for the next century”, International Journal of Physical Distribution and Logistics Management, Vol. 24 No.7, pp. 35–47. |
| [19] | Lee, C. W., Kwon, I.-W. G., & Severance, D. (2007 ), “Relationship between supply chain performance and degree of linkage among supplier, internal integration, and customer. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, Vol. 12 No. 6, pp. 444–452. |
| [20] | Li, P.-C., & Lin, B.-W. (2006), “Building global logistics competence with Chinese OEM suppliers”, Technology in Society, Vol. 28 No. 3, pp. 333-348. |
| [21] | Lings, I. N. (2000), “Internal marketing and supply chain management. Journal of Service Marketing, Vol. 14 No. 1, pp. 27-43. |
| [22] | Liu, J., Zhang, S., & Hu, J. (2005), “A case study oof an inter-enterprise workflow-supported supply chain management system”, Information and Management, Vol. 42 No. 3, pp. 54-441. |
| [23] | Malhotra, A., Gosain, S., & El Sawy, O.A. (2005). Absortive capacity configurations in supply chains:gearing for partner-enabled market knowledge creation 1. MIS Quarterly, 29(1), 87-145. |
| [24] | Melnyk, S. A., Lummus, R. R., Vokurka, R. J., Burns, L. J., & Sandor, J. (2009). Mapping the future of supply chain management: a Delphi study. International Journal of Production Research, 47(16), 4629-4653. |
| [25] | Mentzer, J. T., DeWitt, W., Keebler, J. S., Min, S., Nix, N. W., Smith, C. D., et al. (2001). Defining Supply Chain Management. Journal of Business Logistics, 22(2), 1-25. |
| [26] | Power, D. (2005). Supply chain management integration and implementation: a literature review. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, 10 (4), 252–263. |
| [27] | Sharif, A. M., & Irani, Z. (2012). Supply Chain Leadership: Exploring the paradigm shift towards supply chain leadership. International Journal of Production Economics(0). |
| [28] | Stank, T. P., & Traichal, P.A. (1998). Logistics strategy, organizational design, and performance in a cross-border environment. . Logistics and Transportation 34 (1), 75–86. |
| [29] | Stock, G. N., Noel P.G., & John D.K. (2000). Enterprise logistics and supply chain structure: the role of fit. Journal of Operations Management 18, 531–547. |
| [30] | Stock, G. N., Greis, N.P., & Kasarda, J.D. (1998). Logistics, strategy and structure: a conceptual framework. International Journal of Operations and Production Management, 18(1), 37–52. |
| [31] | Tompkins, C. A. (1992). Using and Interpreting Linear Regression and Correlation Analyses: Some Cautions and Considerations. Clinical Aphasiology, 21, 35-46. |
| [32] | VanVactor, J. D. (2011). A case study of collaborative communications within healthcare logistics. Leadership in Health Services, 24(1), 51-63. |
| [33] | Weck, M. (2006). Knowledge creation and exploitation in collaborative R&D projects: lessons learned on success factors. Knowldge and Process Management, 13(4), 252. |
| [34] | Wu, C. (2008). Knowledge creation in a supply chain. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, 13(3), 241-250. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML