-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Management
p-ISSN: 2162-9374 e-ISSN: 2162-8416
2013; 3(1): 6-11
doi:10.5923/j.mm.20130301.02
Direct Effect of Service Quality Dimensions on Customer Satisfaction and Customer Loyalty in Nigerian Islamic Bank
Mu’azu Saidu Badara 1, Nik Kamariah Nik Mat 2, Abubakar Muhd Mujtaba 1, Abdalla Nayef Al-Refai 1, Abdulkadir Musa Badara 1, Faruq Muhammad Abubakar 1
1Candidates, Othman Yeop Abdullah Graduate School of Business, Universiti Utara Malaysia
2College of Business, Universiti Utara Malaysia
Correspondence to: Nik Kamariah Nik Mat , College of Business, Universiti Utara Malaysia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Due to the importance of Islamic finance to the Muslims world, recently Islamic Banking is formerly established in 2011 in Nigeria in order to join their counterpart in the Muslims world. Due to its new existence, there is very limited information on the customers’ perceptions towards the Islamic banks. Therefore, the objective of this study is to examines the direct effect of service quality dimensions on customer satisfaction and customer loyalty in Nigerian Islamic Bank. Primary data measuring service quality consisting of six dimensions: tangibility, reliability, responsiveness, assurance, empathy and compliance (24 items); customer satisfaction (4-items) and customer loyalty (4-items) were collected from 209 Nigerian students studying at Universiti Utara Malaysia. Data were analyzed using Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) using AMOS 16. Convergent validation was performed using Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) and composite reliability. The finding of the study reveals that responsiveness is a significant predictor of customer staisfaction and assurance is significant predictor of customer loyalty. This implies that customers will be satisfied when the bank staff are responsive and provide fast banking service. Additionally, to maintain loyal customers Islamic banks should give assurance in terms of Islamic banking compliance.
Keywords: Service Quality, Customer Satisfaction, Customer Loyalty, Islamic Banks, Nigeria
Cite this paper: Mu’azu Saidu Badara , Nik Kamariah Nik Mat , Abubakar Muhd Mujtaba , Abdalla Nayef Al-Refai , Abdulkadir Musa Badara , Faruq Muhammad Abubakar , Direct Effect of Service Quality Dimensions on Customer Satisfaction and Customer Loyalty in Nigerian Islamic Bank, Management, Vol. 3 No. 1, 2013, pp. 6-11. doi: 10.5923/j.mm.20130301.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The emergence of Islamic banking in the Muslim world has remained the most inspiring financial and economic phenomenon of the 20th century[1]. Hence, countries like Pakistan, Iran and Sudan adopted the Islamic financial system as the mainstream for their banking and economic activities[2]. Other countries embraced the dual banking system include among others; Malaysia, Bahrain, Saudi Arabia, Egypt and Algeria[3]. In Nigeria, recently the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) enacted new provisions for the proper establishment and operation of Islamic banking through what it conceptualized as “Non-Interest Financial Institutions” (NIFI) under section 33(1) (b) of the CBN ACT 2007 and section 4 (1) (c) of the Regulation on the scope of Banking activities and ancillary matters No.3 of 2010[4]. Therefore, Islamic banking in Nigeria has become a growing concept due to increased economic empowerment of Muslims, even though the bank serve as a means oftransaction for both Muslims and non- Muslims customers. Nevertheless, Muslims’ continuous to model their lives in accordance with the Shariah (Islamic Law), i.e. avoiding interest rates or engaging in any activities or business that is contrary to Islamic Jurisprudence. Islamic banking refers to a system of banking or banking activity that is consistent with Islamic law ‘Shariah’ principles and guided by Islamic economics[5] Due to its new existence in Nigeria, there is very limited information on the customers’ perceptions such as customer loyalty, customer satisfaction and service quality towards the Islamic banks. In view of the above, this study intends to examine the direct effect of service quality dimensions on customer satisfaction and customer loyalty in Nigerian Islamic Bank.Customer loyalty plays an important role in the development of various business organizations. For example [6] noted that under a good service relationship chain, profitability and growth of a company is a result from customer loyalty[7] explained that customer satisfaction entails the full meeting of customer expectation of the products and services. Service quality has been postulated to have a great impact on firm’s performance[8]. Similarly, it is widely accepted that service quality, customer value and satisfaction are the most important sources of gaining competitive advantage for manufacturing and service organizations[9]. Therefore, due to countries cultural differences and different banks,[8] recommend future studies to examine service quality, customer satisfaction and loyalty in different banks of different countries. In view of this, this research intends to examine direct effect of service quality dimensions on customer satisfaction and customer loyalty in Nigerian Islamic Bank. This paper proceeds to Section 2 which covers literature review, while section 3 contains the research framework, methods, measurement of variables and the results of the study; the last section is concerned with the managerial implications of the study and the recommendations for future research.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Customer Loyalty
- Customer loyalty improves the profitability of a company, for instance the result finding of[10] revealed that customer loyalty could lead to an increase in profit.[11] Describes customer loyalty as “a deeply held commitment to re-buy or re-patronize a preferred product consistently in the future situational influences and marketing efforts that might cause switching behavior. Therefore, loyal customer should be seen as a prosperous and valuable sale source that help the organization make better future plans. Hence, loyal customers typically create greater value to a company[6]. It is also found that effective relationship marketing strategy helps the organization to understand customers’ needs, so that organizations can serve their customers better than their competitors, which finally leads to cost reduction and customer loyalty[12].
2.2. Customer Satisfaction
- Satisfaction can be considered as a feeling of happiness when a person achieves his or her goals, wants or motivation[6]. Customer satisfaction has been regarded as a fundamental determinant of long-term consumer behavior [11]. In the Islamic banking industry, customers have put the criteria of customer satisfaction towards service quality provided by their banks[13]. Banks have provided innovative methods of satisfying customers, such as internet banking and online system, telephone and call center. According to[14], convenience and competitiveness of the bank are two important factors which are likely to influence the overall satisfaction levels of a customer. Thus, measuring customer satisfaction leads to an increase in the efficiency of the organization.
2.3. Service Quality
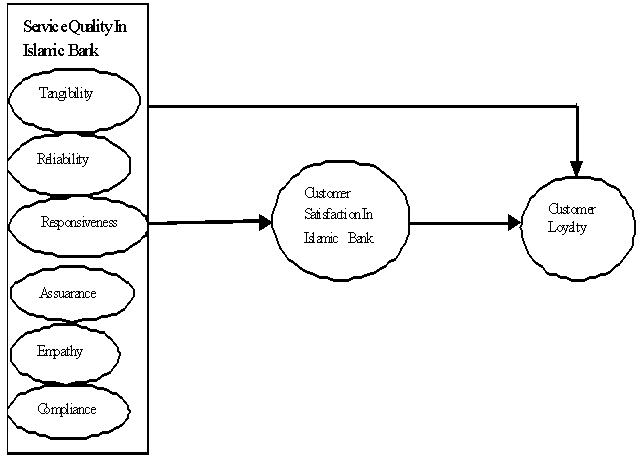
- Service quality is defined as the outcomes of the customer’s overall evaluation of the differences between service expectations and the actual service performance[15]. Therefore, service quality is conceptualized as amultidimensional construct consisting of five dimensions,[15]. The five dimensions of service quality include: (1) tangibility(appearance of physical components); (2) reliability (dependability of service provider and accuracy of performance); (3) responsiveness (promptness and helpfulness); (4) assurance (knowledge and courtesy of employees and their ability to inspire trust and confidence); and (5) empathy (caring, individualized attention the firm gives its customers)[13]. Therefore,[16] used the SERVQUAL dimensions in examining service quality in Islamic banking.Compliance refers to the strict adherence to the sharia law stipulation which prohibits Islamic banks from engaging in businesses considered unlawful under Islamic law such as gambling, alcohol selling, pornography and so forth[17]. Compliance dimension, as argued by[13] must be added to the five dimensions of[15] for its the philosophical foundation of Islamic banking and is one of the dimension is the work of[16] which reveals that Islamic banking customers give special consideration to compliance in choosing bank. Therefore, this dimension adopted as one of the dimension of service quality in measuring Islamic bank in Nigeria.
2.4. The Relationship between Service Quality Dimensions and Customer Loyalty
- Service quality is linked to customer loyalty[8]. Research has shown that service quality has strong influences on buying intentions of the customers[18]. Some other researchers also provided the strong empirical evidences supporting the fact that service quality increases the customer intentions to remain with any company. For example,[19] found out that service quality results in increased market share and repeated sales that ultimately leads to customer loyalty. Similarly,[8] found that service quality has effect on the customer loyalty. Therefore, the following hypotheses are formulated:H1: Tangibility has a significant effect on customer loyalty in Islamic bank in NigeriaH2: Reliability has a significant effect on customer loyalty in Islamic bank in NigeriaH3: Responsiveness has a significant effect on customer loyalty in Islamic bank in NigeriaH4: Assurance has a significant effect on customer loyalty in Islamic bank in NigeriaH5: Empathy has a significant effect on customer loyalty in Islamic bank in NigeriaH6: Compliance has a significant effect on customer loyalty in Islamic bank in Nigeria
2.5. The Relationship between Service Quality Dimensions and Customer Satisfaction
- Banks ability to deliver good services influences the level of customer satisfaction. For instance,[16] suggested that there is a strong link between SERVQUAL and customer satisfaction. Also[18] emphasis the importance of service quality and customer satisfaction, likewise[14] found that the performance of the service provider on core and relational dimensions of services was an important driver for customer satisfaction in retail banking. Similarly, the results of the recent studies by ([13];[8]) reveals significant result between service quality and customer satisfaction.H7: Tangibility has a significant effect on customer satisfaction in Islamic bank in NigeriaH8: Reliability has a significant effect on customer satisfaction in Islamic bank in NigeriaH9: Responsiveness has a significant effect on customer satisfaction in Islamic bank in NigeriaH10: Assurance has a significant effect on customer satisfaction in Islamic bank in NigeriaH11: Empathy has a significant effect on customer satisfaction in Islamic bank in NigeriaH12: Compliance has a significant effect on customer satisfaction in Islamic bank in Nigeria
2.6. The Relationship between Customer Satisfaction and Customer Loyalty
- Studies have widely highlighted the relationship between customer satisfactions and customer loyalty for example ([20];[21];[22]) emphasized on the importance of customer satisfaction, as it is a significant predictor of customer loyalty. Likewise,[20] declared that a contended customer exhibits greater retention and expressed significantly positive impact of customer satisfaction on customer loyalty. Similarly,[8] found positive relationship between customer satisfaction and customer loyalty.H13: There is positive relationship between customer satisfaction and customer loyalty in Islamic bank in Nigeria.
2.7. Underpinning Theory Oliver Theory of Loyalty
- In this study, customer loyalty was measured by their behavioral intention in terms of repurchase intention, word-of-mouth and first-in-mind. These measures were proven to be useful in previous research[6]. Therefore, theory of planned behaviour would be use to support the research framework for understanding the customer loyalty. The theory of planned behavior (TPB;[23]) postulates that intention could be the best determinant of an individual behavior. Thus, individual who has a strong intention is likely to engage in the behavior than the one low intention. In this context, the theory of planned behavior posits that the relationship between service quality and customer loyalty will be mediated by the customer satisfaction. Conceptual Framework
3. Methodology
- The data for this study were obtained through a survey questionnaire administered to the Nigerian students in University Utara Malaysia. Based on the population of Nigerian students in UUM of 440 students, the sample size was 205[24] and simple random for sampling technique. The data collection method was based on personally administered questionnaires to the students in which 240 questionnaires were administered and 209 were completed and returned. This represents 87% of the respond rate.[25] Opined that a minimum of 60% response rate is acceptable.Measurement of the ConstructsThe six service quality dimensions (tangibility reliability, responsiveness, assurance, empathy and compliance) were measured by four items each dimension totaling 24 items adopted from the study carried out by ([15];[16]). Customer satisfaction adopted from[13] and loyalty adopted from[8] was measured by four items respectively. Thus, these items were adapted in order to suit Islamic banking industry in Nigerian context. Each of the adapted items was assessed on a 7-point scale ranging from strongly disagree (1) to strongly agree (7). Analysis MethodStructural equation modeling through Analysis of Moment Structures (AMOS) 16.0 was used for model fit. Descriptive Statistics and composite reliability analysis.
4. Result and Discussion
4.1. Descriptive Statistic
- The descriptive statistic shows the direction of responses. Therefore, 97.1% of the respondents were male and the remaining 2.9 % were female customers. This implies that the number of male customers out-weigh the female. 40.4 % of the respondents are at the age between 31-40 years old, 30.3% 41-50, 28.8% 21- 30 and above 50 years is 0.5%. With regards to educational level of the respondents 18.8%, are Bachelor’s degree students, 77.4% of the respondents are Masters Degree students and 3.8% PhD students. Similarly, most of the students have account with the banks while some have friends whose operate with the bank in Nigeria.
4.2. Data Screening
- Data was examined for outliers using Mahanolobis Distance (D2) method whereby two cases were found outliers and deleted. Further, the data were detected for normality through standardized z-score and those data found not normal were transformed using cdfnorm function. Composite reliabilityComposite reliability measures the reliability of a construct in the measurement model (AMOS Model). Composite reliability is calculated using normalized SPSS data (full hypothesized model estimates). Composite reliability enables the overall internal consistency of a construct or convergence validity. Therefore, composite reliability is interpreted like a Cronbach’s alpha for internal consistency reliability estimate. A composite reliability of 0.7 or greater is considered acceptable[26]. Therefore the composite reliability of the variables under studies is above 0.7 therefore considered acceptable.
4.3. Hypotheses Testing
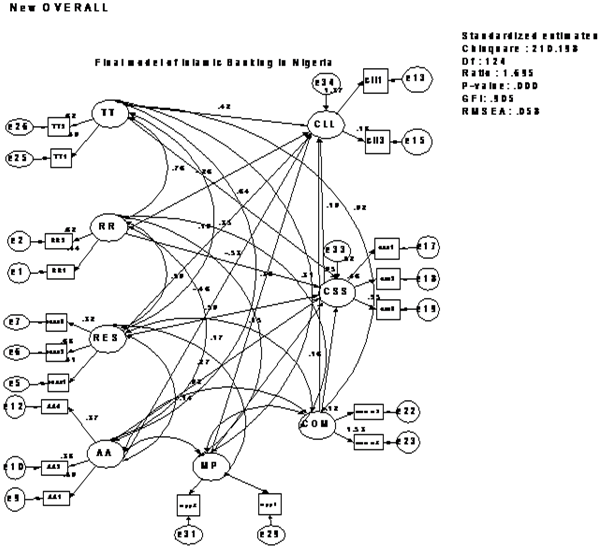
- This study examined mediating effect of customer satisfaction on the relationship between service quality and customer loyalty in Nigerian Islamic Bank. Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) is been performed to ascertain the fit of the measurement models. Initially, the fit indices of the hypothesized model (see Appendix 1) indicated that the data did not fit model adequately (X2 = 946.204; df = 436; p = 0.000; a ratio of X2 to df = 2.170; GFI = 0.783; and RMSEA = 0.075. However, after deleting some items using modification indices, the fit indices of the revised hypothesized model indicate an adequate fit with X2 = 210.198; df = 124; p = 0.000; a ratio of X2 to df = 1.695; GFI = 0.905; and RMSEA =0.058.The interpretation of the hypotheses results is summarized in Table 1. The result indicates that responsiveness has a significant positive effect on customer satisfaction (ß=0. 0747; CR= 1.965; P<0.05). This finding is consistent with the findings of[8]. Likewise assurance has significant positive effect on customer loyalty (ß= -1.047; CR= -2.367; P<0.05) this finding is consistent with the findings of[8]. Thus, H9 & H4 are supported. Therefore, other hypotheses are rejected because their p-value is greater than 0.05 respectively.
5. Managerial Implications, Limitations and Suggestion for Future Research
- This study highlights that customers of Islamic bank of Nigeria consumers are satisfied with products and services provided by the bank. In fact, responsiveness and assurance dimensions were the main important factors of service quality in Nigerian Islamic banks as equally found significant by[8] Therefore, Islamic banks are required to do more promotion and focus on strategic choice in providing products and services which are more innovative in order to gain competitive advantage. Islamic banking should provide financial counseling to attract Muslims and non- Muslims customers to use more Islamic banking products and services. One of the limitations of this study is the collection of data from University students and therefore, the findings of the study cannot be generalized. Second, the study was done on a cross-sectional basis. Therefore, to overcome some of these limitations, future studies should consider the possibility of increasing the sample size by including more customers of the banks in their studies. In addition, it is important future studies to carry out a longitudinal research in order to assess the direct effects of the independent variables on the dependent variables respectively.
Appendix
References
| [1] | Mustapha, D. Ibrahim, M & Adewale, A. (2011). Establishment and operation of IB in Nigeria: Perception study on the role of CBN. Australian Journal of Business and Management Research 1(2), 54-67. |
| [2] | Bashir, A.M. (2000), Assessing the Performance of Islamic Banks: Some Evidence from the Midd Middle East. Paper retrieved on June 12, 2006. |
| [3] | Shady, Q. (2008) Investors await CBN's Rules on Islamic Banking. Paper Retrieved April 10, 2008from http://www.guardiannewsngr.com/business/article01//indexn2. |
| [4] | Sanusi .l.S, (2011). Islamic finance in Nigeria: Issues and challenges lecture delivered at Markfield Institute of Higher Education (MIHE), Leicester, Uk. |
| [5] | Nasib, H. ( 2008). Islamic Finance – A Global Proposition. Capco Institute Bulletin, 26 June. |
| [6] | Boonlertvanich, K. (2011). Effect of customer perceived value on satisfaction and customer loyalty in banking service: the moderating effect of main-bank status. International Journal of Business Research, 11(6), 40-54. |
| [7] | Oliver, R. (1980). A cognitive model of the antecedent and consequences of satisfaction decisions. Journal of Marketing, 17(10), 460-9. |
| [8] | Zafar, M., Zafar, S., Asif, A., Hunjra, A. I, & Ahmad, M. (2012). Service quality, customer satisfaction and loyalty: An empirical analysis of banking sector in Pakistan. Information Management and Business Review, 4(3), 159-167. |
| [9] | Parasuraman, A., Berry, L. L. & Zeithaml, V. A. (1991). Understanding customer expectations of service. Sloan Management Review, 32(3), 39-48. |
| [10] | Oliver, R.L. (1997). Satisfaction: A Behavioral Perspective on the Customer, Irwin McGraw-Hill, Boston, MA. |
| [11] | Ndubisi,O.(2004).Understanding the Salience of Cultural Dimensions on Relationship Marketing, its Underpinnings and Aftermaths. Cross Cultural Management, 11(3), 70-89 |
| [12] | Amin, M & Isa, Z. (2008). An examination of the relationship between service quality perception and customer satisfaction: A SEM approach towards Malaysian Islamic banking. International Journal of Islamic and Middle Eastern Finance and Management, 1(3), 191 – 209. |
| [13] | Levesque, T., & McDougall, G. (1996). Determinants of customer satisfaction in retail banking. International Journal of Bank Marketing, 14(7), 12-20. |
| [14] | Parasuraman, A., ZeithmaI,V.A., &Berry,L.L.(1988).SERVQUAL:A multiple item Scale for measuring consumer perceptions of service quality. Journal of Retailing, 64, 12-40. |
| [15] | Othman, A. & Owen, L.(2002).The multidimensionality of CARTER models to measure customer service quality in Islamic banking industry: a study in Kuwait Finance House. International Journal of Islamic Financial Services, l3(4),1-12. |
| [16] | Siddiqui, N.(1992).Banking without interest, Markazi maktaba Islam. New Delhi. |
| [17] | Cronin, J. J., & Taylor, S. A. (1992). Measuring service quality: A re-examination and extension. Journal of Marketing, 56(3), 55-68. |
| [18] | Buzzell, R. D., & Gale, B. T. (1987). The PIMS Principles: Linking Strategy to Performance. The Free Press, and New York. |
| [19] | Rust, R., & Zahorik, A. J. (1993). Customer Satisfaction, Customer Retention, and Market Share. Journal of Retailing, 69(2), 193–215. |
| [20] | Patterson, P., & Spreng, R. (1997). Modeling the relationship between perceived value, satisfaction and repurchase intentions in a business-to-business, services context: An Empirical examination. International Journal of Service Industry Management, 8(5), 414-434. |
| [21] | Taylor, S. A., & Baker, T. L. (1994). An Assessment of the relationship between Service quality and customer satisfaction in the formation of consumers’ purchase intentions. Journal of Retailing, 70(2), 163- 178. |
| [22] | Ajzen, I. (1985). From intentions to actions: A theory of planned behavior. In J. Kuhl & J. Beckman (Eds.), Action-control: From cognition to behavior (pp. 11-39). Heidelberg: Springer. |
| [23] | Krejcie, R, V & Morgan, D. (1970). Determining sample size for research activities. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 30, 607-610. |
| [24] | Kiess, H. O., & Bloomquist, D. W. (1985). Psychological research methods: conceptual approach: Allyn & Bacon. |
| [25] | Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research, 18, 39-50. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML