-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Management
p-ISSN: 2162-9374 e-ISSN: 2162-8416
2012; 2(4): 80-86
doi: 10.5923/j.mm.20120204.01
Comprehensive Motor Insurance Demand in Ghana: Evidence From Kumasi Metropolis
Dadson Awunyo-Vitor
Department of Agricultural Economics, Agribusiness and Extension, Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, Kumasi, Ghana
Correspondence to: Dadson Awunyo-Vitor , Department of Agricultural Economics, Agribusiness and Extension, Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, Kumasi, Ghana.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This study examines the determinants of comprehensive motor insurance demand in Ghana. Data was collected from private car owners who were registering their vehicle at Driver and Vehicle Licensing Authority (DVLA) regional office in Kumasi. The study used logit model to assess factors influencing demand for comprehensive motor insurance. The results revealed that, demand for comprehensive motor insurance is significantly influenced by income, value of the vehicle, age of the vehicle, perception of the premium and claim procedure. The price of comprehensive motor insurance negatively affected the demand. Generally, wealthy people and individuals who used bank loan to purchase vehicle are more likely to purchase comprehensive motor insurance. In addition, claim procedures and the premium if perceived satisfactory would improve demand for comprehensive motor insurance. Hence to encourage demand for comprehensive motor insurance, insurance companies should target wealthy car owners and individual who use bank loan to purchase their vehicles. In addition insurance companies should reduce the time taken to process claims. Finally policy makers should place emphasis on designing comprehensive insurance with attractive premium. Results of this study will be useful to insurance companies in improving demand for comprehensive motor insurance.. The information would also benefit stakeholders in the insurance industry in Ghana especially policy makers as how to improve demand for comprehensive insurance in a sustainable manner.
Keywords: Insurance Demand, Comprehensive Motor Insurance, Driver And Vehicle Licensing Authority (DVLA) Kumasi Ghana
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Insurance could be described as the purchase of security or the assured, anxious to protect oneself against a risk. It is a form of risk management strategy used to hedge against risk of contingent loss. Vehicle usage has embedded morbidity and mortality risk plus loss through theft and fire in several countries[18]. In view of this Motor vehicle insurance was developed to take care of the possible loss that may arise from use of motor vehicles[2],[19]. Motor insurance is an important form of contract arising out of or in connection with the use of motor vehicle. This take the form of equitable transfer of the risk of a loss, from the vehicle owner to the insurer in exchange for a premium, and can be thought of as a guaranteed for devastating loss. Motor insurance, which is also known as Automobile insurance, is gradually becoming the most common form of insurance. Motor insurance was introduced to protect motorist from potentially enormous financial loss from operating a vehicle. Therefore, policy makers require motorist to purchase motor insurance cover to protect innocent third parties as well as the art faultmotorist from liability[21],[1]. There are two primary types of motor insurance in Ghana; these are: third party insurance and comprehensive motor insurance.The risk that is normally covered by third party is the cost of repairing the vehicle following an accident while comprehensive motor insurance policy cover the risk of the cost of repairing the vehicle following an accident, the cost of a new vehicle if it is stolen or damaged beyond economic repairs as well as legal liability claim against the driver or owner of the vehicle following the vehicle causing damage to a third party[11]. Comprehensive car insurance is not an obligation in most countries of the world. However, if a car owner want to guard against financial jeopardy, comprehensive auto insurance is the best because it covers compensation for car accidents and other kinds of misfortune. If damage is made to another party, harm to the person or damage to a property, this car insurance policy will safeguard policy holder in that kind of situation. It also covers the policy holder’s own vehicle and medical expenses. However, this policy has the highest premiums compared to the third party auto insurance policy. Moreover the coverage for the damages to policy holder’s car and the other party's vehicle, comprehensive insurance covers damages that consequences to other non-car crash incidents.Comprehensive car insurance cover losses that policy holder’s vehicle may incur due to fire, vandalism theft or natural disaster. This type of insurance will cover vehicle from natural disasters like severe storms to flooding. Fully comprehensive auto insurance is of great help depending on the type of vehicle you want to insure. This type of insurance offers a peace of mind, in the case where catastrophic events were to happen. Unlike third party insurance which has a fixed cover and it is for only accident liability and collision, comprehensive insurance is an insurance that will protect and reimburse you with your losses directly. While other types of insurance are generally only for the benefit of third party this type of insurance pay for any losses sustained during unforeseen accidents. Comprehensive coverage will allow policy holder to quickly recover from any losses if vehicle is intentionally damaged, stolen, or damaged in the event of a natural disaster like fire or flood. This kind of coverage is of great help to assist in recovering losses and it will fill the gap that third party insurance policy may leave open: particularly because this policy does not cover losses in full. Therefore, for one to reap the full benefit of insurance there is the need to obtain complete insurance cover offered by comprehensive motor insurance policy as the third party insurance does not adequately cover loss to car owners and compensate injured victims during accident. For example reference[1] observed that over three quarters of a million people are killed and tens of millions injured on the roads in low income countries each year.Many of these victims are from poor households, therefore, fair and timely compensation systems will help bereaved families and injured victims recover from the shock of a road crash. This can be achieved through the use of comprehensive motor insurance as third party insurance claim is often inadequate. However, a study by[2] on type of motor insurance used by motorist in Ghana indicates that only 12% of motor insurance subscribers used comprehensive motor insurance.With enormous benefit of comprehensive insurance over the third party insurance, why are motorist not taken up comprehensive motor insurance. This leads to the question of what determine demand for comprehensive motor insurance. Thus the focus of this paper is to examine factors which influence purchase of comprehensive motor insurance in Ghana taken the case of newly registered private cars owners in Kumasi Metropolis. In examining the determinants of comprehensive motor insurance purchase decision of private car owners, insurers and government policy makers can better understand the limitations and or opportunities involved in fulfilling the overall risk reducing need of private motor vehicle owners.
2. Determinants of Demand for Insurance
- The theory of demand for insurance has been based on expected utility in economics and assured preference for certain issues over uncertain ones of the same magnitude[22],[25]. Demand for insurance is a decision to purchase not only the apparent current condition of the product but also its future conditions[9]. Reference[4] asserts that a consumer widens it economic scope of discretion and opportunity by protecting themselves from financial loss in the event of accident, fire or theft. Therefore price of insurance is an essential determinant in the determination of demand for insurance[24]. Reference[6] noted that individual’s income and wealth, the price of insurance, the probability of loss and individual degree of risk aversion and[22] assert that the purchase of insurance that provides adequate cover in terms of loss decreases the probability of financial crisis when risk crystallises.Reference[10] examined insurance demand in developed and developing countries between 1984 and 1998 and finds a strong positive relationship between income and insurance demand. This supports the economic theory which hypothesizes positive correlation between income level and insurance demand. The demand for any product or service is affected by its price in case of insurance this was proved empirically by[8] and[10] where they observed significant negative relationship between insurance premium and insurance demand. The primary motive of purchasing insurance is risk aversion to avoid loss; therefore the level of risk aversion theoretically may correlate with insurance demand. Reference[5] used level of education as a proxy for risk aversion and found that a high level of education correlate with demand for insurance. Reference[14] studied demand for insurance by considering three different sets of variables; first, variables stimulating demand as a result of insurer efforts second, variables affecting household saving decision and lastly, variables determining ability to pay. Their study revealed that insurance demand is positively affected by change in income and wealth status of the consumer. Reference[3] also used a data from 12 countries to examine factors influencing demand for insurance. They found that the initial wealth status of the individual exhibit significant relationship with decision to insure.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Collection
- The target population comprised owners of private vehicles in year 2011 at the regional office of DVLA in Kumasi. The data for the study was collected by use of well structured questionnaires through interviews between the January and June 2011. This is because majority of the vehicles are registered within this period. A simple random sample of 350 vehicle owners was interviewed.
3.2. Analytical Framework
- The respondents’ decision to demand or not to demand comprehensive motor insurance
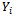 was assumed to be dependent on his assessment of the marginal cost and benefits associated with the use and non-use of comprehensive motor insurance respectively. Based on his assessment he may decide to purchase or not to purchase comprehensive motor insurance. In reality we do not observe this marginal cost and benefit hence dependent variable
was assumed to be dependent on his assessment of the marginal cost and benefits associated with the use and non-use of comprehensive motor insurance respectively. Based on his assessment he may decide to purchase or not to purchase comprehensive motor insurance. In reality we do not observe this marginal cost and benefit hence dependent variable 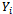 . One can only observe whether respondent purchase comprehensive motor insurance or not through responses to question in the survey questionnaire. Hence another variable
. One can only observe whether respondent purchase comprehensive motor insurance or not through responses to question in the survey questionnaire. Hence another variable 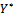 is defined such that:
is defined such that: Thus vehicle owners’ decision to demand comprehensive motor insurance is dichotomous, involving two mutually exclusive alternatives. The car owner may either purchase comprehensive motor insurance or may not This yields a binary dependent variable
Thus vehicle owners’ decision to demand comprehensive motor insurance is dichotomous, involving two mutually exclusive alternatives. The car owner may either purchase comprehensive motor insurance or may not This yields a binary dependent variable 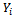 which takes on the value of 1 if car owner demand comprehensive motor insurance and 0 if he does not demand/ purchase comprehensive motor insurance which is influenced by a set of factors (
which takes on the value of 1 if car owner demand comprehensive motor insurance and 0 if he does not demand/ purchase comprehensive motor insurance which is influenced by a set of factors (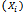 .
.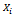 Comprises individual and household characteristics as well as institutional factors, the relationship between
Comprises individual and household characteristics as well as institutional factors, the relationship between 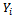 and
and 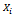 can be presented as:
can be presented as: 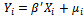 | (1) |
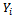 and
and 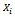 are defined as above and
are defined as above and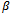 is a parameter of interest and
is a parameter of interest and 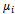 the disturbance term. Linear Probability Model (LPM), probit and logit models can be used to analyse qualitative response or binary choice models such as equation 1.The Linear Probability Model (LPM) can be used to analyse equation 1. However,[17],[7],[13] have noted that though LPM can be used to analyse binary models the estimated probability values can lie outside the normal 0-1 range. Hence probit and logit models are advantageous over LPM in that the probabilities are bound between 0 and 1. Moreover, these model best fits the non-linear relationship between the probability and explanatory variables. Due to the above shortcomings of the LPM, logit model was adopted for this study.
the disturbance term. Linear Probability Model (LPM), probit and logit models can be used to analyse qualitative response or binary choice models such as equation 1.The Linear Probability Model (LPM) can be used to analyse equation 1. However,[17],[7],[13] have noted that though LPM can be used to analyse binary models the estimated probability values can lie outside the normal 0-1 range. Hence probit and logit models are advantageous over LPM in that the probabilities are bound between 0 and 1. Moreover, these model best fits the non-linear relationship between the probability and explanatory variables. Due to the above shortcomings of the LPM, logit model was adopted for this study. 3.3. The Model
- The logit model adopted for the study is specified as
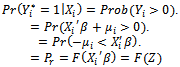 | (2) |
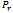 is the probability that a car owner will make a particular choice or probability that a car owner would purchase comprehensive motor insurance
is the probability that a car owner will make a particular choice or probability that a car owner would purchase comprehensive motor insurance 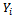 is the dependent variable (demand for comprehensive motor insurance)
is the dependent variable (demand for comprehensive motor insurance) 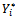 is the threshold value of the dependent variable. The above equation
is the threshold value of the dependent variable. The above equation 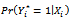 yields
yields 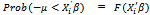 where
where 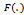 is cumulative distribution function (cdf) assuming logistic distribution we have[17] .
is cumulative distribution function (cdf) assuming logistic distribution we have[17] .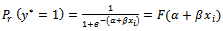 | (3) |
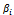 of the logit model do not provide direct information about the effect of the changes in the explanatory variable and the probability of demand for comprehensive motor insurance. The relative effect of each explanatory variable on the likelihood that a car owner will demand comprehensive motor insurance is given by:
of the logit model do not provide direct information about the effect of the changes in the explanatory variable and the probability of demand for comprehensive motor insurance. The relative effect of each explanatory variable on the likelihood that a car owner will demand comprehensive motor insurance is given by: 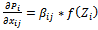 | (4) |
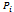 is the mean dependent variable whose value is given in the logit result as
is the mean dependent variable whose value is given in the logit result as 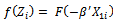 | (5) |
3.4. Choice of variables and expected effects
- Guided by related studies[23],[6],[16],[18] socio economic attributes were identified and hypothesis constructed regarding demand for comprehensive motor insurance by private vehicle owners. The age of the respondents (X1) was included in the model because it is used as a proxy for maturity and the potential ability to understand and use insurance[18]. It was expected to be positively related to demand for comprehensive insurance, and was measured in years. An increase in the age of the vehicle (X2) reduces incentive to demand comprehensive insurance as the age of the vehicle is directly related to its economic value and performance. It was expected to have negative influence on demand for comprehensive insurance and was measured in years. Income (X3) was chosen because it serves as a proxy for the measurement of net worth of the respondent.The income level of the respondents was expected to be positively related to demand for comprehensive insurance. This is because the higher their income levels the more likely they would purchase good and expensive car with higher risk and the more likely they would be able to pay the premium. It was specified as total income of the respondent in Ghana Cedis per annum. The level of education of the respondents (X4) was expected to have a positive effect on their demand for comprehensive motor insurance. This is because the educated are expected to understand operations of insurance companies and benefit of comprehensive motor insurance. This is because education is said to be a major factor that influences the decision to demand insurance[15]. It was measured as a number of years spent in formal schooling Source of fund to purchase the car, (X5). If loan is used to purchase the car then there is a higher likelihood of demanding comprehensive motor insurance as most of the financier require that vehicle purchase with their loan are insured comprehensively. The value of the vehicle (X6) is expected to have positive relationship with decision to purchase comprehensive motor insurance. This is because the higher the value of the car the higher tendency to protect their investment. This value of was specified in Ghana Cedis. The perception of the application procedures (X7) was expected to have a negative effect on demand for comprehensive motor insurance because once a person perceives the application procedures as cumbersome; he or she will put less effort to demand comprehensive motor insurance. It was measured as a dummy. A value of 1 is assigned to respondents who perceived the application procedure to be cumbersome and 0 otherwise.The higher the respondent perceive the premium (X8), to be high the lower their demand will be for comprehensive motor insurance. This variable is expected to have a negative effect on demand for comprehensive motor insurance. It was measured as a dummy where a value of 1 is assigned to respondents who perceive premium to be high and 0 otherwise.The more the respondents perceive claim procedure to be difficult (X9), the lesser likely they are to demand comprehensive insurance. It was measured as a dummy. Gender (X10) classification is important in this type of analysis because in Ghana as in many African societies, women are considered to be less endowed financially, which have implication for demand for comprehensive insurance because of the premium. Therefore, demand for comprehensive motor insurance is expected to be different between men and women. The gender is specified as a dummy variable which takes value of 1 if the respondent is male and 0 otherwise. It is hypothesised that male respondents are more likely to demand comprehensive motor insurance compared to female car owners. The empirical model is specified as :
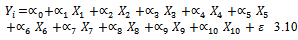 Where
Where 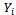 take value of 1 if a respondent purchase comprehensive motor insurance and zero if otherwise.
take value of 1 if a respondent purchase comprehensive motor insurance and zero if otherwise. 4. Results and Discussion
- The results of the study have been presented in two sections. In the first section, a description of the socioeconomic characteristics of the sampled respondents is presented. In the second section, the econometric result on the factors influencing demand for comprehensive motor insurance is also presented.
4.1. Descriptive statistics
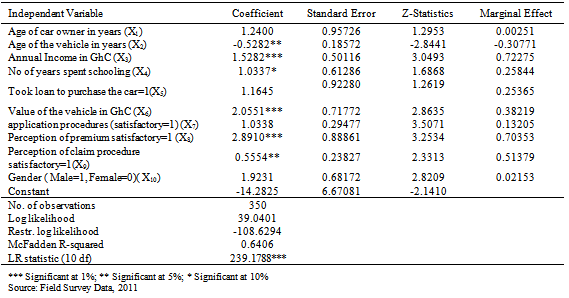
- The descriptive statistics of the variables shown in Table 1 were considered to influence demand for comprehensive motor insurance. The average age of car owners who purchased comprehensive motor insurance is 45.7 years compared to 43.9 for those who did not purchase comprehensive motor insurance. Though, no significant difference exists between the ages of the two groups of the respondents, car owners who purchase comprehensive motor insurance are generally older than those who did not purchase comprehensive motor insurance. There is a significant difference in the age of vehicles insured by the two groups of respondents. Those who did not purchase comprehensive motor insurance have older vehicles with average age of 9.2 years as compared to those who purchase comprehensive motor insurance with average age of 5.8 years. This is an indication that age of vehicle might influence demand for comprehensive motor insurance.Car owners in this study generally have high level of education. Basically majority of them have tertiary education. Those who purchased comprehensive motor insurance had average years of schooling as 15.2 years of formal education which is higher than 14.5 years of formal education for those who did not purchase comprehensive motor insurance. However, there was no significant difference between them.Car owners’ perception of comprehensive application procedure varied between the two groups of respondents. On a dummy scale of between zero and one, car owners who purchase comprehensive motor insurance perceived the procedure as generally satisfactory, scoring as high as 0.83 which is statistically different from 0.29 scored by those who did not purchase comprehensive motor insurance. Perception of the premium may apriori affect demand for comprehensive motor insurance.. Both categories of car owners perceived premium differently with statistical difference between them. Respondents’ perception of claim procedure was ascertained. Car owners who purchased comprehensive motor insurance perceived claim procedure to be satisfactory with a score of 0.84, as compared to those who did not purchase comprehensive motor insurance. The respondents were distinguishable in terms of income and value of the vehicle. There is significant difference in the income and value of the vehicle by the two groups of private car owners. Respondents who purchase comprehensive motor insurance had higher income and more expensive car in term of value than their counterparts who did not purchase comprehensive motor insurance. This suggests that income and value of car might correlate with probability of comprehensive insurance demand. Generally larger proportion of respondent who purchase comprehensive motor insurance used credit facility to acquire their vehicles as compared to those who did not purchase comprehensive motor insurance, though statistically insignificant. On the average more male car owners purchase comprehensive motor insurance as compared to their female counterparts scoring an average of 0.76 and for third party insurance they score 0.52 on a dummy scale of 1 for male and 0 for female.
4.2. Regression Results
- The logit regression gave a McFadden R – squared of about 0.64 which implies that all the explanatory variables included in the model are able to explain about 64 percent of the probability of purchase of comprehensive motor insurance. The log likelihood ratio (LR) statistic is significant at 1 percent, meaning that all the variables included in the model jointly influence the probability of purchase of motor insurance (Table 2). Given these two goodness of fit measures, it can be concluded that the logit model used has integrity and is appropriate. The age of the vehicle significantly influence demand for comprehensive motor insurance. The coefficient of the vehicle age was negative and significant at 5% level of significance. This implies that older vehicles are less likely to be insured comprehensively. This might the due to the fact that the value of older vehicle might be low and the owner knows that in case of accident, theft or fire their loss is low hence no need to insure the vehicle comprehensively.As expected, the coefficient of income level was found to positively relate to probability of purchase of comprehensive motor insurance and was also found to be significant at 1%. This can be attributed to the fact that this people have the money to pay the premium of comprehensive motor insurance hence are more likely to demand comprehensive motor insurance. One Ghana Cedi increase in income would increase probability of demand for comprehensive motor insurance by 72% (Table 2). This finding is consistent with the findings of[15] who observed that income levels influence individuals’ and their decisions to purchase comprehensive motor insurance. Also, formal education attainment conformed to the apriori expectation and was found to be significant at 10%. This may be due to the fact that the educated are able to understand the need for appropriate insurance and are able to seek more information regarding their right and responsibility hence have a higher likelihood of purchasing comprehensive insurance.The coefficient of the value of the vehicle also conformed to the a priori expectation and was found to be significant at 1%. This implies that the higher the value of the vehicle the higher probability of demand for comprehensive motor insurance. This might be due to the fact that those who can afford expensive vehicle also have the money to pay for comprehensive motor insurance. In addition due to the high value the vehicle may be prone to theft hence it is important they seek comprehensive insurance which adequately cover loss from fire, theft and accident.
|
|
- The coefficient of respondents’ perception on premium for comprehensive motor insurance also met the a priori expectation of positive relationship with probability of demand for comprehensive insurance and was found to be significant at 1%. Those who perceive the premium to be satisfactory are 70% more likely to demand comprehensive motor insurance as compared to those who perceive it as high. The perception of respondent regarding claim procedures negatively influenced their probability of purchase of comprehensive motor insurance and was found to be significant at 5%. Private car owners who perceive claim procedure to be satisfactory are more likely to demand comprehensive motor insurance by 51%. The gender coefficient was found to be consistent with the a priori expectation but insignificant.
5. Conclusions
- The result of the study indicates that there are number of factors influencing comprehensive motor insurance demand by private car owners in Ghana. The key factors include income, value of the car, age of the vehicle, perception of the premium and claim procedure. Income of the vehicle owner, the age of the car and value of the care are indications of the wealth of the car owner. Thus the wealthy car owners are more likely to demand comprehensive motor insurance. This may be attributed to the value of the premium on comprehensive motor insurance. This is because if respondent perceive premium to be high are less likely to purchase comprehensive motor insurance. Furthermore, claim procedure has negative influence on demand for comprehensive motor insurance. Thus a satisfactory claim procedure in terms of time taken to process claim would improve demand for comprehensive motor insurance. The insurance companies should improve upon claim processing procedure in terms of number of days taken to process claims.To improve demand for comprehensive motor insurance policy makers should place emphasis on designing comprehensive motor insurance with competitive premium. Furthermore, education on comprehensive motor insurance policy should target car owners in higher income group.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The author is grateful to Mr. Jamil Badu, Regional Accountant, Driver and Vehicle Licensing Authority (DVLA) and all the insurance companies operating within the premises of DVLA in Kumasi for their assistance during data collection.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML