-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Mining Engineering and Mineral Processing
p-ISSN: 2166-997X e-ISSN: 2166-9988
2015; 4(1): 18-27
doi:10.5923/j.mining.20150401.03

Flotation Behavior of Iranian Oxidized Zinc Ore Using Different Types of Collectors (Cationic, Anionic and Mixed (Cationic/Anionic))
Seyed Hamid Hosseini1, Mohamad Taji2
1Mining Engineering Department, Islamic Azad University, South Tehran Branch, Tehran, Iran
2Mining Engineering Department, Islamic Azad University, Shahroud Branch, Shahroud, Iran
Correspondence to: Seyed Hamid Hosseini, Mining Engineering Department, Islamic Azad University, South Tehran Branch, Tehran, Iran.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

In this study, the flotation of oxidized zinc ore from Angooran ore in the presence of cationic collector such as dodecylamine (DDA), anionic collectors such as oleic acid (OA), potassium amyl xanthate (KAX), hexyl mercaptan (HM) and mixed collector (cationic/anionic) was investigated. The parameters of the flotation process such as recovery, grade and the effect of using some collectors (sodium sulphide and copper sulphate at different pH) were investigated. According to this investigation, the maximum flotation recovery was found to be 84.5% with 24.5% zinc content using the cationic collector DDA at pH 11.5. The flotation results using mixed collector (DDA and KAX) showed that when the KAX is increased, the recovery also increased but it has no significant variation in comparison with DDA flotation results. The lowest recovery was seen, when KAX and HM are used alone in batch flotation and it demonstrates the poorest flotation results in comparison to the other reagents. The results of oleic acid flotation also have no significant variation for recovery in comparison with cationic flotation but no selectivity is observed.
Keywords: Oxidized zinc ore, Dodecylamine, Oleic acid, KAX, Mercaptan, Mixed collector, Bench flotation
Cite this paper: Seyed Hamid Hosseini, Mohamad Taji, Flotation Behavior of Iranian Oxidized Zinc Ore Using Different Types of Collectors (Cationic, Anionic and Mixed (Cationic/Anionic)), International Journal of Mining Engineering and Mineral Processing , Vol. 4 No. 1, 2015, pp. 18-27. doi: 10.5923/j.mining.20150401.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Some of most important sources of zinc ore are oxidized zinc minerals including, smithsonite (ZnCO3), willemite (Zn2SiO4), hydrozincite (2ZnCO3.3Zn(OH)2), zincite (ZnO) and hemimorphite (Zn2SiO3.H2O). However, flotation of oxidized lead and zinc, in particular zinc minerals, is much more difficult than the flotation of corresponding sulphide minerals [1]. Oxidized zinc ores have long been an important source of zinc which can be floated with long chain primary amines as collector after sulphidizing with sodium sulphide [2]. Oxidized zinc ore may be concentrated by flotation in the presence of a soluble sulphide and soluble compound of an aliphatic amine containing from 8-18 carbon atoms [3]. Abramov also stated the best process for the flotation of smithsonite was by using of laurylamine acetate as a collector after sulphidizing the mineral with sodium sulphide. His results showed that the flotation properties of minerals depended on the pH [4]. Some researchers stated that smithsonite could be collected with fatty acids. The former, with a COOH radical, may be compared to carbon dioxide, which gives insoluble carbonates. Hence, fatty acids can collect the carbonates [5, 6]. Generally, flotation of oxidized lead and zinc, in particular zinc minerals, is much more difficult than the flotation of corresponding sulphide minerals. The main flotation characteristics of these minerals are lower selectivity and higher reagent consumption. The most common flotation technique to be used commercially is sulphidization with Na2S, followed by treatment with conventional collectors, namely xanthates for lead oxides and amine for zinc oxides [7]. A large part of the test program was devoted to finding the best collector for the smithsonite. Several amines were tested but a DDA derived from vegetable oil proved to be the most suitable [8]. According to previous works of authors, the size fraction of -125+75 µm in order to decrease over grinding was selected as the best amount of the liberation degree and the result of heavy liquid separation (HLS) confirmed it. However, the applicability of the gravity concentration was in size fraction of –150+125 µm [9]. The feed to the oxide zinc flotation circuit requires careful desliming prior to flotation and is then floated with a relatively large amount of sulphidizing agent and a cationic collector, with frother added as required. Investigators originally reported best results at pH levels between 10.5 and 11.5, although some ores respond well to the process at lower pH levels. Reagent consumptions are usually of the order of 1000 g/t to 7500-g/t sodium sulphide or sodium hydrosulphide, and 50 g/t to 300 g/t cationic collector. Gaudin stressed that hexyl and amyl xanthate can be used for collecting of smithsonite but the process is not selective enough for practice [10]. Barbery et al., 1977, reported that xanthates, simple alkyl amines such as DDA and also fatty acids can be used for flotation of oxidized zinc ore [11]. Sodium sulphide proved to be the most satisfactory sulphidizing agent, both from the point of view of being cheaper than sodium hydrogen sulphide and also by virtue of generating a high pH. When the pH dropped there was a drop in recovery. The amount of sulphidizing reagent and pH of the pulp must be carefully controlled [12-18]. Sodium sulphide is a preferred soluble sulphide, other sulphides, which may be used, include, for example, calcium sulphide, barium sulphide and ammonium polysulphide [19]. The activating effect of sodium sulphide is strongly dependent on time. The increase in sulphidization leads to an increase in the hydrophobicity of the surface of minerals. Excess of sodium sulphide acts as depressant for oxidized lead and zinc minerals because adsorption of divalent sulphide ion on the surface of lead oxide minerals increase the negative charge which prevents the adsorption of collector [20]. Önal et al., 2005 showed that the increasing the sodium sulphide from 2.25 to 4.5 g/l decreased the zinc flotation recovery [21]. In the present study, the flotation behavior of oxidized zinc ore from Angooran deposit, Iran was studied using several cationic, anionic and mixed (cationic/anionic) collectors by means of bench scale flotation studies.
2. Materials and Methods
- The oxidized zinc ore samples were obtained from Angooran deposit, Iran. The chemical analysis showed the representative ore sample contains 9.6% ZnO, 62.5% SiO2, 16.5% Al2O3, 2.25% K2O, 1.85% Fe2O3, 1.36% PbO and 0.45% TiO2. By combining the information obtained from chemical analysis, XRD and ore microscopy, approximate mineralogical composition of the ore samples can be shown included smithsonite (16%), mimetite (0.6%), quartz (52%), sericite (16.5%), kaolinite (12%), iron oxides minerals (1.5%), rutile (0.4%) and other minerals (1%) [22]. The representative ore sample, after crushing, was ground in a laboratory stainless steel ball mill having a critical speed of 80%. After grinding, the material was deslimed at -20 µm size and used for bench scale flotation tests. Dodecylamine (99% purity) was obtained from Fluka Chemie, Switzerland. Potassium amyl xanthate with 90% purity was purchased from Shandong Qixia Flotation Reagent Co. Ltd, China. Oleic acid (99.9% purity), sodium sulphide and copper sulphate (99% purity) were procured from Merck KGaA, Germany. Methyl mercaptan (99.5% purity) was purchased from SIGMA-ALDRICH and ethyl mercaptan (97% purity) and hexyl mercaptan (97% purity) were obtained from Fluka Chemie, Switzerland. Analytical grade HCl and NaOH were used for pH adjustment in all experiments. Tap water was used in all experiments. The chemical analysis of tap water showed that iron 0.5 mg/ dm3, copper 0.75 mg/ dm3, lead 0.03 mg/dm3, manganese 0.3 mg/dm3, zinc 2.25 mg/dm3, calcium 30 mg/dm3, magnesium 50 mg/ dm3. (Total hardness of Tehran drinking water as CaCO3 is 300 mg/dm3).The bench flotation tests were performed with oxidized zinc ore samples. The experiments were conducted on 20% of solid in pulp ratio in a Denver flotation cell operating at 1500 rpm with a constant flow of air (the maximum permitted by system). The ore sample, after being crushed, was ground in a laboratory stainless steel ball mill having a critical speed of 80%. The d80 of the products was -100 µm. The various amounts of reagents used in the oxidized zinc flotation, were added at different rates of concentrations. The conditioning time of collectors was 5 minutes. In amine flotation, the Na2S was added with a conditioning time of 3 minutes at different concentrations. In KAX flotation, the copper sulphate (1500 g/t) was added with a 3 minute of conditioning time. The pine oil as a frother and sodium silicate (1000 g/t) were used with a conditioning time of 2 min. Flotation was conducted for 30 minutes and the pH of the pulp was adjusted using HCl and NaOH for all tests. The model with rectangular distribution of floatability has been applied in the evaluation of flotation results. This model is evaluated by fitting the flotation results from batch flotation tests. The mathematical form of this model may be written as follows [23, 24]:
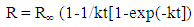 | (1) |
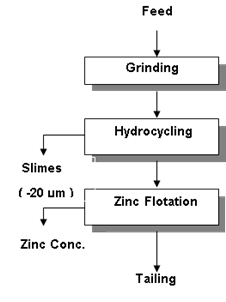 | Figure 1. Experimental flow sheet |
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Bench Scale Flotation with DDA
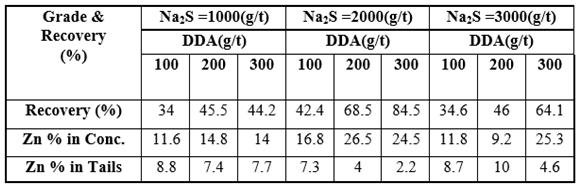
- The bench flotation tests were performed with 100, 200 and 300 g/t of DDA concentrations and sulphidizing agent of sodium sulphide (1000, 2000, 3000 g/t) were used in the flotation experiments. The concentrate grade and recovery of zinc ore flotation for various amounts of DDA with sodium sulphide (2000 g/t) as sulphidizing agent are shown in Figure 2. The recoveries of all zinc ore flotation products during the different times were calculated. Figure 3 depicts the collecting time vs. recovery when sodium sulphide and DDA were used 2000 g/t and 3000 g/t, respectively. The grade and the recovery of the zinc ore in the concentrate and the tailing products in terms of the quantity of DDA and sodium sulphide are given in Table 1.
|
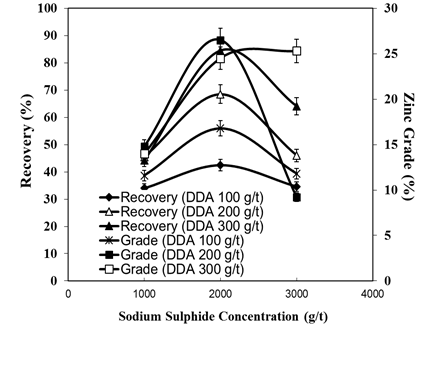 | Figure 2. Concentrate grade and recovery of zinc ore flotation for various amounts of DDA in sodium sulphide solutions |
 | Figure 3. Zinc ore flotation at various collection times (Na2S 2000 g/t; DDA 300 g/t) |
3.2. Bench Scale Flotation with Oleic Acid
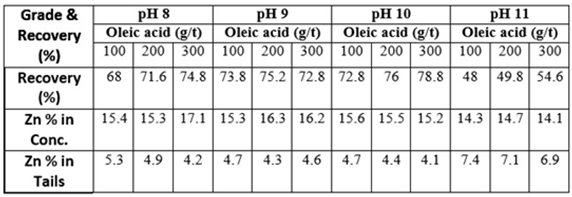
- The bench flotation tests were performed with 100, 200 and 300 g/t of OA concentrations as a function of pH. The results are illustrated in Figure 4. The grade and the recovery of the zinc mineral in the concentrate and tailings in terms of the quantity of oleic acid are given in Table 2. Figure 5 illustrates the flotation times vs. zinc recovery using 300 g/t oleic acid.
|
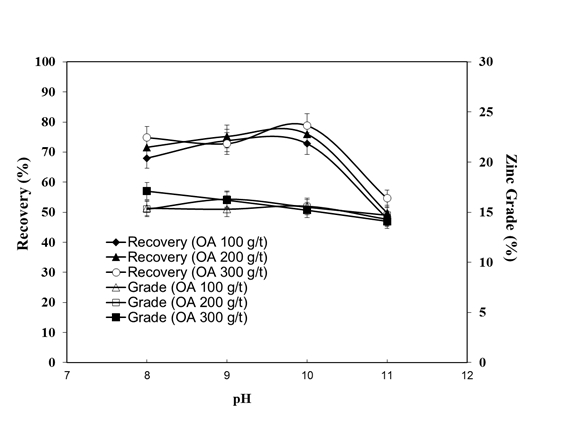 | Figure 4. Grade and recovery of zinc flotation with various oleic acid concentrations |
 | Figure 5. Zinc ore flotation at various collection times with oleic acid concentration 300 g/t |
3.3. Bench Scale Flotation Using KAX
- The flotation recovery and grade curves of zinc ore as a function of KAX consumption are illustrated in Figure 6. The grade and the recovery of the oxidized zinc mineral in the concentrate and tailing in terms of the quantity of KAX are given in Table 3. Figure 7 depicts the collecting time vs. recovery with KAX concentration 600 g/t.
|
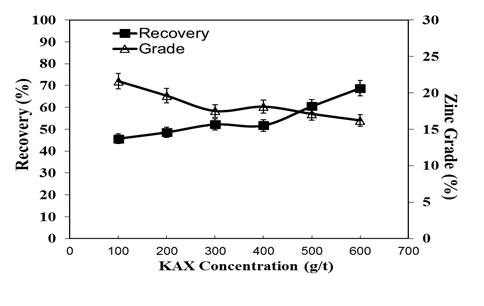 | Figure 6. Grade and recovery of zinc flotation for various KAX concentrations |
 | Figure 7. Zinc ore flotation at various collection times with KAX 600 g/t |
3.4. Bench Scale Flotation Using Mercaptans
- The authors carried out the zinc ore flotation tests using methyl mercaptan (MM), ethyl mercaptan (EM) and hexyl mercaptan (HM) as collector [30]. Table 4 shows the zinc grade and the flotation recovery, in terms of the quantity of MM, EM and HM at pH 9. Figure 8 illustrates the zinc grade and flotation recovery using different types of mercaptans at different pH. Figure 9 depicts the collecting time vs. recovery with HM concentration 600 g/t at pH 9.
|
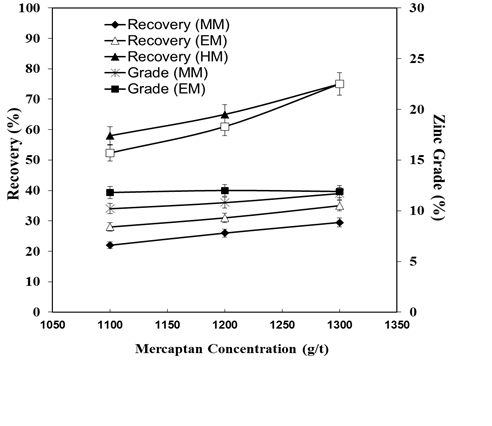 | Figure 8. Zinc ore flotation recoveries as a function of pH at methyl, ethyl and hexyl mercaptan concentration of 1300 g/t |
 | Figure 9. Zinc ore flotation at various collection times for Hexyl mercaptan at pH 9 [30] |
3.5. Bench Scale Flotation with Mixed Collector
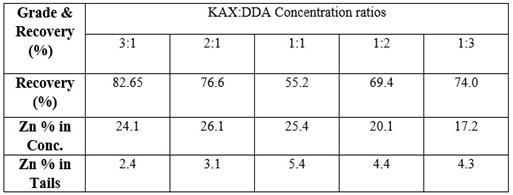
- The flotation experiments were performed with mixed (Cationic/Anionic) collector concentrations. In these experiments, the effect of mixture ratios was investigated. The mixture ratio of KAX: DDA was changed as 3:1, 2:1, 1:1, 1:2 and 1:3. The oxidized zinc ore flotation results are shown in Figure 10. The grade and the flotation recovery of the oxidized zinc mineral in the concentrate and tailing in terms of the quantity of KAX: DDA concentration ratios are given in Table 5.The previous results of smithsonite flotation recovery by means of Hallimond tube was determined 96.6% using mixed collector at pH 9.5 [31]. As it is seen from Figure 10 and Table 5, the highest flotation recoveries were found 3:1 and 2:1 of concentration ratios (KAX: DDA) which are 82.65 and 76.6 %, respectively. The zinc % in tails was variated from 2.1% to 5.4%. The optimum flotation recovery and zinc grade according to the lowest zinc % in tails, were 86.5% and 24.1%, respectively.The R∞ and k values were calculated by statistical software as 87.59 and 0.775, respectively. From Figure 11, it can be concluded that the optimum collection time is 15 minutes.
|
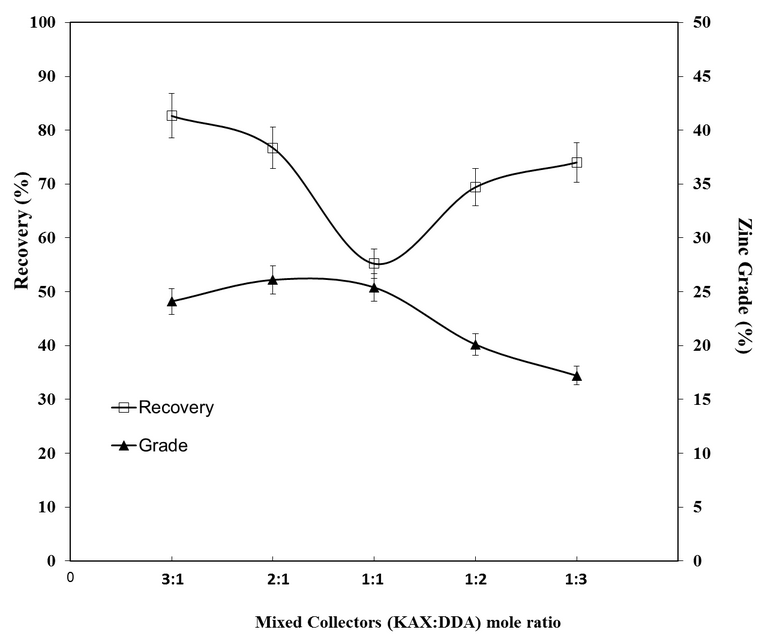 | Figure 10. Grade and recovery of zinc flotation for various mixed collector concentration ratio |
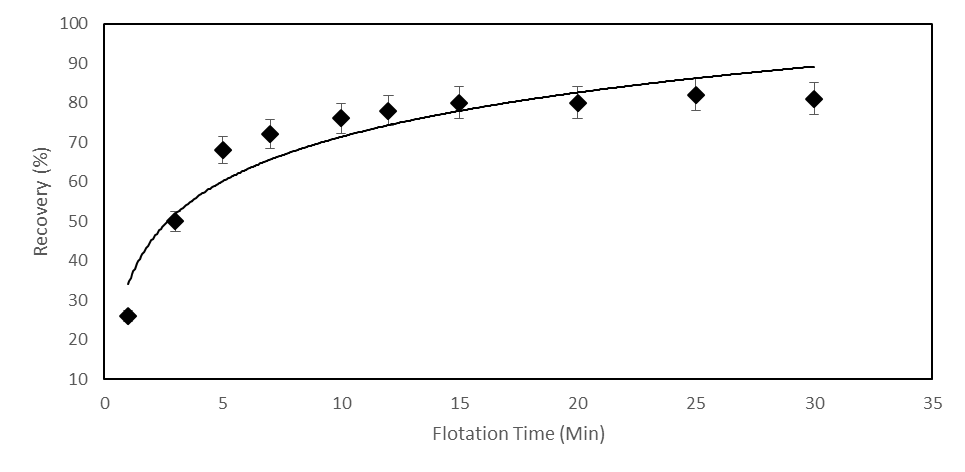 | Figure 11. Zinc ore flotation at various collection times for mixed collector (KAX and dodecylamine, concentration ratio 3:1) at pH 9.5 |
4. Conclusions
- The following conclusions were obtained from the present research:1) Based on zinc ore batch flotation tests, the maximum flotation recovery and zinc grade were obtained when it was used DDA as collector. The zinc ore flotation recovery and zinc grade were 84.5% and 24.5%, respectively.2) When it was used the mixed collector of KAX and DDA in different concentration ratios of the collectors, the optimum zinc flotation recovery and zinc grade were 82.65% and 24.1%, respectively, for the mixed collector concentration ratio (KAX: DDA) of 3:1. Hence, the grade variation is from 17.2% to 26.1% but zinc flotation recovery for the highest zinc grade (26.1) was 76.6% for the mixed collector concentration ratio (KAX: DDA) of 2:1. The flotation results using mixed collector (KAX+DDA) show that with increasing the KAX concentration, the recovery is increased.3) The zinc ore flotation results using oleic acid also have no significant variations for recovery in comparing with amine flotation but no selectivity is observed. 4) When it is used KAX or HM alone in zinc ore batch flotation, the poorer flotation results are obtained.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors acknowledge Calcimine Co. for providing the ore samples, which were used in this investigation. The assistance of colleagues at Tehran Azad University, Department of Mining Engineering, Tehran, Iran, especially Mr. Mahdi Samanipour is much appreciated. We also would like to thank Mr. Patrick Kerr (Minepromet) for helping us linguistically to improve the English version of this paper.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML